SLB-L2 Topology Example
This figure shows the SLB-L2 topology used in this document.
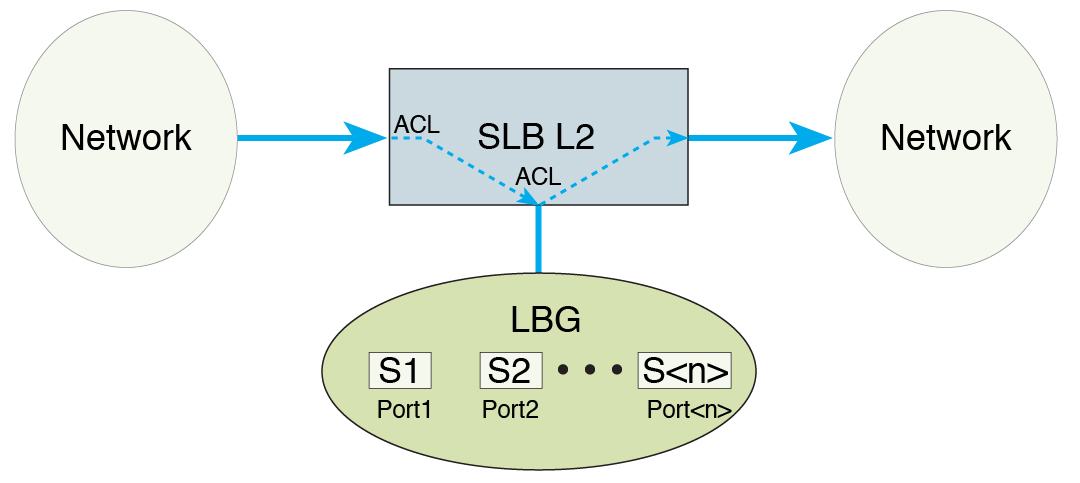
In SLB-L2, all traffic operates within the same subnet, which means that no routing takes place in the load distribution data path. Traffic that needs to be load balanced is first be filtered out by ACL at the ingress port. If data is permitted by the port, ACL redirects the traffic to an LBG. Traffic leaving the switch ports within an LBG can be tagged with a unique VLAN ID before reaching the servers connected to the ports. After the servers process the data, all traffic that enters the switch with the tagged VLAN ID is redirected to an egress port of the switch.
You can configure ingress and egress ports as the same or as different ports, referred to as a bump-in-the-wire configuration, where the servers are the "bumps" in the wire for packet processing. SLB-L2 divides ingress traffic into multiple flows and hashes them into multiple server members. This mechanism enables simultaneous processing of multiple data flows, increasing the overall throughput of the wire.