4 Alarms
This chapter provides recovery procedures for platform and application alarms.
4.1 Alarm Categories
This chapter describes recovery procedures to use when an alarm condition or other problem occurs on the server. For information about how and when alarm conditions are detected and reported, see Detecting and Reporting Problems.
When an alarm code is reported, locate the alarm in Table 4-1. The procedures for correcting alarm conditions are described in Recovering From Alarms.
Note:
Sometimes the alarm string may consist of multiple alarms and must be decoded in order to use the Alarm Recovery Procedures in this manual. If the alarm code is not listed, see Decode Alarm Strings.Platform and application errors are grouped by category and severity. The categories are listed from most to least severe:
-
Critical Platform Alarms
-
Critical Application Alarms
-
Major Platform Alarms
-
Major Application Alarms
-
Minor Platform Alarms
-
Minor Application Alarms
Table 4-1 shows the alarm numbers and alarm text for all alarms generated by the platform and the EPAP application. The order within a category is not significant.
Table 4-1 Platform and Application Alarms
4.2 EPAP Alarm Recovery Procedures
This section provides recovery procedures for platform and application alarms. The alarm categories are listed by severity.
4.3 Critical Platform Alarms
4.3.1 1000000000002000 - Uncorrectable ECC Memory Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that chipset has detected an uncorrectable (multiple-bit) memory error that the ECC (Error-Correcting Code) circuitry in the memory is unable to correct.
Severity: Critical
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.1.14TpdFanErrorNotifyTpdEccUncorrectableError
Alarm ID: TKSPLATCR141000000000002000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support to request hardware replacement.
4.5 Major Platform Alarms
Major platform alarms involve hardware components, memory, and network connections.
4.5.1 32300 3000000000000001 – Server Fan Failure
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that a fan on the application server is either failing or has failed completely. In either case, there is a danger of component failure due to overheating.
Description: This alarm indicates that a fan in the EAGLE fan tray in the EAGLE shelf where the E5-APP-B is "jacked in" is either failing or has failed completely. In either case, there is a danger of component failure due to overheating.
Severity: Major
OID: TpdFanErrorNotifyTpdFanErrorNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.1
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA13000000000000001
Recovery
Note:
4.5.2 32301 3000000000000002 - Server Internal Disk Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates the server is experiencing issues replicating data to one or more of its mirrored disk drives. This could indicate that one of the server’s disks has either failed or is approaching failure.
Severity: Major
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.2TpdFanErrorNotifyTpdIntDiskErrorNotify
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA23000000000000002
Recovery
4.5.3 32303 3000000000000008 - Server Platform Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates an error such as a corrupt system configuration or missing files, or indicates that syscheck itself is corrupt.
Severity: Major
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.4TpdFanErrorNotifyTpdPlatformErrorNotify
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA43000000000000008
Recovery
- Run syscheck in Verbose mode (see procedure Run Syscheck Manually).).
- Contact My Oracle Support and provide the system health check output.
4.5.4 32304 3000000000000010 - Server File System Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that syscheck was unsuccessful in writing to at least one of the server’s file systems.
Severity: Major
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.5TpdFanErrorNotifyTpdFileSystemErrorNotify
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA53000000000000010
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.5.5 32305 3000000000000020 - Server Platform Process Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that either the minimum number of instances for a required process are not currently running or too many instances of a required process are running.
Severity: Major
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.6TpdFanErrorNotifyTpdPlatProcessErrorNotify
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA63000000000000020
Recovery
4.5.6 32307 3000000000000080 - Server Swap Space Shortage Failure
Alarm Type: TPD
Note:
The interface identified as eth01 on the hardware is identified as eth91 by the software (in syscheck output, for example).Severity: Major
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.8TpdFanErrorNotifyTpdSwapSpaceShortageErrorNotify
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA83000000000000080
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.5.7 32308 3000000000000100 - Server Provisioning Network Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Note:
The interface identified as eth01 on the hardware is identified as eth91 by the software (in syscheck output, for example).Severity: Major
OID: TpdFanErrorNotifyTpdProvNetworkErrorNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.9
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA93000000000000100
Recovery
- Verify that a customer-supplied cable labeled TO CUSTOMER NETWORK is securely connected to the upper right port on the rear of the server on the EAGLE backplane.to the appropriate server. Follow the cable to its connection point on the local network and verify this connection is also secure.
- Test the customer-supplied cable labeled TO CUSTOMER NETWORK with an Ethernet Line Tester. If the cable does not test positive, replace it.
- Have your network administrator verify that the network is functioning properly.
- If no other nodes on the local network are experiencing problems and the fault has been isolated to the server or the network administrator is unable to determine the exact origin of the problem, contact My Oracle Support.
4.5.8 32309 3000000000000200 – Server Eagle Network A Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm is generated by the MPS syscheck software package and is not part of the TPD distribution.
Note:
If these three alarms exist, the probable cause is a failed mate server.-
3000000000000200-Server Eagle Network A Error
-
3000000000000400-Server Eagle Network B Error
-
3000000000000800-Server Sync Network Error
-
One or both of the servers is not operational.
-
One or both of the switches is not powered on.
-
The link between the switches is not working.
-
The connection between server A and server B is not working.
-
The eth01 interface (top ethernet port on the rear of the server A) connects to the customer provisioning network.
-
The eth02 interface (2nd from top ethernet port on the rear of the server A) connects to port 3 of switch A.
-
The eth03 interface (2nd from bottom ethernet port on the rear of the server A) connects to port 3 of switch B.
-
The eth04 interface (bottom ethernet port on the rear of the server A) is an optional connection to the backup customer provisioning network.
-
The interfaces on the switch are ports 1 through 20 (from left to right) located on the front of the switch.
-
Ports 1 and 2 of switch A connect to ports 1 and 2 of switch B.
-
Ports 5 through 21 of switch A can be used for links to the Main SM ports (SM A ports) on the EAGLE.
Severity: Major
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.10
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA103000000000000200
Recovery
4.5.9 32310 3000000000000400 – Server Eagle Network B Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm is generated by the MPS syscheck software package and is not part of the TPD distribution.
Note:
If these three alarms exist, the probable cause is a failed mate server.- 3000000000000200-Server Eagle Network A Error
- 3000000000000400-Server Eagle Network B Error
- 3000000000000800-Server Sync Network Error
-
One or both of the servers is not operational.
-
One or both of the switches is not powered on.
-
The link between the switches is not working.
-
The connection between server A and server B is not working.
-
The eth01 interface (top ethernet port on the rear of the server B) connects to the customer provisioning network.
-
The eth02 interface (2nd from top ethernet port on the rear of the server B) connects to port 4 of switch A.
-
The eth03 interface (2nd from bottom ethernet port on the rear of the server B) connects to port 4 of switch B.
-
The eth04 interface (bottom ethernet port on the rear of the server B) is an optional connection to the customer backup provisioning network.
-
The interfaces on the switch are ports 1 through 20 (from left to right) located on the front of the switch.
-
Ports 1 and 2 of switch A connect to ports 1 and 2 of switch B.
-
Ports 5 through 21 of switch B can be used for links to the Backup SM ports (SM B ports) on the EAGLE.
Severity: Major
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.11
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA113000000000000400
Recovery
4.5.10 32311 3000000000000800 – Server Sync Network Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm is generated by the MPS syscheck software package and is not part of the TPD distribution.
Note:
If these three alarms exist, the probable cause is a failed mate server.-
3000000000000200-Server Eagle Network A Error
-
3000000000000400-Server Eagle Network B Error
-
3000000000000800-Server Sync Network Error
Note:
The sync interface uses eth03 and goes through switch B. All pairs are required.Severity: Major
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.12
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA123000000000000800
Recovery
4.5.11 32312 3000000000001000 - Server Disk Space Shortage Error
Alarm Type: TPD
-
A filesystem has exceeded a failure threshold, which means that more than 90% of the available disk storage has been used on the filesystem.
-
More than 90% of the total number of available files have been allocated on the filesystem.
-
A filesystem has a different number of blocks than it had when installed.
Severity: Major
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.13
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA133000000000001000
Recovery
4.5.12 32313 3000000000002000 - Server Default Route Network Error
Alarm Type: TPD
syscheck in Verbose mode will provide information about which type of problem is occurring. Caution:
When changing the network routing configuration of the server, verify that the modifications will not impact the method of connectivity for the current login session. The route information must be entered correctly and set to the correct values. Incorrectly modifying the routing configuration of the server may result in total loss of remote network access.Severity: Major
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.14
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA143000000000002000
Recovery
4.5.13 32314 3000000000004000 - Server Temperature Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: The internal temperature within the server is unacceptably high.
Severity: Major
OID: TpdTemperatureErrorNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.15
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA153000000000004000
Recovery
4.5.14 32315 3000000000008000 – Server Mainboard Voltage Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that one or more of the monitored voltages on the server mainboard have been detected to be out of the normal expected operating range.
Severity: Major
OID: TpdMainboardVoltageErrorNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.16
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA163000000000008000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.5.15 32317 3000000000020000 - Server Disk Health Test Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: Either the hard drive has failed or failure is imminent.
Severity: Major
OID: TpdDiskHealthErrorNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.18
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA183000000000020000
Recovery
- Immediately contact My Oracle Support for assistance with a disk replacement.
- Perform the recovery procedures for the other alarms that accompany this alarm.
- If the problem has not been resolved, contact My Oracle Support.
4.5.16 32318 3000000000040000 - Server Disk Unavailable Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: The smartd service is not able to read the disk status because the disk has other problems that are reported by other alarms. This alarm appears only while a server is booting.
Severity: Major
OID: TpdDiskUnavailableErrorNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.19
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA193000000000040000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.5.17 32321 3000000000200000 – Correctable ECC Memory Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that chipset has detected a correctable (single-bit) memory error that has been corrected by the ECC (Error-Correcting Code) circuitry in the memory.
Severity: Major
OID: TpdEccCorrectableErrorNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.22
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA223000000000200000
Recovery
- No recovery necessary. If the condition persists, contact My Oracle Support to request hardware replacement.
4.5.18 32334 3000000400000000 - Multipath Device Access Link Problem
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: One or more "access paths" of a multipath device are failing or are not healthy, or the multipath device does not exist.
Severity: Major
OID: TpdMpathDeviceProblemNotify1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.35
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA353000000400000000
Recovery
- My Oracle Support should do the following:
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.5.19 3000000800000000 – Switch Link Down Error
This alarm indicates that the switch is reporting that the link is down. The link that is down is reported in the alarm. For example, port 1/1/2 is reported as 1102.
Recovery Procedure:
- Verify cabling between the offending port and remote side.
- Verify networking on the remote end.
- If problem persists, contact My Oracle Support to verify port settings on both the server and the switch.
4.5.20 32336 3000001000000000 - Half-open Socket Limit
Alarm Type: TPD
Description:This alarm indicates that the number of half open TCP sockets has reached the major threshold. This problem is caused by a remote system failing to complete the TCP 3-way handshake.
Severity: Major
OID: tpdHalfOpenSocketLimit 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.37
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA37 3000001000000000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.5.21 32337 3000002000000000 - Flash Program Failure
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates there was an error while trying to update the firmware flash on the E5-APP-B cards.
Severity: Major
OID: tpdFlashProgramFailure 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.38
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA383000002000000000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.5.22 32338 3000004000000000 - Serial Mezzanine Unseated
Alarm Type: TPD
Description:This alarm indicates the serial mezzanine board was not properly seated.
Severity: Major
OID: tpdSerialMezzUnseated 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.2.39
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMA393000004000000000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.6 Major Application Alarms
The major application alarms involve the EPAP software, RTDBs, file system and logs.
4.6.1 4000000000000001 - Mate EPAP Unavailable
One EPAP has reported that the other EPAP is unreachable.
Recovery
4.6.2 4000000000000002 - RTDB Mate Unavailable
The local EPAP cannot use the direct link to the Standby for RTDB database synchronization.
Recovery
4.6.3 4000000000000004 - Congestion
The EPAP RTDB database record cache used to keep updates currently being provisioned is above 80% capacity.
Recovery
4.6.4 4000000000000008 - File System Full
This alarm indicates that the server file system is full.
Recovery
- Call My Oracle Support for assistance.
4.6.5 4000000000000010 - Log Failure
This alarm indicates that the system was unsuccessful in writing to at least one log file.
- Call My Oracle Support for assistance.
4.6.7 4000000000000040 - Fatal Software Error
A major software component on the EPAP has failed.
Recovery
- Restart EPAP software. See Restarting the EPAP Software
- Capture the log files on both EPAPs (see Saving Logs Using the EPAP GUI) and contact My Oracle Support.
4.6.8 4000000000000080 - RTDB Corrupt
A real-time database is corrupt. The calculated checksum did not match the checksum value stored for one or more records.
Recovery
- Capture the log files on both EPAPs (see Saving Logs Using the EPAP GUI) and contact My Oracle Support.
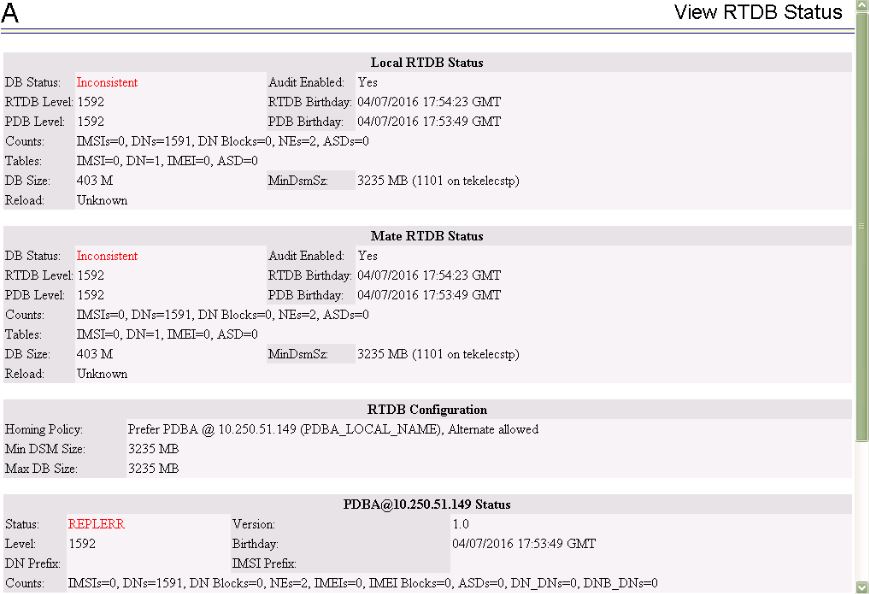
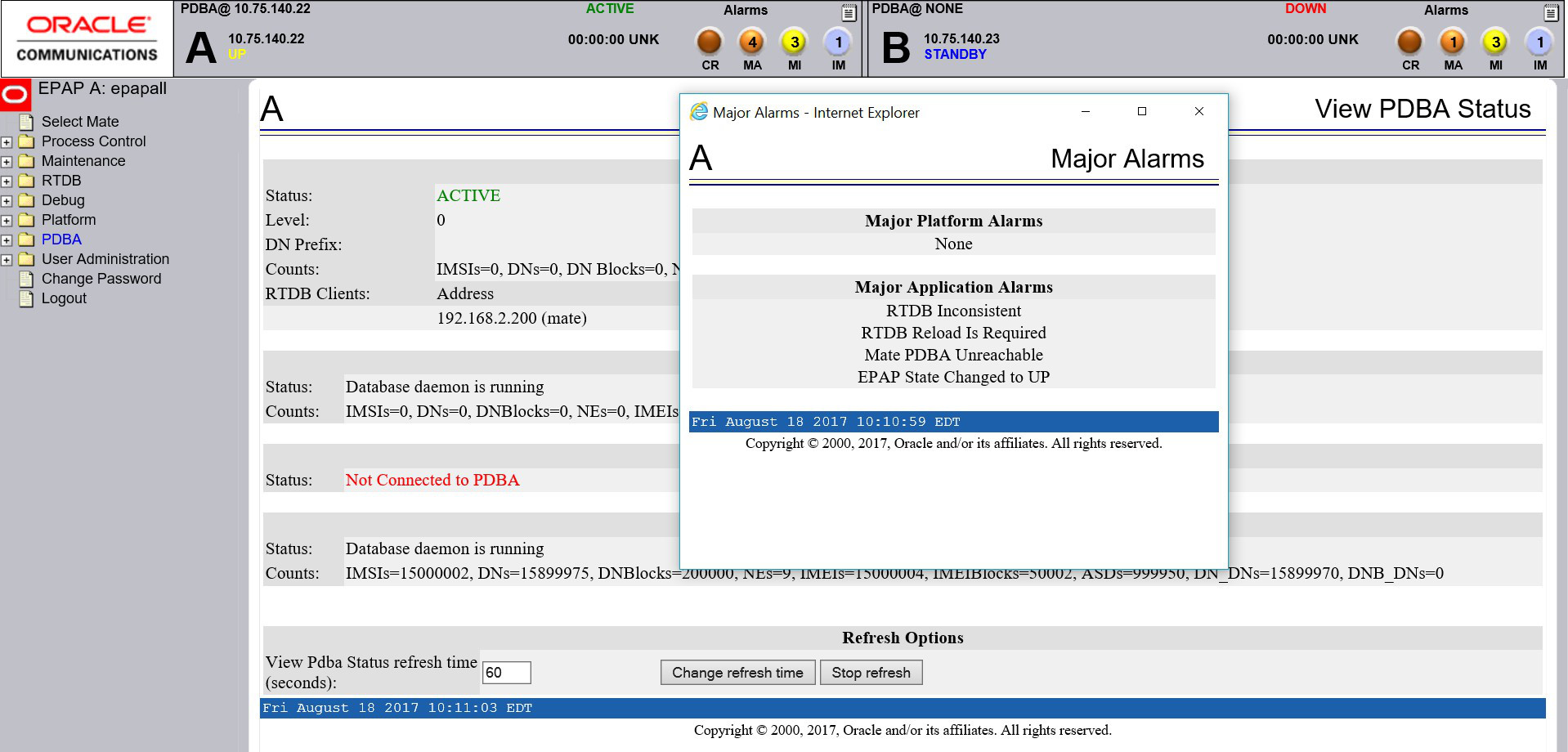
4.6.9 4000000000000100 - RTDB Inconsistent
This message indicates one or more of the following conditions:
-
The real-time database for one or more Service Module cards is inconsistent with the current real-time database on the Active EPAP fixed disks
-
RTDBs detect that it is ahead of an ACTIVEPDBA that it just connected to (probably a PDBA switchover has occurred, or a restore from a backup of PDB with a previous db level)
-
RTDB timestamp of most recent level does not match the PDBAs record of that timestamp.
Recovery
4.6.10 4000000000000200 - RTDB Incoherent
This message usually indicates that the RTDB database download is in progress.
When the download is complete, the following UIM message will appear:
0452 - RTDB reload complete
Recovery
- If this alarm displays while an RTDB download is in progress, no further action is necessary.
- If this alarm displays when an RTDB download is not in progress, capture the log files on both EPAPs (see Saving Logs Using the EPAP GUI) and contact My Oracle Support.
4.6.11 4000000000001000 - RTDB 100% Full
The RTDB on the EPAP is at capacity. The EPAP RTDB is not updating.
You may be able to free up space by deleting unnecessary data in the database.
This error can result from one of the following conditions on the EAGLE:
- The EPAP Data Split feature is not ON
- The epap240m STP option is not ON (E5-SM8G-B card required)
- The 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via split database feature is OFF at EPAP and OFF at Eagle
- The 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via split database feature is OFF at EPAP and ON at Eagle
Recovery
- On the EAGLE, turn ON the optional EPAP Data Split feature to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- On the EAGLE, turn ON the epap240m STP option (E5-SM8G-B card required) to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- Turn ON the optional 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via Split database feature on the EPAP and Eagle to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- Contact My Oracle Support for assistance.
4.6.12 4000000000002000 - RTDB Resynchronization In Progress
This message indicates that the RTDB resynchronization is in progress.
Recovery
- No further action is necessary.
4.6.13 4000000000004000 - RTDB Reload Is Required
This message indicates that the RTDB reload is required for one of the following reasons:
-
The PDB Birthday on the EPAP reporting the error does not match the mate EPAP’s PDB Birthday.
-
The transaction logs did not contain enough information to resynchronize the databases (the transaction logs may be too small).
Caution:
If both sides are reporting this error, contact My Oracle Support.
If only one side is reporting this error, use the following procedure.
Recovery
4.6.14 4000000000008000 - Mate PDBA Unreachable
This message indicates that the other PDBA is unreachable.
Recovery
4.6.15 4000000000010000 - PDBA Connection Failure
The local EPAP RTDB process cannot connect to the local PDBA.
Recovery
4.6.16 4000000000020000 - PDBA Replication Failure
Provisioning data is no longer being exchanged from the Active PDB to the Standby PDB.
- Run
savelogs(see Saving Logs Using the EPAP GUI). - Contact My Oracle Support.
4.6.17 4000000000040000 - RTDB DSM Over-Allocation
At least one Service Module card in the attached EAGLE has insufficient memory to provision the RTDB entry. No more provisioning will be allowed to the RTDB until this issue is resolved.
Recovery
- Install Service Module cards in the attached EAGLE with sufficient memory to accommodate the expected size of the RTDB.
- Contact My Oracle Support for assistance.
4.6.18 4000000000080000 - RTDB Maximum Depth Reached
For ELAP 7.0 or earlier, this alarm indicates that the maximum depth has been reached for a tree. If the alarm was initiated during a data update, the update will continually fail until there is manual intervention. RTDB data is stored as inverse tree structures. The trees have a maximum depth allowed.
This alarm indicates that the maximum depth has been reached for a tree. If the alarm was initiated during a data update, the update will continually fail until there is manual intervention. RTDB data is stored as inverse tree structures. The trees have a maximum depth allowed.
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.6.19 4000000000100000 - No PDBA Proxy to Remote PDBA Connection
This message indicates that the PDBA Proxy feature is disabled or the software is down.
Recovery
4.6.20 4000000000200000 - DSM Provisioning Error
A coherent SM RTDB is more than 1000 levels behind the EPAP RTDB.
Recovery
4.6.21 4000000000800000 - EPAP State Changed to UP
The standby EPAP state was changed from STANDBY to UP.
Recovery
4.6.22 4000000004000000 - RTDB Overallocated
At least one Service Module card in the attached EAGLE has insufficient memory to provision the RTDB entry. No more provisioning will be allowed to the RTDB until this issue is resolved.
This error can result from one of the following conditions on the EAGLE:
- The EPAP Data Split feature is not ON
- The epap240m STP option is not ON (E5-SM8G-B card required)
- The 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via split database feature is OFF at EPAP and OFF at Eagle
- The 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via split database feature is OFF at EPAP and ON at Eagle
Recovery
- On the EAGLE, turn ON the optional EPAP Data Split feature to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- On the EAGLE, turn ON the epap240m STP option (E5-SM8G-B card required) to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- Turn ON the optional 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via Split database feature on the EPAP and Eagle to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- Contact My Oracle Support for assistance.
4.6.23 4000000020000000 - Mysql Lock Wait Timeout Exceeded
If MySQL is not able to get a lock to write to the PDB table, then an alarm is raised after 15 minutes when the lock wait timeout is exceeded.
Occasionally, a transaction can hang for a longer time, particularly in a multi-threaded environment, and also due to some underlying hardware failure on the disk, kernel bugs, and so on.
Recovery
Restart the PDB software.
4.7 Minor Platform Alarms
Minor platform alarms involve disk space, application processes, RAM, and configuration errors.
4.7.1 32500 5000000000000001 – Server Disk Space Shortage Warning
Alarm Type: TPD
- A file system has exceeded a warning threshold, which means that more than 80% (but less than 90%) of the available disk storage has been used on the file system.
- More than 80% (but less than 90%) of the total number of available files have been allocated on the file system.
Severity: Minor
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.1
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI15000000000000001
Recovery
- Examine the syscheck output to determine if the file system
/var/TKLC/epap/free/var/TKLC/elap/freeis low on space. If so, continue to step 2a; otherwise skip to step 3. - Delete unnecessary files, as follows, to free up space on the free partition:
- Contact My Oracle Support, and provide the system health check output.
4.7.2 32501 5000000000000002 – Server Application Process Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that either the minimum number of instances for a required process are not currently running or too many instances of a required process are running.
Severity: Minor
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.2
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI25000000000000002
Recovery
4.7.3 5000000000000004 - Server Hardware Configuration Error
Recovery
- Run
syscheckin verbose mode. - Call My Oracle Support for assistance.
4.7.4 32506 5000000000000040 – Server Default Router Not Defined
Alarm Type: TPD
Caution:
When changing the server’s network routing configuration it is important to verify that the modifications will not impact the method of connectivity for the current login session. It is also crucial that this information not be entered incorrectly or set to improper values. Incorrectly modifying the server’s routing configuration may result in total loss of remote network access.Severity: Minor
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.7
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI75000000000000040
Recovery
- Run syscheck in verbose mode (see procedure Running the System Health Check).
- Contact My Oracle Support, and provide the system health check output.
- To define the default router:
- Run
syscheckagain. If the alarm has not been cleared, go to 6 - Run
savelogsto gather all application logs, (see Saving Logs Using the EPAP GUI). - Contact My Oracle Support.
4.7.5 32507 5000000000000080 – Server Temperature Warning
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that the internal temperature within the server is outside of the normal operating range. A server Fan Failure may also exist along with the Server Temperature Warning.
Severity: Minor
OID: tpdTemperatureWarningNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.8
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI85000000000000080
Recovery
4.7.6 32508 5000000000000100 – Server Core File Detected
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that an application process has failed and debug information is available.
Severity: Minor
OID: tpdCoreFileDetectedNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.9
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI95000000000000100
Recovery
4.7.7 32509 5000000000000200 – Server NTP Daemon Not Synchronized
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that the NTP daemon (background process) has been unable to locate a server to provide an acceptable time reference for synchronization.
Severity: Minor
OID: tpdNTPDeamonNotSynchronizedNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.10
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI105000000000000200
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.7.8 32511 5000000000000800 – Server Disk Self Test Warning
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: A non-fatal disk issue exists.
Severity: Minor
OID: tpdSmartTestWarnNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.12
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI125000000000000800
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.7.9 32514 5000000000004000 – Server Reboot Watchdog Initiated
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that the hardware watchdog was not strobed by the software and so the server rebooted the server. This applies to only the last reboot and is only supported on a T1100 application server.
Severity: Minor
OID: tpdWatchdogRebootNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.15
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI155000000000004000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.7.10 32518 5000000000040000 – Platform Health Check Failure
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm is used to indicate a syscheck configuration error.
Severity: Minor
OID: tpdPlatformHealthCheckFailedNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.19
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI195000000000040000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.7.11 32519 5000000000080000 – NTP Offset Check Failed
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This minor alarm indicates that time on the server is outside the acceptable range (or offset) from the NTP server. The Alarm message will provide the offset value of the server from the NTP server and the offset limit that the application has set for the system.
Severity: Minor
OID: ntpOffsetCheckFailedNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.20
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI205000000000080000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.7.12 32520 5000000000100000 – NTP Stratum Check Failed
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that NTP is syncing to a server, but the stratum level of the NTP server is outside of the acceptable limit. The Alarm message will provide the stratum value of the NTP server and the stratum limit that the application has set for the system.
Severity: Minor
OID: NtpStratumCheckFailedNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.21
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI215000000000100000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.7.13 325295000000020000000 – Server Kernel Dump File Detected
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that the kernel has crashed and debug information is available.
Severity: Minor
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.30
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI305000000020000000
Recovery
- Run syscheck in Verbose mode (see Running the System Health Check).
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.7.14 325305000000040000000 – TPD Upgrade Failed
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm indicates that a TPD upgrade has failed.
Severity: Minor
OID: tpdServerUpgradeFailDetectedNotify 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.31
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI315000000040000000
Recovery
4.7.15 325315000000080000000– Half Open Socket Warning
Alarm Type: TPD
This alarm indicates that the number of half open TCP sockets has reached the major threshold. This problem is caused by a remote system failing to complete the TCP 3-way handshake.
Severity: Minor
Instance: May include AlarmLocation, AlarmId, AlarmState, AlarmSeverity, and bindVarNamesValueStr
HA Score: Normal
Auto Clear Seconds: 0 (zero)
OID: eagleXgDsrTpdHalfOpenSocketWarningNotify1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.32
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI325000000080000000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.7.16 5000000100000000 – Server Upgrade Pending Accept/Reject
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: This alarm is generated if an upgrade is not accepted or rejected after the upgrade.
Severity: Minor
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.323.5.3.18.3.1.3.33
Alarm ID: TKSPLATMI33
Alarm Value: 5000000100000000
Recovery
To clear this alarm, the upgrade should be accepted/rejected via the platcfg menu.
4.7.17 5000004000000000 - Platform Data Collection Error
Alarm Type: TPD
Description: Platform Data Collection Error
Severity: Minor
OID: tpdPdcError
Alarm ID: 5000004000000000
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.8 Minor Application Alarms
Minor application alarms involve the EPAP RMTP channels, RTDB capacity, and software errors.
4.8.1 6000000000000001 - RMTP Channel A Down
Channel A of the IP multicast mechanism is not available.
Recovery
4.8.2 6000000000000002 - RMTP Channel B Down
Channel B of the IP multicast mechanism is not available.
Recovery
4.8.3 6000000000000008 - RTDB 80% Full
For ELAP 7.0 or earlier, the RTDB on the EPAP or DSM is approaching capacity (80%).
The RTDB on the EPAP or DSM is approaching capacity (80%).
This error can result from one of the following conditions on the EAGLE:
- The EPAP Data Split feature is not ON
- The epap240m STP option is not ON (E5-SM8G-B card required)
- The 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via split database feature is OFF at EPAP and OFF at Eagle
- The 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via split database feature is OFF at EPAP and ON at Eagle
Recovery
- On the EAGLE, turn ON the optional EPAP Data Split feature to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- On the EAGLE, turn ON the epap240m STP option (E5-SM8G-B card required) to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- Turn ON the optional 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via Split database feature on the EPAP and Eagle to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- Contact My Oracle Support for assistance.
4.8.5 6000000000000020 - Standby PDBA Falling Behind
This is an indication that there is a congestion condition affecting updates to the standby PDBA. The amount of time between an update being committed in the Active PDB and the same update being committed in the Standby PDB has reached an unacceptable level.
- Provisioning activity is very heavy
- The provisioning network is experiencing errors or latency
- Server maintenance functions (such as backups, restores, imports, exports, etc) are occurring
Recovery
4.8.6 6000000000000040 - RTDB Tree Error
For ELAP 7.0 or earlier, this alarm indicates either that the depth is greater than the theoretical maximum or that some other general problem has been found with a tree. RTDB data is stored as inverse tree structures. The trees have maximum theoretical depths based on the number of records in the tree.
This alarm indicates either that the depth is greater than the theoretical maximum or that some other general problem has been found with a tree. RTDB data is stored as inverse tree structures. The trees have maximum theoretical depths based on the number of records in the tree.
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.8.7 6000000000000080 - PDB Backup failed
The PDB backup failed because of at least one of the following conditions:
-
A manual backup script was not able to create PDB backup successfully
-
A PDB backup was already in progress when Automatic PDB backup attempted to start
-
A PDB restore was in progress when the Automatic PDB backup attempted to start
To verify the exact failure condition, refer to the error string in the log file.
Note:
This alarm will also clear if the Automatic PDB/RTDB backup executes successfully during the next scheduled backup time.Recovery
- To clear this alarm immediately, perform one of the following:
-
Cancel the Automatic PDB / RTDB backup via the EPAP GUI as follows:
Note:
Automatic PDB / RTDB Backup will have to be rescheduled if it is cancelled.-
Log in to the User Interface screen of the EPAP GUI (see Accessing the EPAP GUI).
-
From the menu, select Maintenance>Automatic PDB/RTDB Backup to display the automatic backup screen.
-
From the Automatic PDB/RTDB Backup screen, select None as the Backup Type.
-
Select the Schedule Backup button to complete the cancellation.
Automatic PDB/RTDB Backup will have to be rescheduled. Refer to Administration Guide to reschedule the Automatic PDB / RTDB Backup.
-
- Perform a manual backup via the EPAPGUI (see Backing Up the PDB).
-
4.8.8 6000000000000100 - Automatic PDB Backup failed
The PDB backup failed because of at least one of the following conditions:
-
The mate machine was not reachable.
-
The SCP command to transfer of PDB backup file to mate fails
-
The transfer of Automatic PDB Backup to Mate fails
-
The transfer of Automatic PDB Backup to mate failed due to disk space shortage on mate
-
The remote machine was not reachable
-
The connection to remote host failed for SFTP of the PDB Backup file
-
The SFTP to the remote host failed for Automatic PDB Backup
-
The login or password configured for the Remote machine is wrong for the configured user
-
The Destination File Path to store the PDB Backup file in Remote machine configured by the user does not exist
-
The transfer of the Automatic PDB Backup to the remote failed due to disk space shortage on the remote
To verify the exact failure condition, refer to the error string in the log file.
Note:
This alarm will clear if the Automatic PDB / RTDB backup executes successfully during the next scheduled backup time.Recovery
To clear this alarm immediately, cancel the Automatic PDB/RTDB backup via the EPAPGUI, as described in 1 through 4.
Note:
Automatic PDB/RTDB Backup will have to be rescheduled if it is cancelled.4.8.9 6000000000000200 - RTDB Backup failed
The RTDB backup failed because of at least one of the following conditions:
-
The manual backup script (backupRtdb.pl) was not able to create RTDB Backup successfully.
-
The EPAP software could not be successfully stopped in order for Automatic RTDB Backup to start.
-
Another user has already stopped the EPAP Software before the script stops the EPAP Software for Automatic RTDB Backup
-
Another user is currently stopping the EPAP Software. The Automatic RTDB Backup script cannot stop the EPAP Software.
-
The GUI Server returned an error when trying to get a lock from it for Automatic RTDB Backup.
-
Not able to connect to GUI server for Automatic RTDB Backup
-
The EPAP software was not running when it was to be stopped for Automatic RTDB Backup
-
The mate machine is not reachable.
Note:
This alarm will clear if the Automatic PDB/RTDB backup executes successfully during the next scheduled backup time.Recovery
- To clear this alarm immediately, perform one of the following:
-
Cancel the Automatic PDB/RTDB backup in the EPAP GUI.
Note:
Automatic PDB/RTDB Backup will have to be rescheduled if it is cancelled.-
Log in to the User Interface screen of the EPAP GUI (see Accessing the EPAP GUI).
-
From the menu, select Maintenance>Automatic PDB/RTDB Backup to display the Automatic PDB/RTDB Backup screen.
-
From the Automatic PDB/RTDB Backup screen, select None as the Backup Type.
-
Select the Schedule Backup button to complete the cancellation. Automatic PDB/RTDB Backup will have to be rescheduled. Refer to Administration Guide to reschedule the Automatic PDB/RTDB Backup.
-
- Perform a manual backup via the EPAP GUI as described in Backing Up the RTDB.
-
4.8.10 6000000000000400 - Automatic RTDB Backup failed
The RTDB backup failed because of at least one of the following conditions:
-
The mate machine is not reachable.
-
Automatic RTDB Backup file transfer to the Mate failed.
-
Unable to connect to Remote host IP Address for Automatic RTDB Backup.
-
Automatic RTDB Backup file transfer to the Remote failed.
-
The incorrect login or password configured for Automatic RTDB Backup.
-
The destination path does not exist in remote machine IP Address for Automatic RTDB Backup.
To verify the exact failure condition, refer to the error string in the log file.
Note:
This alarm will clear if the Automatic PDB/RTDB backup executes successfully during the next scheduled backup time.Recovery
4.8.11 6000000000001000 - SSH tunnel not established
One or more SSH tunnels has been enabled in the past, but the cron job was not able to re-establish the SSH tunnel with all of the Authorized PDBA Client IP addresses.
Recovery
- Verify that the Customer Provisioning Application (CPA) machine is up and running.
- If the CPA machine is not running, restart it and wait for the alarm to clear.
- If the CPA machine is running, or if the alarm does not clear, contact My Oracle Support.
- If the alarm text is "SSH tunnel down for <IP>", verify that the port specified for SSH tunneling is not in use on the remote machine.
4.8.12 6000000000002000 - RTDB 90% Full
The RTDB on the EPAP is approaching capacity (90%).
This error can result from one of the following conditions on the EAGLE:
- The EPAP Data Split feature is not ON
- The epap240m STP option is not ON (E5-SM8G-B card required)
- The 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via split database feature is OFF at EPAP and OFF at Eagle
- The 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via split database feature is OFF at EPAP and ON at Eagle
Recovery
- On the EAGLE, turn ON the optional EPAP Data Split feature to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- On the EAGLE, turn ON the epap240m STP option (E5-SM8G-B card required) to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- Turn ON the optional 120M DN and 120M IMSIs via Split database feature on the EPAP and Eagle to allow more room for the provisioned data.
- Contact My Oracle Support for assistance.
4.8.13 6000000000004000 - PDB 90% Full
The PDB on the EPAP has exceeded 90% of purchased capacity.
Recovery
For assistance or additional information, contact My Oracle Support.
4.8.14 6000000000008000 - PDB 80% Full
The PDB on the EPAP has exceeded 80% of purchased capacity.
Recovery
For assistance or additional information, contact My Oracle Support.
4.8.15 6000000000010000 - PDB InnoDB Space 90% Full
The storage space in InnoDB Engine on the EPAP is approaching capacity (90%).
Recovery
- Purchase additional provisioning database capacity licenses.
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.8.16 6000000000040000 - RTDB Client Lagging Behind
This alarm is generated if the RTDB was not up while provisioning was done at the PDB, or if there is latency in the network resulting in RTDBs receiving updates late.
Note:
This alarm may occur during import and should eventually clear when the RTDB process catches up.Recovery
The provisioning at the PDBs can be stopped until the RTDBs reach the same level.
4.8.17 6000000000080000 - Automatic Backup is not configured
The Automatic Backup is not configured at the PDB only.
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.8.18 6000000000100000 - EPAP QS Replication Issue
The EPAP Query Server is not reachable, not associated, or disconnected from the EPAP.
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.8.19 6000000000200000 - EPAP QS Lagging Behind
The EPAP Query Server is not in synch with the EPAP and is falling behind from a threshold set by the user.
Recovery
- Contact My Oracle Support.
4.8.20 6000000000400000 - License capacity is not configured
The license capacity has never been set or the license capacity is set to 0.
By default, up to 120M can be provisioned if license capacity is not set. To use the EPAP Expansion to 480M Database Entries feature, additional capacity (i.e., Required Capacity - Current Purchased Capacity) must be purchased before adjusting the license capacity using the following procedure. For capacity over 255M, 480G drive modules are required.
Recovery
For assistance or additional information, contact My Oracle Support.
4.8.21 6000000000800000 - Long wait on write for PDBI update
- Issue the uiEdit command
where <time in seconds> is the time value that a PDBI connection is allowed to hold a write connection before triggering the alarm."PDBI_LONG_WAIT_ALARM_TIME" <time in seconds> - Investigate the alarm banner on the EPAP GUI for the alarm text "Long wait on write for PDBI update"; or, identify the alarm bit 6000000000800000 from the connected EAGLE; or, find the alarm number 45121 from the SNMP NM server.
- If the alarm is triggered, find the PDBI connection information by issuing the
grep
command in the"Throw alarm for connection" pdba.err.*
directory./usr/TKLC/epap/logs - Clear the alarm to release the PDBI write connection in question.
4.8.22 6000000001000000 - NE count mismatch between PDB and RTDB
Customer should schedule a cron job in “/etc/cron.d/TS.EXAP” for “/usr/TKLC/appl/bin/checkNEsanity.pl” in order to raise the alarm, when there is count mismatch between PDB and RTDB for Network Entity (NE). This cron will be scheduled only on the server having RTDB, hence don’t schedule the cron on pdbonly server.
- Cron should be scheduled once in a day.
- Server should not be involved in any other activity at the time when this cron is scheduled, to neglect any impact.
- It will be good to schedule the cron when the provisioning rate is very low or negligible.
- Cron should be scheduled at some specific time of the day when scheduling for once in a day.
For example: To schedule daily once at 05:00 , Sched="daily,1,05:00"
00 05 * * * epapdev /usr/TKLC/appl/bin/checkNEsanity.pl
- When the alarm is observed, savelogs (application logs) is automatically taken for the first time but the customer will have to take the platform logs manually from the platcfg menu. Also, customer can retake the application logs, if more recent logs are needed.
- If we have other RTDBs connected to the same PDB and the DB on them is good, then the customer can restore the backup from one of the other connected RTDBs on this RTDB.
- If all RTDBs connected to the same PDB are show NE mismatch then restore both PDB and RTDB from backup taken from another site having the similar database.
- If the above two options are not feasible, then do a reload from PDB on this RTDB. This will reload the database from scratch on RTDB, from the connected PDB. This process will take time depending upon the total size of the database.
Contact support for any query.