46 DBaaS REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs Based Use Cases
It contains the following sections:
-
Creating Databases Using Database Template With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
-
Creating Empty Schemas and Schemas Based on Profile With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
-
Creating Empty PDBs and PDBs Based on Profile With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
-
Creating Databases Using Snap Clone With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
-
Creating Full Database Clones Using RMAN With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
-
Configuring Custom Database Placement Option Using REST APIs
Getting Started with DBaaS With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
The following figure provides an overview of the different flavors of Enterprise Manager DBaaS.
Figure 46-1 DBaaS Use Cases
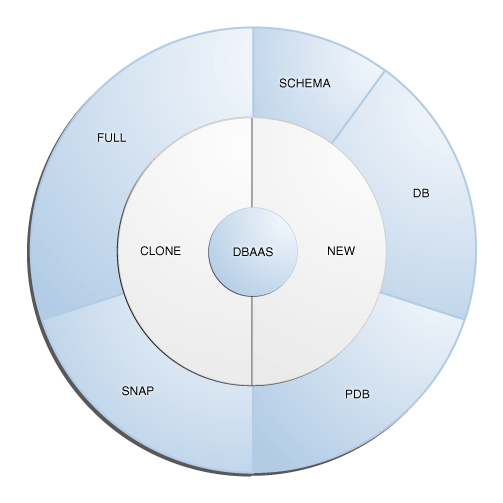
This table lists the DBaaS use cases that are supported in this release and lists the different methods (EMCLI, and REST API) that can be used to run these use cases.
Table 46-1 DBaaS Use Cases
| Service Type | Service Offering | See |
|---|---|---|
|
New |
Creating databases using a database template. |
Creating Databases Using Database Template With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs |
|
New |
Schema:
|
Creating Empty Schemas and Schemas Based on Profile With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs |
|
New |
Pluggable Database:
|
Creating Empty PDBs and PDBs Based on Profile With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs |
|
Migrating or transferring data from one database to another. |
||
|
Snap Clone |
|
Creating Databases Using Snap Clone With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs |
|
Clone |
Full Clone:
|
Creating Full Database Clones Using RMAN With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs |
|
New DBaaS setup |
Multi-Datacenter DBaaS setup |
Creating Databases Using Database Template With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
The DBCA template supports both structure plus data and structure only types. This database provisioning profile is created from the production or source database registered with Enterprise Manager. It supports both structure plus data and structure only types. This option is recommended if the database size being created is less than 50 GB.
The table below shows the list of tasks that are involved in creating a database using the database template based profile.
You can create single instance and cluster databases using database template based profiles.
Note:
In the table below, wherever REST APIs are not available for any steps EM CLI verbs are provided, and vice-versa.
Table 46-2 Creating Databases Using Database Template with REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
| Step | Task | REST APIs | EM CLI Verbs |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Follow the steps in the Getting Started section to enable DBaaS. |
See Getting Started |
See Getting Started |
|
2 |
Create resource providers.
|
See: |
See: |
|
6 |
Create a DBCA template based database provisioning profile. |
||
|
4 |
Create the request settings. |
||
|
5 |
Define quotas for each self service user. |
||
|
7 |
Create a service template based on the profile you have created. |
See Service Templates and Service Template REST API Examples |
|
|
8 |
Configure the Chargeback Service. |
||
|
9 |
While deploying a database, select the service template (associated with the database template based profile) you have created. |
Creating Standby Databases With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
A data guard configuration consists of one primary database and one or more standby databases. The databases in a Data Guard configuration are connected by Oracle Net and may be dispersed geographically. There are no restrictions on where the databases are located, provided they can communicate with each other.
Oracle Data Guard ensures high availability, data protection, and disaster recovery for enterprise data. It provides a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases to enable production Oracle databases to survive disasters and data corruptions. Oracle Data Guard maintains these standby databases as copies of the production database. If the production database becomes unavailable due to a planned or an unplanned outage, the Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage.
The production database, also referred to as the primary database can be either a single-instance Oracle database or an Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) database. A standby database is a transaction-wise consistent copy of the primary database. Using a backup copy of the primary database, you can create one or more standby databases and incorporate them in a Data Guard configuration. Using Enterprise Manager Database as a Service, users with the EM_SSA_ADMINISTRATOR role can setup the DBaaS Cloud with single instance of RAC standby databases.
Note:
In the table below, wherever REST APIs are not available for any steps EM CLI verbs are provided, and vice-versa.
Table 46-3 Creating Standby Databases with REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
| Step | Task | REST APIs | EM CLI Verbs |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Follow the steps in the Getting Started section to enable DBaaS. |
See Getting Started |
See Getting Started |
|
2 |
Set up one or more PaaS Infrastructure Zones. |
||
|
3 |
Define a database pool for provisioning standby databases. |
||
|
4 |
Configure the request settings. |
||
|
5 |
Define quotas for each self service user. |
||
|
6 |
Create either of the following types of profiles:
|
||
|
7 |
Create a service template based on the profile you have created. |
See Service Templates and Service Template REST API Examples |
|
|
8 |
Configure the Chargeback Service. |
||
|
9 |
While deploying a database, select the service template (associated with the DBCA template based profile) you have created. Additionally, you can also specify the standby database information while requesting the database. |
Placement of Standby Databases
You can take advantage of the custom placement option when a Service template is configured with a Standby database. The following example shows the Body for the request submission to support the custom placement for a Standby database.
{
"zone": "/em/cloud/dbaas/zone/F5D6E03052068EE378DEFFD720DA6EEA",
"name": "Request a SI Database1",
"description": "Request a Single Instance Database",
"standby_required":"true",
"params": {
"username": "ssauser1",
"password": "welcome",
"database_sid": "prmdb",
"database_host_name":"mydbhost.mysite.com",
"service_name": "service_1",
"standbydbs":
[
{
"standbydb_name" : "stdby" ,
"standbydb_domain_name":"mysite.com",
"standbydb_type" : "oracle_database",
"standbydb_host_name":"mydbhost.mysite.com"
}
]
}
}
Creating Empty Schemas and Schemas Based on Profile With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
The data content of a database provisioning profile is compiled from an export dump. You can choose to export Schema objects (structure only) or the Schema with data (structure and data).
The table below shows the list of tasks that are involved in creating an empty schema or a schema based on profile.
Note:
In the table below, wherever REST APIs are not available for any steps EM CLI verbs are provided, and vice-versa.
Table 46-4 Creating Schemas with REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
| Step | Task | REST APIs | EM CLI Verbs |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Follow the steps in the Getting Started section to enable DBaaS. |
See Getting Started |
See Getting Started |
|
2 |
Set up one or more PaaS Infrastructure Zones. |
||
|
3 |
Define a database pool for schema as a service. |
||
|
4 |
Configure the request settings. |
||
|
5 |
Define quotas for each self service user. |
||
|
6 |
Create a database provisioning profile. This step is optional and is required if you are importing schemas from a profile. |
||
|
7 |
Create a service template based on:
|
||
|
8 |
Configure the Chargeback Service. |
||
|
9 |
Create the schema based on the service template. |
Creating Empty PDBs and PDBs Based on Profile With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
An Oracle Database can contain a portable collection of schemas, schema objects, and non-schema objects, that appear to an Oracle Net client as a separate database. This self-contained collection is called a pluggable database (PDB). A multi-tenant container database (CDB) is a database that includes one or more PDBs. Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1) and later versions allow you to create many PDBs within a single CDB.
Note:
In the table below, wherever REST APIs are not available for any steps EM CLI verbs are provided, and vice-versa.
Table 46-5 Creating Pluggable Databases with REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
| Step | Task | REST APIs | EM CLI Verbs |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Follow the steps in the Getting Started section to enable DBaaS. |
See Getting Started |
See Getting Started |
|
2 |
Set up one or more PaaS Infrastructure Zones. |
||
|
3 |
Create a database pool for PDB as a service. |
||
|
4 |
Configure the request settings. |
||
|
5 |
Define quotas for each self service user. |
||
|
6 |
Create a database provisioning profile. This step is optional and is not required if you are creating an empty pluggable database. |
||
|
7 |
Create a service template. A service template can contain:
|
||
|
8 |
Configure the Chargeback Service. |
||
|
9 |
While deploying a database, select the service template that you have created. |
Migrating/Transferring Data from One Database to Another
To migrate data from one database to another using EM CLI verbs, follow the steps below:
Creating Databases Using Snap Clone With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
Snap Clone is a Self-Service-Application (SSA) way of creating fast and space-saver clones of huge databases. Clones of the production database are often required for test and development purposes, and it is difficult and time consuming to create these clones, especially if the databases are huge.
Enterprise Manager offers Snap Clone as a way to address this issue, so that thin clones can be created from production databases by using the copy on write technology available in some storage systems. This means that these clones take up little space initially (about 2 GB of writable space required for a thin clone of a multi-terabyte database), and will grow as inserts, updates and deletes are performed. Enterprise Manager offers two solutions with snap clone:
-
Hardware Solution: Vendor specific hardware solution which supports NetApps, Oracle Sun ZFS storage appliance, EMC VMAX, and VNX.
-
Software Solution: Storage agnostic software solution that supports all NAS and SAN storage devices. This is supported through use of the ZFS file system, and the CloneDB feature.
The main features of snap clone are:
-
Self Service Driven Approach: Empowers the self service user to clone databases as required on an ad-hoc basis.
-
Rapid Cloning: Databases can be cloned in minutes and not in days or weeks.
-
Space Efficient: This features allows users to significantly reduce the storage footprint.
This section contains the following sub-sections:
Creating a Snap Clone Using a Profile With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
This table below lists the steps involved in creating a snap clone using a snapshot or an RMAN Image profile.
Note:
In the table below, wherever REST APIs are not available for any steps EM CLI verbs are provided, and vice-versa.
Table 46-6 Creating a Snap Clone Database Using a Profile with REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
| Step | Task | REST APIs | EM CLI Verbs |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Follow the steps in the Getting Started section to enable Snap Clone. |
See Getting Started |
See Getting Started |
|
2 |
Register storage servers.
|
||
|
3 |
Set up one or more PaaS Infrastructure Zones. |
||
|
4 |
Create a database pool. |
||
|
5 |
Configure the request settings. |
||
|
6 |
Define quotas for each self service user. |
||
|
7 |
Set up the Test Master Database and enable snap clone. |
||
|
8 |
Depending on the snap clone solution you are using, do either of the following:
Create a database provisioning profile using a snap clone. |
|
|
|
9 |
Create a service template based on the profile you have created. |
|
|
|
10 |
Configure the Chargeback Service. (this step is optional) |
||
|
11 |
While deploying a database, select the service template you have created. |
Creating a Snap Clone Using Live Database With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
This table below lists the steps involved in creating a snap clone using a live standby database.
Note:
In the table below, wherever REST APIs are not available for any steps EM CLI verbs are provided, and vice-versa.
Table 46-7 Creating Snap Clone Using Live Database With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
| Step | Task | REST APIs | EM CLI Verbs |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Follow the steps in the Getting Started section to enable Snap Clone. |
See Getting Started. |
See Getting Started. |
|
2 |
Register storage servers.
|
See: |
See: |
|
3 |
Set up one or more PaaS Infrastructure Zones. |
||
|
4 |
Create a database pool. |
||
|
5 |
Configure the request settings. |
||
|
6 |
Define quotas for each self service user. |
||
|
7 |
Set up the Test Master Database using a live standby database. |
||
|
9 |
Create a service template. |
See Service Templates and Service Template REST API Examples |
|
|
10 |
Configure the Chargeback Service. (this step is optional) |
||
|
11 |
While deploying a database, select the service template you have created. |
Continuous Sync
A continuous sync setup has a production database and a Test master database which is on a filer (NAS storage). The Test master is an RMAN image backup of the data files and is scheduled to run a backup of the production database at regular intervals. Thereby the Test master database gets continuous/live data from the production database.
To set up a continuous sync database setup, follow the steps below:
Table 46-8 Creating a Continuous Sync Setup Using EM CLI Verbs
| Step | Task | EM CLI Verb |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Add an existing standby database.Currently, this task can be accomplished only via the UI screen. |
Not available |
|
2 |
Create a new Test master from a standby database. |
|
|
3 |
Create a clone. |
|
|
4 |
Promote the clone as the Test master. Currently, this task can be accomplished only via the UI screen. |
Not available |
Creating Full Database Clones Using RMAN With REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
There are two ways of cloning full databases using RMAN. They are:
Creating a Full Database Clone Using RMAN Backup
Database backups created by RMAN (Recovery Manager) are stored as image copies or backup sets. You can create profiles using these backups and use these profiles to create full database clones.
Note:
In the table below, wherever REST APIs are not available for any steps EM CLI verbs are provided, and vice-versa.
Table 46-9 Cloning Databases Using RMAN Backup Profile with REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
| Step | Task | REST APIs | EM CLI Verbs |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Follow the steps in the Getting Started section to enable DBaaS. |
See Getting Started |
See Getting Started |
|
2 |
Set up one or more PaaS Infrastructure Zones. |
||
|
3 |
Create a database pool. |
||
|
4 |
Configure the request settings. |
||
|
5 |
Define quotas for each self service user. |
||
|
6 |
Create one of the following database provisioning profiles:
|
||
|
7 |
Set up the Test Master database. |
||
|
8 |
Create a service template based on the profile you have created. |
See Service Templates and Service Template REST API Examples |
|
|
9 |
Configure the Chargeback Service. |
||
|
10 |
While deploying a database, select the service template you have created. |
Creating a Full Database Clone Using RMAN Duplication (Live Cloning)
Database backups created by RMAN (Recovery Manager) are stored as image copies or backup sets. You can create profiles using these backups and use these profiles to create full database clones.
Note:
In the table below, wherever REST APIs are not available for any steps EM CLI verbs are provided, and vice-versa.
Table 46-10 Creating a Full Database Clone Using RMAN Backup WIth REST APIs and EM CLI Verbs
| Step | Task | REST APIs | EM CLI Verbs |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Follow the steps in the Getting Started section to enable DBaaS. |
See Getting Started |
See Getting Started |
|
2 |
Set up one or more PaaS Infrastructure Zones. |
||
|
3 |
Create a database pool. |
||
|
4 |
Create the test master by using a live standby database. |
||
|
5 |
Configure the request settings. |
||
|
6 |
Define quotas for each self service user. |
||
|
7 |
Create a service template based on the test master. |
See Service Templates and Service Template REST API Examples |
|
|
8 |
Configure the Chargeback Service. |
||
|
9 |
While deploying a database, select the service template you have created. |
Discrete Sync
A discrete sync setup has a production database which is not available for direct cloning operations and thereby with no standby database. The administrator schedules periodic backups on the production database and uses the backups to create the Test master database.
To set up a discrete sync database setup, follow the steps below:
Table 46-11 Creating a Discrete Sync Setup Using EM CLI Verbs
| Step | Task | EM CLI Verb |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Create a Test master database. |
|
|
2 |
Create a full backup. |
|
|
3 |
Create a thin backup. |
|
|
4 |
Create a clone. |
|
|
5 |
Refresh Test master or clones. |
Configuring Custom Database Placement Option Using REST APIs
This section describes the custom database placement feature using REST APIs. See the following sections for further details:
Custom Database Placement Option for Databases Using REST APIs
With the custom database placement option, an SSA user has the option of choosing the host on which the database instance is created. This option has to be enabled in the service template by the SSA Administrator while creating the service template. The SELECT_ORACLE_HOME_OPTION parameter in the JSON body of the service template defines if the SSA User has the option to select the host while requesting for a database instance. If SELECT_ORACLE_HOME_OPTION is set with the value "SELECT_ORACLE_HOME_FROM_REQUEST" the SSA User has the option to choose the database host while requesting the database. If the parameter is not defined, or if the value for the parameter is not set, or if the value is set to "SELECT_ORACLE_HOME_AT_RUNTIME", then the SSA User will not have the option of choosing the database host and the database instance will be created on the host selected by the placement algorithm during the execution of the request.
After the option is set in the service template, the SSA User can perform a GET operation on the service template URI to view the available hosts. The "hosts_for_placement" parameter (in the case of a SI database), and "clusters_for_placement" and "hostsInCluster" parameters (in case of a RAC database) provide the details of the available hosts to the SSA User. The SSA User is then required to define the host name for placing the database in the "database_host_name" parameter in the POST operation for requesting a database instance.
The "database_host_name" parameter is a mandatory parameter if the custom placement option is set in the service template. Note that multiple values for database_host_name request parameter can be provided as comma separated values. For a RAC database request, the number of hosts specified in this parameter should match with the number of nodes configured in the service template, and all of the hosts provided should belong to the same cluster and should be present in the selected zone.
Custom Database Placement Option for Pluggable Databases Using REST APIs
With the custom database placement option, an SSA user has the option of choosing the Container Database (CDB) on which the Pluggable Database (PDB) instance is created. This option has to be enabled in the service template by the SSA Administrator while creating the service template.
The SELECT_TARGET_OPTION parameter in the JSON body of the PDB service template defines if the SSA User has the option to select the host while requesting for a database instance. If SELECT_ORACLE_HOME_OPTION is set with the value "SELECT_TARGET_FROM_REQUEST" the SSA User has the option to choose the CDB while requesting the database. If the parameter is not defined, or if the value for the parameter is not set, or if the value is set to "SELECT_TARGET_AT_RUNTIME", then the SSA User will not have the option of choosing the CDB and the PDB instance will be created on the CDB selected by the placement algorithm during the execution of the request.
After the option is set in the PDB service template, the SSA User can perform a GET operation on the service template URI to view the available CDBs. The "target_nodes_for_placement" parameter provides the details of the available CDBs to the SSA User. The SSA User is then required to define the CDB target name for placing the PDB in the "target_name" parameter in the POST operation for requesting a PDB instance.
The "target_name" parameter is a mandatory parameter if the custom placement option is set in the service template. The CDB target name specified in this parameter should be present in the selected zone.
Service Catalog of Database as a Service
Service catalog is a collection of pre-approved database configurations available to selected consumers for on demand, self service provisioning. It enforces consistency and automation, and helps reduce the database management overhead.
Service catalog offers:
-
Self-service provisioning which provides IT agility
-
Enterprise-wide service catalog which provides standardization and compliance
-
Database cloning using snap clone which saves time and storage space
-
Metering, chargeback and quota which ensures service governance
-
Performance and lifecycle management which guarantees service levels
-
Patching, upgrading and configuration automation which lowers operational costs
For more information on service catalog watch the video at - https://apex.oracle.com/pls/apex/f?p=44785:24:0::::P24_CONTENT_ID,P24_PREV_PAGE:9590,1.
The following section explains the REST APIs required for setting up a sample multi-datacenter DBaaS.
Multi-Datacenter DBaaS Setup
Multi-datacenter DBaaS setup is the best possible structure of DBaaS configuration in an enterprise with multiple data centers where all aspects related to data safety, recovery and backup are considered at the highest levels.
Figure 46-2 Multi-Datacenter DBaaS Setup
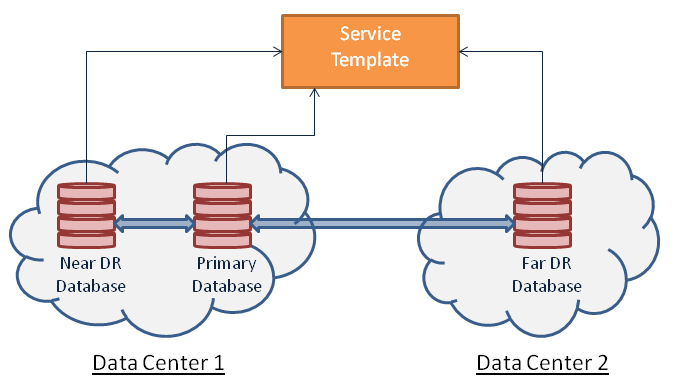
Multi-datacenter DBaaS setup requires creating a Primary RAC software pool and two Standby software pools. Of the two standby software pools, the near disaster recovery (DR) pool is a RAC software pool and the other, which is the far DR is a single instance software pool. After the software pools are created, the service template is created to establish the relation between the software pools. This setup is offered as a Multi-datacenter DBaaS setup to the SSA user.
The topics covered under this section are:
Administrator Steps for Creating the Multi-Datacenter DBaaS Setup
This section explains the steps to setup the Multi-datacenter DBaaS using REST APIs. For the EM CLI verb equivalent of the REST APIs run the emcli invoke_ws command for each of the REST APIs in the steps below. For details on emcli invoke_ws command, refer to EM CLI Verbs for Database as a Service Administrator.
Follow the steps below to setup the Multi-datacenter DBaaS:
The platinum DBaaS setup is ready to be administered.
SSA User REST API Request for Using the Multi-Datacenter DBaaS Setup
To request a multi-datacenter DBaaS setup with a near DR and a far DR, issue the REST API request shown below.
Table 46-20 Configuration to Create a Database with Two Standby Databases
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
|
URI |
https://<OMS_HOST>:<OMS_CONSOLE_PORT>/em/cloud/dbaas/zone/82CF1C28FA20A183C99D13 8FF8065F19 |
|
Request headers |
Authorization: basic ZGVtb3VzZXI6ZGVtb3VzZXI= Content-Type: application/oracle.com.cloud.common.DbPlatformInstance+json Accept: application/oracle.com.cloud.common.DbPlatformInstance+json |
|
Body |
{
"based_on": "/em/cloud/dbaas/dbplatformtemplate/CC3BBB665A6BC6FFE040F00AEF252456",
"name": "Platinum1",
"description": "Create Database with 1 Standby RAC database & 1 Standby SI database",
"start_date": "2014-08-13T14:20:00ZAsia/Calcutta",
"end_date": "2014-08-13T17:20:00ZAsia/Calcutta",
"params":
{
"username": "Master Account username for the DB",
"password": "Master Account Password for the DB",
"database_sid" : "platinum1" ,
"service_name" : "Name of the additional service to be created",
"standbydbs":
[
{
"standbydb_name":"Near DR",
"standbydb_sid":"NR1"
},
{
"standbydb_name":"Far DR",
"standbydb_sid":"FR1"
}
]
}
} |
|
Request method |
POST |