Transports for Communication
Transports are configuration objects that represent a concrete communication channel to a trading partner using a specific protocol such as AS2, AS4, REST, RosettaNet, or FTP. You add one or more transports to a trading partner to send or receive business documents from the partner.
AS2 and FTP (which includes SFTP) are the currently supported protocols for B2B trading partner mode. If you want to use another protocol adapter in B2B for Oracle Integration, you can do so only using the standalone mode.
- To select a transport in a project:
- In the navigation pane, click Projects.
- Click the project in which to select the transport.
- Click B2B
 .
.
- In the Trading partners section, click the trading partner in which to select the transport.
- To select a transport in a standalone environment:
- In the navigation pane, click B2B, then Trading partners.
- Click the trading partner in which to select the transport.
- Click the Transports & agreements tab.
- A connection that you create and configure to point to the external trading partner's endpoint. As part of this configuration, you provide the host name, port, URL, user name/password credentials, and other details that your trading partner provides to you.
- Additional configurations (for example, a directory path for FTP or an encryption algorithm for AS2).
- A pair of integrations, one for receiving messages and another for sending messages. These integrations are automatically created for you. See Integrations Used For B2B Processing.
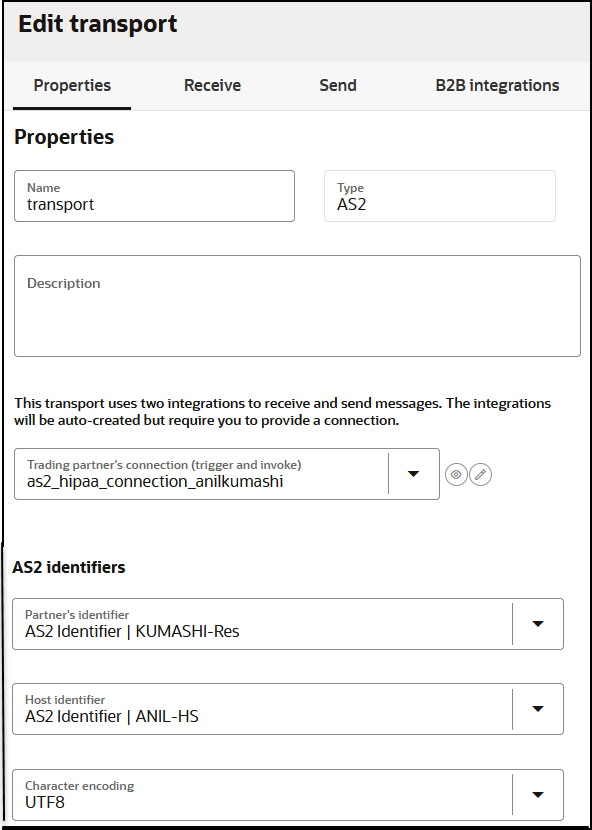
- Properties tab:
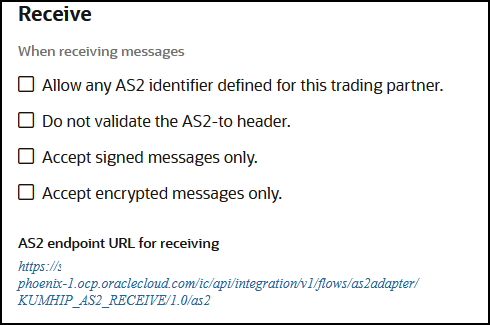
- Receive tab:
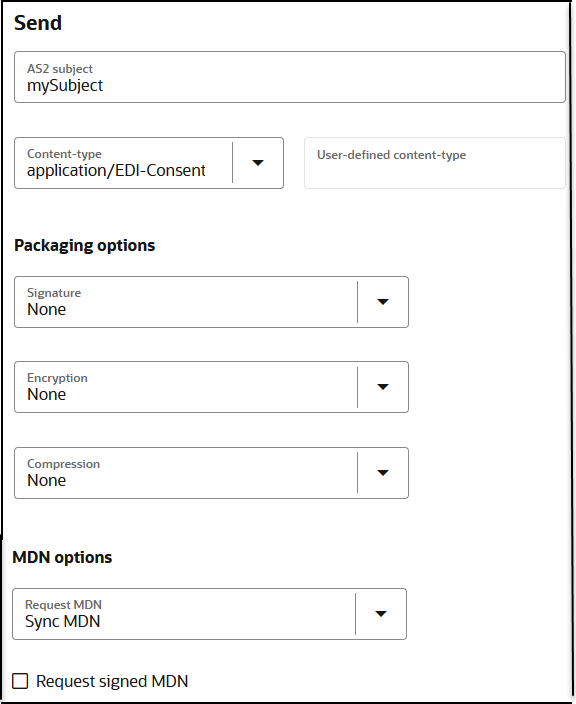
- Send tab:
- B2B integrations tab:
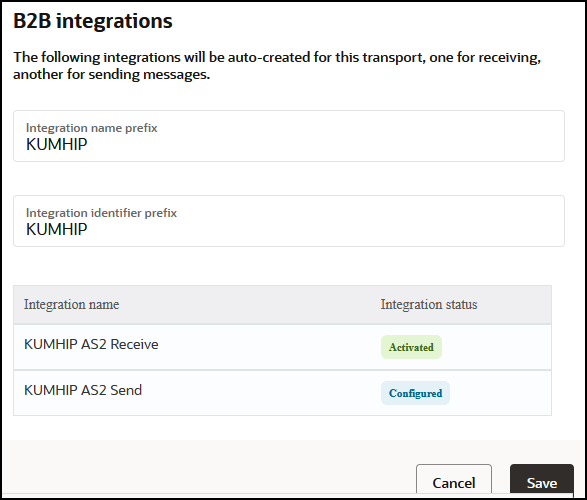
- Create a transport: Adds a definition for the transport. The pair of B2B integrations are automatically created and permanently linked to this transport.
- Deploy a transport: Makes the transport visible for runtime processing and also activates the B2B integrations. This transport can now receive and send messages.
- Redeploy a transport: Applies configuration changes to the runtime on-the-fly without disrupting message processing (with some restrictions).
- Undeploy a transport: Hides the transport from runtime processing and also deactivates the B2B integrations. This transport can no longer receive and send messages.
- Delete a transport: Removes the definition and also deletes the B2B integrations.
See Define Transports.
AS2
Applicability Statement 2 (AS2) is an HTTP-based protocol designed for B2B that adds a comprehensive set of data security features around data confidentiality, data integrity/authenticity, and nonrepudiation.
The AS2 specification is covered by RFC 4130. B2B for Oracle Integration supports AS2 versions 1.0 and 1.1.
An AS2 transport offers configuration options specific to AS2 that work in conjunction with the AS2 connection and the certificate management user interface.
- Use the Oracle Integration certificate management capabilities by uploading your certificate. In the navigation pane, click Settings, then Certificates..
- Enter the signing and encryption certificate alias in the AS2 Adapter connection selected in the AS2 transport.
- Select an encryption and signing algorithm in the AS2 transport configuration.
The simplest AS2 communication uses no encryption, signing, and compression. If you are learning about AS2, you can start simple and add the security layers later.
There is the concept of an electronic read receipt in AS2, officially known as Message Disposition Notification (MDN). It is a transport level acknowledgment used as a confirmation that the other party has received your message intact. B2B for Oracle Integration generates and consumes MDN messages (when enabled) and correlates them to the original transmissions. The Track B2B Messages page, described later, enables you to view the AS2 messages and MDN acknowledgments.
More details about the AS2 transport are provided. See Define Transports.
FTP
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) are commonly used for B2B communications. An FTP transport also works in conjunction with an FTP Adapter connection.
In an FTP Adapter connection, you specify the hostname, port, credentials, and other security configurations. In the FTP transport, you enter the input and output directories, file name pattern, and other details.
One important aspect of an FTP transport is that the receiving side polls the input directory on a time-based schedule. You can set up the schedule by selecting the Receive schedule option of the actions menu for an FTP transport.
More details about the FTP transport are provided. See Define Transports.
RosettaNet
RosettaNet is a global standard for electronic B2B communication and collaboration in the supply chain management industry. RosettaNet includes a set of standardized message formats, business processes, and implementation frameworks to facilitate electronic data exchange and collaboration between trading partners.
The RosettaNet standards are described in GS1 US RosettaNet Standards. B2B for Oracle Integration supports all PIPs.
RosettaNet supports nonrepudiation. This feature enables B2B for Oracle Integration to verify the integrity and origin of a RosettaNet 2.0 business message that is transmitted and received from a trading partner. This includes nonrepudiation of origin and content and nonrepudiation of receipt. No trading partner can deny receiving the message. The Track B2B messages page, described later, enables you to view the RosettaNet messages.
More details about the RosettaNet transport are provided. See Define Transports.
REST
You can exchange inbound and outbound messages with trading partners over the REST transport in B2B for Oracle Integration. The REST transport is useful for trading partners that don't use EDI or RosettaNet and can exchange messages using web forms or WebUI.
More details about the REST transport are provided. See Define Transports.
AS4
Applicability Statement 4 (AS4) is an open standard for the secure exchange of B2B documents using web services. Secure document exchange is governed by WS-Security, including XML encryption and XML digital signatures. The payload is considered agnostic, meaning the document type (purchase order, invoice, or others) is not tied to a defined SOAP action or operation. AS4 enables you to use custom XML and EDI/X12 document standards.
- Inbound user message:
- Plain
- Decryption
- Sign verification
- Decompression
- Outbound user message:
- Plain
- Encrypted
- Signed
- Compressed
- Send payload as an attachment
- Sending MDN
- Synchronous plain
- Receiving MDN
- Synchronous plain
- Error handling
- Failed authentication
- Decryption failure
- Decompression failure
More details about the AS4 transport are provided. See Define Transports.