Oracle Autonomous Database for Google Sheets
The Oracle Autonomous Database add-on ![]() enables you to query tables using SQL or Analytic Views using a wizard directly from Google Sheets for analysis.
enables you to query tables using SQL or Analytic Views using a wizard directly from Google Sheets for analysis.
The Oracle Autonomous Database add-on for Google Sheets must comply with Privacy Policy. For information on details of privacy policy, see Oracle Autonomous Database for Google Sheets Privacy Policy Details.
How does the add-on for Google Sheets work?
To query an Analytic View or Tables from the Autonomous Database, you must select an Analytic View or Table to work with. While retrieving data from the Analytic View, you can configure the query according to your requirements. You can select specific hierarchies and create custom calculations on the wizard. The add-on configures your query and returns the result to the Google Sheets. You can save the results of your queries locally in the Google Sheet. The add-on can also query the schema directly to which you have access. Using the Web UI, you can also view reports and analyses you create in the Data Analysis menu in the Data Studio tool.
To use the add-on, you must enable Web Access on the Autonomous Database account. You must have the CONNECT, DWROLE, RESOURCE and ADPUSER roles grant in the SQL worksheet to access the Google Sheets add-on.
- The Download Microsoft Excel/Google Sheets add-in is available to you under the Downloads menu of your Database Actions instance only if you have the
ADPUSERrole. - The Oracle Autonomous Database add-on for Google Sheets is not supported in Safari web browser.
- Install the add-on from Google Workspace Marketplace
The The Oracle Autonomous Database add-on for Google Sheets is available in Google Workspace Marketplace. - Download Connection File
To connect to the Autonomous Database, you can download a connection file from the Database Actions instance and import it to the Google Sheet add-on you have setup. - Connecting to Autonomous Database
The Oracle Autonomous Database add-on for Google Sheets enables you to connect to multiple Autonomous Databases with a single add-on using the Connections feature. The add-on connects to Google Sheets by providing authentication to Google. Multiple users or databases can connect simultaneously to the add-on. However, only one connection can remain active. - Generate Client ID and Client Secret using UI
In this section you use the Web UI to obtain theclient_idandclient_secret. - Authorize Google Sheets to use Autonomous AI Database
After your identity is determined using OAuth authentication, Google Sheets needs permission to access the Autonomous AI Database. - Natural Language in Google Sheets
You can use Natural Language Query to query the Oracle Autonomous AI Database using the Natural Language menu in the Oracle Autonomous Database for Google Sheets "add-on". - Data Analysis in Google Sheets
Selecting Data Analysis opens an Oracle Autonomous Database wizard in the Google sheet. - Run Direct SQL Queries
The Oracle Autonomous Database add-on for Google Sheets lets you run SQL queries to work with your data in a Google Sheet. With the add-on, you can type your SQL code in the SQL editor area and click Run to run the command. - Read and Access Data Using Table Hyperlinks in Google Sheets
Table Hyperlinks in Oracle Autonomous Database provide secure, preauthenticated URLs that allow read-only access to data stored in tables, views, or the result of SQL queries. - About Autonomous Database menu
Use this option to view details about the add-in. - Share or Publish
Once you generate the query results in the Google Sheet, you can share it with other users. With sharing, creates a copy of the worksheet and sends it with the design tools hidden and worksheet protection turned on. - Oracle Autonomous Database for Google Sheets Terms of Service
You can view the following Terms of Service here: - Oracle Autonomous Database for Google Sheets Privacy Policy Details
Effective Date:10/4/2024 - Oracle Autonomous Database for Google Sheets Support
Welcome to the support page for the Oracle Autonomous Database for Google Sheets. This resource is designed to assist you with any issues or questions you may have while using the add-on.
Parent topic: The Data Analysis Tool
Download Connection File
To connect to the Autonomous Database, you can download a connection file from the Database Actions instance and import it to the Google Sheet add-on you have setup.
- Navigate to the launchpad of your Database Actions instance, and select the DOWNLOAD MICROSOFT EXCEL/ GOOGLE SHEETS ADD-IN Card. Click the Download Connection File button in the Google Sheets tab of the Downloads page to import the connection file to the Google Add-in.
-
This connection file will allow you to connect to the Autonomous Database with the logged-in user. You can import only those connection files to Google Add-ins that you download from the current Autonomous Database instance.
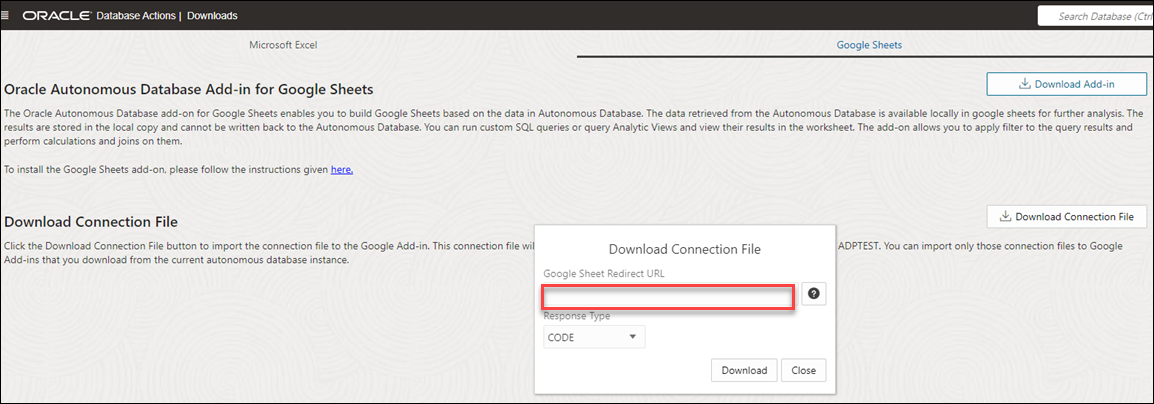
Description of the illustration download-connection-file.png - Selecting the Download Connection File button downloads a connection file in JSON format. You can view the downloaded file in your
Downloadsfolder.
Parent topic: Oracle Autonomous Database for Google Sheets