A virtual host is a server, or pool of servers, that can host multiple domain names (for
example, company1.api.example.com and company2.api.example.com).
This enables you to run more than one website, or set of REST APIs, on a single host
machine (for example, 192.0.2.11). Each domain name can have its own
hostname, paths, APIs, and so on. For example:
https://company1.api.example.com:8080/api/v1/test https://company2.api.example.com:8080/api/v2/test https://company3.api.example.com:8080/api/v2/test
The API Gateway implements name-based virtual hosting, in which the
client HTTP Host header is used as the routing criteria during path resolution
(for example, Host company1.api.example.com). This means that you can have
multiple domains running on the same hardware (IP address), while this is not apparent to
the client or end user.
For example, the following URL invokes the company2.api.example.com virtual host:
https:/company2.api.example.com/api/v1/test
This results in the following message at runtime:
POST /api/v1/test HTTP/1.1 Host: company2.api.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=SampleConfidentialApp&client_secret=......
![[Important]](../common_oracle/images/admon/important.png) |
Important |
|---|---|
|
To support name-based virtual hosts, you must first ensure that your Domain Name System
(DNS) server has been updated to map each hostname to the correct IP address (for example,
|
When your DNS server has been updated to map each hostname to the correct IP address, you can then configure the API Gateway for virtual hosting.
You can configure virtual hosts at the HTTP service level. This means that these settings are applied to the HTTP service and to any child resolvers. To configure a virtual host at the HTTP service level, perform the following steps:
-
In the Policy Studio tree, select an HTTP service (for example, Listeners > API Gateway > Default Services > Virtual Hosts).
-
Right-click, and select Add a Virtual Host.
-
Configure the following settings in the Virtual Host dialog:
-
Name:
Enter a unique name of the virtual host.
-
Enabled:
Select whether the virtual host processing is enabled. This is enabled by default.
-
Hosts:
Specify the list of domains that you wish to host under this HTTP service. To add a host, click Add at the bottom right, and enter the domain name (for example
company1.api.example.com).You can also specify domain names using wildcards already configured in your DNS (for example
*.example.com:/8080orcompany3.api.example.com.*). For details on configuring DNS wildcards, see the API Gateway Administrator Guide.
-
When you have configured a virtual host at the HTTP service level, you can also configure the following child resolvers:
-
Relative path
-
Static content provider
-
Static file provider
-
Servlet application
To configure a child resolver, perform the following steps:
-
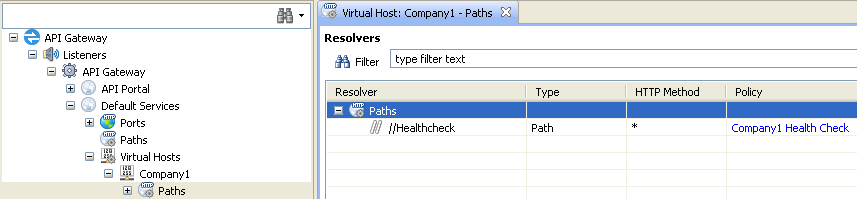
In the Policy Studio tree, select the Paths node under the virtual host, and right-click to add a resolver (for example, Add relative path).
-
In the Resolve path to policies dialog, click the browse button beside the Path Specific Policy field, and select a policy to run on this path.
For example, if an inbound request to /Healthcheck matches on company1.api.*,
the Company1 Health Check policy is executed. Otherwise, the global Health
Check policy for the HTTP service is executed (in this case, Default Services).