Contents
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) enables client-side code running in a browser in a particular domain to access resources hosted in another domain in a secure manner. Cross-origin requests are typically not permitted by browsers, and CORS provides a framework in which cross-domain requests are treated as same-domain requests.
For example, using CORS, JavaScript embedded in a web page can make an HTTP
XMLHttpRequest to a different domain. This is used to send an HTTP
or HTTPS request to a web server, and to load the server response data back into
the script. The following diagram shows an example CORS architecture:
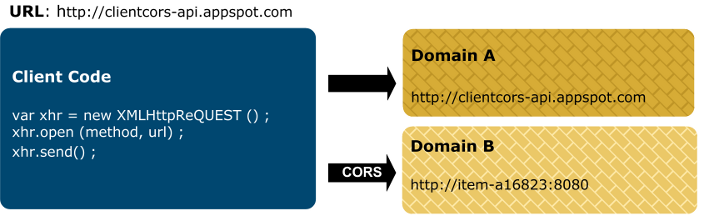
This example is described as follows:
-
A user browses to the following URL:
http://client.cors-api.appspot.com
-
The client page displayed on the left contains JavaScript that attempts to access resources in Domain A (
http://client.cors-api.appspot.com), and in Domain B (http://item-a16823:8080). -
Attempts by the browser to access resources in Domain A are granted because Domain A is the same domain in which the JavaScript code is running.
-
When the browser attempts to access resources in Domain B, it must use the CORS protocol because Domain B is in a different domain than that in which the JavaScript code is running. In this way, CORS enables client JavaScript code running in the browser in Domain A to access resources in Domain B.
The CORS standard provides CORS HTTP headers that enable servers to serve resources to permitted
origin domains. Browsers support these CORS HTTP headers and enforce their restrictions. Browsers
can also send preflight CORS requests to retrieve supported methods from the
server using an HTTP OPTIONS method. Then on approval from the server, the browser
client can send the request with the appropriate HTTP request method.
The CORS HTTP request headers are as follows:
-
Origin -
Access-Control-Request-Method(preflight only) -
Access-Control-Request-Headers(preflight only)
To enable CORS support in API Gateway, you must first add a CORS profile in Policy Studio:
-
In the Policy Studio tree, select Libraries > CORS Profiles.
-
Right-click, and select Add a CORS Profile, and configure the settings on the following tabs.
Configure the following general settings:
-
Name:
Unique name of the CORS profile. Defaults to
Cross Origin Resource Sharing. -
Enable CORS:
Specifies whether CORS processing is enabled for the profile. Enabled by default.
The Origins table enables you to configure the list of origins that are allowed to access resources configured with this CORS profile, or exposed by a specific HTTP service. Click Add at the bottom right to add an origin.
You can specify origins using the following values:
-
*(permits all values supplied in the CORSOriginheader) -
Domain (for example,
http://client.corsapi.appspot.com) -
Wildcarded value (for example,
http://*.appspot.comorhttp://client.corsapi.appspot.com:*)
The Allowed Headers table enables you to configure the list of HTTP headers
that are permitted when requesting a resource exposed by this CORS profile or HTTP service.
The list of headers is defined by the value of the Access-Control-Request-Headers
CORS header. Click the Add button at the bottom right of the screen to
add an allowed header to the table.
![[Note]](../common_oracle/images/admon/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
The list of allowed headers is checked only during a CORS preflight |
The Exposed Headers table enables you configure the list of CORS HTTP response headers that are exposed to the client. Click the Add button at the bottom right of the screen to add an exposed header to the table.
You can specify the list of CORS headers that are exposed to the client, in response to a resource exposed by this profile or HTTP service. You do not need to include the following simple HTTP response headers:
-
Cache-Control -
Content-Type -
Content-Language -
Expires -
Last-Modified -
Pragma
The Support credentials setting specifies whether resources using this
CORS profile or HTTP service support user credentials. When this option is selected, the
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials CORS header is sent in the response, with
a value of true. This setting is not selected by default.
You can also configure a CORS profile at the HTTP service level. This means that the settings configured for the profile are also applied to any child resolvers of this HTTP service. For example, this may be useful when using a third-party load balancer, and you need to configure a CORS profile for the default API Portal HTTP service, and specify the load balancer address as an origin.
To configure CORS at the HTTP service level, perform the following steps:
-
In the Policy Studio tree, select an HTTP service (for example, Listeners > API Gateway > Default Services).
-
Right-click, and select Edit to display the HTTP Services dialog.
-
Select CORS tab, and click the browse button to select a preconfigured CORS profile. By default, no profile is selected, which means that CORS is disabled.
-
In the Select CORS Profile dialog, if no profiles have already been configured, right-click CORS Profiles, and select Add a CORS Profile. You can also right-click an existing profile, and select Edit to update its settings. For details on CORS settings, see the section called “Add a CORS profile”.

For more details on HTTP services, see Configure HTTP services.
By default, the CORS profile set at the parent HTTP service level is used for all child resolvers of the HTTP service. However, you can override this at the relative path level as follows:
-
In the Policy Studio tree, select a list of relative paths (for example, API Gateway > Listeners > Default Services > Paths).
-
In the Resolvers screen on the right, right-click a resolver, and select Edit to display the dialog.
-
Select CORS tab, and in the CORS Usage field, select Override CORS using the following profile. By default, no CORS profile is selected, and the parent settings are used.
![[Note]](../common_oracle/images/admon/note.png)
Note Relative paths can act as HTTP services, and can accommodate child resolvers. This means that when a relative path has children, and has a CORS profile configured, by default, the children use the parent profile (unless a child overrides it).
-
In the CORS Profile field, click the browse button to select a preconfigured CORS profile.
-
If no CORS profiles have already been configured, right-click CORS Profiles, and select Add a CORS Profile. You can also right-click an existing profile, and select Edit to update its settings. For details on CORS settings, see the section called “Add a CORS profile”.

![[Note]](../common_oracle/images/admon/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
Similarly, you can also override CORS for the following relative path resolvers:
|
For more details on relative paths and resolvers, see Configure relative paths.