Contents
- Overview
- Hierarchy of SSL certificates in a domain
- How SSL certificates are generated for domain processes
- Add the first Admin Node Manager to the domain
- Add a Node Manager to the domain
- Add an API Gateway instance to the domain
- Change a Node Manager to an Admin Node Manager
- Regenerate all SSL certificates in a domain
The Admin Node Manager (ANM) is the central administration server for an API Gateway domain, and is responsible for performing management operations across the domain. The Node Manager (NM) on each machine manages all the local API Gateways on that machine, regardless of the group they are in. This includes collecting monitoring information, managing dynamic settings, deploying configuration, and so on.
In addition to managing the local API Gateways on its host, the Admin Node Manager communicates with the Node Managers
in the domain to perform management operations across the domain. In this architecture, the Node Managers only
communicate with the Admin Node Manager, and the API Gateway Manager, Policy Studio, and managedomain tools
connect to the Admin Node Manager. For more details on Admin Node Manager architecture, see the API Gateway Concepts
Guide.
![[Important]](../common_oracle/images/admon/important.png) |
Important |
|---|---|
It is recommended that you configure at least two Admin Node Managers in an API Gateway domain for high availability.
This topic describes how to use the using the managedomain command to configure and secure
multiple Admin Node Managers in a domain.
|
API Gateway uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for communications between all processes in a domain. This includes internal management traffic between the Admin Node Manager, Node Manager, and API Gateway instances, as shown in the diagram.
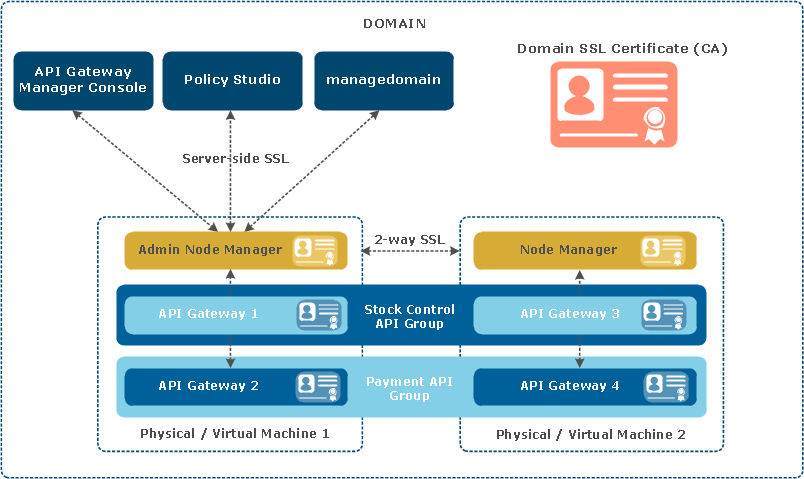
This diagram is described as follows:
-
Server-side SSL authentication is used for communication between the Admin Node Manager and client applications (Policy Studio, API Gateway Manager,
managedomain). -
Mutual SSL is used for communication between Admin Node Managers and Node Managers, and also between Node Managers and API Gateway instances.
-
Each Admin Node Manager, Node Manager, and API Gateway process has an associated SSL certificate used in the SSL session for inter-process communication. These certificates are also used to determine whether a process is a Node Manager or an Admin Node Manager.
-
The domain SSL certificate is the Certificate Authority (CA) used to sign the SSL certificates generated for each Admin Node Manager, Node Manager, and API Gateway process.
![[Note]](../common_oracle/images/admon/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
| The SSL inter-process communication discussed in this topic refers to system-level management communication only. This is not related to any SSL communication with back-end services, or any SSL ports that the API Gateway exposes for business traffic. |
Each time you register a new Admin Node Manager or Node Manager, or create a new API Gateway instance, a new SSL certificate is generated for inter-process communication. Each SSL certificate associated with an Admin Node Manager, Node Manager, or API Gateway instance is signed by the same CA. You must use one of the following options to sign these SSL certificates:
| Signing option | Description |
|---|---|
| System-generated CA key and certificate | By default, a system-generated CA key and certificate is used to sign all SSL certificates. The system creates a private key and self-signed certificate on the first Admin Node Manager to be registered. All subsequent requests for new SSL certificates for inter-process communication are processed by this Admin Node Manager which has the CA key. |
| User-provided CA key and certificate | Provide your own CA key by specifying a P12 file that contains a key and certificate. The system uses this CA key to sign all new SSL certificates for inter-process communication. |
| External CA |
A private key and Certificate Signing Request (CSR) file are generated by the
system, and then you can take this CSR to your chosen external CA. When you
receive the certificate from the external CA, you must submit the certificate
to managedomain, which then completes registering the new
Admin Node Manager, Node Manager, or API Gateway instance associated with that certificate.
|
These options are available when using managedomain to register a new Admin Node Manager
or Node Manager, or to create a new API Gateway instance, and when regenerating all SSL certificates
for the domain. These options are also available when editing a host in managedomain
(for example, when you change a Node Manager to an Admin Node Manager a new certificate is generated).
![[Note]](../common_oracle/images/admon/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
| Private keys for the SSL certificates are always generated and stored on the host that uses them. This applies to a system-generated CA key, a key for an Admin Node Manager or Node Manager SSL certificate, or a key for an API Gateway SSL certificate for inter-process communication. |
You can use a third-party external CA to sign the SSL certificates (for example, Verisign). This is the typical approach that is recommended in a production environment. For more details, see your external CA user documentation.
In a development environment, you can install API Gateway on a locked down host to act as an external CA for
testing purposes. No license is required because only managedomain is running. This external
CA host stores a system-generated CA private key and certificate. You can use managedomain
to process CSRs and output certificates.
In this scenario, the CSR file is generated by an API Gateway installation on another host (with a Node Manager
and API Gateways running), and transported to the external CA installation out-of-band. The certificate file
generated by the external CA is transported back out-of-band to the installation that created the CSR and
where the new Node Manager or API Gateway is created. The certificate is specified to managedomain
using the submit certificate option to complete Node Manager host registration or API Gateway creation.
![[Important]](../common_oracle/images/admon/important.png) |
Important |
|---|---|
When registering the first Admin Node Manager, you must run managedomain -i on the host
that will run the Admin Node Manager. This generates the private key for the Admin Node Manager, and private keys
must always be generated where they are used. No SSL certificates are provided out-of-the-box
.
|
To register the first Admin Node Manager in the domain and sign its SSL certificate with a system-generated CA key, run the following command:
managedomain -i
This command generates the CA private key, and a self-signed certificate. It also generates the
Admin Node Manager private key and certificate signed by self-signed CA certificate. This command uses
the --sign_with_generated option by default, which means that the SSL certificates
are signed with a system-generated CA private key and certificate. There are no Node Managers
running in the domain to call yet.
To register the first Admin Node Manager in the domain and sign its SSL certificate with a user-provided CA key, run the following example command:
managedomain -i --sign_with_user_provided --ca=/home/keys/test.p12
This command generates the Admin Node Manager private key and certificate signed by user-provided CA certificate.
To register the first Admin Node Manager in the domain and sign its SSL certificate with an external CA, run the following example command:
managedomain -i --sign_with_external_ca
This command generates the Admin Node Manager private key and the CSR for the certificate. It then prompts you to take your CSR file to your external CA and return with the signed certificate.
When you have the signed certificate, use the following command to submit the certificate and finish creating the Admin Node Manager configuration:
managedomain --submit_cert --cert cert.pem
In a production environment, you can use the --sign_with_external_ca option, and take the
generated CSR to an external CA (for example, Verisign). Alternatively, in a development environment,
you can run the following command to generate the certificate on an isolated API Gateway installation:
managedomain --sign_csr --csr nodemanager.csr
This command creates a certificate signed using the system-generated CA key. It writes the
certificate to a file, displays the file name so you can retrieve and copy to the host running
managedomain, and complete registration of the new Node Manager.
![[Tip]](../common_oracle/images/admon/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
If you wish to avoid using a system-generated self-signed certificate, you can manually copy
a user-provided CA private key and certificate to the following locations:
apigateway/groups/certs/private/domain.p12 apigateway/groups/certs/private/domainkey.pem apigateway/groups/certs/domaincert.pem |
In addition to the example commands already shown, you can specify the following options when
using managedomain to sign SSL certificates for inter-process communication:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--domain_passphrase |
Encrypt a newly generated domain.p12, or unlock a user-provided
domain.p12.
|
--domain_name |
Specify the Distinguished Name (DName) for a system-generated CA certificate.
Defaults to CN=Domain.
|
--sign_alg |
Specify the certificate signing algorithm (for example, sha1,
sha256, or sha512). Defaults to sha1.
|
--subj_alt_name |
Specify a subject alternative name content for the Admin Node Manager certificate.
This is used by web browsers during the SSL handshake exchange. You can specify
this multiple times, for example:
--subj_alt_name "DNS.1=name.oracle.com" --subj_alt_name "DNS.2=othername.oracle.com" --subj_alt_name "IP.1=10.142.1.2" |
--key_passphrase |
You can also encrypt temporary private key files stored on disk. For example, for the Admin Node Manager private key before it is consumed and written to the Node Manager configuration. |
The steps for adding a Node Manager or Admin Node Manager are different because there is now an Admin Node Manager running in the domain that must be invoked to add the new Node Manager.
To add a Node Manager to the domain and sign its SSL certificate with a system-generated CA key, run the following command:
managedomain -a --sign_with_generated --anm_host my_anm.com
This command generates the Node Manager private key, obtains the Node Manager certificate from the Admin Node Manager, and completes registration of the new Node Manager in the domain.
To add a Node Manager to the domain and sign its SSL certificate with a user-provided CA key, run the following command:
managedomain -a --sign_with_user_provided --ca=/home/keys/test.p12 --anm_host my_anm.com
This command signs the new Node Manager certificate with the user-provided CA key and certificate, and completes registration of the new Node Manager in the domain.
To add a Node Manager to the domain and sign its SSL certificate with an external CA, run the following command:
managedomain -a --sign_with_external_ca --anm_host my_anm.com
This command performs similar steps to adding the first Admin Node Manager to the domain and signing with an external CA.
When you have the signed certificate, use the following command to submit the certificate and finish creating the Node Manager configuration:
managedomain --submit_cert --cert cert.pem
You can use the --is_admin option to specify whether the process is an Admin Node Manager
or Node Manager. For more details, see the section called “Change a Node Manager to an Admin Node Manager”. See also
the section called “Additional certificate generation options”.
This section describes the options for signing an API Gateway instance SSL certificate when adding an API Gateway instance to the domain.
To add an API Gateway instance to the domain and sign its SSL certificate with a system-generated CA key, run the following example command:
managedomain -c -n APIGateway1 -g Group1
This command uses the --sign_with_generated option by default.
To add an API Gateway instance to the domain and sign its SSL certificate with a user-provided CA key, run the following example command:
managedomain -c -n APIGateway1 -g Group1 --sign_with_user_provided --ca=/home/keys/test.p12
To add an API Gateway instance to the domain and sign its SSL certificate with an external CA, run the following example command:
managedomain -c -n APIGateway1 -g Group1 --sign_with_external_ca
This command performs similar steps to adding the first Admin Node Manager to the domain and signing with an external CA.
When you have the signed certificate, use the following command to submit the certificate and finish creating the API Gateway configuration:
managedomain --submit_cert --cert cert.pem
See also the section called “API Gateway as external CA” and the section called “Additional certificate generation options”.
![[Tip]](../common_oracle/images/admon/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
When you add a Node Manager to the domain using the -a option, you can add it as
a Node Manager or Admin Node Manager. For more details, see the section called “Add a Node Manager to the domain”.
The section that follows describes how to change whether it is a Node Manager or Admin Node Manager
at a later stage.
|
An existing Node Manager in a domain can only communicate with API Gateway instances on the same host machine, and only an Admin Node Manager can connect to a Node Manager. This means that if you have a single Admin Node Manager in a domain, this is a single point of failure for management capabilities. If the single Admin Node Manager fails, you cannot manage or monitor the domain or deploy configuration. However, you can change an existing Node Manager to act as an Admin Node Manager in the domain. A domain can run with any number of Admin Node Managers, but it is recommended that you have at least two Admin Node Managers in a domain.
You can change the admin capabilities of the Node Manager running on the host local to
managedomain using the --edit_host option. This enables you to
change a Node Manager to an Admin Node Manager, or change an Admin Node Manager to a Node Manager. Changing
admin capabilities means that the tags on the process in the topology are updated, and a new
SSL certificate is generated.
The same options for signing an SSL certificate for a Node Manager or API Gateway instance (described in the preceding sections) are available when changing a Node Manager to an Admin Node Manager, or an Admin Node Manager to a Node Manager.
![[Note]](../common_oracle/images/admon/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
To change admin capabilities of an Admin Node Manager or Node Manager, you must run You cannot remove admin capabilities when there is only one Admin Node Manager in a domain because there must be at least one Admin Node Manager in a domain. |
When host1.com has an Admin Node Manager, to change admin capabilities from Admin Node Manager
to Node Manager, run the following example command:
managedomain --edit_host --host host1.com
In this case, because host1.com is an Admin Node Manager and the --is_admin
parameter is not passed, managedomain interprets this command as a change of
capabilities from Admin Node Manager to Node Manager. This command uses the --sign_with_generated
option by default.
When host1.com has a Node Manager, to change admin capabilities from Node Manager
to Admin Node Manager, run the following example command:
managedomain --edit_host --host host1.com --is_admin
In both cases, the command generates and updates the private key and certificate in the local Node Manager configuration, and prompts you to reboot the Node Manager.
![[Important]](../common_oracle/images/admon/important.png) |
Important |
|---|---|
To remove admin capabilities from the first registered Admin Node Manager, you must first move the
following directories to another Admin Node Manager:
apigateway/groups/certs apigateway/groups/certs/privateOtherwise, you will not be able to remove admin capabilities. This only applies to a system-generated CA key. |
When host1.com has an Admin Node Manager, to change admin capabilities from Admin Node Manager to
Node Manager, run the following example command:
managedomain --edit_host --host 10.142.12.31 --sign_with_user_provided --ca=/home/keys/test.p12
When host1.com has a Node Manager, to change admin capabilities from Node Manager
to Admin Node Manager, run the following example command:
managedomain --edit_host --host host1.com --sign_with_user_provided --ca=/home/keys/test.p12 --is_admin
In both cases, the command performs the same steps described in the section called “Sign Node Manager certificate with system-generated CA key”, and the same conditions apply.
When host1.com has an Admin Node Manager, to change admin capabilities from Admin Node Manager to
Node Manager, run the following example command:
managedomain --edit_host --host host1.com --sign_with_external_ca
When host1.com has a Node Manager, to change admin capabilities from Node Manager
to Admin Node Manager, run the following example command:
managedomain --edit_host --host host1.com --sign_with_external_ca --is_admin
In both cases, this command performs similar steps to adding the first Admin Node Manager to the domain and signing with an external CA.
When you have the signed certificate, use the following command to submit the certificate and finish updating the Node Manager configuration:
managedomain --submit_cert --cert cert.pem
See also the section called “Additional certificate generation options”.
- Sign certificates in domain with system-generated CA key
- Sign certificates in domain with user-provided CA key
- Sign certificates in domain with external CA
- Reset passphrase for CA private key
- Change domain SSL certificate expiry date
- Admin Node Manager backup and disaster recovery
- Location of SSL private keys and certificates
This section explains how to regenerate all SSL certificates used for inter-process communication in the domain. You can do this using a system-generated self-signed CA key and certificate, a user-provided CA key and certificate in a P12 file, or an external CA.
You can also change the domain certificate management option. For example, if the domain was first configured to use a system-generated CA key and certificate to sign all SSL certificates, you can change to a user-provided CA key and certificate, or an external CA. However, you must use the same option on all hosts in the domain.
![[Important]](../common_oracle/images/admon/important.png) |
Important |
|---|---|
|
You must first regenerate on the Admin Node Manager host that will hold the system-generated self-signed CA key. This may or may not be the same host that held the system-generated self-signed CA key before regeneration. If you select a different host to hold the CA private key and certificate, you must delete the old CA private key and certificate from the other Admin Node Manager host to prevent certificates being signed by two different CA keys. This must be done before regeneration. |
To regenerate all certificates on a host and sign with a system-generated key, run the following command on each host in the domain:
managedomain --regen_certs
This command uses the --sign_with_generated option by default. It regenerates the CA
private key and self-signed certificate, and private keys and certificates for the Admin Node Manager,
Node Manager, and API Gateway instances on the host that the command was run.
After regenerating certificates, you must reboot the Node Manager and API Gateway instances on the local machine.
![[Tip]](../common_oracle/images/admon/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
| When you regenerate certificates on the first Admin Node Manager, a Node Manager or API Gateway does not need to be running. When you regenerate certificates on subsequent hosts, the Admin Node Manager holding the CA key must be running because it is used to sign the certificates. This applies only for system-generated CA keys. |
To regenerate all certificates on a host and sign with a user-provided key, run the following example command on each host in the domain:
managedomain --regen_certs --sign_with_user_provided --ca=/home/users/qa.p12 --domain_passphrase foo
This command generates the private keys for the Node Manager and API Gateway instances and signs their certificates. After regenerating the certificates, you must then reboot the Node Manager and API Gateway instances on the local machine.
In this case, managedomain does not communicate with an Admin Node Manager when regenerating
certificates. The order of hosts selected for certificate regeneration does not matter. An Admin Node Manager
does not need to be running when certificates are regenerated or submitted.
To regenerate all certificates on a host and sign with an external CA, run the following command on each host in the domain:
managedomain --regen_certs --sign_with_external_ca
This command generates the private keys for the Node Manager and API Gateway instances. You are prompted to take the CSR files to your CA and return with the signed certificates.
When you have the signed certificates, run the following command for each certificate:
managedomain --submit_cert --cert cert.pem
After regenerating certificates, you must reboot the Node Manager and API Gateway instances on the local
machine. In this case, managedomain does not talk to an Admin Node Manager when regenerating
certificates. The order of hosts selected for certificate regeneration does not matter. An Admin Node Manager
does not need to be running when certificates are regenerated or submitted.
![[Tip]](../common_oracle/images/admon/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
You can use managedomain in interactive mode (option 24) to regenerate a subset
of certificates on the host. If you regenerate the CA key and certificate, the Node Manager and all
API Gateway certificates are automatically generated. If you do not regenerate the CA key and certificate,
you can choose whether to regenerate the Node Manager certificate, and which API Gateway certificates to
regenerate. For more details, see Managedomain command reference.
|
If a system-generated CA private key is used, you can reset the passphrase on the command line as follows:
managedomain --change_domain_passphrase --old_passphrase "oldpass" --new_passphrase "newpass"
You can only run this command on the host that has the domain.p12 file. It does not affect any
of the SSL certificates that have already been generated. If a new SSL certificate is to be generated (due
to a new Node Manager or new API Gateway instance), the new domain passphrase must be provided to unlock the
CA private key. This command modifies local files only. It does not communicate with any Node Managers
in the domain.
By default, the SSL certificates are valid for 100 years. To change this value, edit the
apigateway/skel/openssl.cnf file, and change the value of the default_days
setting in the CA_default section.
[CA_default] . . default_days = 36500 . .
This setting applies to signing with a system-generated or user-generated CA key, or if you are using an API Gateway installation as an external CA. If you are using a third-party external CA, the CA decides on the expiry date.
When the default_days setting is changed, all newly signed certificates have the new expiry date.
You do not need to reboot the Node Manager. However, you must regenerate certificates if you wish to modify
the expiry date of existing certificates.
For more details, see the section called “Location of SSL private keys and certificates”.
This section explains how to create a backup Admin Node Manager for signing certificates, and how to set up an
Admin Node Manager for signing certificates from a backup domain.p12 file.
If you are using a system-generated CA private key and certificate, the CA private key and certificate are only on the first Admin Node Manager registered in the domain. You can manually copy this CA private key and certificate to other Admin Node Managers so that there is always a backup Admin Node Manager available to sign certificates. Alternatively, you can copy the CA private key and certificate only when there is a problem with the first Admin Node Manager (for example, it is no longer running).
To create a backup Admin Node Manager that can sign certificates, copy the following files from Admin Node Manager 1 to Admin Node Manager 2:
apigateway/groups/certs/domaincert.pem apigateway/groups/certs/index.txt apigateway/groups/certs/serial apigateway/groups/certs/private/domain.p12 apigateway/groups/certs/private/domainkey.pem
You do not need to reboot Admin Node Manager 2 to be able to sign certificates. You can test the Admin Node Manager’s ability to sign certificates by taking down Admin Node Manager 1. Connect the client to Admin Node Manager 2, and add an API Gateway instance on any Node Manager that is running.
![[Important]](../common_oracle/images/admon/important.png) |
Important |
|---|---|
You can decide when and if to copy the CA private key to limit the copies of this sensitive data. You
must always backup the domain.p12 file after the registration of the first Admin Node Manager in
some secure offline location.
|
You can set up an Admin Node Manager for signing certificates from a backup domain.p12 file only.
Perform the following steps:
-
Copy the
domain.p12file toapigateway/groups/certs/private/. -
Create an
apigateway/groups/certs/serialfile with contents of01. -
Create an empty
apigateway/groups/certs/index.txtfile. -
Parse
domain.p12intodomainkey.pemanddomaincert.pem(if these files were not backed up originally). For example, assuming a passphrase offredfor the CA private key:cd apigateway/groups/certs/private openssl pkcs12 -in domain.p12 -out ../domaincert.pem -nokeys -passin pass:fred openssl pkcs12 -in domain.p12 -out domainkey.pem -nocerts -passin pass:fred -passout pass:fred
![[Tip]](../common_oracle/images/admon/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
| For more details, see the OpenSSL user documentation. |
This section describes the locations of the SSL private keys and certificates for the CA, Node Manager, and API Gateway instances.
The location of the CA private key and certificate depends on how they are signed.
System-generated CA private key and certificate:
If SSL certificates are signed by a system-generated CA private key and certificate, the CA private
key and certificate are written to disk when the first Admin Node Manager is created by managedomain:
-
CA private key:
apigateway/groups/certs/private/domainkey.pem -
CA private key and certificate:
apigateway/groups/certs/private/domain.p12 -
CA certificate:
apigateway/groups/certs/domaincert.pem
![[Warning]](../common_oracle/images/admon/warning.png) |
Warning |
|---|---|
The files in apigateway/groups/certs/private are security sensitive because they contain
the private key. This directory must have restricted access. These files are not copied to any other
Node Manager, and must be backed up elsewhere. If the CA private key and certificate are lost, you
must recreate certificates for the entire domain before adding new Node Managers or API Gateways.
|
The CA private key files can be encrypted by a passphrase. You must enter this with
managedomain when creating a new Node Manager or API Gateway. This is used to
unlock the CA private key and sign the new SSL certificate.
User-provided CA private key and certificate:
If SSL certificates are signed by a user-provided key and certificate, the key and certificate are in a
location managed by the user. A .p12 file containing the private key and certificate must
be made available to managedomain when a new Node Manager or API Gateway is created. The
CA certificate is copied into the API Gateway configuration because it is part of the SSL certificate
chain.
External CA private key and certificate: If SSL certificates are signed by an external CA, the CA private key remains with the external third-party CA, or isolated API Gateway installation acting as an external CA. The CA certificate is copied to the API Gateway configuration because it is part of the SSL certificate chain.
The Node Manager private key and certificate chain are stored in the Node Manager configuration in the following directory:
apigateway/conf/fed
The private key is encrypted using the entity store passphrase.
The API Gateway private key and certificate chain are stored in the following directory:
apigateway/groups/group-2/instance-1/conf/certs.xml
The private key is encrypted with the group configuration passphrase.
![[Warning]](../common_oracle/images/admon/warning.png) |
Warning |
|---|---|
When Node Managers and API Gateway instances are being registered, private keys are written in
apigateway/groups/certs/private/temp/instance-id and nodemanager-id.
Temporary security sensitive files are removed on completion. If an external CA is signing the
certificate, sensitive files may exist for a considerable time, so this directory must have
restricted access. You can encrypt this sensitive data using the --key_passphrase
parameter.
|