13 Oracle JCA Adapter for Microsoft Message Queueing
Learn how to use the Oracle JCA Adapter for Microsoft Message Queueing, which provides access to MSMQ functionality and works with the Oracle BPEL Process Manager (Oracle BPEL PM) and Oracle Service Bus (OSB). The Adapter also supports processing of various message formats from MSMQ through the Native Format Translation framework (nXSD).
Oracle JCA Adapter for MSMQ Concepts and Features
Microsoft Message Queueing (MSMQ) is a message infrastructure and a development platform for creating distributed, loosely-coupled messaging applications for the Microsoft Windows operating system.
Message queuing applications use message queuing to communicate across heterogeneous networks with computers that might be offline. Microsoft message queuing provides guaranteed message delivery, routing, security, transaction support and priority based routing.
Message Queues are logical containers that MSMQ uses to store and later forward those messages, thus providing the basis for loosely-coupled aspects of Message Queuing. Queuing applications send messages to the queue without needing to know when the messages are processed and which receiving application actually processes the message.
Applications that use MSMQ create/locate a queue, connect to the queue, navigate the queue, send/receive messages from a queue and use the MSMQ queue properties to define the behavior of the queue where applicable and needed.
MSMQ Terminology
In addition to having familiarity with basic MSMQ concepts, it is important to understand basic MSMQ terminology as background to using the MSMQ Adapter. While you should consult the relevant Microsoft documentation for a thorough understanding of the MSMQ technology, the following definitions help you understand the MSMQ product at a level that complement your use of the MSMQ Adapter.
-
Public Queues – A queue registered in the directory service that can be located by any Message Queuing application. This enables the MSMQ application to locate and open a queue anywhere within its domain. Public queues enable multi-hop scenarios, where messages are replicated throughout the Active Directory Service.
-
Private Queues–A queue registered on the local computer (and not in the directory service) that typically cannot be located by other applications.
-
MSMQ queue – A temporary storage location from where messages can be sent and received reliably, as and when conditions permit.
-
MSMQ user message queues – Queues that are either private or public.
-
Remote Queue – A queue manager is a Message Queuing service that delivers, receives, authenticates, and routes messages, and maintains information in the directory service. For an application, a remote queue is a queue that is hosted by a queue manager other than the one with which the application communicates.
-
Distribution Lists – Distribution lists are public lists of destinations that are stored in Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS).
-
ADDS – Active Directory Domain Services is a directory service implemented by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It is included in most Windows Server operating systems.
-
Transactional Queues – A queue that contains transactional messages. Transactional queues can only contain transactional messages, which are messages sent within a transaction. You can use transactional messages to pair the sending or receiving of any message with an action in another operation. Using transactional messages ensures that the unit of work is carried out as an atomic operation.
-
NonTransactional Queues – A queue that contains only non-transactional messages. Message Queuing does not allow transactional messages in non-transactional queues.
-
Foreign Queue – A queue that resides on a computer that does not run Message Queuing (a foreign computer).
jCOM and the MSMQ Adapter
The MSMQ Adapter uses Oracle WebLogic jCOM to enable interaction with MSMQ v5.0. jCOM assists in providing Java-to-COM integration.
Background
Specifically, WebLogic jCOM provides a runtime component that implements both COM/DCOM over Distributed Computing Environment Remote Procedure Call, and Remote Method Invocation (RMI) over the Java Remote Method protocol/Internet Inter-ORB Protocol distributed components infrastructures. This makes the objects on the other side of an interaction appear as if they were native objects for each environment.
The DCOM (Distributed Component Object Model) mode uses the Component Object Model (COM) to support communication among objects on different computers.
In a WebLogic jCOM application running in DCOM mode, the COM client communicates with WebLogic Server DCOM protocol.
In native mode, COM clients make native calls to WebLogic Servers (COM-to-WLS) and WebLogic Servers make native calls to COM applications.
For both COM-to-WLS and WLS-to-COM applications, because native mode uses native code dynamically loaded libraries (DLLs)—compiled and optimized specifically for the local operating system and CPU—using Native mode results in better performance.
Implications for the MSMQ Adapter
The implications for use with the MSMQ Adapter are that you can use Native Mode when the MSMQ server and the SOA server are installed on the same machine. The SOA server installed must be a Windows Platform and not another platform, such as a Linux Platform.If the MSMQ Adapter and MSMQ are installed on the same system, you can enable Native Mode at both the jCOM protocol level and at the MSMQ Adapter level. When you use Native Mode, the MSMQ Adapter can directly interact with the MSMQ server because they are on the same system, rather than your having to use DCOM protocols to communicate (which are used when the MSMQ adapter and the MSMQ server are on two different machines). Ensuring that MSMQ Adapter does not use the DCOM protocol to interact with MSMQ COM components provides you with performance benefits.
Security
When the MSMQ Adapter needs to make an outbound connection to the MSMQ server, it must sign on with valid security credentials. In accordance with the J2CA 1.5 Specification, the WebLogic Server supports both container-managed and application-managed sign-on for outbound connections. The MSMQ Adapter can leverage either of these methods to sign on to the Enterprise Information System.
Component-managed Sign-On
With component-managed sign-on, the component itself supplies the necessary security credentials when making the call to obtain a connection to an Enterprise Information System.The application server invokes the createManagedConnection method of ManagedConnectionFactory by passing a null Subject instance.
Container-Managed Sign-On
Container managed sign-on enables a user to sign-on to Oracle WeblogicServer and also to access the Enterprise Information System through the resource adapter without having to sign-in separately to the Enterprise Information System.
Because the Oracle WebLogic server and MSMQ maintain independent security realms, this is achieved by using credentials mapping. Oracle WebLogic Server security principals are mapped to the corresponding credentials required to access the Enterprise Information System.
Logging and Diagnosability
The MSMQ Adapter employs the MSMQ Adapter logging framework provided by the Adapter Framework component to capture any runtime logs.
The MSMQ adapter produces the following logs:
-
oracle.soa.adapter.msmq -
oracle.soa.adapter.msmq.transaction -
oracle.soa.adapter.msmq.connection -
oracle.soa.adapter.msmq.inbound -
oracle.soa.adapter.msmq.outbound
Each logger can be set to TRACE:32 to enable debug logging for that area or the oracle.soa.adapter.msmq logger can be set to TRACE:32 to enable complete logging for the MSMQ Adapter. Any exception emanating from the MSMQ Adapter has a corresponding error code and error message
MSMQ Adapter and High Availability
The MSMQ Adapter is deployable in an active-active topology. As part of its implementation, the MSMQ Adapter enables each poller thread to poll the queue for the next available message. Each poller thread uses the receive API; on a successful read the message is removed from the queue. This ensures there is no message duplication when the MSMQ Adapter is deployed in an active/active topology.
Set Up MSMQ on Windows Server 2008
To use MSMQ on a Windows Server 2008 installation, enable the following features for a Windows Server on which MSMQ is to be installed. Consult the relevant Microsoft documentation for more setup and configuration information.
-
Message Queuing Server. For more information on installation, see the Microsoft document Installing Message Queuing (MSMQ) at http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa967729.aspx
-
Directory Service Integration (for Public Queues and Distribution Lists). The prerequisite specifically requires Active Directory Domain Services (AD_DS) configured on a Windows 2008 Server system. Active Directory Domain Services is required to access MSMQ public queues, otherwise only private queues are available for MSMQ Adapter use cases.
-
Message Queuing DCOM Proxy
After successful installation, Message Queuing appears under the Features link in the Microsoft Server Manager console window.
Set Up Oracle Weblogic Server for COM
To set up the Oracle WebLogic server for use with COM:
-
Enable jCOM for the server that deploys the SOA MSMQ Adapter.
Note that if jCOM is enabled on the SOA server, while activating the MSMQ Adapter, the target on which it should be deployed must be the SOA server itself. The jCOM must be enabled on the managed server to which the adapter is targeted. See Enable jCOM in Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help.
-
When WebLogic is installed on a Windows machine that is running Microsoft Message Queuing, you can configure native mode though the configuration option ‘Enable Native Mode' as described in Servers: Protocols: jCOM in Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help.
-
Finally, enabling jCOM requires a restart of the corresponding server that deploys the SOA MSMQ Adapter. Restart the WebLogic Server.
Transaction Management and Error Handling
For more information on Transaction Management and Error handling as it applies to Adapters in general, see Adapter Framework.
Transaction Management
MSMQ Adapter transaction support defaults to LocalTransaction. The MSMQ Adapter does not support XA Transactions. Transactional queues are supported when used in local transaction semantics.
For both inbound and outbound error cases, the MSMQ Adapter starts an internal MSMQ transaction if the TransactionMode property of the JCA-managed connection factory is set to Single.
If the TransactionMode property of the JCA-managed connection factory is set to None, the MSMQ Adapter does not start a transaction on the MSMQ side; the messages are produced and consumed in a non-transactional way.
The TransactionMode property value of None is required when receiving and sending messages to or from a Non-transactional queue.
Fault Handling
The MSMQ Adapter can handle faults encountered when producing or consuming a message to or from an MSMQ queue
If a fault occurs, the message is delivered to a BPEL recovery queue and/or is retried based on the nature of the fault, and depending if the error is retriable or non-retriable. For more information on handling Adapter Faults, see Error Handling.
Because the MSMQ Adapter does not support XA transactions, XA-retriable errors are not supported.
XA retriable errors refer to the errors that occur in context of an XA transaction. The adapters can throw PCRetriable or XARetriable exceptions. However, because there is no XA when used with MSMQ Adapter, the MSMQ Adapter does not allow for XA errors.
Outbound Retriable Errors
The MSMQ Adapter performs retries according to configured binding properties. If these binding properties are not specified, the retry is carried out by fault policies, if they are included as part of the composite application.
For more information on MSMQ binding properties, see Table 13-3 (MSMQ Adapter Binding Properties).
MSMQ Adapter Features
The Oracle MSMQ Adapter provides the following features:
-
Sending Messages to MSMQ Private Queues
-
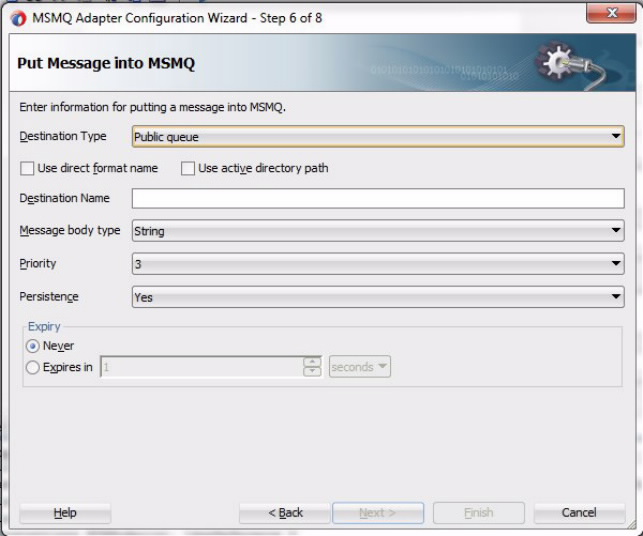
The MSMQ Adapter enables sending a message to a local private queue. When using the MSMQ Adapter Configuration Wizard to model an MSMQ Adapter reference, you can model an enqueue operation that is used to send (or Put) a message to an MSMQ queue.
-
The MSMQ Adapter enables sending a message to a local transactional private queue. When using the MSMQ Adapter Configuration Wizard to model an MSMQ Adapter reference, you can model an enqueue operation that is used to send a message to a local transactional MSMQ queue.
Note:
It is important to understand the relevance of the MSMQ
TransactionModeproperty, which indicates if the connection participates in a transaction when sending and receiving a message. Values for this property are [Single|None].If the value is Single, the local and remote MSMQ queues to which the message is sent should be transactional. If the value is Single, the local MSMQ queue from which the message is retrieved should be Transactional.
If the value is None and the queues to which the message is sent are transactional, a ResourceException occurs.
-
-
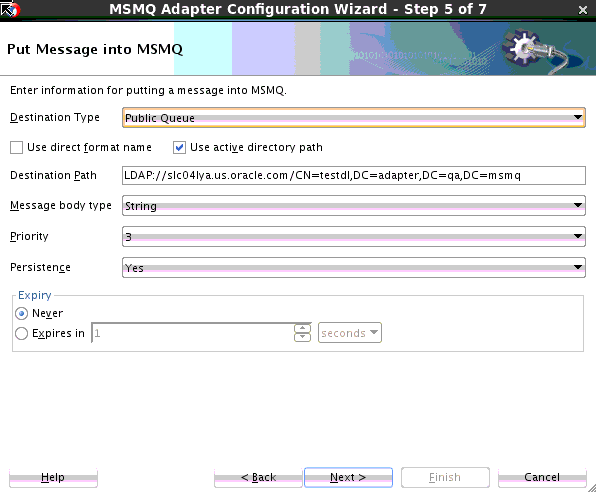
Sending messages to MSMQ Public Queues
-
The MSMQ Adapter enables sending a message to a local public queue. When using the MSMQ Adapter Configuration Wizard to model an MSMQ Adapter reference, you can model an enqueue operation. You can use this enqueue operation to send a message to a public MSMQ queue.
-
The MSMQ Adapter enables you to send a message to a local transactional public queue. When using the MSMQ Adapter Configuration Wizard to model an MSMQ Adapter reference, you can model an enqueue operation. You can use this enqueue operation to send a message to a MSMQ queue.
-
-
Sending Messages to MSMQ Distribution Lists
-
The MSMQ Adapter enables you to send a message to a Distribution List. When using the MSMQ Adapter Configuration Wizard to model an MSMQ Adapter reference, you can configure an enqueue operation to send a message to a MSMQ distribution list.
-
-
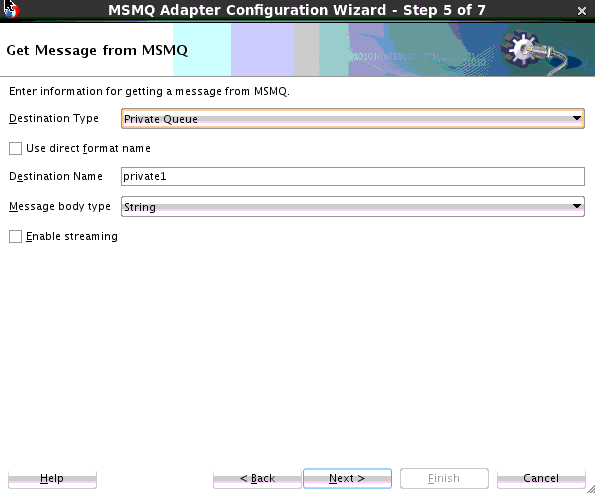
Consuming or Receiving Messages from a Private MSMQ Queue
-
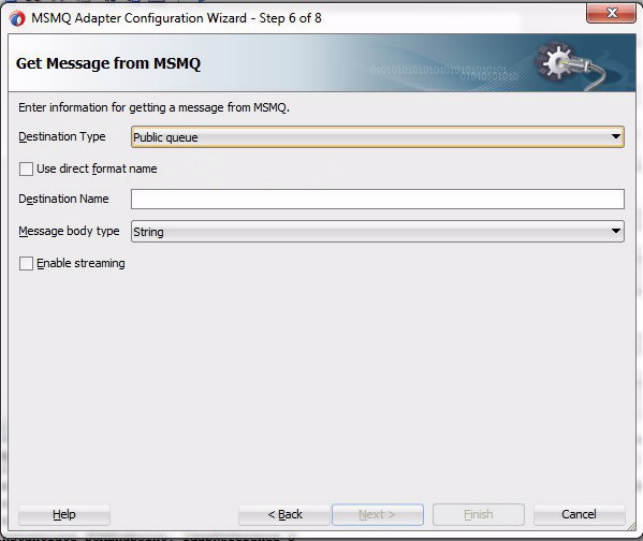
The MSMQ Adapter enables you to consume or receive of a message from a local private MSMQ queue. The default behavior is for the next available message on the queue to be available for consumption.
To do this, use the MSMQ Adapter Configuration wizard to model a Dequeue operation that enables consumption of a message from an MSMQ private queue.The MSMQ Adapter enables message consumption from a local private transactional MSMQ queue and supports an operation called dequeue.
To do this, use the Configuration Wizard to create the dequeue that consumes or receives a message from a transactional MSMQ queue.
-
-
Receiving Messages from a Public MSMQ Queue
-
The MSMQ Adapter enables reception of a message from a public MSMQ queue. The MSMQ Adapter supports an operation called dequeue that you configure when modeling an adapter service and is used to consume or receive a message from a MSMQ queue.
-
The MSMQ Adapter enables reception of a message from a public transactional MSMQ queue. You can use the MSMQ Adapter Configuration Wizard operation called dequeue that is used to receive a message from a transactional MSMQ queue.
-
MSMQ Properties Supported
The MSMQ Adapter includes several JCA properties. They are provided here and in the properties appendix for your convenience.
See Table 13-1 for a list of JCA properties.
Table 13-1 MSMQ Adapter JCA Properties
| Property | Description | Default Value | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Indicates if the message is sent to a public queue, private queue or a group of queues as identified by the distribution list name. The values are;
|
None |
Yes |
|
|
Name of the MSMQ queue. |
None |
Yes, if UseActiveDirectoryPath is False |
|
|
The string that identifies a DistributionList or Public queue as represented in ActiveDirectory. An example string is listed below; LDAP://MyLDAPServer/CN=MyQueue,CN=msmq,CN=MyComputer,CN=Computers,DC=MyDomain,DC=MyCompany,DC=COM |
None |
Yes, if UseActiveDirectoryPath is True |
|
|
Boolean that allows for Active Directory Path to be used to identify a public queue instead of queue name. This property is applicable when DestinationType is ‘ |
False |
- |
|
|
Boolean that allows for Direct Format name to be used for public and private queues. |
False |
- |
|
|
Priority can be set to any integer value between 7 and 0 (the default is 3). 7 means higher priority. 0 means lowest priority. Highest priority implies faster processing |
3 |
- |
|
|
This property specifies a time limit (in seconds) for the message to be retrieved from the target queue. The value is assigned to |
-1 (infinite |
- |
|
|
The property is used to specify express (non-persistent) or recoverable (persistent) messaging. Express messaging provides faster throughput. Recoverable messaging guarantees that the message is delivered even if a computer crashes while the message is en route to the queue. The values are: Persistent, Non-Persistent. |
Persistent |
- |
|
|
The operation to be carried out. The supported values for OperationType are |
None |
Yes |
|
|
Values are |
String |
Yes |
|
|
Boolean that enables payload to be streamed |
False |
- |
See Table 13-2 for a list of Normalized Properties related to the MSMQ Adapter. Also indicated is the Adapter processing direction for each property.
Table 13-2 MSMQ Adapter Normalized Properties
| Property Name | Description | Direction |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The property indicates when a message is sent. |
Inbound |
|
|
The property specifies a message's priority. This overrides |
Inbound/Outbound |
|
|
The property specifies a time limit (in seconds) for the message to be retrieved from the target queue. This overrides |
Inbound/Outbound |
|
|
The property specifies a time limit (in seconds) for the message to reach the queue. Message Queuing uses the enterprise-wide setting for the time-to-reach-queue interval if none is specified here. |
Inbound/Outbound |
|
|
Identifies the message using an MSMQ-generated message identifier. |
Inbound |
|
|
The property specifies how Message Queuing delivers the message. This overrides |
Inbound/outbound |
|
|
The property provides the length of the message body in bytes. |
Inbound |
|
|
The property indicates when the message arrived at the queue. |
Inbound |
See Table 13-3 for a list of Binding Properties that apply to the MSMQ Adapter.
Table 13-3 MSMQ Adapter Binding Properties
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
adapter.msmq.receive.timeout |
The time (in milliseconds) that Message Queuing waits for a message to arrive before starting another poll-cycle. The default value is one second (1). |
|
adapter.msmq.dequeue.threads |
Number of poller threads that is initialized when endpoint activation occurs. This enables the adapter to wait for a specified time to receive a message before next poll cycle is initiated. When specified, the value of adapter.msmq.dequeue.threads is used to spawn multiple inbound poller threads; multiple inbound threads can be used to improve performance The default value is 1. |
Use the Connection Factory Configuration properties when you configure Connection Factories for the MSMQ Adapter. See Table 13-4. Also indicated is the processing direction for each property.
Table 13-4 MSMQ Adapter Connection Factory Configuration
| Property Name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
|
|
IP Address of the MSMQ host. |
- |
|
AccessMode |
Identifies if the connection factory allows for native access or not. Values are [ |
DCOM |
|
|
Indicates if the connection participates in a transaction when sending and receiving a message. Values are [Single|None].If Single, the local and remote MSMQ queues to which the message is sent should be transactional. If Single, the local MSMQ queue from which the message is retrieved should be Transactional.If None and the queues to which the message is sent are transactional, there is a ResourceException. |
|
|
User |
Identifies a user. |
- |
|
Password |
Password for the specified user. |
- |
|
|
Domain of the MSMQ host. |
- |
MSMQ Adapter Configuration Wizard Flow
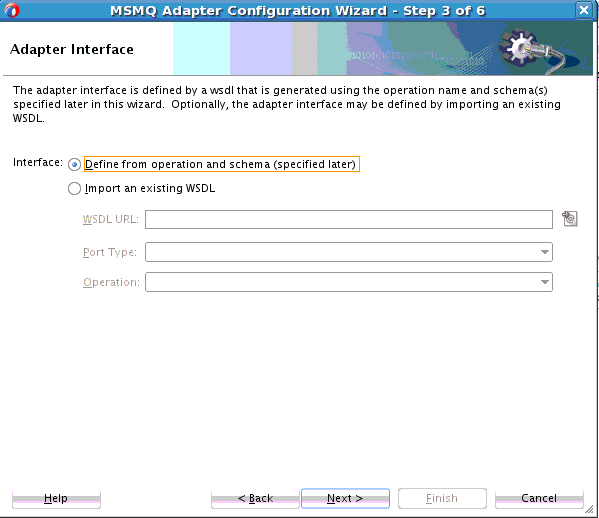
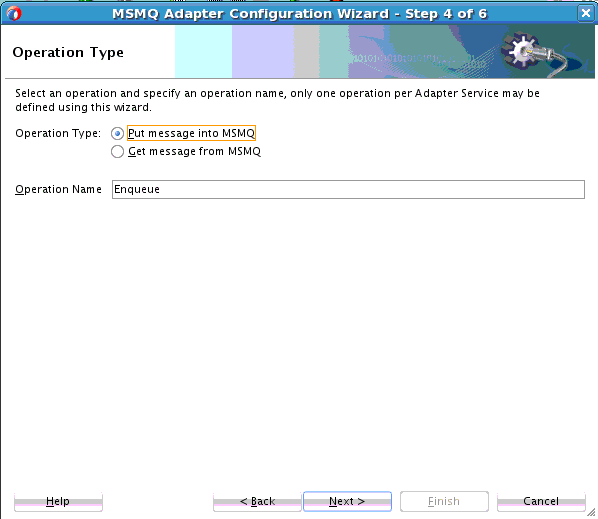
Use the MSMQ Adapter Configuration Wizard to create and configure an MSMQ Adapter.
Sample MSMQ Adapter Connection Factory Properties
The following are sample MSMQ Adapter connection factory properties, within Fusion Middleware Control. Locate them at Home >Summary of Deployments >MSMQAdapter > Configuration> Outbound Connection Pools. Select the New option and provide the JNDI a name; for example, eis/MSMQ/MSMQAdapter_NonTrans1.
Properties include:
MSMQ_AccessMode=DCOM MSMQ_Domain=adapter.test.msmq MSMQ_Host=slc04lya.us.mydomain.com MSMQ_Password=Welcome12 MSMQ_TransactionMode= NONE MSMQ_User=Administrator
MSMQ Adapter Design-time Artifacts
The Adapter configuration Wizard generates the JCA, WSDL and the XML Schema artifacts based on the interaction and message definition.
Sample JCA File for an MSMQ Enqueue Operation
Following is the sample JCA file, specifying a WSDL for an MSMQ Enqueue Operation.
Example - Sample JCA File for an MSMQ Enqueue Operation
<adapter-config name="enqueueOp" adapter="msmq" wsdlLocation="../WSDLs/enqueueOp.wsdl"
xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/
blocks/adapter/fw/metadata">
<connection-factory location="eis/MSMQ/MSMQAdapter"/>
<endpoint-interaction portType="EnqueueOperation_ptt" operation="EnqueueOperation">
<interaction-spec
className="oracle.tip.adapter.msmq.v2.jca.
MSMQInteractionSpec">
<property name="BodyType" value="ByteArray"/>
<property name="DestinationPath" value="dest"/>
<property name="TimeToLive" value="-1"/>
<property name="Delivery" value="Persistent"/>
<property name="DestinationType" value="PUBLIC_QUEUE"/>
<property name="UseDirectFormatName" value="true"/>
<property name="OperationType" value="Enqueue"/>
<property name="Priority" value="5"/>
<property name="UseActiveDirectoryPath" value="true"/>
</interaction-spec>
</endpoint-interaction>
</adapter-config>
Sample JCA for an MSMQ Dequeue Operation
The following sample JCA, specifying for a WSDL for a Dequeue Operation.
Example - Sample JCA for an MSMQ Dequeue Operation
<adapter-config name="dequeueOp" adapter="msmq"
wsdlLocation="../WSDLs/dequeueOp.wsdl"
xmlns="http://platform.integration.oracle/blocks/adapter/
fw/metadata">
<connection-factory location="eis/MSMQ/MSMQAdapter"/>
<endpoint-activation portType="DequeueOperation_ptt"
operation="DequeueOperation">
<activation-spec
className="oracle.tip.adapter.msmq.v2.
jca.MSMQActivationSpec">
<property name="BodyType" value="String"/>
<property name="DestinationType"
value="PUBLIC_QUEUE"/>
<property name="UseDirectFormatName" value="false"/>
<property name="DestinationName" value="dest"/>
<property name="OperationType" value="Dequeue"/>
<property name="EnableStreaming" value="false"/>
</activation-spec>
</endpoint-activation>
</adapter-config>
Design-Time WSDL Artifacts
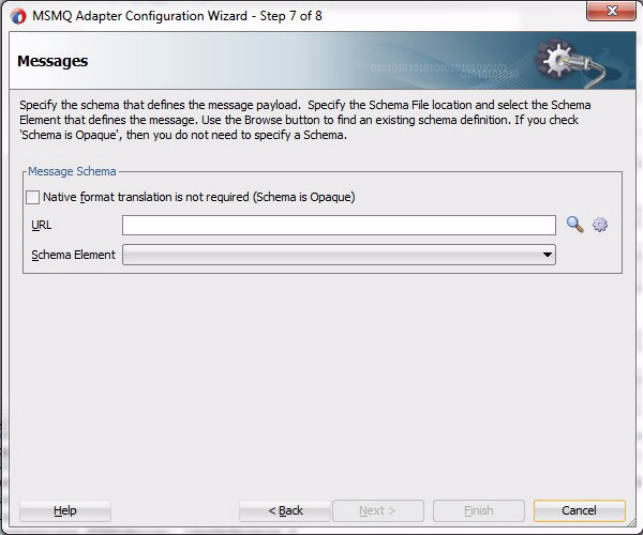
A WSDL file is generated when you click Finish in the MSMQ Adapter Configuration Wizard. The schema you specified within the Schema Page is imported in the generated WSDL.
WSDL for MSMQ Enqueue Operation
The following WSDL is generated for a Base64Binary Enqueue operation.
Example - MSMQ Adapter WSDL for Enqueue Operation
<wsdl:definitions
name="msmqService" targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/
pcbpel/adapter/msmq/ MSMQAdapterUseCases/Project1/msmqReference"
xmlns:jca="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/wsdl/jca/"
xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
xmlns:tns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter/ msmq/MSMQAdapterUseCases/Project1/msmqReference"
xmlns:opaque="http://xmlns.oracle.com/
pcbpel/adapter/opaque/"
xmlns:plt="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2003/05/
partner-link/">
<plt:partnerLinkType name="Enqueue_plt" >
<plt:role name="Enqueue_role" >
<plt:portType name="tns:Enqueue_ptt" />
</plt:role>
</plt:partnerLinkType>
<wsdl:types>
<schema targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/
pcbpel/adapter/opaque/"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" >
<element name="opaqueElement"
type="base64Binary" />
</schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:message name="Enqueue_msg">
<wsdl:part name="opaque" element=
"opaque:opaqueElement"/>
</wsdl:message>
<wsdl:portType name="Enqueue_ptt">
<wsdl:operation name="Enqueue">
<wsdl:input message="tns:Enqueue_msg"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:portType>
</wsdl:definitions>
WSDL for MSMQ Adapter Dequeue Operation
The following example shows a WSDL for an MSMQ Adapter Dequeue Operation.
MSMQ Adapter Dequeue Operation WSDL
<wsdl:definitions
name="mqService"
targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter
/msmq/MSMQAdapterUseCases/Project1/msmqService"
xmlns:jca="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/wsdl/jca/"
xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
xmlns:tns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/adapter /msmq/MSMQAdapterUseCases/
Project1/msmqService"
xmlns:pc="http://xmlns.oracle.com/pcbpel/"
xmlns:imp1="http://platform.integration.oracle/
blocks/adapter/fw/metadata/
msmqSchema"
xmlns:plt="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/
2003/05/partner-link/">
<plt:partnerLinkType name="Dequeue_plt" >
<plt:role name="Dequeue_role" >
<plt:portType name="tns:Dequeue_ptt" />
</plt:role>
</plt:partnerLinkType>
<wsdl:types>
<schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/
2001/XMLSchema" >
<import namespace="http://platform.integration.oracle/
blocks/adapter /fw/metadata/msmqSchema"
schemaLocation="../Schemas/msmqSchema.xsd" />
</schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:message name="Dequeue_msg">
<wsdl:part name="body" element="imp1:message"/>
</wsdl:message>
<wsdl:portType name="Dequeue_ptt">
<wsdl:operation name="Dequeue">
<wsdl:input message="tns:Dequeue_msg"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:portType>
</wsdl:definitions>
MSMQ Use Cases
The following use cases provide a walkthrough of various uses of the MSMQ Adapter:
Enqueue/Dequeue a Message from a Public Queue
In this use case, follow these steps to create an application that enqueues and dequeues messages from an MSMQ public queue:
Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. Perform the following steps to create an application and a project:
- In the Application Navigator of JDeveloper, click New Application. Then select SOA Application. The Name your application page is displayed.
- Enter
Enq_Deq_PublicAppin the Application Name field, and click Next. The Name your project page is displayed. - Enter
Enq_Deq_Publicin the Project Name field, and click Next. - Select Composite With BPEL in the Composite Template box, and click Finish. The Create BPEL Process - BPEL Process page is displayed.
- Enter
BPELPublicin the Name field, select Define Service Later from the Template list. - Click OK. The
Enq_Deq_PublicAppapplication and theEnq_Deq_Publicproject appear in the design area.
Creating the Inbound Oracle MSMQ Adapter Service
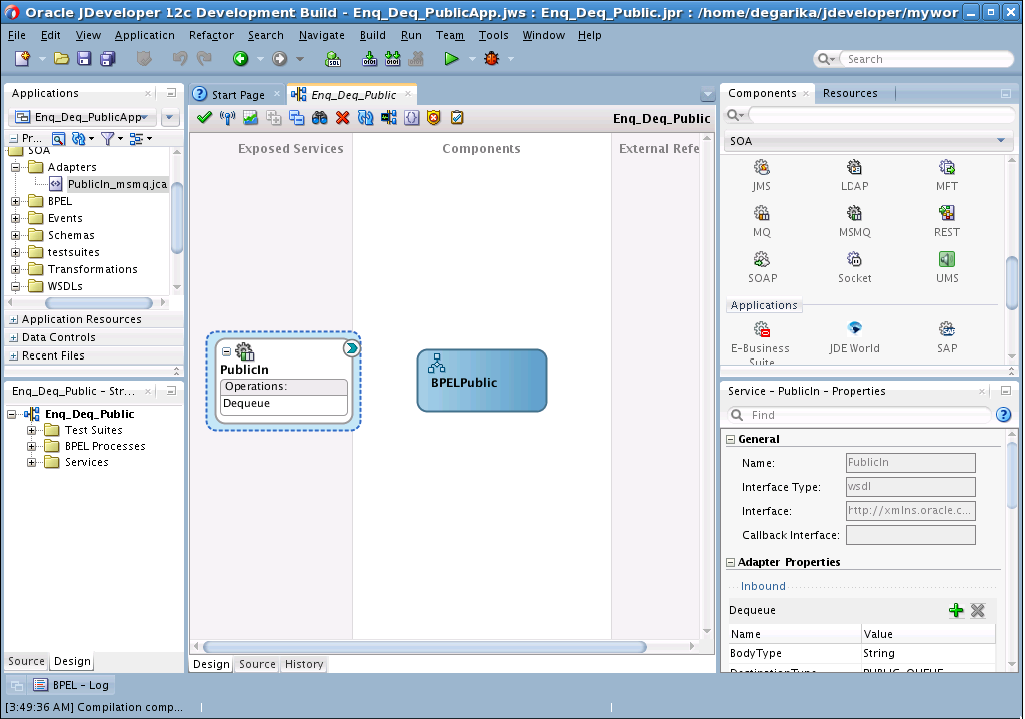
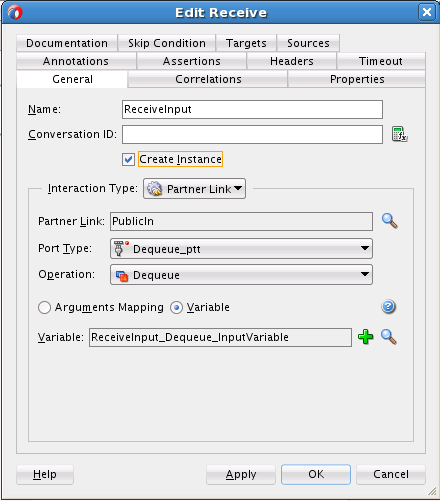
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle MSMQ Adapter service to dequeue messages from the Microsoft messaging queue (MSMQ):
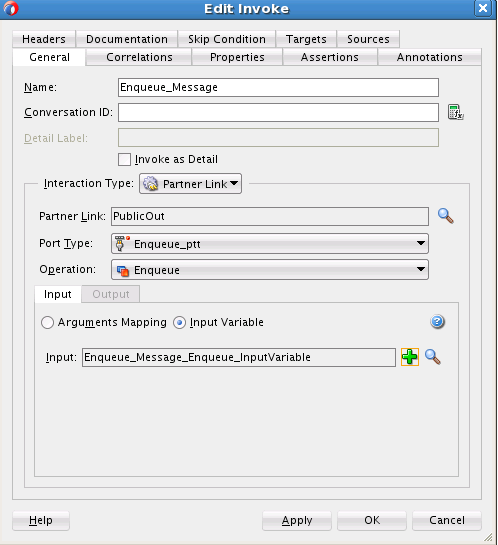
Creating the Outbound Oracle MSMQ Adapter Service
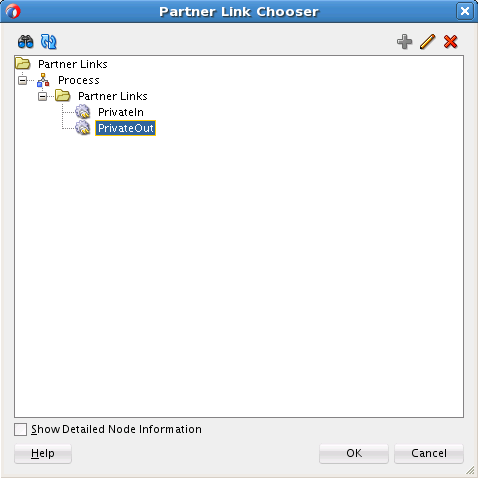
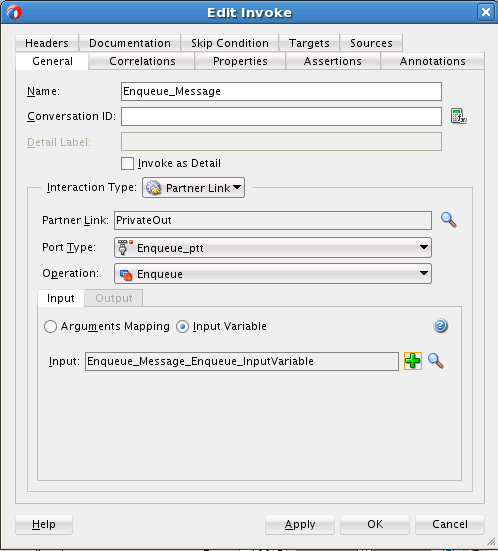
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle MSMQ Adapter service to enqueue a message from one Microsoft messaging queue to another Microsoft messaging queue:
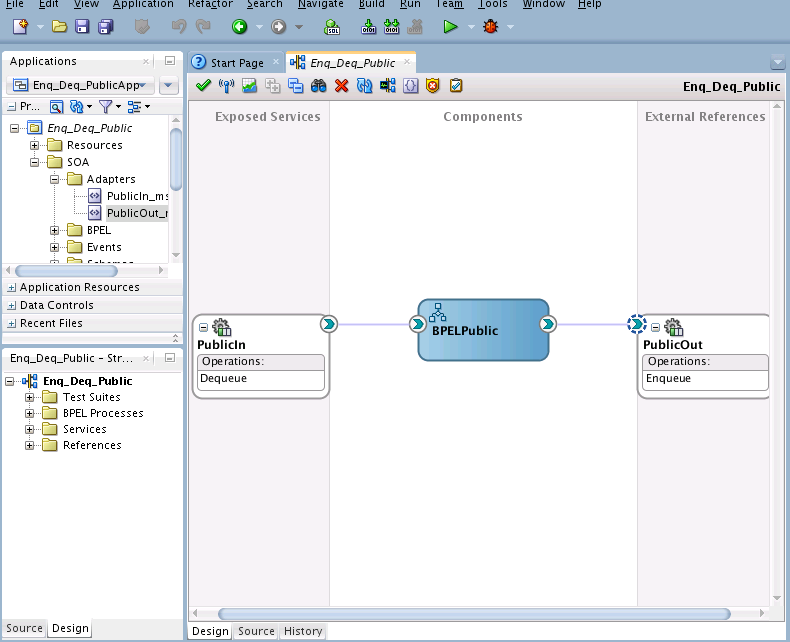
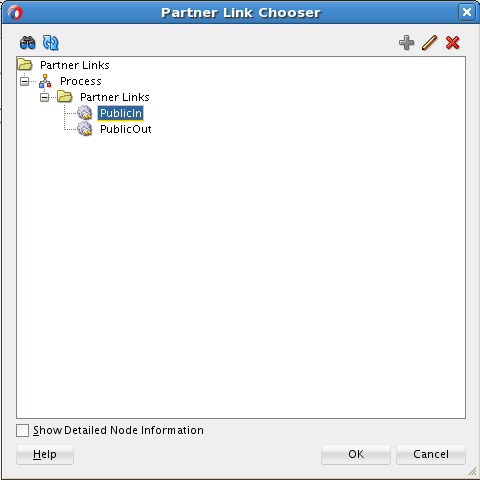
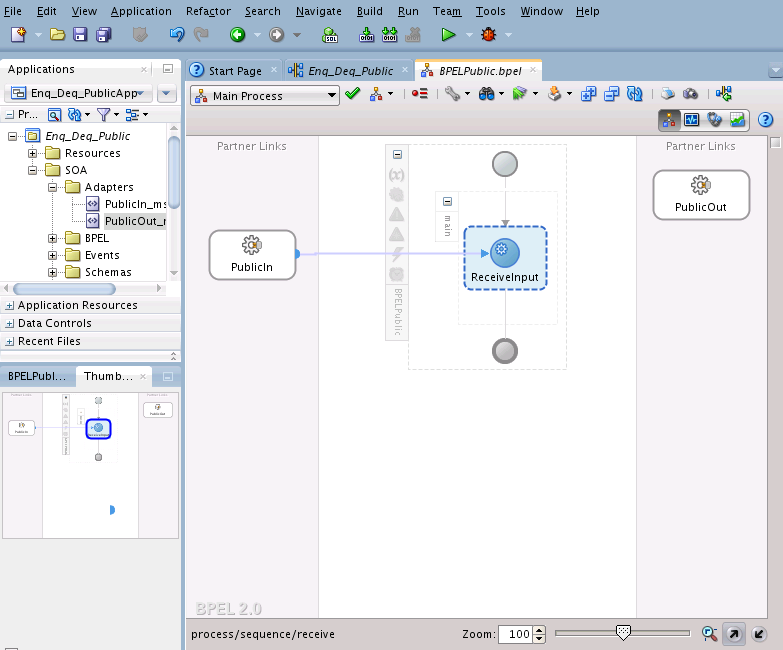
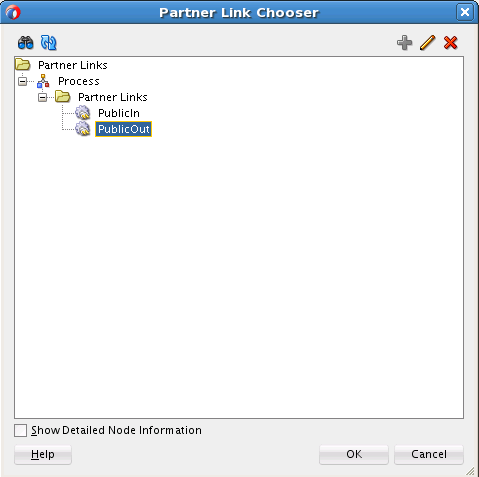
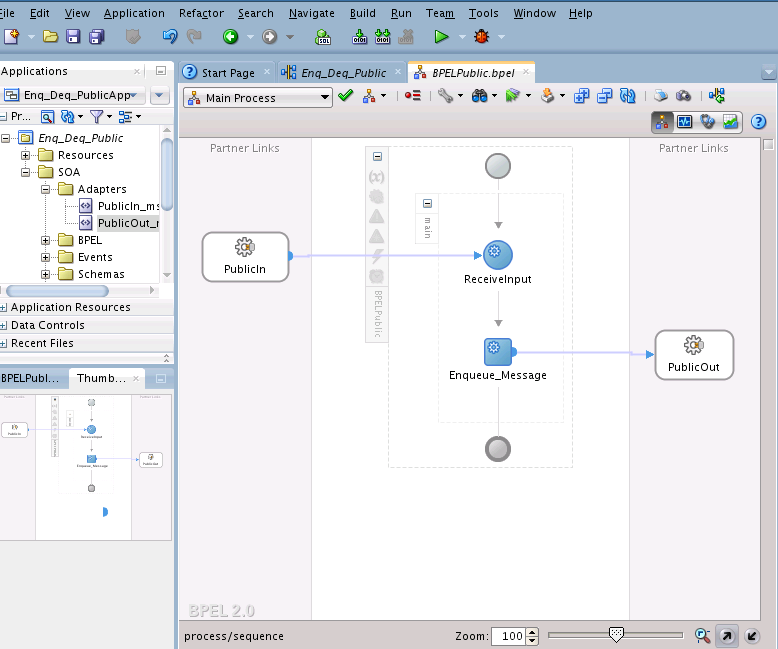
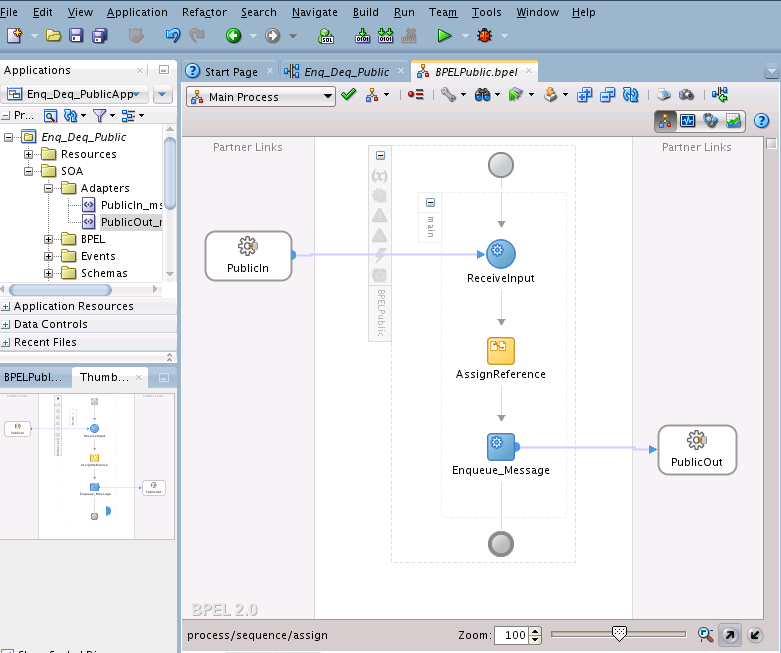
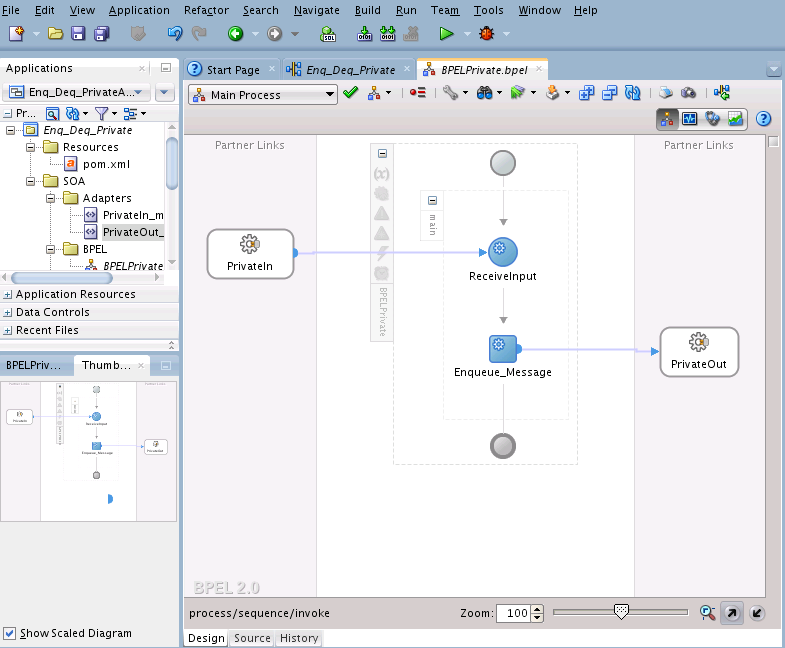
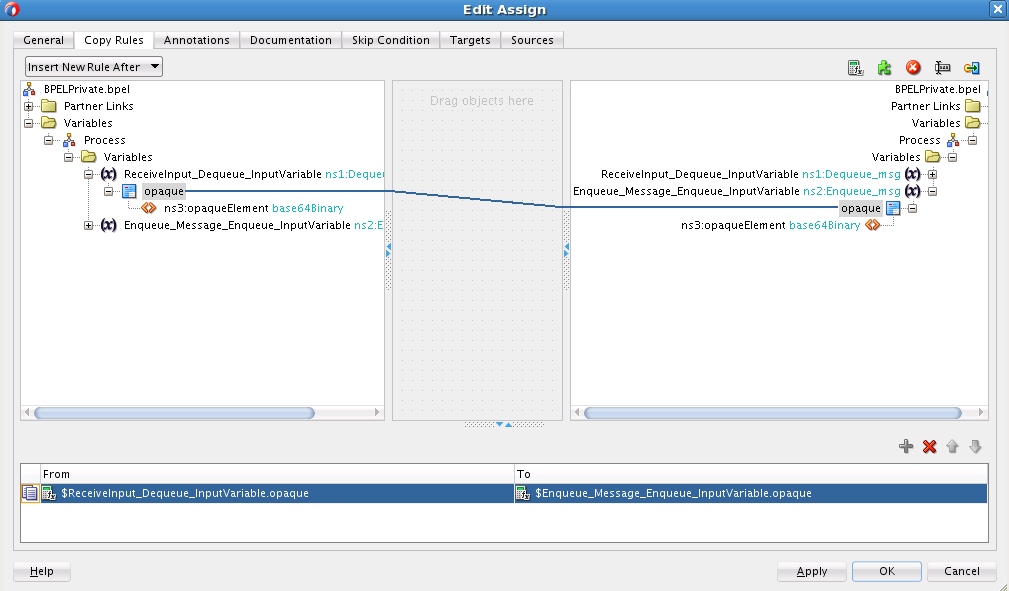
Wiring Services and Activities
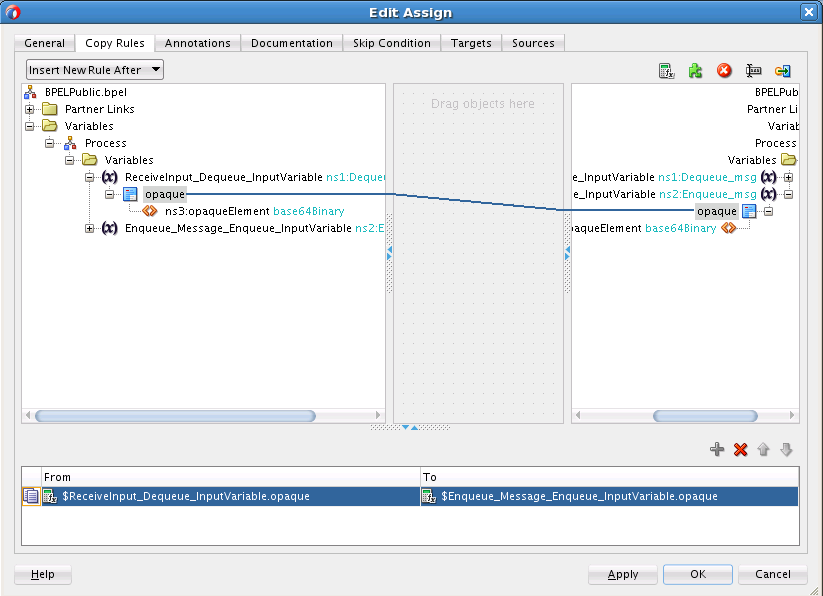
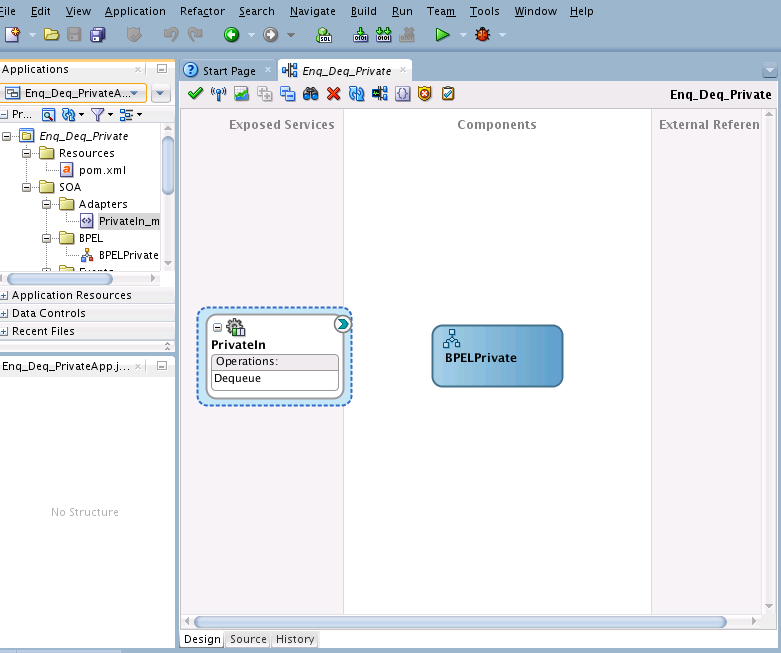
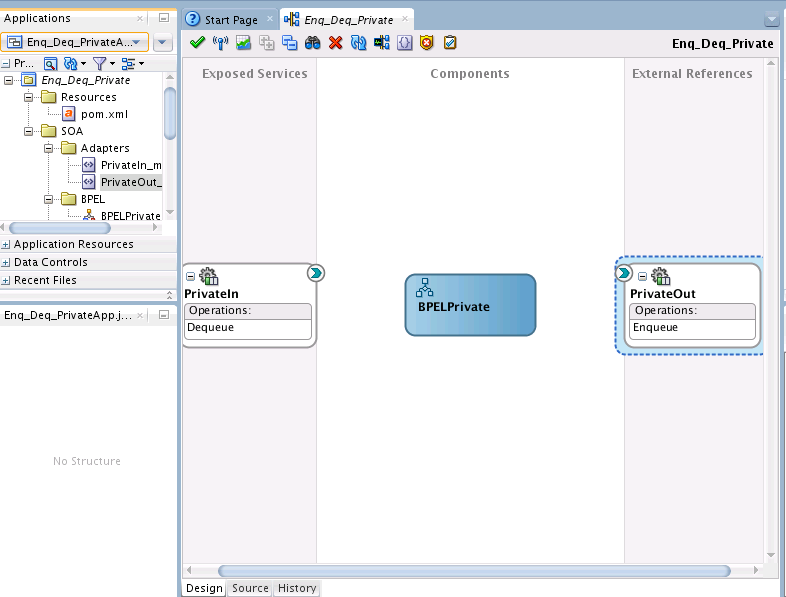
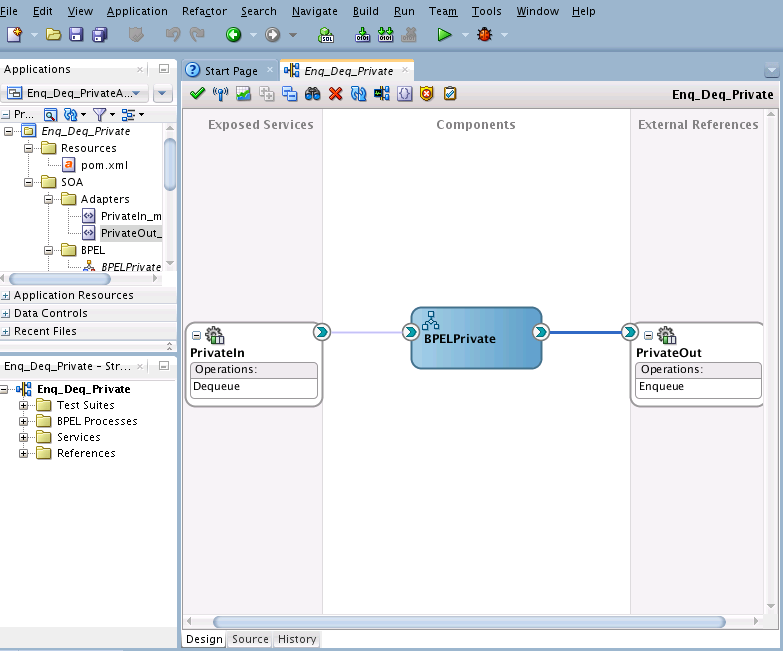
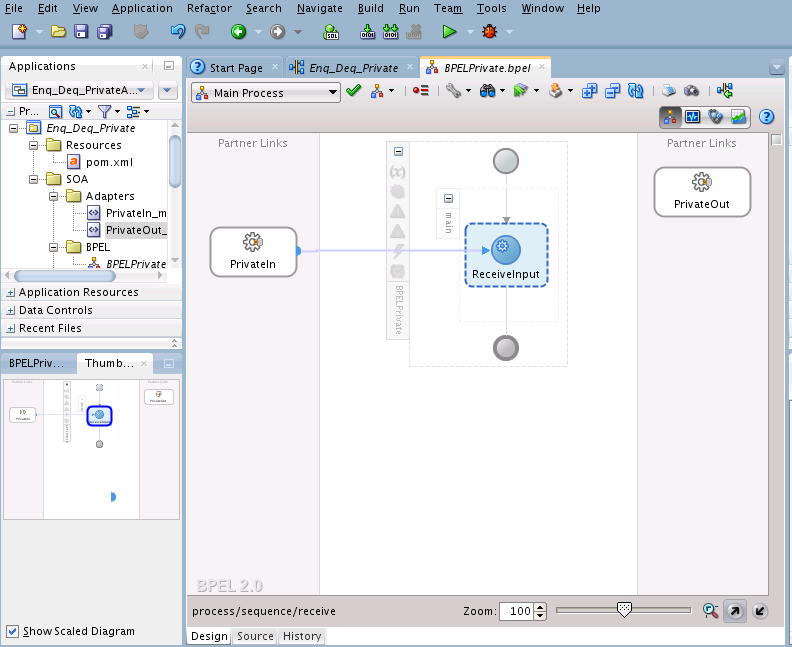
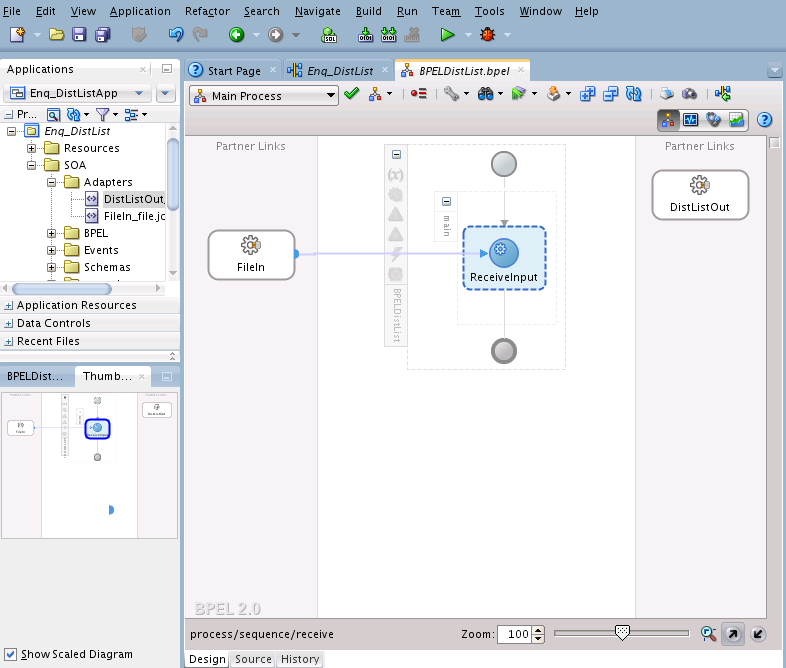
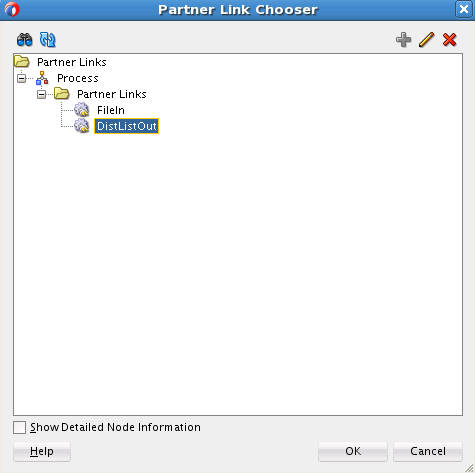
You must assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound Adapter service, BPEL process, and the Outbound Adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
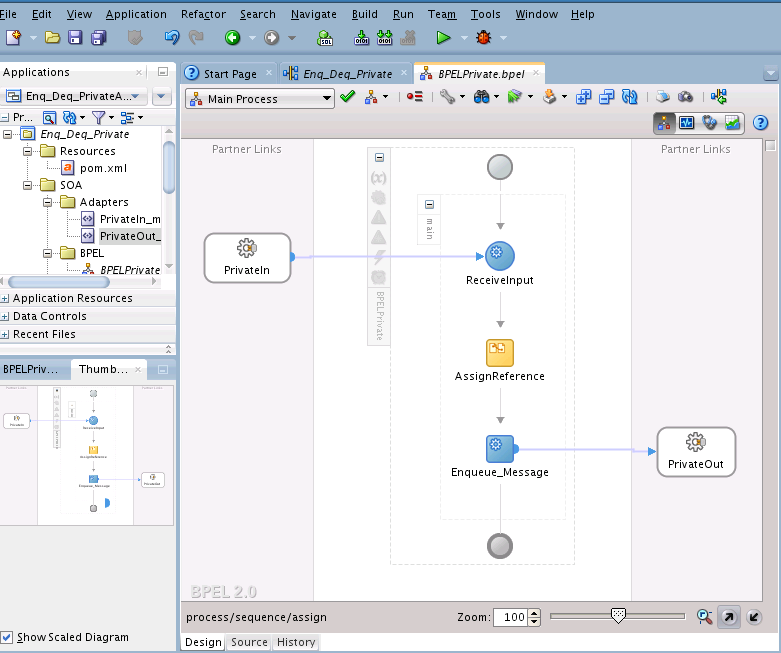
Enqueue/Dequeue a Message from a Private Queue
In this use case, follow these steps to create an application that enqueues and dequeues messages from an MSMQ private queue:
Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. Perform the following steps to create an application and a project:
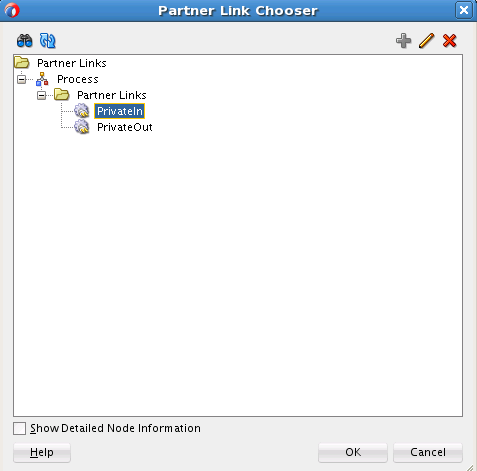
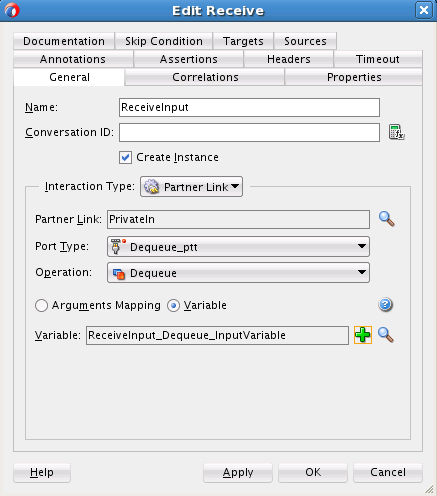
Creating the Inbound Oracle MSMQ Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle MSMQ Adapter service to dequeue messages from the Microsoft messaging queue (MSMQ):
Creating the Outbound Oracle MSMQ Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle MSMQ Adapter service to enqueue a message from one Microsoft messaging queue to another Microsoft messaging queue:
Wiring Services and Activities
You must assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound Adapter service, BPEL process, and the Outbound Adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components:
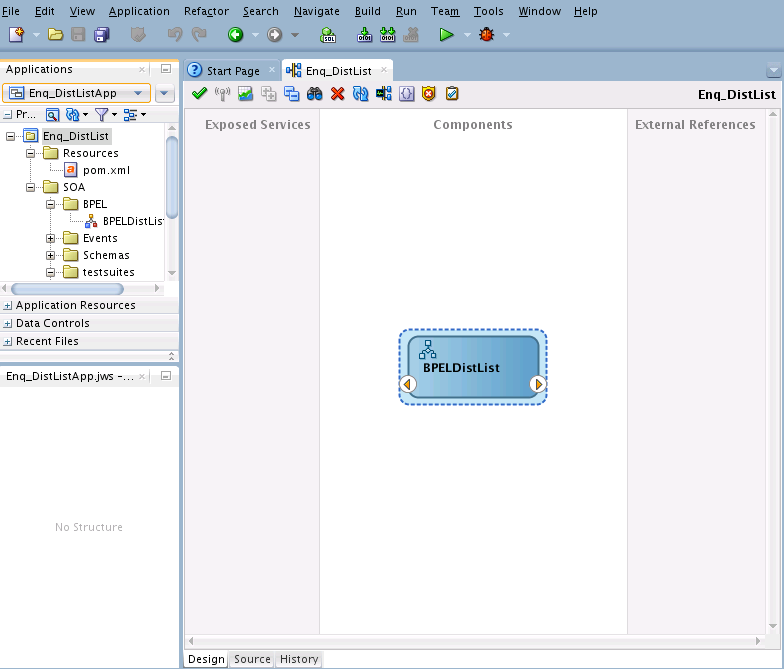
Enqueuing a Message to a Distribution List
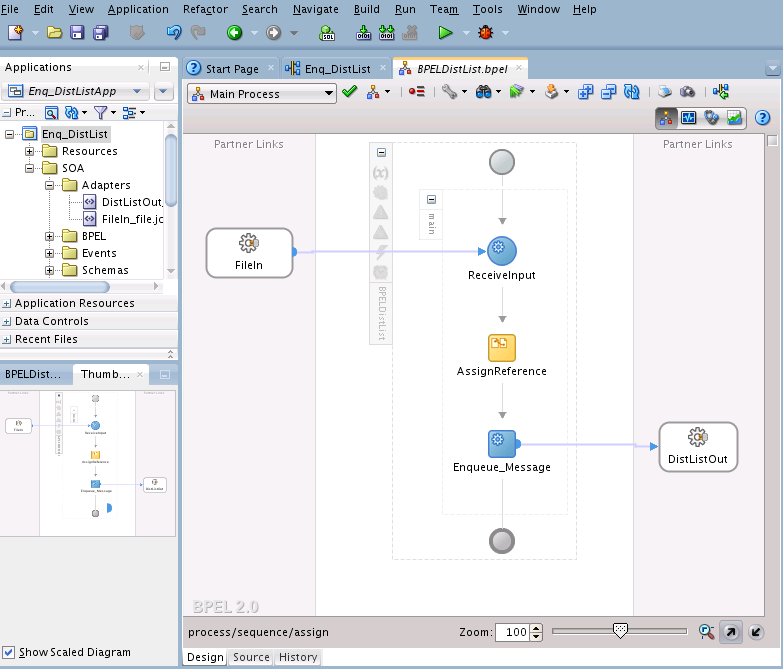
In this use case, follow these steps to create an application that enqueues MSMQ messages to a distribution list:
Designing the SOA Composite
You must create a JDeveloper application to contain the SOA composite. Perform the following steps to create an application and a project:
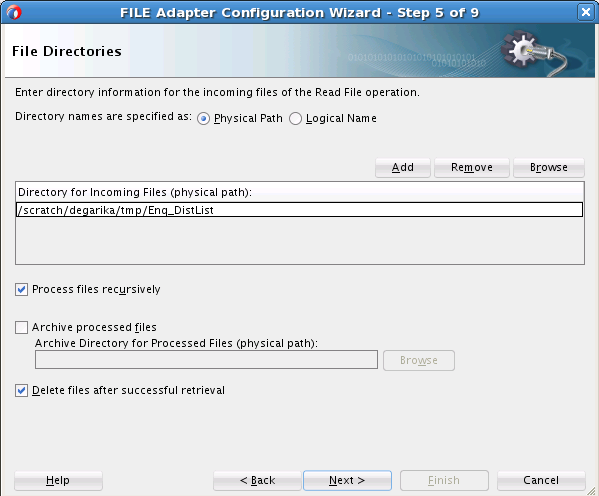
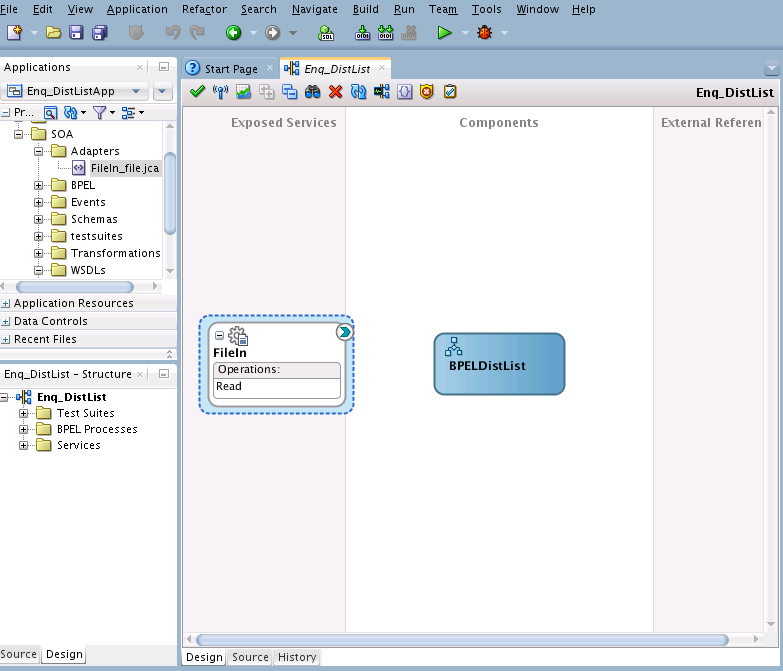
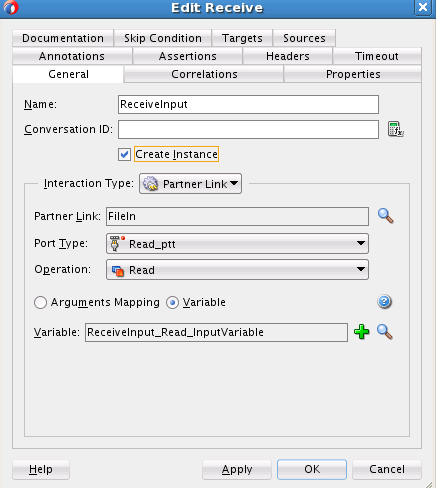
Creating the Inbound Oracle File Adapter Service
Perform the following steps to create an inbound Oracle File Adapter service to read a file from local directory:
Creating the Outbound Oracle MSMQ Adapter Service
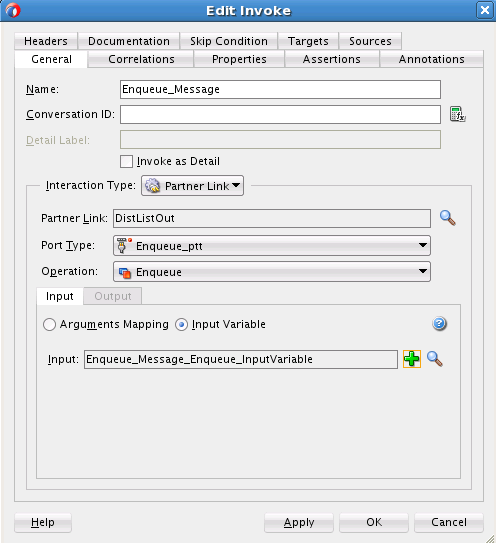
Perform the following steps to create an outbound Oracle MSMQ Adapter service to enqueue the message from a local directory to a distribution list:
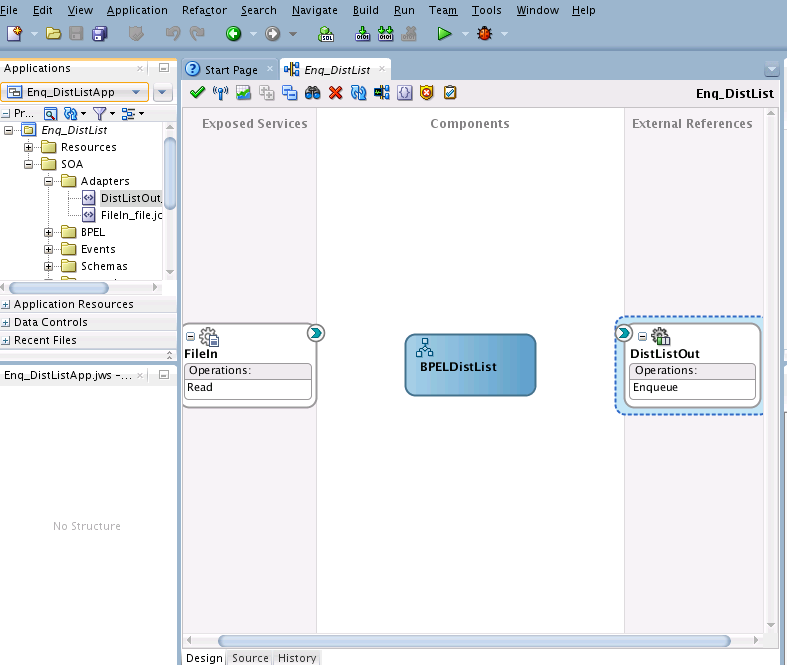
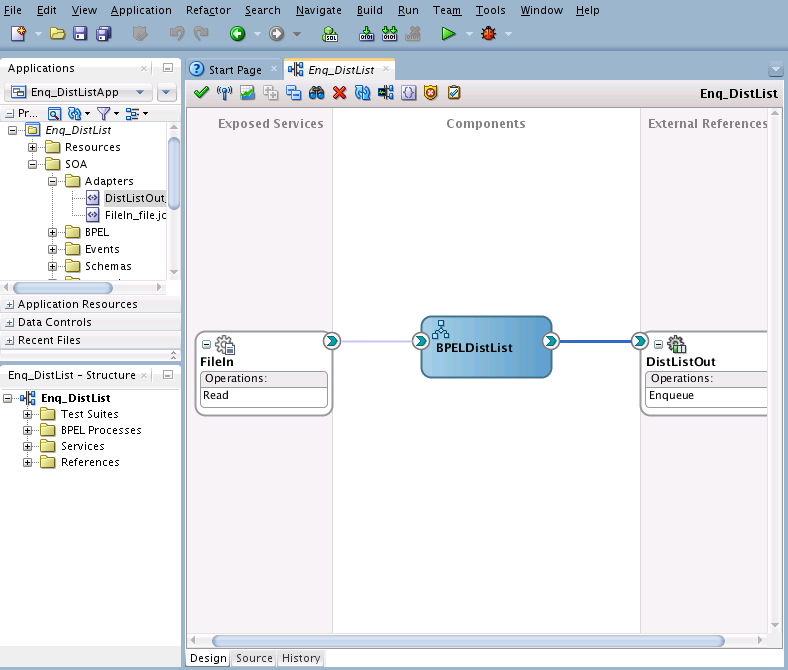
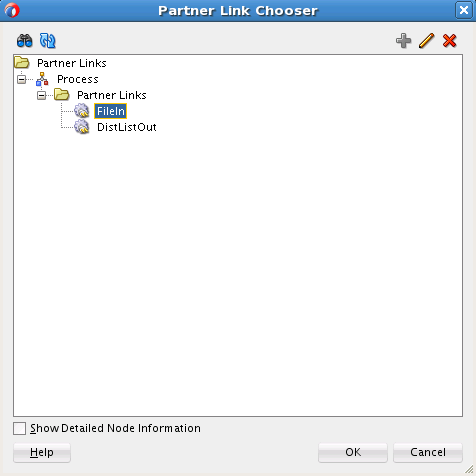
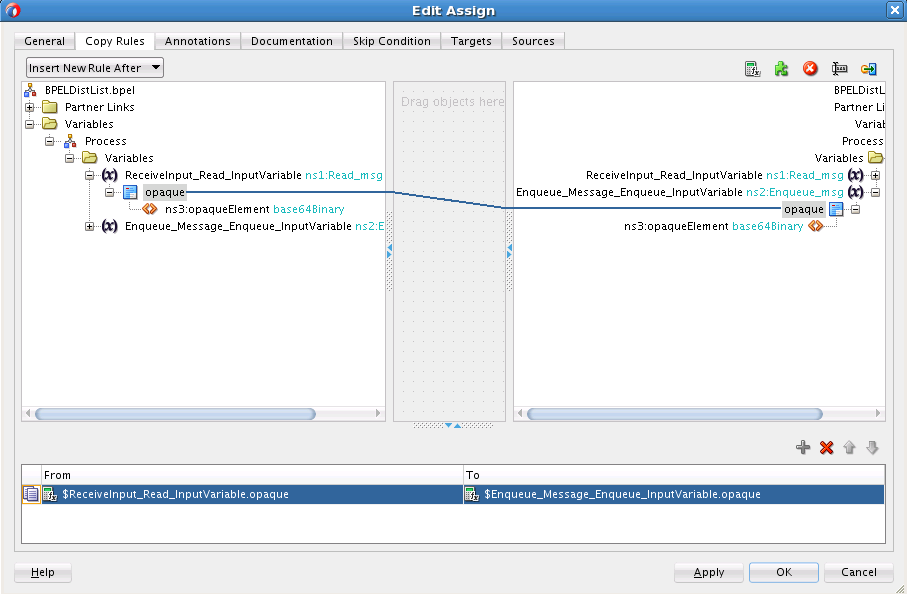
Wiring Services and Activities
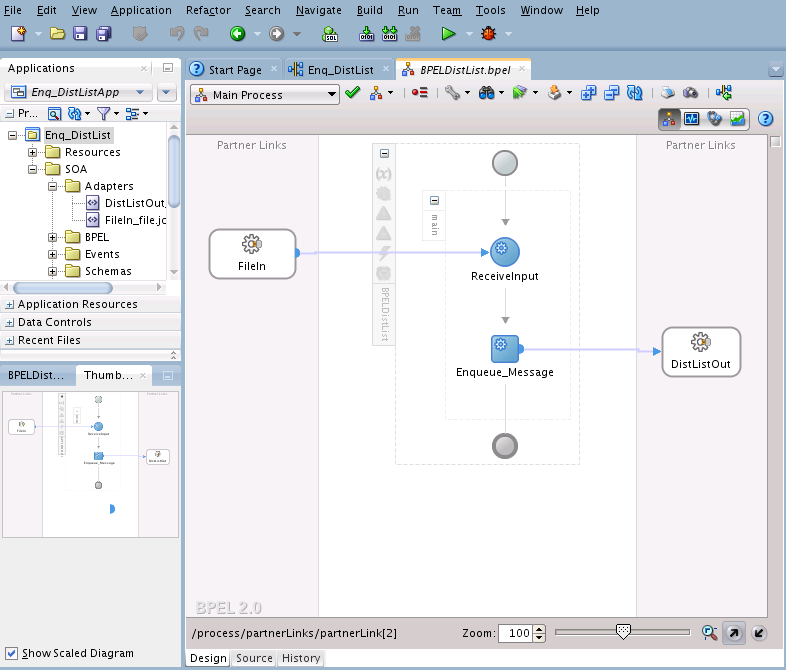
You must assemble or wire the three components that you have created: Inbound adapter service, the BPEL process, and the Outbound adapter reference. Perform the following steps to wire the components: