12 Oracle JCA Adapter for LDAP
Figure 12-1 LDAP Adapter Architecture Diagram
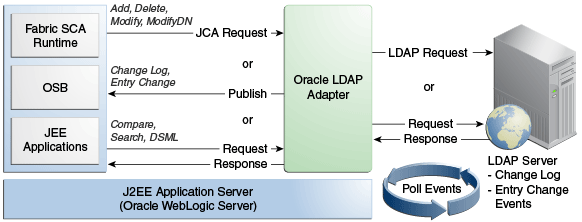
Description of "Figure 12-1 LDAP Adapter Architecture Diagram"
Figure 12-1 illustrates how the Oracle LDAP Adapter exposes synchronous and asynchronous service interfaces that can be used to execute CRUD operations on a target directory server. It illustrates how the Oracle LDAP Adapter can poll for change events from a source directory server and publish these events, thereby acting as a publication service. The LDAP Adapter also provides a DSML synchronous service which takes a DSMLv2 request, executes it on the target directory server and returns the DSMLv2 response.
The LDAP Adapter provides an extensive solution for configuring and connecting to the LDAP Server in a SOA SCA environment. The runtime component provides physical connectivity to the external LDAP Server. It can act as a reference, supporting Outbound services sending requests to the LDAP Server. It can also act as a service, supporting Inbound Services polling to change events on the LDAP Server.
This chapter includes the following sections:
LDAP Concepts
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), is an Internet protocol for accessing information directories. A directory service is a distributed database application designed to manage the entries and attributes in a directory. LDAP runs over TCP/IP. LDAP enables clients to access different directory services based on entries. It makes the entries, along with their attributes and values, available to users and other applications, on a controlled-access basis.
The Oracle Adapter for LDAP provides rich support for LDAPv3 defined operations in addition to support for extensions. It also supports DSMLv2 and can be used as a DSML gateway service. The adapter can be configured to listen and publish change events from a source directory server. In addition, the adapter guarantees once and only once message delivery, high-availability, policy-based retry and fault-handling, automatic fail-over and several other features.
LDAP Entries, Attributes and Values
An LDAP directory contains entries that contain information pertaining to an entity. Each of the entry's attributes has a name and one or more values. The names of attributes are most often mnemonic strings, such as cn for common name, or mail for email address. For example, a company might have an employee directory. Each entry in the employee directory represents an employee. The employee entry contains such information as the name, e-mail address, and phone number. See the following example:
cn: John Doe mail: johndoe@mydomain.com mail: jdoe@mydomain.com telephoneNumber: 471-6000 x.1234
Each part of the descriptive information, such as an employee's name, is known as an attribute. In the example, the Common Name (cn) attribute, represents the name of the employee. The other attributes are mail and telephoneNumber.
Each attribute can have one or more values. For example, an employee entry can contain a mail attribute whose values are johndoe@mydomain.com and jdoe@oracle.com. In the previous example, the mail attribute contains two mail values.
LDAP Directory Structure
The organization of a directory is a tree structure. The topmost entry in a directory is known as the root entry. This entry normally represents the organization that owns the directory.
Entries at the higher level of hierarchy represent larger groupings or organizations. Entries under the larger organizations represent smaller organizations that make up the larger ones.
The leaf nodes (or entries) of the tree structure represent the individual persons or resources.
Distinguished Names and Relative Distinguished Names
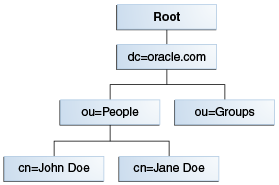
An entry is made up of a collection of attributes that have a unique identifier called a distinguished name (DN). A DN consists of a name that uniquely identifies the entry at that hierarchical level.
In the example below, John Doe and Jane Doe are different common names (cn) that identify different entries at that same level.
A DN is also a fully qualified path of names that trace the entry back to the root of the tree. For example, the distinguished name of the John Doe entry is:
cn=John Doe, ou=People, dc=mydomain.com
A relative distinguished name (RDN) is a component of the distinguished name. For example, cn=John Doe, ou=People is a RDN relative to the root RDN dc=mydomain.com.
DNs are used to describe the fully qualified path to an entry while an RDN is used to describe the partial path to the entry relative to another entry in the tree.Figure 12-2 illustrates an example of an LDAP directory structure with distinguished names and relative distinguished names.
LDAP Service and Service Client
A directory service is a distributed database application designed to manage the entries and attributes in a directory. A directory service also makes the entries and attributes available to users and other applications. The Oracle Internet Directory server is an example of a directory service. Other directory services include Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition and Microsoft Active Directory.
A directory client accesses a directory service using the LDAP protocol. A directory client can use one of several client APIs available in order to access the directory service.
Referrals
The Oracle LDAP Adapter APIs query the results of a search based unspecified referral criteria. The search results can consist of a number of referrals.A referral is an entity that is used to redirect a client's request to another server. A referral contains the names and locations of other objects.
For example, an LDAP server sends a referral to the client to indicate that the information that the client has requested can be found at another location (or locations), possibly at another server or several servers.
The referral contains the URL of the LDAP server that holds the actual entry. The LDAP URL contains the server's host/port and an object's DN.
LDAP Adapter Configurations
The section given an overview of various LDAP Adapter configurations.
Controls
Controls provide a mechanism for extending existing operations in LDAP. Controls can be passed along with request operations in the LDAP adapter.
If included with the operation request message, you can use control information to provide additional information about the way the operation should be processed.
Request Control Format
The format of a request control is name-criticality-value tuples:
requestControls="controlName1|controlOID:criticality:prop1:value1:prop2:value2;
controlName|controlOid is the unique name/oid of the control that must be passed along with a request operation.
criticality is a boolean attribute that signifies the behavior if the control passed along with a request is not supported by the target directory server.You can optionally provide a value string that represents values that can be passed to a request control.
LDAP Control Restrictions
There are several restrictions in using LDAP controls with the LDAP Adapter:
-
An unsupported control with criticality as
trueraises an exception and the LDAP operation is not executed on the target directory server. -
Controls that are only applicable to an operation are executed. If not applicable, then the controls passed along with the operation are ignored.
-
Some controls are only applicable to a single operation whereas some controls are relevant to multiple operations. For example,
subtreeDeleteRequestControlis only applicable to the delete operation whereasassertionRequestControlis applicable to all operations. -
Controls that are not understood by the LDAP Adapter are treated as generic. The behavior of such controls is not well defined.
-
Only request controls are supported. The LDAP Adapter does not support Response controls.
See Table 12-1 for a list of Directory Servers, controls and LDAP Adapter operations.
Table 12-1 Supported Directory Server Controls and LDAP Adapter Operations
| Operations | Controls (Name) | Controls (OID) | Microsoft Active Directory | ODSEE(Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition) | OID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search |
ManageDsaITRequestControl |
2.16.840.1.113730.3.4.2 |
Not Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
|
- |
ServerSideSortRequestControl |
1.2.840.113556.1.4.473 |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
|
- |
GetEffectiveRightsRequestControl |
1.3.6.1.4.1.42.2.27.9.5.2 |
Not Supported |
Supported |
Not Supported |
|
- |
MatchedValuesRequestControl |
1.2.826.0.1.3344810.2.3 |
Not Supported |
Not Supported |
Not Supported |
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Delete |
SubtreeDeleteRequestControl |
1.2.840.113556.1.4.805 |
Supported |
Not Supported |
Not Supported |
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Modify |
PermissiveModifyRequestControl |
1.2.840.113556.1.4.1413 |
Supported |
Not Supported |
Not Supported |
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
ModifyDN |
No control listed in wizard |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Non Default Control Configuration for Design Time Wizard
The LDAP Adapter configuration wizard enables you to attach request controls along with an operation.The Attach Control screen operates in the following manner:
-
By default, only the controls applicable to an operation and supported by the connected directory server are listed in the wizard.
-
Example:
assertionRequestandSubtreeDeleteare controls applicable to the delete operation; but if the target directory server does not support the subtree delete operation, only theassertionRequestis listed. -
You can choose to add from other supported controls. These controls are treated as generic and you should test these controls thoroughly as the runtime behavior of these controls is not well-defined.
Control Availability
By default, only a few frequently used control names are displayed within the LDAP Configuration Wizard. If you want the Wizard to display the control names for non-named controls, you must follow these manual steps to update control definitions and provide the appropriate names and details.
LDAP Browser
Use the LDAP Browser Page to show the Directory Information Tree (DIT). The Browser is called from LDAP Configuration Adapter wizard when you select Browse. See Figure 12-3.
Figure 12-3 The LDAP Browser Shown in Context
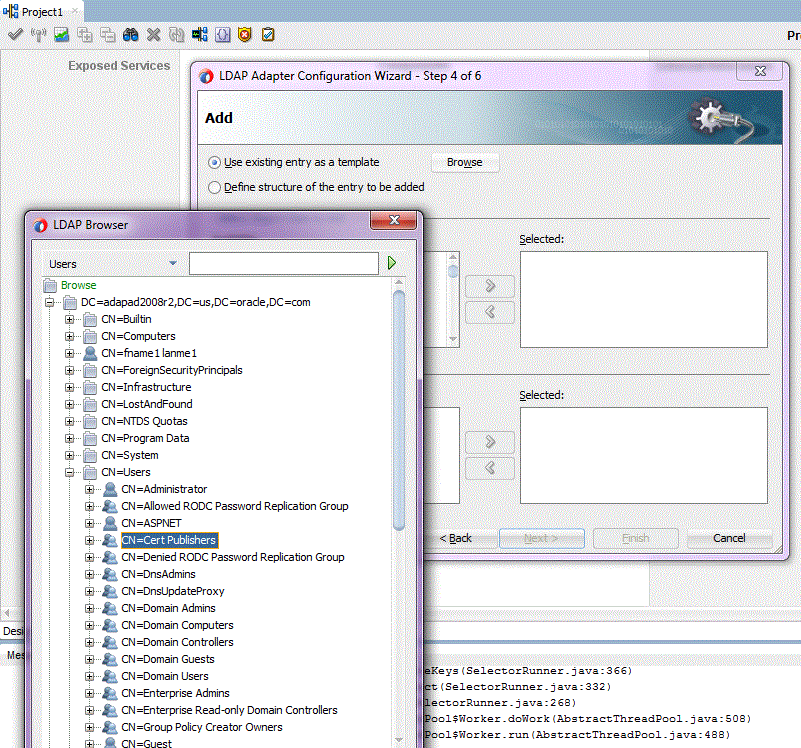
Description of "Figure 12-3 The LDAP Browser Shown in Context"
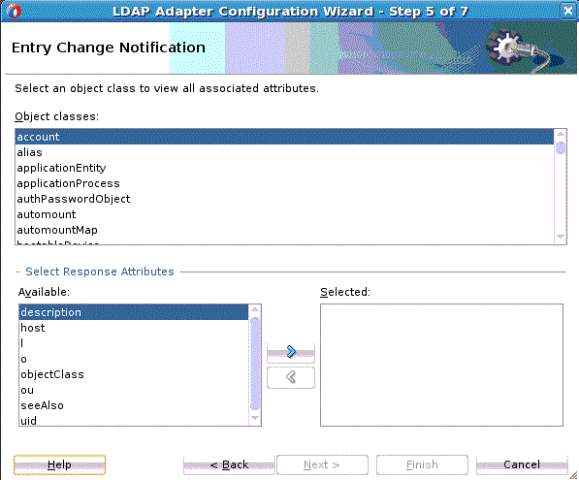
To choose an entry, select the entry in the DIT and click the OK button. The selected entry is used further in the LDAP Adapter Configuration wizard as a baseDN for a Search operation you perform, the Entry Change Notification operation or as a template for the Add operation.
Attribute Viewer
To see attributes related to an item, double-click the selected entry.
The Attribute viewer displays in a two-column layout. The left column contains the attribute descriptions (or names), the right column contains the attribute values. Each line represents a name-value pair. The section immediately previous, the attributes table displays the distinguished name of the current entry. See Figure 12-4.
Figure 12-4 The LDAP Configuration Wizard Browser Attribute Viewer
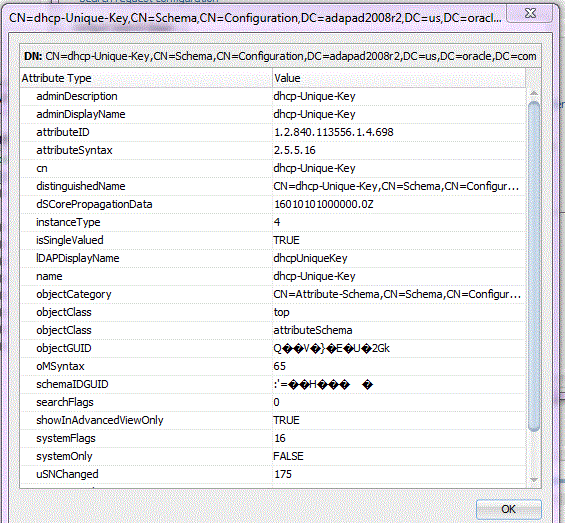
Description of "Figure 12-4 The LDAP Configuration Wizard Browser Attribute Viewer"
Folding
The directory information tree of the LDAP directory is displayed in its natural hierarchical structure. The first hierarchy level contains the base entries. When expanding an entry its direct children are fetched from directory. While browsing the directory, the LDAP Browser attempts to find if a fetched entry has children. Entries without children cannot be expanded.
By default, large browse results are folded into virtual folders each with 100 entries. The displayed tree is thus smaller. The number of fetched items is limited by 1000 items for performance improvements. To operate with folders with over 1000 records you can use the Search operation. See Figure 12-5.
Figure 12-5 The LDAP Adapter Configuration Wizard LDAP Browser Directory Folding
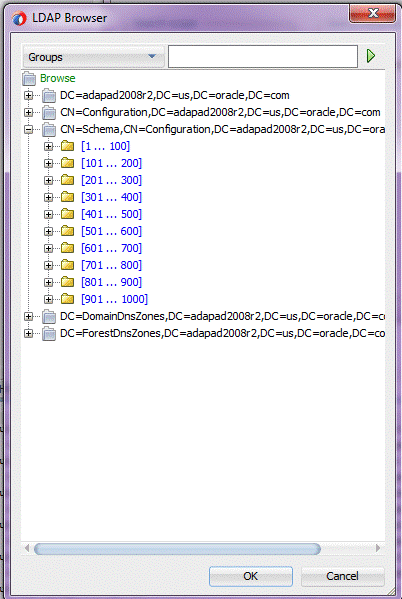
Description of "Figure 12-5 The LDAP Adapter Configuration Wizard LDAP Browser Directory Folding"
Searching
The Search operation is an alternative approach that you can use when browser does not load the expected entries.You can search the DIT by specifying a single search attribute and value. The search is processed over the whole subtree. There is no limitation on the quantity of search results.
In the left combo-box. you can select the Search attribute from the list of commonly used attributes: cn, givenName, mail, member, objectClass, sn, telephoneNumber, uniqueMember.
Use the option Groups to specify that the Search is processed among the entries that are groups.
Use the option Users to indicate that the search are processed among the entries that are persons, accounts, or users.
Enter the search value in the right input field. Use '*' as wildcard as needed.
Figure 12-6 LDAP Configuration Wizard Browser Showing Supplying a Wildcard to the Search Operation within the LDAP Browser
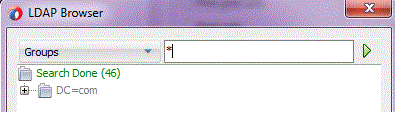
Description of "Figure 12-6 LDAP Configuration Wizard Browser Showing Supplying a Wildcard to the Search Operation within the LDAP Browser"
To start the search operation, select the green triangle button on the right side.In the left combobox, select FilterType.LDAPFilter to set the LDAP search filter in the right field manually.
Figure 12-7 LDAP Configuration Wizard Browser Showing Supplying a Filter to the Search Operation within the LDAP Browser
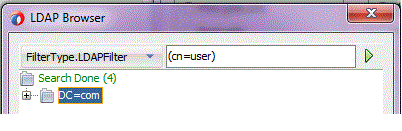
Description of "Figure 12-7 LDAP Configuration Wizard Browser Showing Supplying a Filter to the Search Operation within the LDAP Browser "
Oracle LDAP Adapter Features
The LDAP protocol and the LDAP adapter provide fast read-access to directory information.
The LDAP Adapter supports both inbound and outbound messages and includes the following features, as detailed in this section:.
-
Note:
The LDAP Adapter does not provide any transaction support on outbound messages.
Configuring the LDAP Adapter
You use the LDAP Configuration Wizard to configure the LDAP Adapter, to model LDAP services through contextual options and browsing on the LDAP directory schema. The LDAP Adapter wizard requires a connection to the target LDAP directory server which can you configure in the following manner.
JNDI Connection Pool Properties for the LDAP Adapter
Table 12-2 provides JNDI connection pool properties for the LDAP Adapter.
Table 12-2 JNDI Connection Pool Properties for the LDAP Adapter
| Property Name | Description | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Distinguished Name required to bind to directory server. Example, cn=orcladmin |
cn=Directory Manager |
Yes (Needed when using an authentication method other than anonymous.) |
|
|
Host name of the directory server. |
localhost |
Yes |
|
|
JNDI string location pointing to a valid XA data source. Example: jdbc/SOADataSource |
None |
Yes (if the LDAP Adapter has to be used on the inbound direction.) |
|
|
Sets the operation timeout. If the response is not received from the directory server in the timeout period, the operation is abandoned and an exception is raised. Example: 1000 |
False |
No |
|
password |
Password of the directory server. |
welcome |
Yes (Needed when using an authentication method other than anonymous.) |
|
|
Port on which directory server is running.. |
389 |
yes |
|
hostName |
Host name of the directory server. |
Localhost |
Yes |
|
port |
Port where the LDAP service is running. |
389 |
Yes |
|
|
SecurityProvider is the provider url which the SSL context should use. Example: ldaps://myhost.example.com:636 |
None |
No |
|
|
Key management protocol. Example: SSLl |
None |
No, required only if useSSL or startTLS is selected. |
|
|
If set to true, the client blindly trusts any certificated that the server might present. |
ture |
No, required only if useSSL or startTLS is selected. Set this to false if server certificate has to be validated with truststore. |
|
trustStorePassword |
Specifies the password needed to access the trust store contents. |
None |
No |
|
|
Specifies file system path to the trust store file that the client uses for server authentication. |
false |
No. required only if SSL or startTLS is used. |
|
|
The Java provider name. Example: JKS |
None |
No, required only if SSL or startTLS is used. |
|
|
Specifies if a secure channel must be established |
False |
No |
|
|
Specifies if startTLS might be turned on for secure communication later on within a plain non-ssl connection. |
False |
No, do not set this to true when useSSL is set to true. This need to be enabled when non-ssl plain port is used for server connection. |
Note:
Replace the default values with the actual values that you got from the supported target directory server installations and redeploy LdapAdapter with the updated deployment plan.Outbound Operations
The LDAP Adapter supports the following operations outbound from the LDAP Adapter.
-
Add
-
Delete
-
Modify
-
ModifyDN
-
Compare
-
Search
-
DSML
Note:
The LDAP Adapter does not provide any transaction support for outbound operations.Add Operation
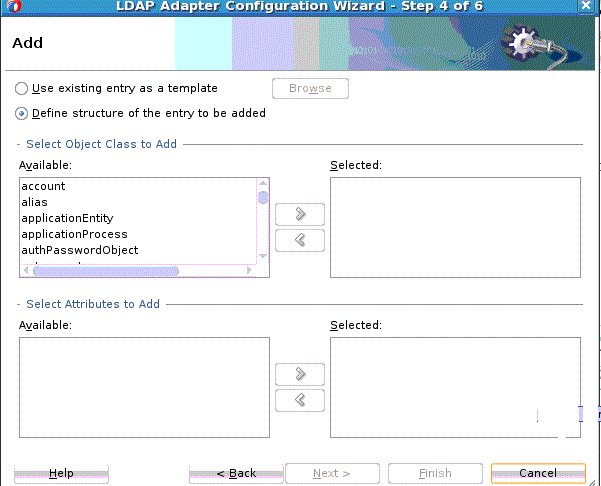
The Add operation adds an entry with a given DN and a set of attributes. It returns an error if the entry to add already exists, or if the given operation could not be completed.
To use the LDAP Configuration Wizard Add operation:
Delete Operation
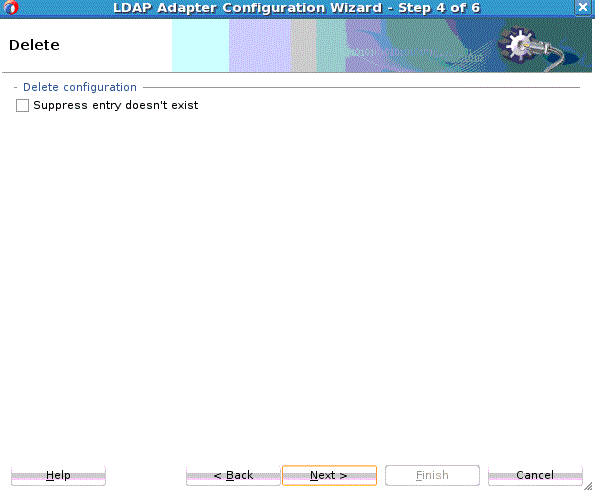
The LDAP Delete operation deletes an entry with a given DN.You can optionally add controls along with the LDAP Delete request. The Delete operation returns an error if the given entry cannot be deleted or does not exist. It also returns an error if a critical control attached with the request message is not supported by the target Directory Server.
To use the Delete operation:
Modify Operation
The LDAP Modify operation alters an existing entry in the Directory Server.
Types of alterations performed with Modify include: Add, Delete, and Replace.
-
Add: Creates the attribute if it does not exist, and adds the specified values. If the attribute already exists, the specified value is added to the attribute values. The Add operation must contain at least one value, and all values of the attribute must be unique.
-
Delete: Deletes specified values from the attribute. If no values are specified, or if all existing values of the attribute are specified, the attribute is removed. Mandatory attributes cannot be removed.
-
Replace: Creates the attribute if necessary, and replaces all existing values of the attribute with the specified values. If you want to keep any existing values of a multi-valued attribute, you must include these values in the replace operation. A replace operation with no value removes the entire attribute if it exists, and is ignored if the attribute does not exist.No changes are made to the directory unless all the operations succeed. If the connection fails during a modification, it is unpredictable if the modification occurred.
To use the LDAP Configuration Wizard Modify operation:
-
Select the Modify Operation from the Operation Type Screen. The Modify Operation screen appears.
Figure 12-11 The LDAP Configuration Wizard Modify Select Object Classes Page
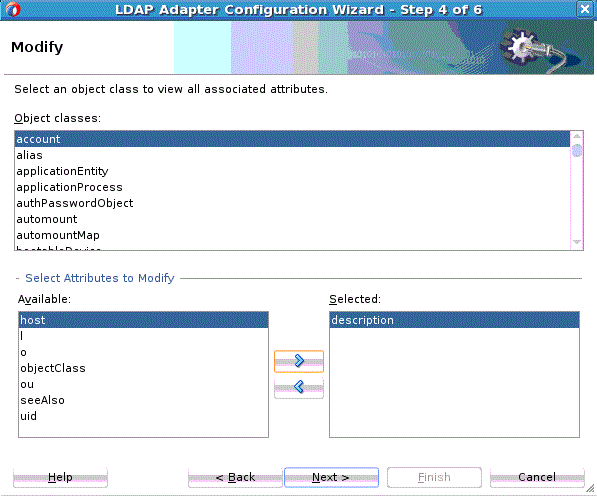
Description of "Figure 12-11 The LDAP Configuration Wizard Modify Select Object Classes Page" -
Select from the list of Object classes on this page. From the list of Available attributes to Modify, select attributes that can be modified, and move them to Selected. You can also remove them from selected by using the left arrow key. Click Next.
-
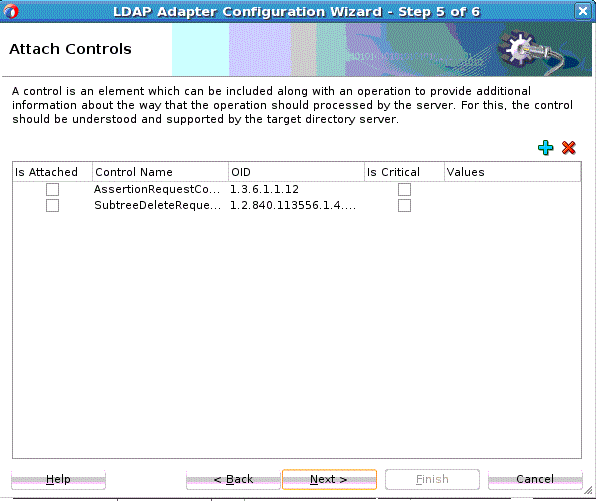
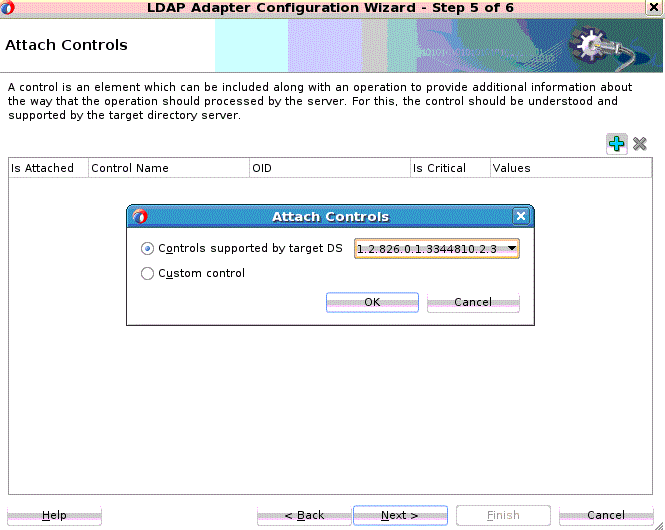
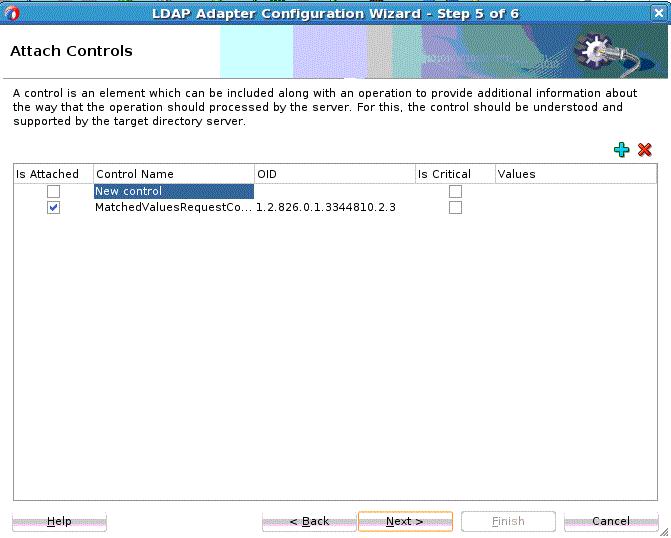
The Attach Controls Page appears. See Figure 12-12.
Use the green plus to add custom controls, or controls provided by the target Directory Server. An example is shown below. Select controls needed, and provide values by entering in the Values column.
Note:
Consult your target directory server documentation for supported controls. Check the relevant operation in this chapter before attaching a control. The LDAP Adapter might not support all controls supported by the target directory server.
Figure 12-12 The LDAP Configuration Wizard Modify Attach Controls Page
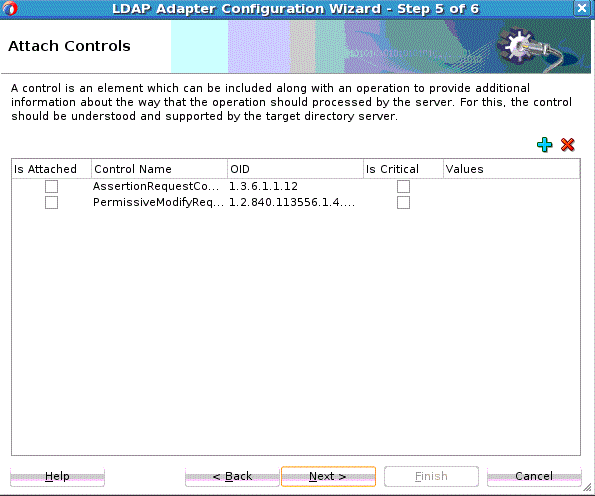
Description of "Figure 12-12 The LDAP Configuration Wizard Modify Attach Controls Page" -
Click Next. The Modify Finish screen displays the names of the LDAP Service WSDL, xsd and jca files.
ModifyDN Operation
The LDAP ModifyDN operation can be used to change the distinguished name of an entry in the Directory Server. It can also alter the RDN of the entry and/or it can move the entry below a new parent. If the target entry has subordinate entries, then it may be used to move or rename that subtree.
To use the ModifyDN operation:
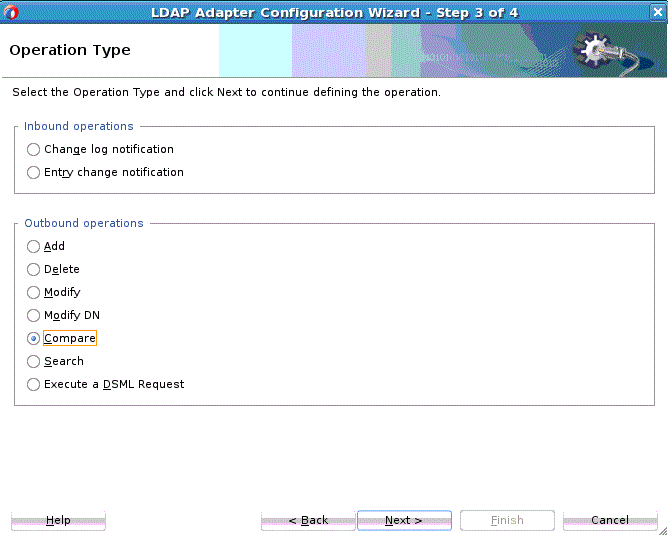
Compare Operation
The LDAP Compare operation determines whether a specified entry contains a given attribute value.
To use the LDAP Adapter Compare Operation:
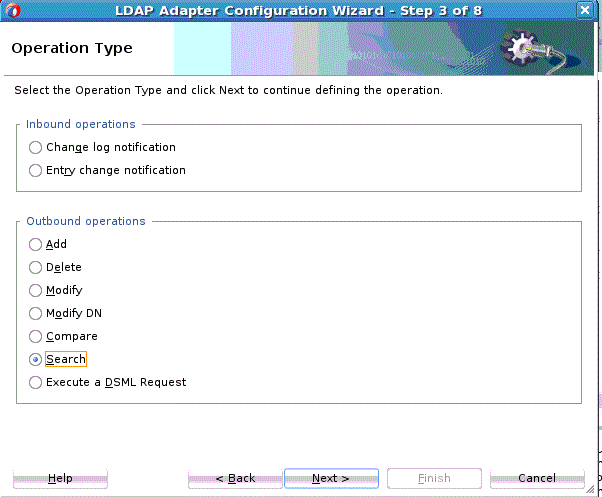
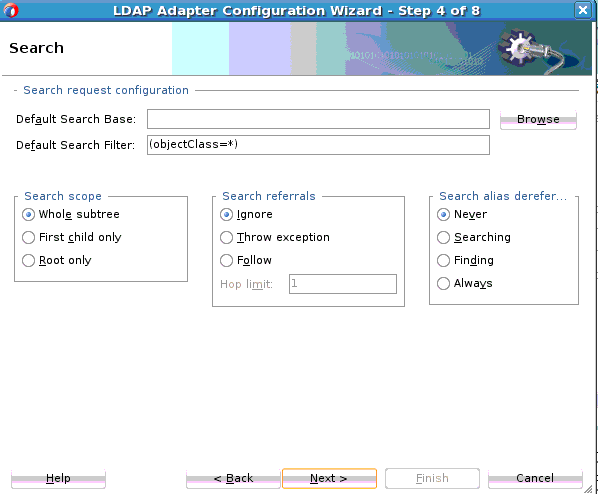
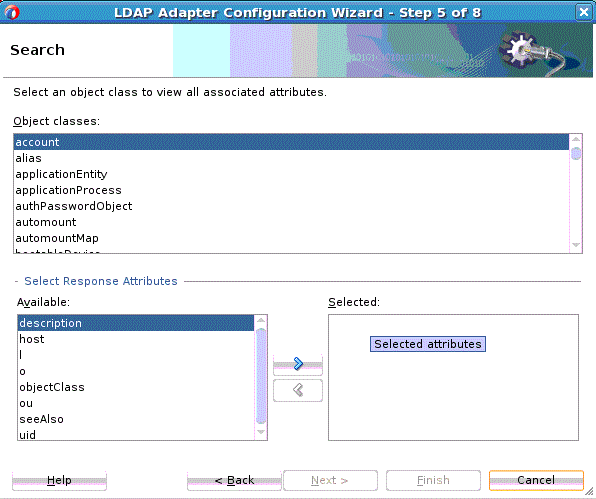
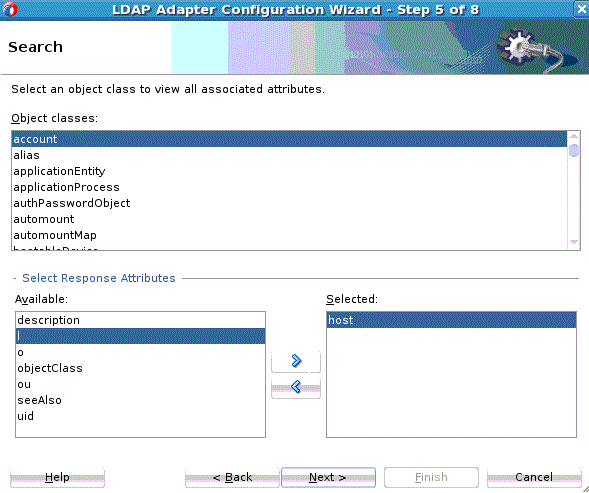
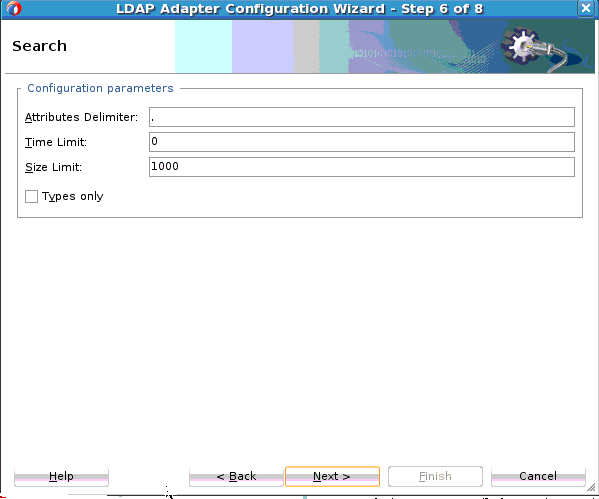
Search Operation
The LDAP Adapter Search operation can be used to identify entries in the Directory Server that match a given set of criteria. It may return zero or more entries, and also zero or more referrals. The Search operation includes the following criteria.
-
The base DN, which specifies the location in the DIT in which to perform the search.
-
The search scope, which specifies the scope of entries at or below the base DN to consider when processing the search.
-
The dereference policy to use if any aliases are encountered during processing.
-
The size limit, which specifies the maximum number of entries that should be returned from the search (or –1 for no limits on the search results).
-
The time limit, which specifies the maximum length of time in seconds that the server should spend processing the search (or zero if there should not be a maximum number of entries).
-
The types only flag, which indicates whether the entries returned should include attribute types only or both types and values.
-
The search filter, which specifies the criteria to use to identify matching entries.
-
The search attributes that indicate which attributes should be included in matching entries
-
Controls you can attach along with the search request, and return an error if a critical control attached with the request message is not supported by the target Directory Server.
Note:
In the current version, binary types are not supported and attribute values are always encoded as utf8 Strings.
To use the outbound Search operation:
DSML Operation
DSML operations express LDAP requests and responses as XML document fragments. Use the LDAP Adapter DSML screen to specify an execute a DSML request and to optionally enter a Maximum request size for that DSML request on the LDAP Operations Screen.
To use the DSML Execute Request:
-
Specify DSML on the LDAP Operation Type Screen.
-
The DSML Screen appears. See Figure 12-22.
On this screen, optionally enter the Maximum DSML Request Size. Set this property if you want to control the maximum number of requests that can participate in a DSML batch request. The incoming DSML request is executed if and only if the total number of contained requests is less than this number.
Figure 12-22 The LDAP Adapter Configuration DSML Configuration Page
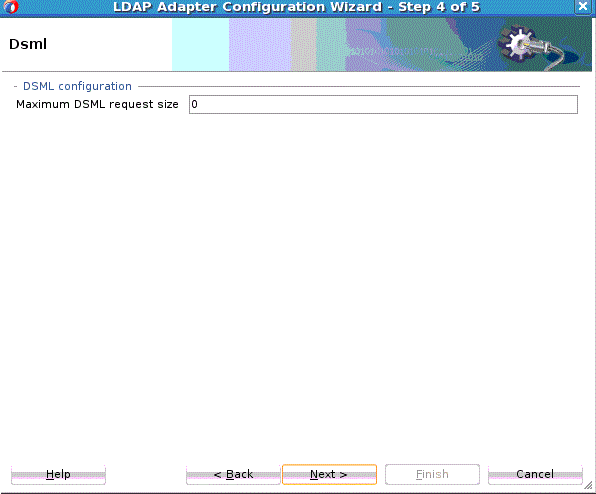
Description of "Figure 12-22 The LDAP Adapter Configuration DSML Configuration Page" -
Click Next. The DSML Operation Finish screen appears, showing the LDAP WSDL, jca and xsd files.
Inbound LDAP Adapter Features
The LDAP Adapter supports publishing events from a Directory Server. Specifically, it supports one way inbound interactions, asynchronous event publishing from the directory server through the asynchronous notification model.
The LDAP Adapter listens for events such as addition, deletion, or modification of an entry in the directory information tree and publishes such events. The LDAP event consumer singleton connects and listens for changes on the directory server according to a chosen strategy and processes/publishes such events to LDAP Adapter clients.
By default, the LDAP Adapter publishes events in the order they are received from the directory server.
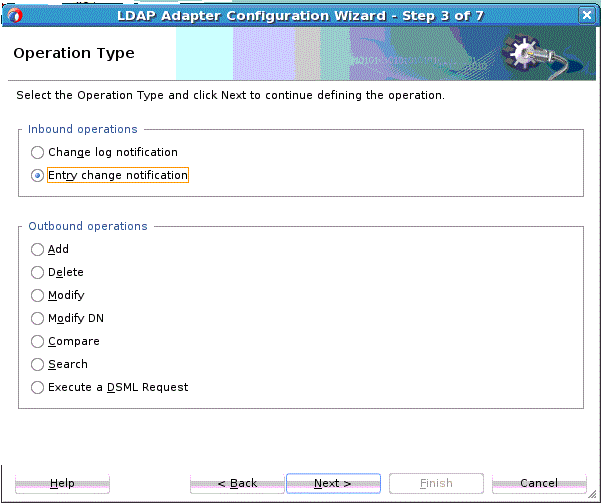
The LDAP Adapter provides two type of inbound activities:
LDAP Adapter Entry Change Notification
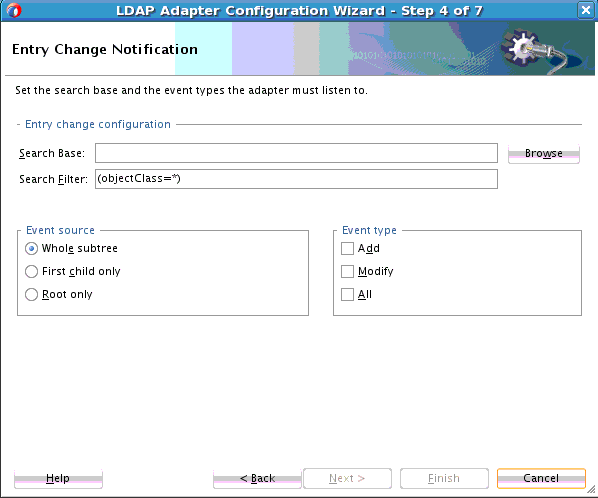
Entry Change Notification enables you to obtain entries that are created or modified on a source directory server. The result contains the modified entry along with information about the type of modification.
This mechanism is based on a timestamp-based search; it does not require any external configuration and is supported by most Directory Servers. With time-based search, a search is done for all entries after a base time stamp. The base time stamp is updated for subsequent timestamp-based searches.
In search, the LDAP Adapter returns results up unto the latest time stamp, it then updates the base time stamp to the latest time stamp. The time interval you configured indicates when the next iteration of the timestamp-based search for all events next occurs.
Time stamp-based search only provides notifications of added or modified entries. With Entry Change Notification, there is no provision to find out deleted entries. This mechanism only notifies about the changed entry that is, it indicates if an entry has been changed, and does not divulge details of the changes that occurred.
There is no way to differentiate between a modify and modifyDN operation as there is no provision to find out deleted entries.
Specifically, Entry Change Notification does not provide notification when an entry enters or leaves the scope of a result set due to a modifyDN operation or when a Modify operation acts on a attribute value that is used in a search filter.
Time-stamp based search does not work with multi-master setups of the Directory Server because the time stamp is generated using the clock on each of the servers and can therefore appear in a non-linear order on a given replica.
Because Entry Change Notification uses Timestamp-based search, which is based on the operational attributes createTimestamp and modifyTimestamp, these attributes should be available, indexed and functional in the directory server for timestamp based search to work properly.
You might see the Unavailable Critical Extension exception in the LDAP Adapter client logs, if any of these attributes are not indexed and functioning correctly.
Refer to your directory server documentation to help ensure these attributes are indexed properly, so they are available during the time stamp search.
Note:
PageSize configuration does not work when connecting to the Oracle Internet Directory server and should not be used with that server. If configured, the number of events happening over the pageSize limit are not processed.
LDAP Adapter Change Log Notification
The Change Log Notification event provides a detailed log of modifications that were done on entries in Directory Server.
The event includes change details and reconstructs the request message that was executed on the source server that led to this change. This event is particularly useful if the same request is to be replayed on a target server. The Change Log Notification is a very powerful feature in that it provides details on activities.
You can use Change Log Notification to incrementally synchronize a source LDAP directory with other sub-systems. As this mechanism is not part of the LDAP specification, you should check your Directory Server's implementation and the Oracle certification matrix before using this feature, as it might require specific configuration on the source Directory Server before you can use it.
Change Log Notification is not available on a server instance that is configured as either a dedicated directory server or a dedicated replication server.
Change Log Notification LDAP Adapter Configuration Wizard Flow
Follow these general steps to configure Change Log Notification. The steps assume you have performed prior steps in the general flow, and you are now at the Operations Type Screen.
Change Log Notification Errors
The following table lists Change Log Notification Errors.
| Error Name | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Inbound adapter service's connection to the Directory Server is down. This is an |
Remote Fault with appropriate error message. Adapter should retry the connection to the Directory Server. |
|
|
Change log mechanism is not supported by the target Directory Server. This is an |
Fatal exception and inbound service stops. |
|
|
The change number is invalid or not recognized by the Directory Server. Contact your Directory Server administrator. Provide a valid change number. The change number may be invalid or purged and no longer recognized.You can manually provide a new change number in the database. This is an |
This leads to a fatal exception because the inbound service does not identify the initial change number and hence cannot start processing. |
|
EndpointActivationError |
Validation fails while activating the endpoint due to one or more activation spec errors. This is an LdapValidationException |
Binding fault. |
|
SizeLimitExceededException |
Specified Size Limit Was exceeded. |
.- |
|
TimeLimitExceededException |
Specified Time Limit was exceeded. |
- |
Note:
During runtime, error/status codes that are raised by an LDAP server does not get sent back to the client or displayed in the server.
Entry Change Notification Error Conditions
The following table lists possible errors related to entry change notification through the LDAP Adapter. Included are the error name, a description of the error name and the status the in which the configuration is left after the error is reported.
Table 12-3 Entry Change Notification Error Conditions
| Error Name | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Inbound adapter service's connection to the DS is down. This is an |
Remote Fault with appropriate error message. The LDAP Adapter should retry the connection to the DS. |
|
|
Malformed baseDN in event scope. This is an |
Binding fault. |
|
|
Search filter is malformed according to string representation of ldap filters. See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/ rfc2254.txt This is an |
Binding fault. |
|
|
Adapter inbound service configuration is invalid due to one or more reasons. This is an |
Binding fault with the appropriate message indicating the violation. |
|
|
Validation fails while activating the endpoint due to one or more activation spec errors. This is an |
Binding fault. |
|
|
Occurs if there was an error while processing an event received from the directory server. This is an |
The fault is retried according to configured retry parameters and rejected once the appropriate retries are done. |
Logging
The following logs are available for the LDAP Adapter. You can view these Runtime Loggers from the WebLogic Remote Console. The logging level for each is inherited from the parent.
-
oracle.soa.adapter.ldap.inbound -
oracle.soa.adapter.ldap.outbound -
oracle.soa.adapter.ldap.connection -
oracle.soa.adapter.ldap.transaction
Security
The LDAP Adapter must sign-on with valid security credentials. To enable this, the Oracle WebLogic Server supports both container-managed and application-managed sign-on.
Container managed sign-on enables a user to sign-on to Oracle WebLogic server and to access the Enterprise Information System through the resource adapter without having to sign-in separately to the Enterprise Information System.
Because the Oracle WebLogic server and the LDAP Enterprise Information System maintain independent security realms, this is achieved by using credentials mapping. Oracle WebLogic Server security principals are mapped to the corresponding credentials required to access the Enterprise Information System. The Adapter deployment descriptor does not need to store sensitive credential information.
The LDAP Adapter authenticates with LDAP server using simple authentication (Simple Bind). For example, it binds username and password to the directory server.
It does not have support for SASL or any other authentication mechanisms.
LDAP Adapter does not consider additional password policies such as expiry, retries and so on that are provided by the server to which it is connected.
Creating Outbound Credential Mappings
Outbound credential mappings enable you to map WebLogic Server user names to user names in the Enterprise Information System (EIS) to which you want to connect using a resource adapter. You can use default outbound credential mappings for all outbound connection pools in the resource adapter or you can specify particular outbound credential mappings for individual connection pools.
As an alternative to providing the bindDN and password in the ConnectionFactory properties, you can do the following to create credential mappings:
The Credential Mappings you supply take precedence over the bindDN and password properties you have configured in the ConnectionFactory, if you configured any. Use this connection factory as you would use any LDAP connection factory.
After you completed the last step, you have configured the Enterprise Information System User Name and Password that you wanted to use to map the WebLogic Server User.
LDAP over SSL
Secured Sockets Layer, or SSL, provides a secure and encrypted channel for communication between the client and the server. See Figure 12-26 for an overall view of SSL in the LDAP over SSL environment.
Note:
You can change user passwords only over SSL. Check your Active Directory Endpoint settings and switch to use SSL. When you change the user password over SSL, you may get an error when the password complexity is too low. For example, the password does not have uppercase/lowercase/digits/non-alphanumeric characters or the password is too short. Either disable the password complexity setting in Active Directory or use a complex password.In environments in which sensitive data is transferred to remote servers (for example, sending credit card information to HTTP servers), the issue of security is very important. Security in these cases primarily refers to two requirements:
-
Trust in the remote server with which you are exchanging data.
-
Protection from third parties trying to intercept the data
The LDAP Adapter's use of SSL certificates and encryption satisfy these two security requirements.
To gain the trust of clients in SSL environments, servers obtain certificates (typically, X.509 certificates) from recognized certificate authorities. Every client trusts a few parties. If the server is one of these trusted parties, or if the server's certificate was issued by one of these trusted parties, there is trust, even indirectly. This is also known as server authentication. The LDAP Adapter provides this type of server- authentication SSL handshake.
Since there is no notion of a rejected message in the LDAP Adapter, the LDAP Adapter has to raise a non-retriable exception.
Note:
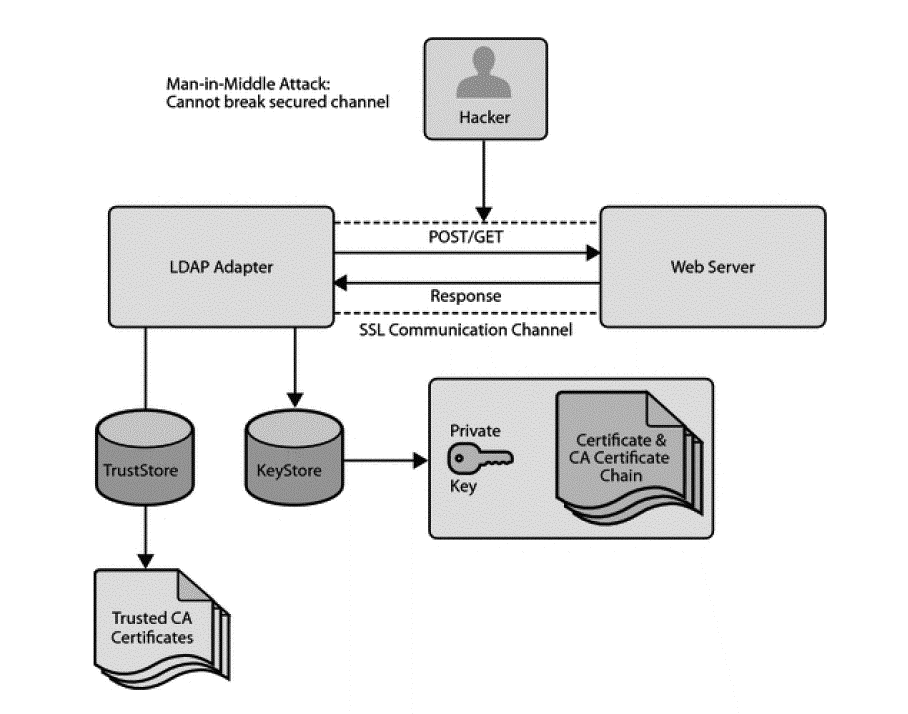
LDAP Adapter only supports server authentication or server-side authentication. It doesn’t support dual authentication, where LDAP server authenticates client certificate with its truststore.See Figure 12-27 for a representation of the use of certificates and a trusted store.
Figure 12-27 Using Certificates and Trusted Store with SSL
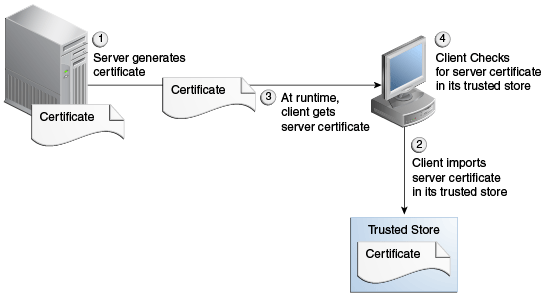
Description of "Figure 12-27 Using Certificates and Trusted Store with SSL"
Payload Size Threshold
You can set the Payload size threshold in the composite.xml as a binding property on the adapter service.
By default, there is no limit on the payload size threshold. However, the LDAP adapter enforces the rule that any message published to Fusion Middleware must be less than the payload size threshold limit. Violating messages are rejected. Because there is no notion of a rejected message in the LDAP Adapter, the Adapter raises a non-retriable exception instead. Results are not going to alter in a re-try scenario so there is no point in retrying the payloadSizeThreshold.
High Availability
The LDAP adapter is highly available and propagates a change once and only once without message loss. The LDAP Adapter is deployed as a singleton in an active cluster. This implies that at any given time, only a single instance of the LDAP Adapter receives notifications from directory servers. The High Availability Support is applicable for inbound operations only. The LDAP Adapter does not provide any transaction support for outbound operations.
LDAP Adapter Exception Handling
LDAP Adapter Exceptions consist of the following types of exceptions:
-
Inbound Retriable Exceptions
-
Non-Retriable Inbound Exceptions
-
Outbound Retriable Exceptions
-
Outbound Non-retriable Exceptions
Inbound Retriable Exceptions
Inbound retriable exceptions are usually connection-related. The LDAP Adapter retries until a connection or the retriable exception condition is corrected.
The following binding properties apply to such exceptions. If retry properties are not specified, retry occurs indefinitely.
Table 12-4 Inbound Retriable JCA LDAP Adapter Properties
| Property Name | Allowed | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
- |
Maximum number of retries before rejection. |
|
|
Measured in seconds |
Time interval between retries. |
|
|
Positive integer |
Retry interval growth factor. |
|
|
- |
Maximum value of retry interval. |
|
|
- |
Upper limit of the entire accumulated duration of all retries; that is, a hard limit. |
Outbound Retriable Exceptions
The LDAP Adapter performs retries according to configured binding properties. If these binding properties are not specified, the retry is carried out by fault policies, if they are included as part of the composite.
The following properties govern outbound retriable exceptions.
Table 12-5 Outbound Retriable LDAP Adapter JCA Properties
| Property Name | Allowed | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
- |
Maximum number of retries before rejection. |
|
|
Measured in seconds |
Time interval between retries. |
|
|
Positive integer |
Retry interval growth factor. |
|
|
- |
Maximum value of retry interval. |
|
|
- |
Upper limit of the entire accumulated duration of all retries; that is, a hard limit. |
|
|
- |
Maximum number of retries before rejection. |
|
|
Measured in seconds |
Time interval between retries. |