3 Working with Document Types and Protocols
This chapter provides information about the document protocols and message types supported by Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration, and describes how to work with document definitions in the healthcare integration user interface.
This chapter contains the following topics:
3.1 Introduction to Document Protocols
Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration supports custom and HL7 V2.x document protocols.
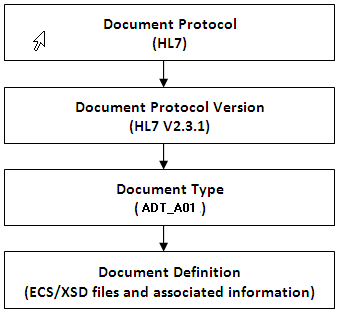
Figure 3-1 displays the document protocols supported in Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration.
Figure 3-1 Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration Document Protocols
Description of "Figure 3-1 Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration Document Protocols"
As part of the document definition, you provide the document guideline files, which are typically created in Oracle Document Editor. (For Custom documents, you cannot use Oracle Document Editor and validation of documents is also not possible.) If validation is enabled, then, at runtime, the payload must conform to the document definition file type you use.
3.1.1 What You Might Need to Know About the Document Hierarchy
You can think of a document protocol as a hierarchy, as shown in Figure 3-2.
A document protocol can consist of multiple document protocol versions. A document protocol version can consist of multiple document types. A document type can consist of multiple document definitions. Typically, you start with one document definition and customize it for different endpoints.
Figure 3-3 shows a document protocol hierarchy as it applies to HL7 V2.3.1.
In the Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration user interface, as you create a document definition, the document protocol hierarchy is reflected in the definition:
DocumentProtocol—Version—DocumentType—DocumentDefinitionName
Example - Document Definition Name for an HL7 Document shows the hierarchy reflected in the definition for an HL7 document.
Document Definition Name for an HL7 Document
Document protocol: HL7Document protocol version: 2.3.1Document type: ADT_A01Document definition: ADT_A01_defThe resulting document definition is:HL7-2.3.1-ADT_A01-ADT_A01_def
3.1.2 What You Might Need to Know About Document Protocols with Acknowledgments
For any message flow that involves an acknowledgment, Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration sends an acknowledgment only once. Resubmission does not generate another acknowledgment if the message has already been acknowledged.
3.2 Using the Custom Document Protocol
Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration supports custom document protocols to create documents required for proprietary transactions. With XML messages, you have the advantage of schema enforcement (XSDs).
With non-XML messages, you can create endpoints for specific message types.
When creating a Custom document, you specify rules to identify the incoming document. For XML documents, specify an XPath expression or an XPath expression and a value, which is the expected result of the expression.
For non-XML documents such as a flat file, you can specify Identification Start Position, End Position, and Identification Value.
3.2.1 What You Might Need to Know About Custom Document Version Parameters
No parameters are required to be set when you create the document version for a Custom document.
3.2.2 What You Might Need to Know About Custom Document Type Parameters
When you create a Custom document type, you can set ebXML messaging service (ebMS) parameters to identify the ebXML document. Figure 3-4 shows the document type parameters for a Custom document.
Figure 3-4 Document Type Parameters for a Custom Document

Description of "Figure 3-4 Document Type Parameters for a Custom Document"
Table 3-1 describes the document type parameters for a Custom document.
Table 3-1 Document Type Parameters for a Custom Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
ebMS Tab |
- |
|
Action name |
The action name for the ebXML header, which is also an identification criteria for inbound and outbound messages. ebMS documents require an action name to avoid run-time errors. |
|
Service name |
The service name for the ebXML header, which is also an identification criteria for inbound messages. ebMS documents require a service name to avoid run-time errors. |
|
Service type |
The service type for the ebXML header, which is also an identification criteria for inbound messages. ebMS documents require a service type to avoid run-time errors. |
|
From Role |
The endpoint that sends the message. A value provided here overrides the Identifiers values supplied on the Profile tab. |
|
To Role |
The endpoint that receives the message. A value provided here overrides the Identifiers values supplied on the Profile tab. |
|
Validate ebMS Header |
When selected, validates inbound ebMS header from role to role. |
3.2.3 What You Might Need to Know About Custom Document Definition Parameters
When you create a Custom document definition (see Creating Document Definitions for more information on creating document definitions), select the identification type—XML or Flat, and set parameters in the tabbed areas. Figure 3-5 shows the document definition parameters for an XML-type Custom document.
Figure 3-5 Document Definition Parameters for an XML-Type Custom Document
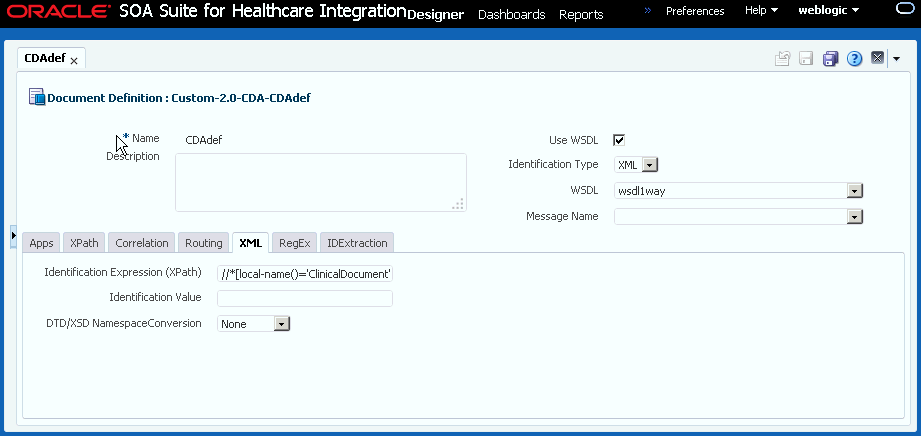
Description of "Figure 3-5 Document Definition Parameters for an XML-Type Custom Document"
Figure 3-6 shows the document definition parameters for a flat-file Custom document.
Figure 3-6 Document Definition Parameters for a Flat-FIle Custom Document
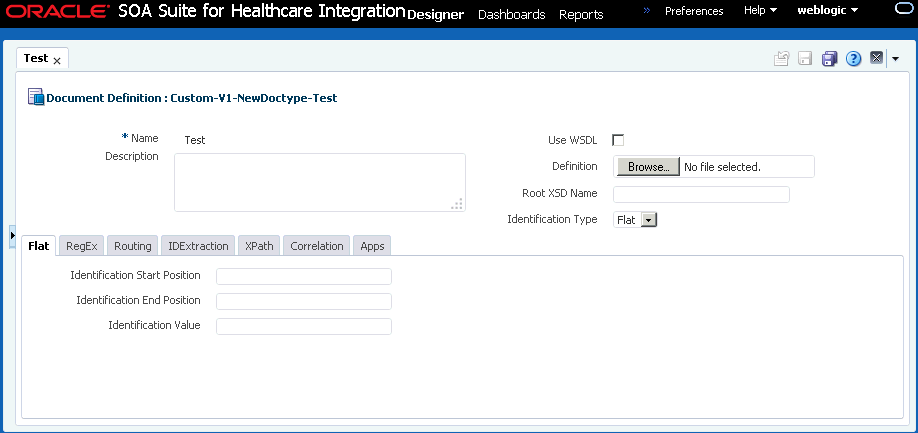
Description of "Figure 3-6 Document Definition Parameters for a Flat-FIle Custom Document"
Table 3-2 describes the document definition parameters for a Custom document.
Table 3-2 Document Definition Parameters for a Custom Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
XML Tab |
(Available if XML is selected from Identification Type) |
|
Identification Expression (XPath) |
Locates a node in the XML payload |
|
Identification Value |
Provides the value to match in the node identified by the Identification Expression. If the values match, then the document is successfully identified. If the value is left blank, then Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration checks for the existence of the node and the document is successfully identified. |
|
DTD/XSD NamespaceConversion |
Select from None, Both, Inbound, or Outbound. |
|
Routing Tab |
- |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application |
|
XPath Tab |
See How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document. |
|
XPath Name1 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Expression1 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name2 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression2 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name3 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression3 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
Correlation Tab |
- |
|
Correlation From XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for initiating the correlation. |
|
Correlation From XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload to initiate the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload for the correlation. |
|
Flat Tab |
- |
|
Identification Start Position |
Used in combination with the end position to retrieve a value from the payload between the start and end positions |
|
Identification End Position |
Used in combination with the start position to retrieve a value from the payload between the start and end positions |
|
Identification Value |
A value between the start and end positions |
|
Apps Tab |
- |
|
Document |
The name of the internal application document. |
|
Action |
A sub-classification within the document. |
|
XSLTFile |
The name of the XSLT file. |
3.2.3.1 How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document
The XPath expression identifies a Custom XML document. You configure the XPath expression when you specify the document type parameters.
The options when configuring an XPath expression are as follows:
3.2.3.1.1 Option 1: Specify the XPath and the Matching Value
Assume that the transaction ID is 12345. Set the parameters as follows:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
|
Identification Value |
12345 |
|
Identification Expression |
//*[local-name() = 'TransactionID']/text() |
Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration compares the value of Identification Expression in the payload to the value specified in Identification Value. If the values match, then the document is identified successfully and the corresponding document type and document protocol version are used to identify the endpoint. Example - Specify the XPath and the Matching Value shows an excerpt of the XML payload for this option.
Example - Specify the XPath and the Matching Value
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Message xmlns:ns1="http://www.example1.org" xmlns:ns2="http://www.example2.org"
xmlns="http://www.example3.org"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:ns="http://www.example4.org">
<MessageHeader>
<Source>201944019</Source>
<Destination>205704856</Destination>
<TransactionID>123456</TransactionID>
<Version>1-0-0</Version>
</MessageHeader>
<Body>
<ns:Case xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.example4.org" ns1:caseCategoryID="1">
<ns1:OfficialProvisionNumber>String</ns1:OfficialProvisionNumber>
</ns:Case>
</Body>
</Message>3.2.3.1.2 Option 2: Check for the Existence of a Node
Assume that you are checking for the existence of a node called registerCommand. Set the parameters as follows:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
|
Identification Value |
Leave blank. |
|
Identification Expression |
/*[local-name()='envelope']/body/transaction/command/*[local-name()='registerCommand'] |
When the Identification Value field is left blank, Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration checks for the node identified in Identification Expression. If a node in the payload matches, then the document is identified successfully. Example - Check for the Existence of a Node shows an excerpt of the XML payload for this option.
Check for the Existence of a Node
<uccnet:envelope xmins:eanucc="http://www.ean-ucc.org/schemas/1.3/eanucc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:uccnet="http://www.uccnet.org/schemas/2.2/uccnet"
communicationVersion="2.2"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.uccnet.org/schemas/2.2/uccnet
http://www.testregistry.net/xmlschema/uccnet/2.2/Envelope.xsd">
<messageHeader>
<messageIdentifier>
<value>791:1_EB3CDC749A1F2BABE03014906CC4605A</value>
</messageIdentifier>
<userId>oraclesupXSD</userId>
<representingParty>
<gin>0060974050142</gin>
</representingParty>
</messageHeader>
<body>
<transaction>
<entityIdentification>
<uniqueCreatorIdentification>856</uniqueCreatorIdentification>
<globalLocationNumber>
<gin>0060974050142</gin>
</globalLocationNumber>
</entityIdentification>
<command>
<uccnet:registerCommand>
<registerCommandHeader type="ADD" />
</uccnet:registerCommand>
</command>
</transaction>
</body>
</uccnet:envelope>3.2.3.1.3 Option 3: Check the Value of an Attribute
Assume that the value of the country attribute is US. Set the parameters as follows:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
|
Identification Value |
US |
|
Identification Expression |
//*/@country |
Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration compares the value of the country attribute to the value set for Identification Value. If the values match, then the document is identified successfully. Example - Check the Value of an Attribute shows an excerpt of the XML payload for this option.
Example - Check the Value of an Attribute
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252" ?>
<MyAddress country="US" xmlns="http://www.example.org"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="PO.xsd">
<name>B2B Buyer</name>
<street>100 Oracle Parkway</street>
<city>Redwood City</city>
<state>CA</state>
<zip>94065</zip>
</MyAddress>3.3 Using the HL7 Document Protocol
Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration implements the Health Level 7 (HL7) version 2.x to exchange documents containing health care information using the Generic exchange or MLLP exchange.
When using HL7, the standard Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration features, such as validation, translation, automatic generation of outbound envelope headers, and acknowledgments, are available.
For information about the organization that created and maintains the HL7 standards, go to http://www.hl7.org.
3.3.1 What You Might Need to Know About HL7 Document Version Parameters
When you create an HL7 document version, you can set various parameters. Figure 3-7 shows document version parameters for an HL7 document.
Figure 3-7 Document Version Parameters for an HL7 Document
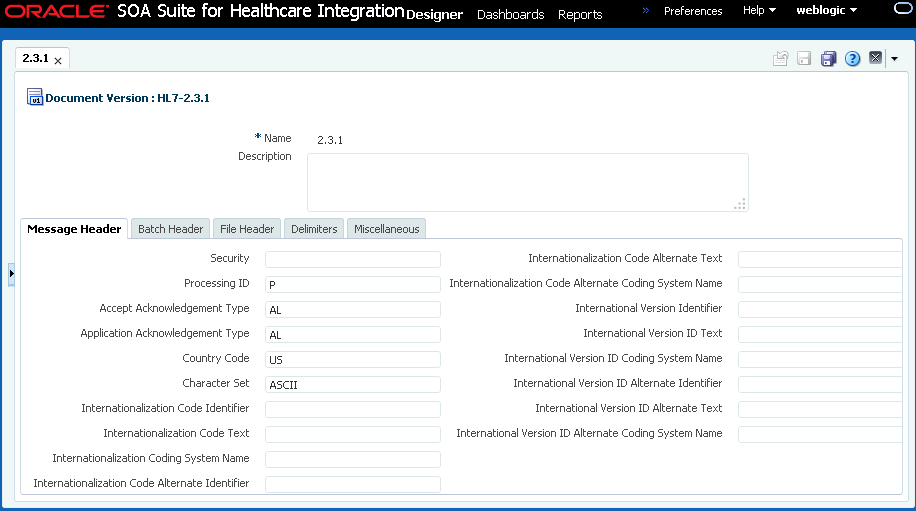
Description of "Figure 3-7 Document Version Parameters for an HL7 Document"
Table 3-3 describes the document version parameters for an HL7 document.
Table 3-3 Document Version Parameters for an HL7 Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Message Header Tab |
- |
|
Security |
In some applications of HL7, this field is used to implement security features. |
|
Processing ID |
MSH.11 - This field is used to decide whether to process the message as defined in HL7 Application (level 7) processing rules. The first component defines whether the message is part of a production, training, or debugging system (refer to HL7 table 0103 - Processing ID for values). The second component defines whether the message is part of an archival process or an initial load (refer to HL7 table 0207 - Processing mode for values). This allows different priorities to be given to different processing modes. |
|
Accept Acknowledgement Type |
Sets the conditions under which application acknowledgments are required to be returned in response to the message. The value AL (always) is supplied. Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration checks the payload (MSH.15) of an incoming message to see if an ACK has to be generated. In some HL7 Systems, MSH.15 is not sent in the payload at all and it is expected that an ACK is still sent. |
|
Application Acknowledgment Type |
MSH.16. The value AL (always) is supplied. |
|
Country Code |
Sets the country of origin for the message. The value US is supplied. |
|
Character Set |
Sets the character set for the entire message. The value ASCII is supplied. |
|
Internationalization Code Identifier |
MSH.19 |
|
Internationalization Code Text |
MSH.19 |
|
Internationalization Coding System Name |
MSH.19 |
|
Internationalization Code Alternate Identifier |
MSH.19 |
|
Internationalization Code Alternate Text |
MSH.19 |
|
Internationalization Code Alternate Coding System Name |
MSH.19 |
|
International Version Identifier |
MSH.12 |
|
International Version ID Text |
MSH.12 |
|
International Version ID Coding System Name |
MSH.12 |
|
International Version ID Alternate Identifier |
MSH.12 |
|
International Version ID Alternate Text |
MSH.12 |
|
International Version ID Alternate Coding System Name |
MSH.12 |
|
Batch Header Tab |
- |
|
Create Batch Header |
Select the box to create batch headers. |
|
Batch Header Ecs File |
Click the Browse button to find an ecs file to override the standard file. If not provided, the provided default file is used. |
|
Batch Security |
BHS.8 |
|
Batch Date |
BHS.7. The system date-time stamp is supplied ( |
|
File Header Tab |
- |
|
Create File Header |
Select the check box to create file headers. |
|
File Header Ecs File |
Click the Browse button to find an ecs file to override the standard file. If not provided, the provided default file is used. |
|
File Security |
FHS.8 |
|
File Date |
FHS.7. The system date-time stamp is supplied ( |
|
Delimiters Tab |
Click Select Hexadecimal Characters next to any of the delimiter fields to provide values. |
|
Element Delimiter |
A single character that follows the segment identifier and separates each data element in a segment except the last. The value 0x7c is supplied. |
|
Escape Character |
The value 0x5c is supplied. |
|
Repeating Separator |
A service character used to separate adjacent occurrences of a repeating data element, or to separate multiple occurrences of a field.The value 0x7e is supplied. |
|
Segment Delimiter |
A syntax character indicating the end of a segment (a logical grouping of data fields) within a message. The value 0x0d is supplied. |
|
Subcomponent Delimiter |
The value 0x26 is supplied. |
|
Subelement Delimiter |
The value 0x5e is supplied. |
|
Miscellaneous Tab |
- |
|
Ignore Envelope Parameters |
Use this option to provide a list of envelope elements, separated by commas, to be ignored during look-up validation. For an HL7 agreement, the possible values include MessageSendingApp, MessageReceivingApp, MessageSendingFacility, and MessageReceivingFacility. |
|
Ack Mode |
Select this option to specify whether to send a single acknowledgment or multiple acknowledgments for inbound batched HL7 messages. |
3.3.2 What You Might Need to Know About HL7 Document Type Parameters
When you create an HL7 document type, you can set various parameters. Figure 3-8 shows the document type parameters for an HL7 document.
Figure 3-8 Document Type Parameters for an HL7 Document

Description of "Figure 3-8 Document Type Parameters for an HL7 Document"
Table 3-4 describes the document type parameters for an HL7 document.
Table 3-4 Document Type Parameters for an HL7 Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Transaction Tab |
- |
|
HL7 Generic ACK |
If selected, Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration sends a generic ACK. Note: The HL7 standard does not specify any Ack generation rules for the errors on file or batch header - only for the message. Oracle B2B does not generate acks for file and batch header errors for HL7 inbound messages (only error reports are generated). |
|
Map ACK Control ID |
Select to enable mapping the MSH.10 of the business message to the MSH.10 of the acknowledgment. Note: This Map ACK Control ID parameter is for the functional ACK. |
|
Accept Acknowledgement |
A functional acknowledgment is generated when MSH.15 has no value. Select None to take no action. Acknowledgment generation is dependent on the value in MSH.15 of the business message. Select AL (always) to generate the acknowledgment under any conditions. Select ER (error/reject) to generate the acknowledgment when the message errors or is rejected. Select SU (successful completion) to generate the acknowledgment when the message is successfully processed. |
For information about how to override document parameters at individual endpoint level see Overriding Document Parameters at the Endpoint Level.
3.3.3 What You Might Need to Know About HL7 Document Definition Parameters
When you create an HL7 document definition (see Creating Document Definitions for more information on creating document definitions), you can set various parameters. Figure 3-9 shows document definition parameters for an HL7 document.
Figure 3-9 Document Definition Parameters for an HL7 Document
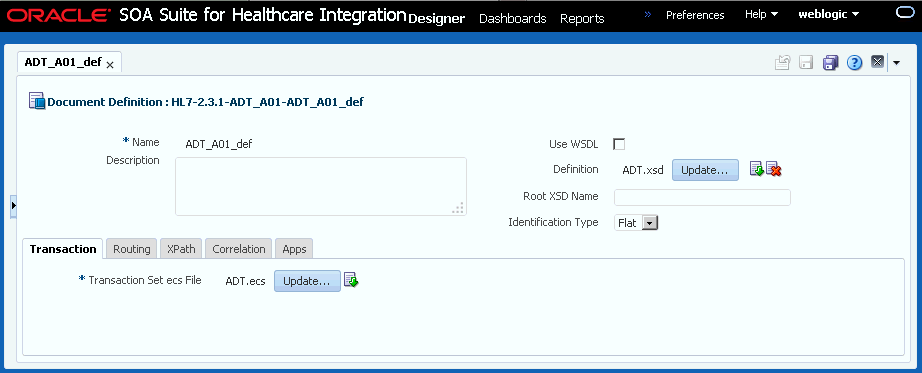
Description of "Figure 3-9 Document Definition Parameters for an HL7 Document"
Table 3-5 describes the document definition parameters for an HL7 document.
Table 3-5 Document Definition Parameters for an HL7 Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Transaction Tab |
- |
|
*Transaction Set ecs File |
Click the Browse button to find the ecs file. |
|
Routing Tab |
- |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application |
|
XPath Tab |
See How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document, for more information. |
|
XPath Name1 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Expression1 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Name2 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Expression2 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Name3 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Expression3 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
Correlation Tab |
- |
|
Correlation From XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for initiating the correlation. |
|
Correlation From XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload to initiate the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload for the correlation. |
|
Apps Tab |
- |
|
Document |
The name of the internal application document. |
|
Action |
A sub-classification within the document. |
|
XSLTFile |
The name of the XSLT file. |
3.3.4 What You Might Need to Know About Using HL7
No business message is produced for an HL7 immediate acknowledgment (transport-level acknowledgment).
Negative acknowledgment messages indicating errors in an HL7 exchange might be truncated because of the 80-character length limitation in HL7 versions 2.1 through 2.5.
3.4 Creating Document Definitions
A document definition specifies the document protocol—the document protocol version and document type—that is used to validate the message. The document definition can be an ECS file, in the case of HL7 messages, or an XSD/DTD, in the case of XML messages.
The same document definition is used by participating endpoints in a transaction. It must adhere to the standards for document protocols, protocol versions, and document types.
Note:
To ensure that the document definition conforms to standards, you can use Oracle Document Editor to create the document guideline files and then use the Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration user interface to import those files when creating the document definition.
After creating transaction set files by using Oracle Document Editor, you use the Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration user interface to create the document definition and import the transaction set files.
Note:
The document version, document type, and document definition are not editable after they are created. You must delete the specific document element (version, type, or definition) and create a new one. Updating the document elements after creation can lead to metadata inconsistency, metadata validation issues, and runtime errors.
To create a document definition:
-
Log on to Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration. The Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration user interface opens with the Configuration tab selected.
-
In the left-hand navigation panel, expand Document Protocol. This displays the list of supported protocols, which are Custom and HL 7 V2.x.
-
Select one of the document protocols, for example HL7, as shown in Figure 3-10, and click the Create button. This displays the Create Document Version window.
Note:
You can also right-click the document protocol name and select Create from the shortcut menu.
Note:
In the Create Document Protocol Version dialog box, enter a protocol version name, for example, 2.3.1.
-
Enter the document protocol version name in the Name field.
-
Specify the document version parameters as applicable, and click OK.
The version is used for document identification and can be case sensitive. Use a fixed syntax that conforms to the protocol standards.
Figure 3-11 shows the document protocol version page for an HL7 V2.3.1 document.
Figure 3-11 Entering Document Protocol Version Information
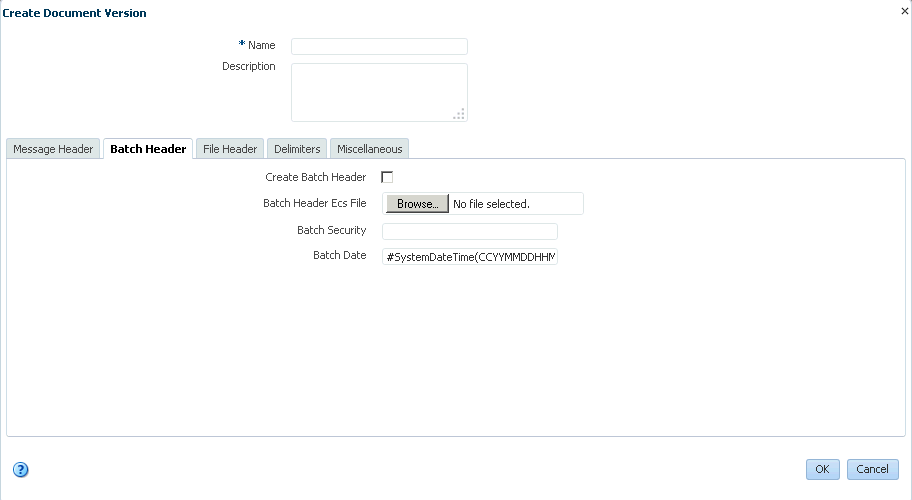
Description of "Figure 3-11 Entering Document Protocol Version Information"For parameter descriptions, see Table 3-3.
-
Click the newly created Version name, and then click the Create button to display the Create Document Type window. Alternatively, you can right-click the version name and select Create from the shortcut menu.
-
Enter a document type name, specify document type parameters as applicable, and then click OK.
Figure 3-12 shows the document type parameters page for an HL7 V2.3.1 document.
Figure 3-12 Entering Document Type Parameter Information
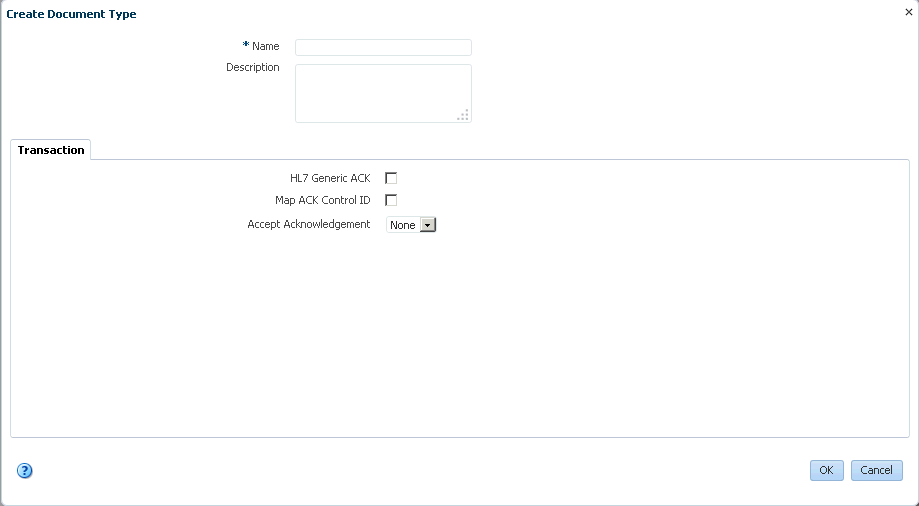
Description of "Figure 3-12 Entering Document Type Parameter Information"For document type parameter descriptions, see Table 3-4.
-
With the new document type name selected, click Create to display the Create Document Definition window.
-
Enter a document definition name and do the following:
-
Browse for an optional definition (XSD) file for any of the document protocols.
-
Browse for the required transaction set ECS file for HL7 or positional flat file.
-
Specify document definition parameters as applicable and click OK.
Figure 3-13 shows the document definition parameters page for an HL7 V2.3.1 document.
Figure 3-13 Entering Document Definition Parameter Information
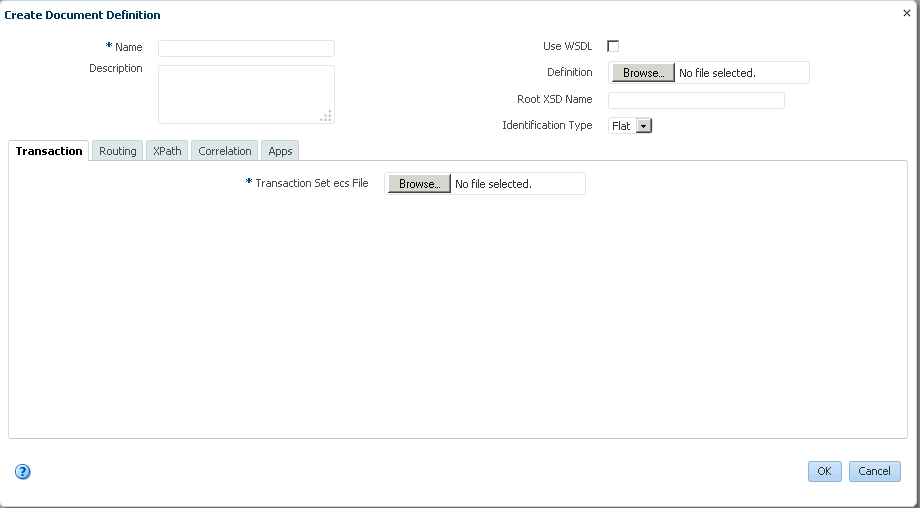
Description of "Figure 3-13 Entering Document Definition Parameter Information"For definition parameter descriptions, see the following:
-
Note:
You can also use the post install script, install the standard library, and import hl7 doctypes file to create a document tree in Healthcare console.