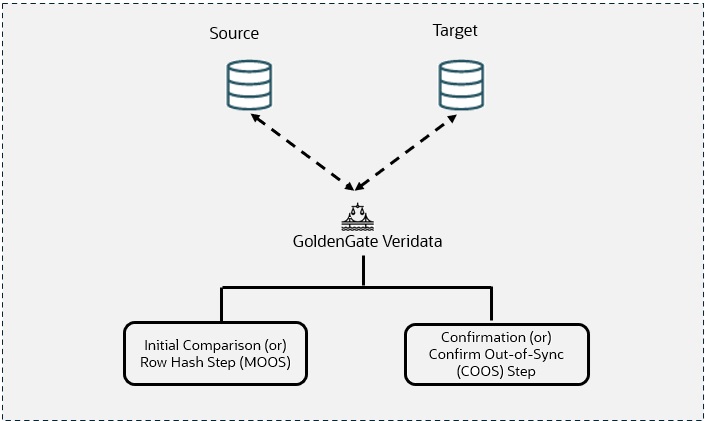
1.4 How Oracle GoldenGate Veridata Works?
- Initial step or Row hash step MOOS – Maybe Out-of-Sync
- COOS - Confirm Out-of-Sync
Figure 1-2 How Veridata Works?
1.4.1 Initial Step or Row Hash Step in Maybe Out of Sync
- Rows retrieved from source/target databases
- Data converted into standard format
- Hashes data and sent to Server
- Out-of-sync rows stored in MOOS queue
After the comparison is initiated, the Oracle GoldenGate Veridata agent retrieves rows from both source and target tables using a specified query.
Oracle GoldenGate Veridata, being a heterogeneous data comparison and repair tool, ensures compatibility by standardizing data types if the source and target databases differ.
Data retrieval involves fetching primary key (PK) column values directly (actual values are fetched), while non-key columns are hashed to minimize network transfer for comparison. This unique hashing process streamlines the comparison process by providing a dependable and efficient means of determining similarities or differences between rows in the source and target databases.
Additionally, it is possible to alter the default hashing option. However, this adjustment may lead to decreased performance and increased network usage, particularly with a higher number of columns. After completing the initial comparison, if Oracle GoldenGate Veridata detects discrepancies in some rows, then it refrains from displaying the comparison results to the user. Instead, it stores these rows in the Maybe Out of Sync (MOOS) queue in memory. This precaution is necessary due to concurrent real-time replication, which may have some replication latency, potentially leading to the out-of-sync rows being in transit. Subsequently, replication will synchronize them again.
Figure 1-3 Initial step or Row hash step MOOS – Maybe Out-Of-Sync
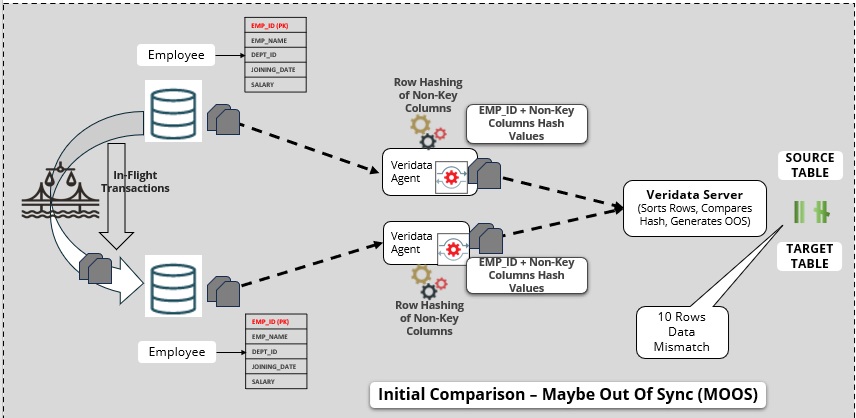
The Employee table contains a primary key column EMP_ID.
- Oracle GoldenGate Veridata retrieves the actual values of
EMP_IDand hashes the values of other non-key columns. - The replication process is in progress. If there are any disparities, for example, if there are 10 rows being out of sync, then Oracle GoldenGate Veridata will not immediately confirm them as out of sync.
- Given the real-time replication setup and concurrent data replication, it is possible that these 10 out-of-sync rows have yet to be replicated to the target. This might be due to latency.
- The out-of-sync rows are stored in the MOOS queue in memory.
Parent topic: How Oracle GoldenGate Veridata Works?
1.4.2 Confirm Out of Sync
- Ensures accurate results by comparing each row
- It happens in parallel with Row hash with configured latency threshold
- Confirm out of Sync requests can be batched
- Good performance for remote databases
- Controlled by a profile setting
- Executing the look ups in parallel
The verification process, known as confirmation or Confirm Out of Sync (COOS), guarantees precise outcomes by validating the status of rows in a dynamic setting. This process entails making conditional inquiries on either the source or target using the rows obtained from the MOOS queue, with the status being assessed as one of the subsequent possibilities:
- In Flight: The row was initially not synchronized during the comparison process, but it has now been corrected. In this scenario, it is presumed that replication or a similar mechanism implemented the modification; however, Oracle GoldenGate Veridata could not verify the synchronization of the rows.
- In Sync: The values from the source row were transferred to the target row either through replication or a similar process. Even if the status shows as in-sync, it does not ensure that the rows are synchronized at any given moment, especially if the underlying tables are constantly changing. However, it does signify that replication is functioning properly.
- Persistently out of sync: After the initial comparison step
occurred, the row remains unchanged, indicating it is likely out of sync.
By default, confirmation processing takes place concurrently with the initial comparison step, but the confirmation of each row is delayed until after a specified replication latency threshold has passed. For example, if the latency is set to 60 seconds and an out-of-sync row is identified during the initial comparison step at 10:00, the confirmation step for that row is postponed until 10:01 to ensure replication can apply any pending changes. After the latency is considered, rows can be definitively marked as Out-of-Sync and cataloged in one or more out-of-sync reports.
Example: Comparing data of the Employee table in both the source and target databases.
After surpassing the latency threshold, the process moves to the second stage known as the COOS step. Here, only the rows that are out of sync are examined, without utilizing hashing. All values from both primary key and non-key columns are retrieved in their original form (actual values). The out-of-sync rows are compared value by value. If the same data inconsistencies persist after this stage, these rows are confirmed as out of sync. You are then presented with details of the out-of-sync rows for further action.
Figure 1-4 Confirm Out of Sync (COOS)
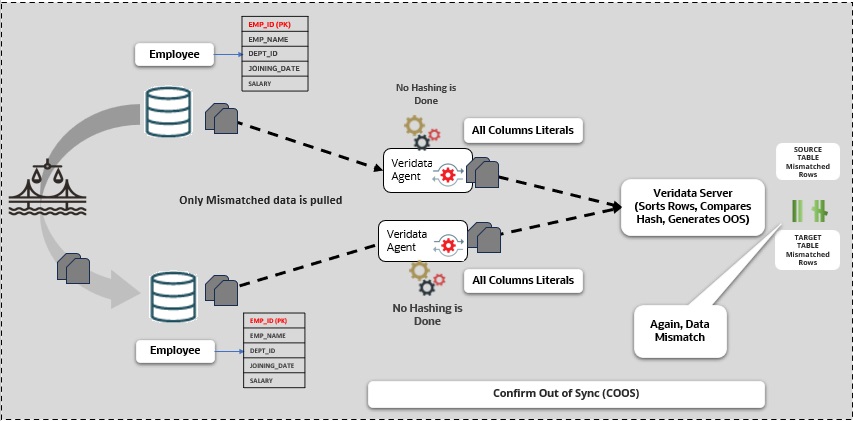
Note:
The latency threshold is crucial in this context. In the previously mentioned scenario, it was established at 60 seconds, but it is adjustable manually. The Delay Confirm-Out-Of-Sync parameter within the Profile Configuration governs this threshold. Users are better acquainted with their replication environment and the daily latency they encounter. Hence, they can customize this parameter according to their requirements.Delay Confirm-Out-Of-Sync By (seconds)
Delays the confirmation step by the specified number of seconds to account for replication lag. Delaying the confirmation step reduces the number of false out-of-sync results that occur because an updated source value was not replicated fast enough.
Note:
You have the option to bypass the two-step-comparison process altogether, specifically skipping the second step known as COOS.The parameter Perform Confirm Out-Of-Sync Step in the Profile Configuration allows users to decide whether to execute or bypass the second step when comparing data in Oracle GoldenGate Veridata.
Perform Confirm-Out-of-Sync Step
Controls whether or not the confirmation step is performed. By default, it is performed. Clear the check box under Value to skip the confirmation step and only perform the initial (row hash) comparison. You might skip the confirmation step if, for example, activity on the source tables is quiesced or if replication is not continuously updating the target table(s).
Parent topic: How Oracle GoldenGate Veridata Works?