1.5 Oracle GoldenGate Veridata Supported Use Cases
In today’s complex, hybrid (Cloud and On-premises) IT environment with
the same data stored in multiple locations or while migrating the data from one system
or application to another, some data discrepancies are almost inevitable. If not
discovered and addressed, bad data can lead to poor decision-making; failed service
level agreements; and, ultimately, operational, financial, and legal risk.
Furthermore, for a comprehensive explanation, the following are the
diverse use cases supported in Oracle GoldenGate Veridata:
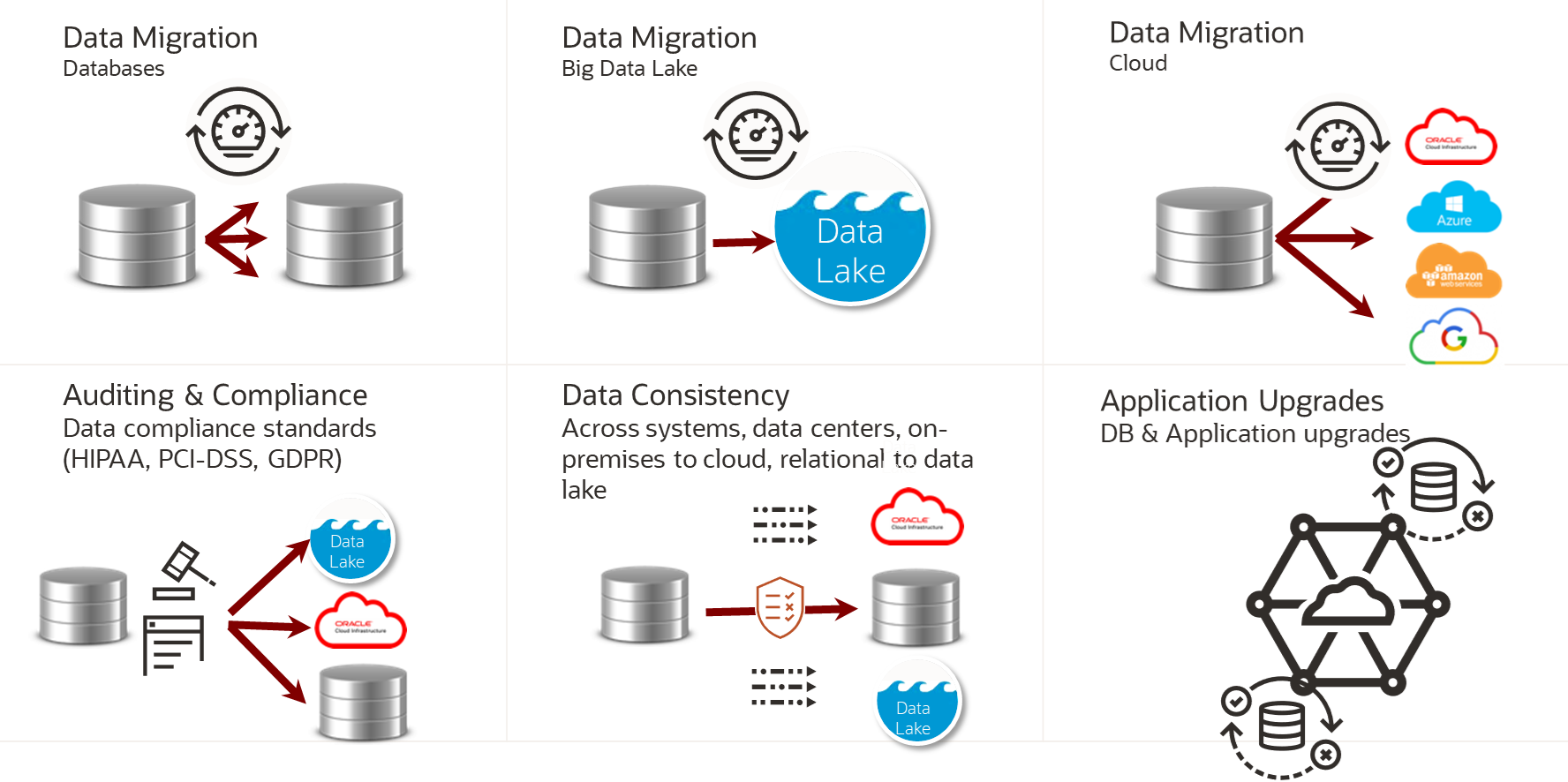
Figure 1-5 Oracle GoldenGate Veridata Use Cases

- Data Migration: It is the process of transferring data from
one location or one system to another. Data migration is a critical task in
various scenarios, including:
- Database Upgrades: When organizations upgrade their software or hardware systems, they often need to migrate data from the old system to the new one. For example, when transitioning to a new database management system (DBMS) or a newer version of an application.
- Cloud migration: Many businesses are moving their data and applications to cloud platforms. Data migration in this context involves moving data from on-premises servers to cloud-based storage or from one cloud provider to another.
- Data center relocation: When a company moves its
data center to a new physical location, data migration is essential to
ensure the continuity of operations.
There are various factors involved in the Data Migration out of which Data Validation post migration is an important task. After the migration is complete, it is essential to verify that the data in the new system functions correctly and retains its integrity.
- Auditing & Compliance: As compliance standards evolve, corporations and their leaders are increasingly required to uphold exceptionally high levels of responsibility. Organizations must ensure their alignment with auditing and compliance standards and furnish data to regulatory authorities, such as Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and others.
- Data Consistency: In any replication scenario, it is essential to ensure data consistency across all systems, whether it involves replicating data between data centers, migrating data from on-premises to the cloud, or transferring data from a relational database to a data lake. It is imperative that no data discrepancies occur.
- Application Upgrades: When conducting application upgrades, numerous Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML) operations are executed on the database tables. If this database has replication configured, it is imperative to ensure that all changes made in the source systems are seamlessly and accurately replicated to the target systems.
Parent topic: Overview