16 Setting Up the PaaS Infrastructure
The PaaS model allows users to create platforms onto which consumers can deploy their own applications. A platform resource is typically comprised of a host, operating system, and application server, and may be virtualized. The platform may also include a database and even multiple hosts in a cluster. This chapter contains the following sections:
About Service Families
A service family can be classified as a group of services that provide a solution for a specific domain. For example, a Database Service provides RDBMS solutions and a WebLogic service provides the Java solutions for J2EE based application development and hosting.
Each service family can contain one or more service types. A service type provides a specialized service within a service family. For example, a database service can contain service types such as database service, schema service, or pluggable database service. A middleware service type can contain WebLogic service, OSB service, or SOA service. Each service type has certain fixed attributes, actions, configurations, metrics, and other properties.
A service instance is a cloud resource that is requested and managed by the self service user. For example, single instance database service instance, WebLogic service instance, and so on.
Common Setup Tasks
This section helps you get started by providing an overview of the common steps that must be performed before you set up a service family.
Table 16-1 Setting Up the Service Family
| Step | Task | Role |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Configure the Software Library. See Setting Up the Software Library section for details. |
Cloud Administrator |
|
2 |
Deploy the necessary plug-ins. See Deploying the Required Plug-ins |
Cloud Administrator |
|
3 |
Define roles for administrators and self service users. See Defining Roles and Assigning Users. |
Super Administrator |
|
4 |
Install the Management Agent on unmanaged hosts so that they can be monitored by Enterprise Manager. See Adding Hosts. |
Cloud Administrator |
|
5 |
Create one or more resource providers. See Creating the Resource Providers. |
Self Service Administrator |
|
6 |
Configure the request settings. See Configuring Request Settings. |
Self Service Administrator |
|
7 |
Set up quotas for self service users. See Setting Up Quotas. |
Self Service Administrator |
Adding Hosts
Oracle Management Agent (Management Agent) is one of the core components of Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. It works in conjunction with the plug-ins to monitor the targets running on a managed host. You must install Oracle Management Agents on your unmanaged hosts to monitor them in Enterprise Manager. See Installing Oracle Management Agents for details.
Creating the Resource Providers
A resource provider is a target that represents the type of resources required to provision a service instance of a specific service type. A PaaS Infrastructure zone is a resource provider which contains one or more hosts. A Software Pool is another resource provider that can contain resources such as Oracle Home targets, Oracle database targets, and so on. Resource providers such as the Database Pool or Middleware Pool are dependent on the PaaS Infrastructure Zone.
Resources can be grouped under a resource provider for easier administration and management. Resource providers allow administrators to enforce policies for service provisioning and capacity planning.
To create a resource provider, follow these steps:
Creating a PaaS Infrastructure Zone
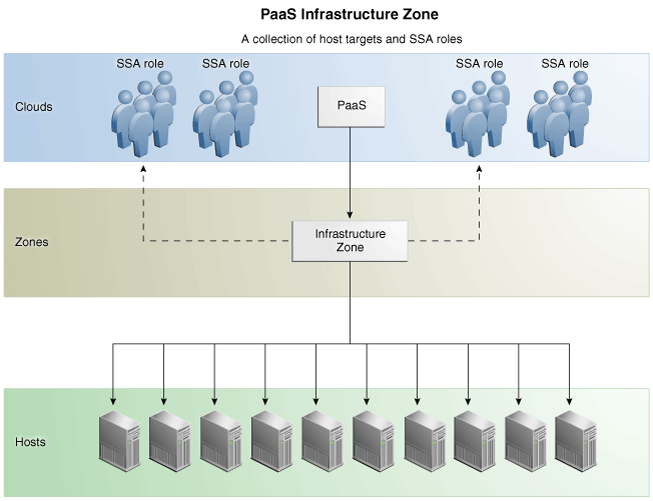
A PaaS Infrastructure Zone can contain a group of hosts. Each zone can contain homogeneous resources of only one type. Each resource in a zone represents a location at which a service instance is to be deployed.
The first step in building a PaaS cloud is to create at least one PaaS Infrastructure Zone, which is done by selecting one more Enterprise Manager host targets and identifying the SSA enabled roles that users will need to in order to request resources in this zone.
Figure 16-1 PaaS Infrastructure Zone
Before you create a PaaS Infrastructure Zone, you must ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
-
The
EM_CLOUD_ADMINISTRATOR,EM_SSA_ADMINISTRATOR, andEM_SSA_USERroles must have been created. See Defining Roles and Assigning Users for details. -
Note:
If you are using an OMS Shared System location in the Software Library, the credentials owner must grant privileges to the
CLOUD_ENGINE_USER. Since theCLOUD_ENGINE_USERis a hidden user account, the owner of the named credential cannot grant View privileges from the Enterprise Manager Console. To address this issue, (especially on a Windows host where OMS Agent Filesystem is the recommended approach for setting up Software Library) you need to run the following EMCLI commands:emcli login -username=<username> -password =<password>emcli grant_privs -name=CLOUD_ENGINE_USER -privileges="GET_CREDENTIAL; CRED_NAME=<namedcred>:CRED_OWNER=<loginusername>" -
You must log in as a user with
EM_CLOUD_ADMINISTRATORprivileges to create a PaaS Infrastructure Zone.
Deleting a PaaS Infrastructure Zone
- From the Enterprise menu, select Cloud, then select Cloud Home. The Cloud Home page appears.
- From the Cloud Home menu, select Resource Providers. The Resource Providers page appears.
- Select a PaaS Infrastructure Zone from the list and click Delete.
- A confirmation message is displayed. Click Delete PaaS Infrastructure Zone to delete the zone.
Creating a PaaS Pool
The second step in building a PaaS cloud is to create software pools (for example, database or middleware Oracle Homes that exist on hosts within the PaaS Infrastructure Zone, or database instances for schema as a service). The figure below shows an example of a PaaS pool.
Figure 16-3 PaaS Pool
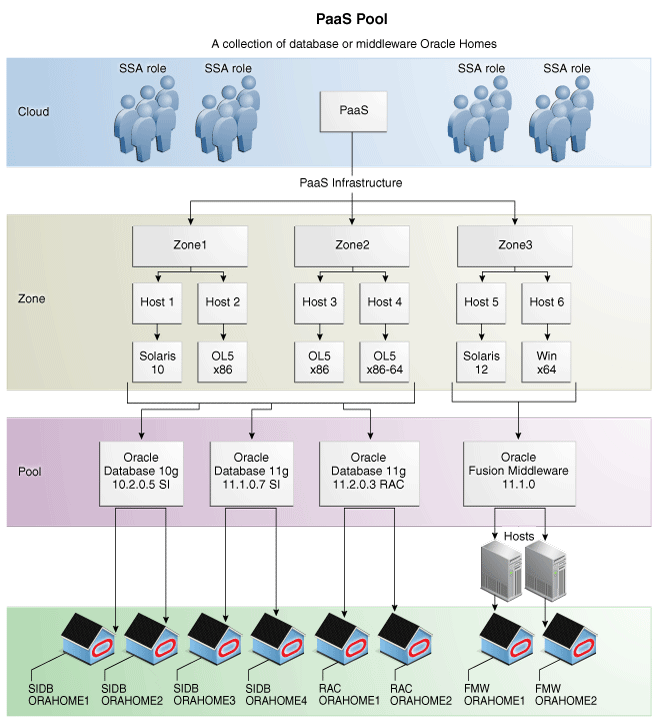
A PaaS pool must be a homogeneous collection of Oracle Homes of the same platform, type, and version. For example, Solaris 10 Oracle Database single instance version 10.2.0.5 or Oracle Enterprise Linux 5 x86-64 WebLogic Server version 10.3.6. For information about creating a Database Pool, see Creating a Database Pool.
Creating a Database Pool
A Database Pool contains a set of resources that can be used to provision a database instance within a PaaS Infrastructure Zone. A database pool is a collection of homogenous targets such as servers or clusters with database software installed. For more details, see Creating a PaaS Pool.
Depending on the type of database service you are setting up, you can do one of the following:
Configuring Request Settings
- All Services: 30 Days
- Database family: 10 days
- Schema service type (Global): 5 days
- Schema service type (
SSAUser1Role): 3 days
SSAUser1 Role) will be applied.
Share Service Instance Settings are taken from the highest enabled level.
For example, if sharing is enabled for All Services, then sharing is allowed for all users regardless of any lower level settings. To turn off sharing for the Middleware family, you must first disable sharing at the All Services level. Then disable sharing for the Middleware family and enable sharing for the other families. Any modified settings must be saved before making another selection. Any changes not applied will be discarded.