Changes in this Release
This preface lists changes in the Oracle Autonomous Health Framework Checks and Diagnostics User's Guide 26.1.
- Terminal Release for HP-UX Platform
Several old operating systems are approaching their end of life, as a result AHF is announcing terminal releases. - New Netperf Profile for Measuring RAC Network Bandwidth
AHF 26.1 introduces a new profile,netperf, which provides a simple and effective way to measure the maximum achievable network bandwidth between Oracle RAC nodes. - Best Practice Reporting for Latest Security Risks
AHF 26.1 integrates DBSAT version 4.1.0 recommendations into the best practice guidance provided in both Oracle Orachk and Oracle Exachk reports, offering enhanced security insights and compliance recommendations. - Enhanced AHF Update Support for Configuration Files with Multiple Base Versions
With AHF 26.1, the Autonomous Health Framework (AHF) update feature is enhanced to support managing AHF configuration files across multiple base versions. This enhancement improves the flexibility and efficiency of configuration management during AHF updates. - Finding Execution Time (in Seconds) for Checks
Starting with AHF 26.1, you can view the execution time for each check to better understand where time is spent during a run. Use the Show Check Timings option from the left pane under Other Settings to display the time taken by individual checks. - Oracle Exachk Automatically Selects the Appropriate User for Switch Data Collection on KVM Dom0
With AHF 26.1, Oracle Exachk automatically selects the most appropriate configured user for switch data collection on KVM Dom0 systems, eliminating unnecessary password prompts and preventing switch collections from being skipped when passwordless equivalency is configured.
Terminal Release for HP-UX Platform
Several old operating systems are approaching their end of life, as a result AHF is announcing terminal releases.
AHF 26.1.0 will be the terminal release for HP-UX platform
This terminal release will continue to be supported on operating systems that are approaching their end of life; however, future AHF releases will not support these operating system versions.
For more information, see Supported Platforms.
Parent topic: Changes in this Release
New Netperf Profile for Measuring RAC Network Bandwidth
AHF 26.1 introduces a new profile, netperf, which provides a simple and effective way to measure the maximum achievable network bandwidth between Oracle RAC nodes.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Changes in this Release
Best Practice Reporting for Latest Security Risks
AHF 26.1 integrates DBSAT version 4.1.0 recommendations into the best practice guidance provided in both Oracle Orachk and Oracle Exachk reports, offering enhanced security insights and compliance recommendations.
Parent topic: Changes in this Release
Enhanced AHF Update Support for Configuration Files with Multiple Base Versions
With AHF 26.1, the Autonomous Health Framework (AHF) update feature is enhanced to support managing AHF configuration files across multiple base versions. This enhancement improves the flexibility and efficiency of configuration management during AHF updates.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Changes in this Release
Finding Execution Time (in Seconds) for Checks
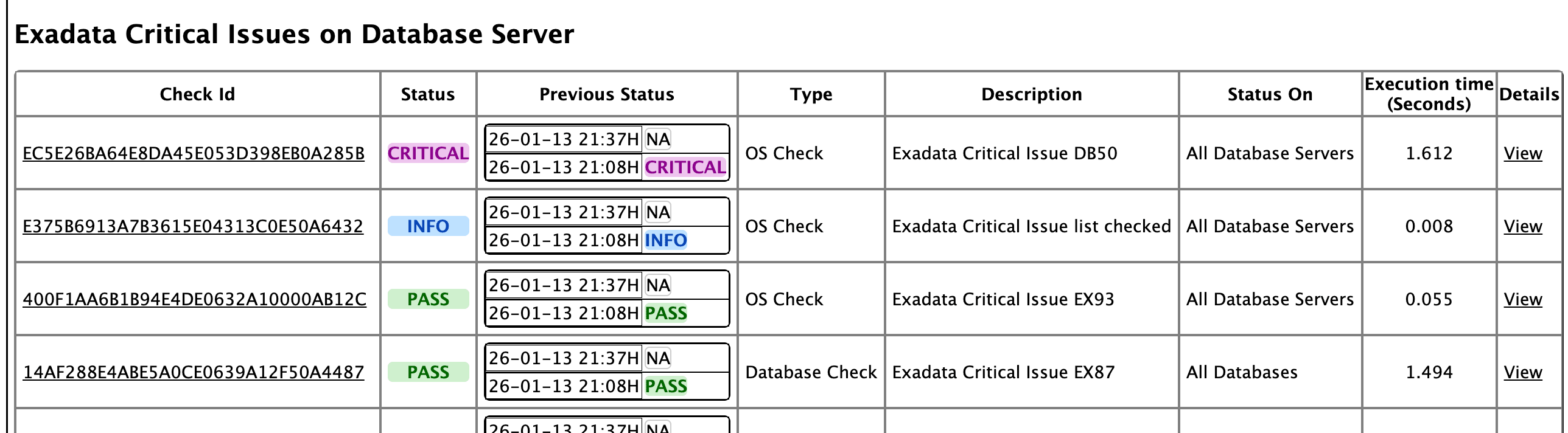
Starting with AHF 26.1, you can view the execution time for each check to better understand where time is spent during a run. Use the Show Check Timings option from the left pane under Other Settings to display the time taken by individual checks.
This information helps you identify checks that consume the most time and may require further investigation or tuning. For better clarity and traceability, it is recommended to use this option in combination with Show Check IDs, which allows you to easily correlate execution times with specific checks.
Figure -1 Show Check Timings
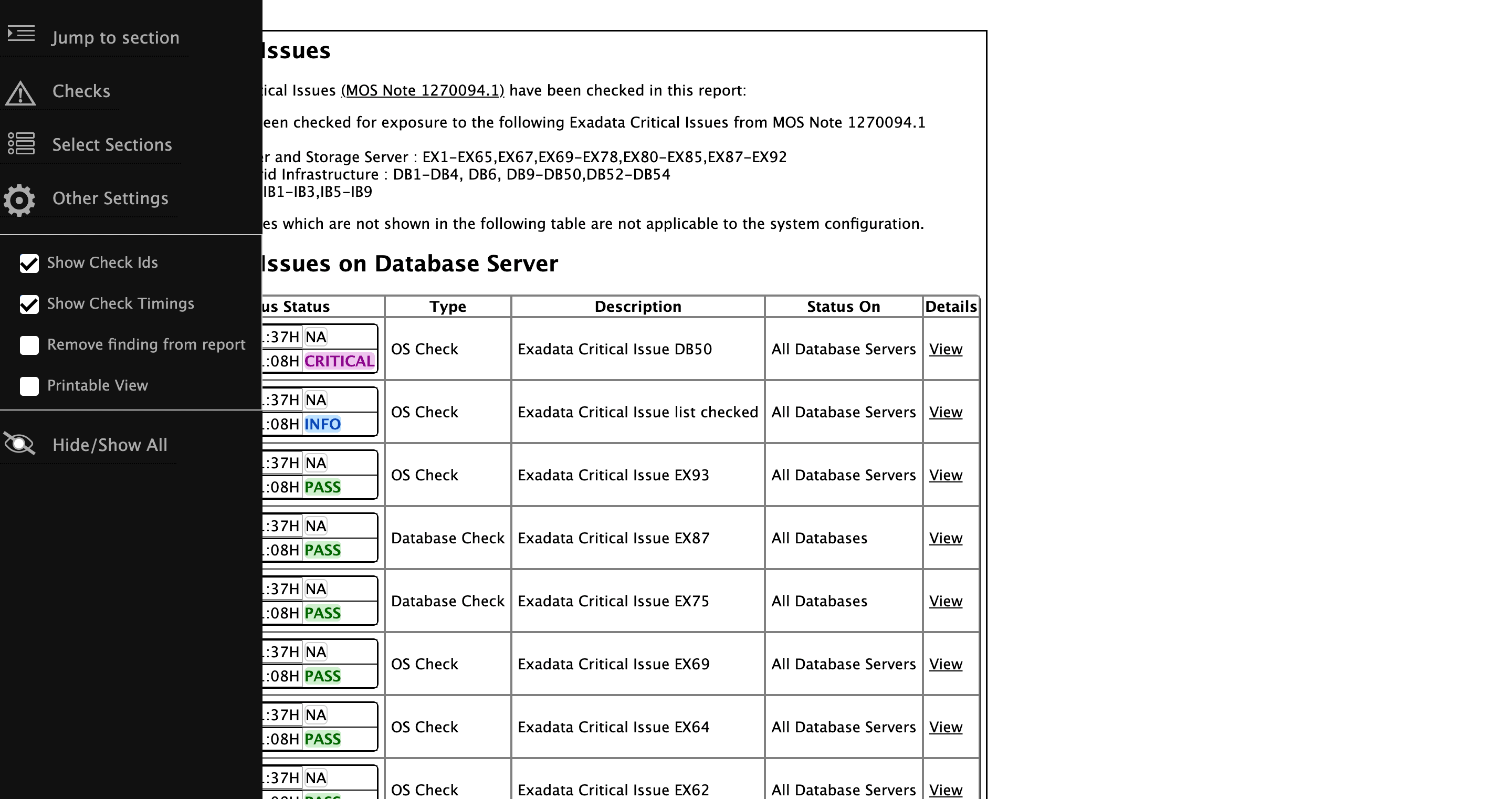
Figure -2 Execution Time
Parent topic: Changes in this Release
Oracle Exachk Automatically Selects the Appropriate User for Switch Data Collection on KVM Dom0
With AHF 26.1, Oracle Exachk automatically selects the most appropriate configured user for switch data collection on KVM Dom0 systems, eliminating unnecessary password prompts and preventing switch collections from being skipped when passwordless equivalency is configured.
Platinum customers often configure different users, such as dbadmin, switchexa, or admin, for passwordless access to switches. Previously, Exachk relied on the default admin user, which could result in password prompts or skipped collections if that user did not have passwordless connectivity.
With this update, Exachk detects the customer’s equivalency configuration and selects the correct switch user automatically. The user selection follows a predefined priority order: dbadmin, switchexa, root, and then admin. Exachk selects the first user in this order that has equivalency or wallet-based credentials configured for all switches, ensuring seamless switch data collection.
In interactive mode, if a user has equivalency or wallet credentials for all switches, Exachk selects that user automatically. If equivalency exists only for a subset of switches, Exachk prompts for the switch user, defaulting to admin. If no equivalency or credentials are found for any switches, Exachk also prompts for the switch user, with admin as the default.
In silent mode, Exachk selects the first user that has equivalency or wallet credentials configured for all switches. If no single user has access to all switches, Exachk chooses the user with access to the maximum number of switches. If no equivalency or credentials are configured for any switches, switch data collection is skipped.
This behavior is consistent regardless of whether the runasroot flag is used. The usernames and priority order are defined by the Platinum team.
Overall, this enhancement improves reliability and automation of switch data collection by ensuring Exachk uses the most appropriate configured user without requiring manual intervention.
Scenario 1
If the dbadmin user has passwordless equivalency (or credentials in the wallet) configured for all switches, Exachk automatically selects dbadmin as the switch user and proceeds with switch data collection without prompting.
# exachk
....
Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-rocea0)
Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-roceb0)
.....Scenario 2
If none of the users (dbadmin, switchexa, root, or admin) have equivalency (or wallet credentials) configured for all switches and silentforce is not used, Exachk prompts the user to specify a switch user. All subsequent switch-related prompts and operations are based on the selected user.
# exachk
....
Enter the RDMA Network Fabric switch user (default: admin):- admin
....
Wallet does not have password for all switches
9 of the included audit checks require admin privileged data collection on RDMA Network Fabric switch
1. Enter 1 if you will enter admin password for each RDMA Network Fabric switch when prompted
2. Enter 2 to exit and to arrange for admin access and run the exachk later.
3. Enter 3 to skip checking best practices on RDMA Network Fabric switch
Indicate your selection from one of the above options for RDMA Network Fabric switch[1-3][1]:-
Is admin password same on all RDMA Network Fabric switch ?[y/n][y]
Enter admin password for RDMA Network Fabric switch :-
Verifying admin password ...Scenario 3
If none of the users (dbadmin, switchexa, root, or admin) have equivalency (or wallet credentials) configured for all switches and silentforce is used, Exachk automatically selects the user with access to the maximum number of switches. All subsequent operations are performed using the selected user.
# exachk -silentforce
....
Wallet does not have password for all switches
9 of the included audit checks require switchexa privileged data collection on RDMA Network Fabric switch
1. Enter 1 if you will enter switchexa password for each RDMA Network Fabric switch when prompted
2. Enter 2 to exit and to arrange for switchexa access and run the exachk later.
3. Enter 3 to skip checking best practices on RDMA Network Fabric switch
Indicate your selection from one of the above options for RDMA Network Fabric switch[1-3][1]:-Example - Exachk Switch User Selection Scenarios
- Exachk is run with
rootuser in silent mode anddbadminuser has switch equivalency setup.# exachk -silentforce .... Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-rocea0) Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-roceb0) ..... - Exachk is run with
rootuser in interactive mode anddbadminuser has switch equivalency setup.# exachk .... Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-rocea0) Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-roceb0) ..... - Exachk is run with
runasrootin silent mode anddbadminuser has switch equivalency setup.# exachk -silentforce -runasroot .... Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-rocea0) Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-roceb0) ..... - Exachk is run with
runasrootin interactive mode anddbadminuser has switch equivalency setup.# exachk -runasroot .... Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-rocea0) Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-roceb0) ..... - Exachk is run with
rootuser in interactive mode and no user has equivalency to all switches.# exachk .... Enter the RDMA Network Fabric switch user (default: admin):- dbadmin .... - Exachk is run with
rootuser in silent mode, no user has equivalency to all switches anddbadminuser has equivalency to all switches except 1.# exachk -silentforce .... Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-rocea0) Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-roceb0) ..... - Exachk is run with
rootuser in interactive mode, no user has equivalency to all switches and no user has equivalency to any switch.# exachk .... Enter the RDMA Network Fabric switch user (default: admin):- dbadmin .... - Exachk is run with
runasrootin interactive mode and no user has equivalency to all switches.# exachk -runasroot .... Enter the RDMA Network Fabric switch user (default: admin):- dbadmin .... - Exachk is run with
runasrootin silent mode, no user has equivalency to all switches anddbadminhas equivalency to all switches except 1.# exachk -silentforce -runasroot .... Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-rocea0) Starting to run dbadmin privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-roceb0) ..... - Exachk is run with
runasrootin interactive mode, no user has equivalency to all switches and no user has equivalency to any switch.# exachk -runasroot .... Enter the RDMA Network Fabric switch user (default: admin):- dbadmin .... - Exachk is run with
rootuser in interactive mode and user enters switch user other thandbadmin,switchexa,rootoradmin.# exachk .... Enter the RDMA Network Fabric switch user (default: admin):- opc .... Starting to run opc privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-rocea0) Starting to run opc privileged commands in background on RDMA Network Fabric switch (nshqaw06sw-roceb0) ....
Parent topic: Changes in this Release