Alter System (Aggregate Storage)
The MaxL alter system statement helps you change the state of the Essbase Server.
Click here for non-aggregate storage version
Use this statement to start and stop applications, manipulate Essbase Server-wide variables, manage password and login activity, disconnect users, kill processes, and shut down the server.
Keywords
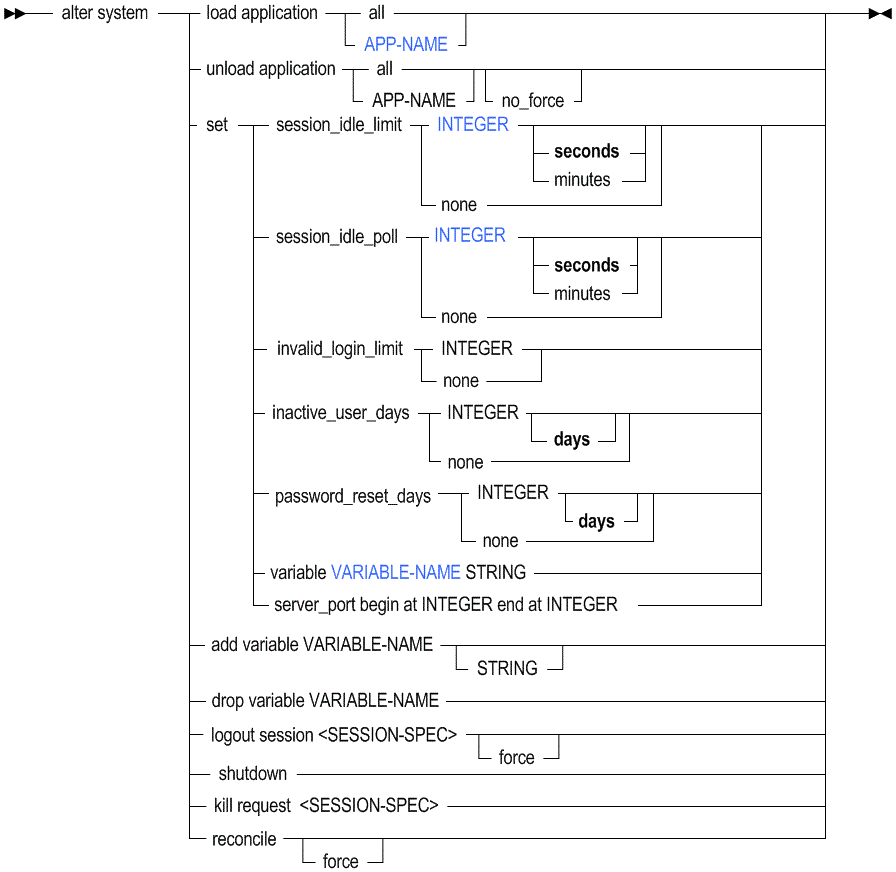
Use MaxL alter system to change the following Essbase Server-wide settings. The role required for most of the statements is System Administrator, with exceptions noted.
- alter system load application …
-
Start an application, or start all applications on the Essbase Server. Requires at least Database Access permission for the application.
Example:
alter system load application ASOSamp; - alter system unload application …
-
Stop an application, or stop all applications on the Essbase Server. Requires at least Database Access permission for the application. Unloading an application cancels all active requests and database connections, and stops the application. If Essbase encounters a problem when trying to cancel active requests and database connections, and stopping the application, an error is logged in the application log.
If you do not want to stop an application if it has active requests and database connections, use the no_force keyword. When using no_force:
-
If the application has active requests and database connections, the application is not stopped; it continues running.
-
If the application does not have active requests and database connections, the application is stopped, as if you used unload application without specifying no_force.
Note:
Unloading an application cancels all active requests and database connections, and stops the application, unless you specify otherwise using no_force. no_force causes Essbase to return an error if active requests are running on the application.
An internal logic error [200] is logged when a database is unable to shut down gracefully when unloading an application or shutting down the system while a process is running on the database.
Example:
alter system unload application ASOSamp no_force; -
- alter system set session_idle_limit …
-
Set the interval of time permitted for a session to be inactive before Essbase Server logs off the user. The minimum limit that you can set is five minutes (or 300 seconds). When the session idle limit is set to none, all users can stay logged on until the Essbase Server is shut down.
The default user idle logout time is 60 minutes. When a user initiates a calculation in the background, after 60 minutes the user is considered idle and is logged out, but the calculation continues in the background.
Because users may mistakenly assume that the calculation stopped when they were logged out, you can do one of the following to correct the user experience:
-
Run the calculation in the foreground
-
Increase the session idle limit in to a time that exceeds the duration of the calculation, or to none
Example:
alter system set session_idle_limit 60 minutes; -
- alter system set session_idle_poll …
-
Set the time interval for inactivity checking. The time interval specified in the session idle poll tells Essbase how often to check whether user sessions have passed the allowed inactivity interval indicated by
session_idle_limit.Example:
alter system set session_idle_poll 300 seconds; - alter system set invalid_login_limit …
-
Set the number of unsuccessful login attempts allowed by any user before the user account becomes disabled. When you change this setting, the counter resets to 0. When the invalid login limit is set to none, there is no limit. By default, there is no limit.
Example:
alter system set invalid_login_limit 3; - alter system set inactive_user_days …
-
Set the number of days a user account may remain inactive before the system disables it. The counter resets when the user logs in, is edited, or is activated by an administrator. When the inactive days limit is set to none, user accounts remain enabled even if they are not used. By default, there is no limit.
Example:
alter system set inactive_user_days 30; - alter system set password_reset_days …
-
Set the number of days users may retain passwords. After the allotted number of days, users are prompted at login to change their passwords. The counter resets for a user when the user changes the password, is edited, or is activated by an administrator. When the password reset days limit is set to none, there is no built-in limit for password retention. By default, there is no limit.
Example:
alter system set password_reset_days 60; - alter system set variable …
-
Change the value of an existing subsitution variable on the system. The value must not exceed 256 bytes. It may contain any character except a leading ampersand (&).
Example:
alter system set variable Month Nov; - alter system set server_port …
-
Expand the port range specified by Essbase configuration properties. Each Essbase application uses two ports from this range. If no more ports are available, an error message is displayed.
Note:
You can expand port ranges only so that the beginning port range is less than SERVERPORTBEGIN and the ending port range is greater than SERVERPORTEND.
Example:
alter system set server_port begin at 32750 end at 33780; - alter system add variable …
-
Create a system-level substitution variable by name, and optionally assign a string value for the variable to represent. You can assign or change the value later using set variable. A substitution variable acts as a global placeholder for information that changes regularly. Substitution variables may be referenced by calculations and report scripts.
If substitution variables with the same name exist at server, application, and database levels, the order of precedence for the variables is as follows: a database-level substitution variable supersedes an application-level variable, which supersedes a server-level variable.
Example:
alter system add variable CurYear '2024'; - alter system drop variable …
-
Remove a substitution variable and its corresponding value from the system.
Example:
alter system drop variable CurYear; - alter system logout session all
-
Terminate all user sessions currently running on the Essbase Server.
Example:
alter system logout session all; - alter system logout session...force
-
Terminate a session (or sessions) even if it is currently processing a request. The request is allowed to proceed to a safe point, and then the transaction is rolled back.
Example:
alter system logout session 3694133190 force; - alter system logout session SESSION-ID
-
Terminate a session by its unique session ID number. To see the session ID number, use display session.
Example:
alter system logout session 3694133190; - alter system logout session by user USER-NAME
-
Terminate all current sessions by a particular user, either across the entire Essbase Server, or limited to a specific application or database.
Example:
alter system logout session by user User1; - alter system logout session by user … on application …
-
Terminate all current sessions by a particular user across a specific application.
Example:
alter system logout session by user User1 on application ASOSamp; - alter system logout session by user on database
-
Terminate all current sessions by a particular user across a specific database.
Example:
alter system logout session by user User1 on database ASOSamp.Basic; - alter system logout session on application
-
Terminate all current user sessions across a specific application.
Example:
alter system logout session on application ASOSamp; - alter system logout session on database
-
Terminate all current user sessions across a specific database.
Example:
alter system logout session on database ASOSamp.Basic; - alter system shutdown
-
Shut down the Essbase Server.
Example:
alter system shutdown; - alter system kill request all
-
Terminate all current requests on the Essbase Server.
Note:
To terminate your own active request in MaxL Shell, press the ESC key.
Example:
alter system kill request all; - alter system kill request SESSION-ID
-
Terminate the current request indicated by the session ID. You can obtain session IDs using display session.
Example:
alter system kill request 3694133190; - alter system kill request by user
-
Terminate all current requests by the specified user on the Essbase Server.
Example:
alter system kill request by user User1; - alter system kill request on application
-
Terminate all current requests on the specified application.
Example:
alter system kill request on application ASOSamp; - alter system kill request on database
-
Terminate all current requests on the specified database.
Example:
alter system kill request on database ASOSamp.Basic; - alter system reconcile
- No longer applicable.
Notes
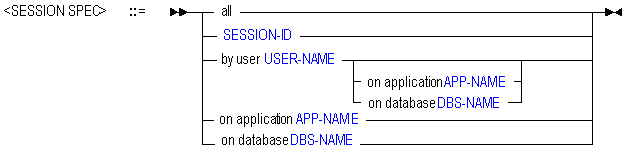
SESSION SPECIFICATION
A session is a single user connection to Essbase Server. The session can be identified by keywords and names indicating context, or by a unique session ID number.
A request is a query sent to Essbase Server by a user or by another process; for example, starting an application or restructuring a database outline. Only one request at a time can be processed in each session.
If a session is processing a request at the time that an administrator attempts to terminate the session, the administrator must either terminate the request first, or use the force keyword available with alter system to terminate the session and the current request.