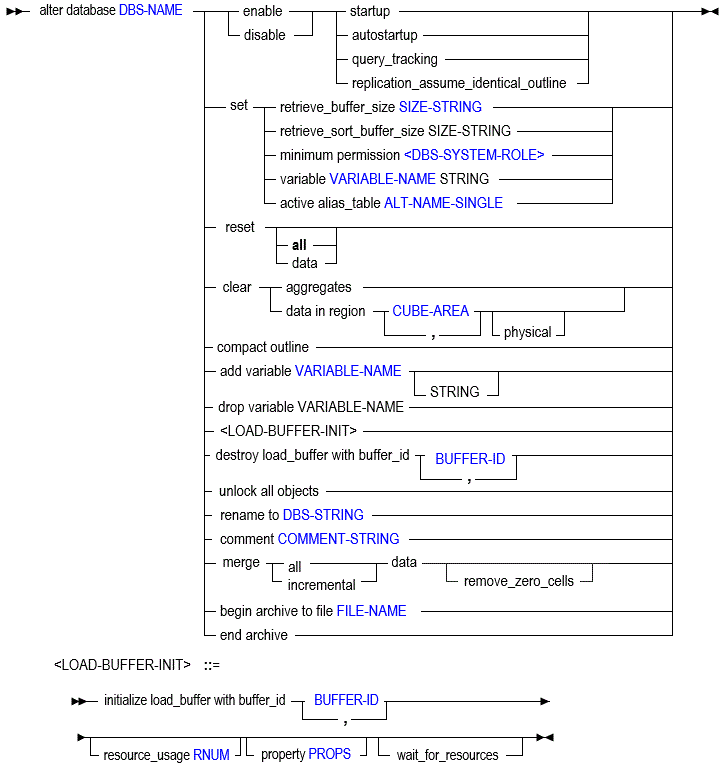
Alter Database (Aggregate Storage)
The MaxL alter database statement for ASO mode helps you change Essbase database-wide settings.
Keywords
You can change aggregate storage (ASO) database settings in the following ways using MaxL alter database. The minimum application permission required for most of the statements is Database Manager, with exceptions noted.
- alter database DBS-NAME enable startup
-
Enable users to start the database directly or as a result of requests requiring the database to be started. Startup is enabled by default.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic enable startup; - alter database DBS-NAME disable startup
-
Prevent all users from starting the database directly or as a result of requests that would start the database. Startup is enabled by default.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic disable startup; - alter database DBS-NAME enable autostartup
-
Automatically start the database when the application to which it belongs starts. Autostartup is enabled by default. This setting is applicable only when startup is enabled.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic enable autostartup; - alter database DBS-NAME disable autostartup
-
Prevent automatic starting of the database when the application to which it belongs starts. Autostartup is enabled by default.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic disable autostartup; - alter database DBS-NAME enable query_tracking
-
Begin collecting query data for this database, to be used for query-based view optimization.
To utilize the results of query tracking, use the optional based on query_data grammar in any of the following statements:
-
query database <dbs-name> list existing_views
Query tracking is on by default. To verify that it's enabled, use
query database appname.dbname get cube_size_info.Note:
Query tracking and query tracing are different.
Query tracking enables you to capture user retrieval statistics against an aggregate storage cube, so that Essbase can make view-based optimizations to improve the performance of aggregations. It is on by default. Related MaxL statements include:
import query_tracking export query_tracking alter database enable query_tracking query database appname.dbname get cube_size_infoQuery tracing helps you monitor Essbase query performance metrics for block storage cubes (including hybrid mode). It is off by default. If you enable it, Essbase logs metrics in a trace report. Related configuration parameters: TRACE_REPORT, QUERYTRACE, QUERYTRACETHRESHOLD, LONGQUERYTIMETHRESHOLD.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic enable query_tracking; -
- alter database DBS-NAME disable query_tracking
-
Stop collecting query data for query-based view optimization. Query tracking is on by default.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic disable query_tracking;Turns off the harvesting of query data for the ASOsamp.Basic database.
- alter database DBS-NAME set retrieve_buffer_size …
-
Change the database retrieval buffer size. This buffer holds extracted row data cells before they are evaluated by the RESTRICT or TOP/BOTTOM Report Writer commands. The default size is 20 KB. The minimum size is 2 KB. Increasing the size may improve retrieval performance.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic set retrieve_buffer_size 20kb; - alter database DBS-NAME set retrieve_sort_buffer_size …
-
Change the database retrieval sort buffer size. This buffer holds data until it is sorted. The default size is 20 KB. The minimum size is 2 KB. Increasing the size may improve retrieval performance.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic set retrieve_sort_buffer_size 20kb; - alter database DBS-NAME set minimum permission …
-
Set a level of permission that all users or groups can have to the database. Users or groups with higher granted permissions than the minimum permission are not affected. This statement is supported for use in EPM Shared Services security mode only.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic set minimum permission no_access; - alter database DBS-NAME set variable …
-
Change the value of an existing subsitution variable on the database. The value must not exceed 256 bytes. It may contain any character except a leading ampersand (&).
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic set variable CurrMonth 'Oct'; - alter database DBS-NAME set active alias_table …
-
Set an alias table as the primary table for reporting and any additional alias requests. Only one alias table can be used at a time. This setting is user-specific; it only sets the active alias table for the user issuing the statement.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic set active alias_table 'Default';To check which alias table is active, use query database.
- alter database DBS-NAME reset
-
Clear all data and linked-reporting objects from the database, but preserve the outline.
Note:
If kernel queries are running when a clear data operation starts, the clear data operation waits for the kernel queries to complete and then the clear data operation proceeds. This information also applies to the reset all and reset data grammar.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic reset; - alter database DBS-NAME reset all
-
Clear all data, Linked Reporting Objects, and the outline.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic reset all; - alter database DBS-NAME reset data
-
Same as using reset.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic reset data; - alter database DBS-NAME clear aggregates
-
Delete all aggregate views.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic clear aggregates;Deletes all aggregate views in the ASOsamp.Basic database.
- alter database DBS-NAME clear data in region …
-
Clear the data in the specified region.
There are two methods for clearing data from a region:
-
Physical, in which the input cells in the specified region are physically removed from the aggregate storage database. The process for physically clearing data completes in a length of time that is proportional to the size of the input data, not the size of the data being cleared. Therefore, you might typically use this method only when you need to remove large slices of data.
For a physical clear, use the MaxL statement with the physical keyword:
alter database appname.dbname clear data in region 'MDX set expression' physical;To save time, you can use a comma-separated list of MDX set expressions to clear from multiple physical regions.
alter database ASOSamp.Basic clear data in region '{CrossJoin({[Promotions].[Coupon]},{[Time].[1st Half]}), CrossJoin({[Promotions].[Coupon]},{[Time].[2nd Half]})}' physical; -
Logical, in which the input cells in the specified region are written to a new data slice with negative, compensating values that result in a value of zero for the cells you want to clear. The process for logically clearing data completes in a length of time that is proportional to the size of the data being cleared. Because compensating cells are created, this option increases the size of the database.
For a logical clear, use the MaxL statement without the physical keyword:
alter database appname.dbname clear data in region 'MDX set expression';
The region must be symmetrical. Members in any dimension in the region must be stored members. When physically clearing data, members in the region can be upper-level members in alternate hierarchies. (If the region contains upper-level members from alternate hierarchies, you may experience a decrease in performance.) Members cannot be dynamic members (members with implicit or explicit MDX formulas), nor can they be from an attribute dimension. For more information, refer to Clear Data from Aggregate Storage Cubes.
To remove cells with a value of zero, use the alter database MaxL statement with the merge grammar and the remove_zero_cells keyword.
Examples:
alter database ASOsamp.Basic clear data in region '{Jan, Budget}' physical;Clears all Budget data for the month of Jan, using the physical method, from the ASOsamp.Basic database.
alter database ASOsamp.Basic clear data in region '{Jan, Budget}';Clears all Budget data for the month of Jan, using the logical method, from the ASOsamp.Basic database.
alter database ASOsamp.Basic clear data in region '{CrossJoin({[Promotions].[Coupon]},{[Time].[1st Half]}), CrossJoin({[Promotions].[Coupon]},{[Time].[2nd Half]})}' physical;Clears two physical regions from the ASOsamp.Basic database.
alter database ASOsamp.Basic clear data in region 'CrossJoin({Jan},{Forecast1, Forecast2})';Clears all January data for the Forecast1 and Forecast2 scenarios from the ASOsamp.Basic database.
-
- alter database DBS-NAME compact outline
-
Compact the outline file to decrease the outline file size. Compaction helps keeps the outline file at an optimal size. After the outline file is compacted, the file continues to grow as before, when members are added or deleted.
Note:
Compacting the outline does not cause Essbase to clear the data. When a member is deleted from the outline, the corresponding record of that member in the outline file is marked as deleted, but the record remains in the outline file. Compacting the outline file does not remove the records of deleted members.
Example:
alter database ASOsamp.Basic compact outline; - alter database DBS-NAME add variable …
-
Create a database-level substitution variable by name, and optionally assign a string value for the variable to represent. You can assign or change the value later using set variable. A substitution variable acts as a global placeholder for information that changes regularly. Substitution variables may be referenced by calculations and report scripts.
If substitution variables with the same name exist at server, application, and database levels, the order of precedence for the variables is as follows: a database level substitution variable supersedes an application level variable, which supersedes a server level variable.
Example:
alter database ASOsamp.Basic add variable Month 'Oct'; - alter database DBS-NAME drop variable …
-
Remove a substitution variable and its corresponding value from the database.
Example:
alter database ASOsamp.Basic drop variable Month; - alter database DBS-NAME initialize load_buffer …
-
Create a temporary buffer in memory for loading data.
Data load buffers are used in aggregate storage databases for allocations, custom calculations, and lock and send operations. Multiple data load buffers can exist on a single aggregate storage database.
You can control the share of aggregate storage cache resources the load buffer is allowed to use and how long to wait for resources to become available before aborting load buffer operations. You can also set properties that determine how missing and zero values, duplicate values, and multiple values for the same cell in the data source are processed.
-
Specify resource_usage RNUM to put constraints on the load buffer.
-
Specify property PROPS to tell Essbase what to do with empty values in the source data.
-
Specify wait_for_resources to wait on processing load buffer operations until resources become available. The wait time is either the amount of time specified by ASOLOADBUFFERWAIT configuration, or the default wait, which is 10 seconds.
Example:
alter database ASOsamp.Basic initialize load_buffer with buffer_id 1 resource_usage .5 property ignore_missing_values, ignore_zero_values;Creates a data-load buffer in memory for the ASOsamp.Basic database. The buffer can use only 50% of available resources. Missing values and zeros in the data source are ignored.
Refer also to Load Data Using Buffers, Load Data into Aggregate Storage Cubes.
-
- alter database DBS-NAME destroy load_buffer …
-
Destroy the temporary data-load memory buffer.
Example:
alter database ASOsamp.Basic destroy load_buffer with buffer_id 1; - alter database DBS-NAME unlock all objects
-
Unlock all objects on the database that are in use by a user or process. You must be a service administrator. Service administrators can unlock any object, but other users can unlock only those objects that they locked.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic unlock all objects; - alter database DBS-NAME rename …
-
Rename the database. When you rename a database, the cube directory is also renamed.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic rename to Basic2; - alter database DBS-NAME comment …
-
Create a description of the database. The maximum number of characters is 80. This description is available to database administrators. To annotate the database for Smart View or other grid client users, use
set noteinstead.Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic comment 'my comment'; - alter database DBS-NAME merge all|incremental data [remove_zero_cells]
-
Merge incremental data slices. Use any of these keywords:
-
all—Merge all incremental data slices into the main database slice.
-
incremental—Merge all incremental data slices into a single data slice. The main database slice is not changed.
-
(Optional) remove_zero_cells—When merging incremental data slices, remove cells that have a value of zero (logically clearing data from a region results in cells with a value of zero).
Examples:
alter database ASOsamp.Basic merge all data;Merges all incremental data slices into the main slice in the ASOsamp.Basic database.
alter database ASOsamp.Basic merge incremental data;Merges all incremental data slices into a single data slice within the ASOsamp.Basic database.
alter database ASOsamp.Basic merge all data remove_zero_cells;Merges all incremental data slices into the main slice in the ASOsamp.Basic database, and removes cells with a value of zero.
-
- alter database DBS-NAME enable replication_assume_identical_outline
-
Optimize the replication of an aggregate storage database when the aggregate storage database is the target and a block storage database is the source and the two outlines are identical.
Replication optimization affects only the target aggregate storage application; the source block storage application is not affected. This functionality does not apply to block storage replication.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic enable replication_assume_identical_outline;To enable this functionality at the server or application level, use REPLICATIONASSUMEIDENTICALOUTLINE configuration instead.
- alter database DBS-NAME disable replication_assume_identical_outline
-
Do not optimize the replication of an aggregate storage database when the aggregate storage database is the target and a block storage database is the source and the two outlines are identical.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic disable replication_assume_identical_outline; - alter database DBS-NAME begin archive to file
-
Prepare the database for backup by an archiving program, and prevent writing to the files during backup. You must be a system administrator to perform this action.
Begin archive achieves the following outcomes:
-
Switches the database to read-only mode. The read-only state persists, even after the application is restarted, until it is changed back to read-write using
end archive. -
Creates a file containing a list of files that need to be backed up. Unless a different path is specified, the file is stored in the database directory.
Begin archive and end archive do not perform the backup; they simply protect the database during the backup process.
Note:
Using the begin archive to file and end archive grammar is the only supported way to backup and recover a database using MaxL.
Example:
alter database ASOSamp.Basic begin archive to file 'asosamp_basic.arc'; -
- alter database DBS-NAME end archive
-
Return the database to read-write mode after backing up the database files.
Note:
Using the begin archive to file and end archive grammar is the only supported way to backup and recover a database using MaxL.