4.8 Use the Python Interpreter in a Notebook Paragraph
An Oracle Machine Learning notebook supports multiple languages. Each paragraph is associated with a specific
interpreter. To run Python commands in a notebook, you must first connect to the Python
interpreter. To use OML4Py, you must import the oml module.
In an Oracle Machine Learning notebook, you can add multiple paragraphs, and each paragraph can be connected to
different interpreters such as SQL or Python. You identify which interpreter to use
by specifying % followed by the interpreter to use:
sql, script, r,
python, conda, markdown.
- Connect to a Python interpreter to run Python commands in a notebook
- Import the Python modules -
oml,matplotlib, andnumpy - Check if the
omlmodule is connected to the Oracle AI Database
Note:
z is a reserved keyword and
must not be used as a variable in %python paragraphs in Oracle Machine Learning notebooks.
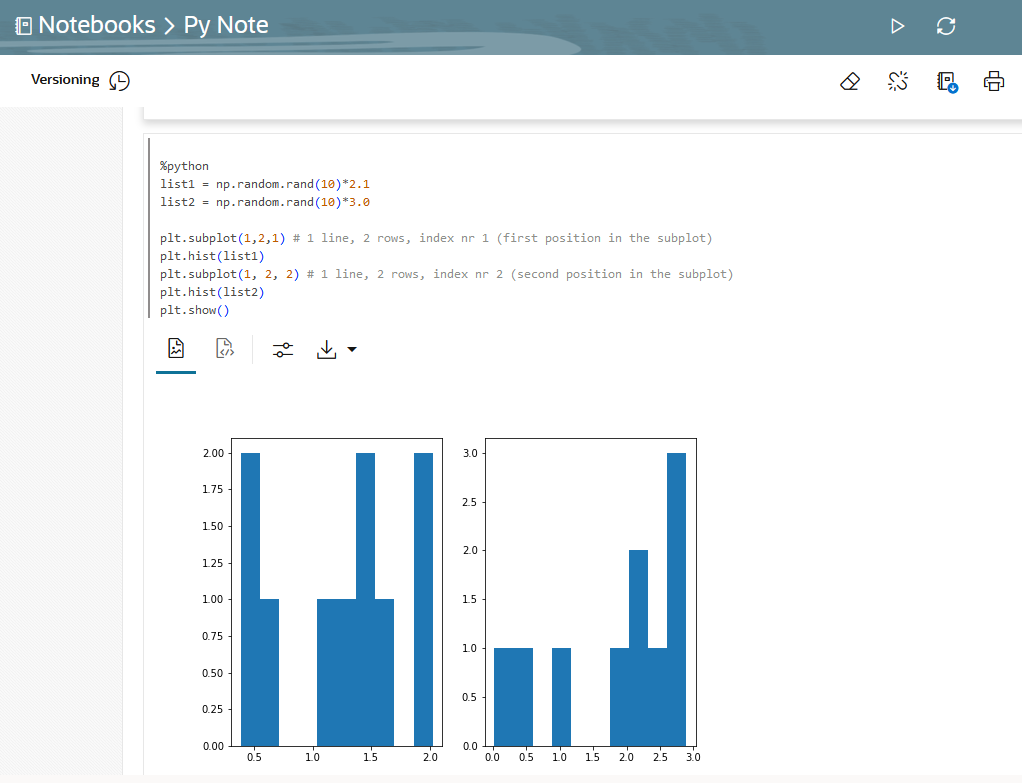
Example to demonstrate the use of the Python modules - matplotlib and numpy , and use random data to plot two histograms.
- About Oracle Machine Learning for Python
Oracle Machine Learning for Python (OML4Py) is a component of Oracle Autonomous AI Database, which includes Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse (ADW), Oracle Autonomous AI Transaction Processing (ATP), and Oracle Autonomous AI JSON Database (AJD). By using Oracle Machine Learning UI notebooks, you can run Python functions on data for data exploration and preparation while leveraging Oracle AI Database as a high-performance computing environment. Oracle Machine Learning User Interface (UI) is available through Autonomous AI Lakehouse (ADW) , Autonomous AI Transaction Processing (ATP) and Autonomous AI JSON Database (AJD) services.
Parent topic: OML Notebooks
4.8.1 About Oracle Machine Learning for Python
Oracle Machine Learning for Python (OML4Py) is a component of Oracle Autonomous AI Database, which includes Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse (ADW), Oracle Autonomous AI Transaction Processing (ATP), and Oracle Autonomous AI JSON Database (AJD). By using Oracle Machine Learning UI notebooks, you can run Python functions on data for data exploration and preparation while leveraging Oracle AI Database as a high-performance computing environment. Oracle Machine Learning User Interface (UI) is available through Autonomous AI Lakehouse (ADW) , Autonomous AI Transaction Processing (ATP) and Autonomous AI JSON Database (AJD) services.
Oracle Machine Learning for Python (OML4Py) makes the open source Python scripting language and environment ready for the enterprise and big data. Designed for problems involving both large and small volumes of data, Oracle Machine Learning for Python integrates Python with Oracle Autonomous AI Database, including its powerful in-database machine learning algorithms, and enables deployment of Python code.
- Perform data exploration, data analysis, and machine learning using Python leveraging Oracle AI Database as a high performance compute engine
- Build and evaluate machine learning models and score data using those models from an integrated Python API using in-database algorithms
- Deploy user-defined Python functions through a REST interface with data-parallel and task-parallel processing
The Python interpreter uses Python 3.13.5 to process Python scripts in Oracle Machine Learning notebooks. To use the interpreter, specify the %python directive at the
beginning of the paragraph. The Python interpreter supports the following Python modules:
cffi-1.15.1contourpy-1.1.0cryptography-43.0.1cycler-0.10.0fonttools-4.49.0joblib-1.4.2kiwisolver-1.4.5matplotlib-3.8.4numpy-2.0.1oracledb-2.4.1packaging-23.1pandas-2.2.2pillow-10.4.0pycparser-2.21pyparsing-2.4.0python_dateutil-2.8.2pytz-2022.1scikit_learn-1.5.1scipy-1.14.0setuptools-70.0.0six-1.16.0threadpoolctl-3.5.0
Related Topics
Parent topic: Use the Python Interpreter in a Notebook Paragraph