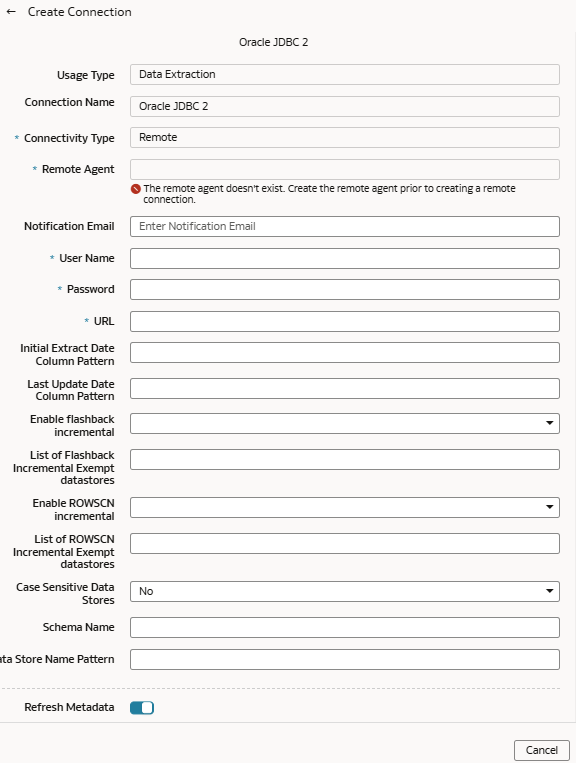
Load Data from Oracle Database Using JDBC into NetSuite Analytics Warehouse (Preview)
As a service administrator, you can use an extract service remote agent to connect to an Oracle database using JDBC and use the data to create data augmentations.
After connecting to an Oracle database using JDBC, the remote agent
extracts the data and loads it into the autonomous data warehouse associated with your
Oracle NetSuite
Analytics Warehouse instance. The remote agent pulls the
metadata through the public extract service REST API and pushes data into object storage
using the object storage REST API. You can extract and load the data from an Oracle
database into Oracle NetSuite
Analytics Warehouse only once every 24 hours.
Ensure that Remote Agent and Oracle JDBC are enabled on the Enable Features page prior to creating this connection. See Make Preview Features Available.