About Ordered Message Processing in Oracle Integration
To ensure that HL7 messages are delivered to target endpoints in the order in which they are received, Oracle Integration implements ordered message processing. Messages are stored in queues to ensure that they are processed in the order received.
Capabilities
It's critical for healthcare messages to be delivered in the correct order to ensure patient safety. Out-of-order messages can result in serious consequences, such as the incorrect administration of medication or treatment. For example, receiving a medication order message out of order with related allergy information may lead to a serious adverse reaction. To prevent out-of-order messaging from occurring, Oracle Integration uses ordered message processing to deliver messages in the correct order.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Queues | A processing mechanism that ensures that messages (specifically, HL7 messages in Oracle Integration) are processed in the order received. |
| Policy | Attached to MLLP Adapter trigger and invoke connections to enforce guaranteed ordering of messages. |
| MLLP Adapter trigger connection | Receives and stages HL7 messages in a queue in the order received. Upon receiving the message, the MLLP Adapter also sends an acknowledgment back to the client application. |
| MLLP Adapter invoke connection | Attached to the queue to receive and route HL7 messages to one or more target endpoints in the order staged in the queue. |
- Message order preservation
- Delivers each message to the target endpoint in the same order as sent by the client application.
- If one message being processed runs into an error, subsequent messages are blocked from being processed to preserve the order.
- If a message recovery occurs on a message after the first failure, the message sequence is maintained. Subsequent messages cannot go through until the first message is successfully processed. Once the failed message is successfully processed, messaging resumes in the same order.
- Delivery guarantees
Every message is ensured to be delivered to the target system at least once.
- Duplicate message and error handling
Duplicate messages adhere to the queue order. Duplicate messages may occur under the following scenarios:
- A message is sent and stored in a queue, and an acknowledgment is sent to the client application, but never received.
- A message is sent and stored in a queue, but a failure occurs when sending the acknowledgment to the client application.
- A message arrives, but fails to be added to the queue. The client never receives the acknowledgment.
- A message fails transformation or translation. In this case. you must resubmit the failed message after making the necessary changes.
- A message is sent to one queue, but fails to be sent to the second outbound queue. This scenario results in a fault and must be resubmitted.
- Support for ordered message processing for parent-to-child integration invocations (local invocations)
- Runtime monitoring
Monitoring of queues is supported, including the current message delivery status and the number of messages in the queue. You can pause delivery for a queue. You can also perform management tasks such as deleting messages from queues, resubmitting failed messages in a queue, and clearing all messages from a queue.
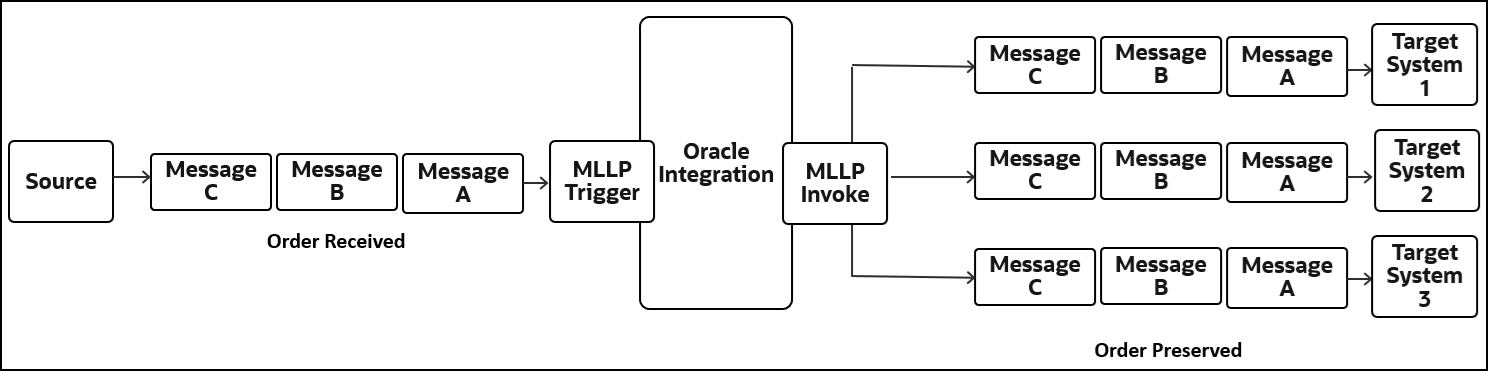
Use Case
- Target system 1
- Target system 2
- Target system 3
- The MLLP Adapter trigger connection receives and captures HL7 messages C, B, and A in that order in a queue and sends an acknowledgment back to the client application.
- The messages are processed in Oracle Integration.
- If the message must be routed to multiple destinations in the queued order, each destination MLLP Adapter invoke connection is associated with the policy.
- When consuming messages from the endpoint-specific queues, the system coordinates with the order of the messages in the queue upon arrival to maintain end-to-end order.
- The MLLP Adapter invoke connection delivers HL7 messages C, B, and A in the queued order to targets 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Ordering is enforced at endpoint processing from the outbound queues.
Restrictions
- Queues are only available for use with the Oracle Integration for Healthcare component of Oracle Integration.
- Queues are only supported with MLLP Adapter trigger and invoke connections.
Note that:
- If you configure an MLLP Adapter trigger connection to use a queue, but don't configure an MLLP Adapter invoke connection to use that queue, there is no end-to-end ordered message ordering.
- You can attach a policy to an MLLP Adapter invoke connection, but if the invoke connection happens in an integration in which there is no MLLP Adapter trigger connection with a policy, the messages won't be placed in queues for re-ordering.
- You can only create and use queues in projects.
- Queues cannot be shared across projects.
- Partitioning of incoming messages is not supported. Each message is treated as an opaque entity. Message ordering is based solely on the time of arrival in Oracle Integration.
- Message processing can fail and be blocked (for example, if the target endpoints are not operational). The system tries to send the message again, which may be blocked again. Messages that get blocked because of retry exhaustion must be manually resubmitted.
- Editing of messages that fail due to missing data is not supported. Messages that cannot be processed due to such failures must be edited with the correct changes and resubmitted manually.