Accurately Derive Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM) using Cost Planning
Cost accountants can now leverage the Cost Planning features to manage complex activities for planning cost drivers and allocating costs, enabling accurate calculation of Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM) in complex global manufacturing environments.
Major features include:
- Allocation tool to obtain accurate COGM from GL, Procurement, Logistics, Maintenance and other supply chain functions
- What-if simulations for planning costs across multiple manufacturing locations, processes, contract manufacturers
- Seamless integration with the Margin Analysis and Margin Comparison dashboards, enabling users to assess the impact of planned costs on gross margins and compare different cost plans to identify the most profitable strategy.
Core Components of Cost Planning
- Flexible Metadata Definition: A configurable metadata layer enables organizations to define how costs are allocated and calculated with fine-grained control over business logic. It consists of three core objects:
- Allocation Scope: Defines the set of items, overheads, or resources for which cost calculations are performed. Users can apply flexible criteria to intelligently group similar entities, ensuring that items with comparable cost behaviors are costed consistently.
- Allocation Pool: Represents a collection of accounting data from financial systems used as the basis for cost allocation. An allocation pool can consist of actual account balances reflecting historical expenses, budget account balances representing planned future costs, or manually estimated amounts for specific business areas not captured in financial systems.
- Allocation Rule: Allows users to define precise allocation methodologies for different types of cost elements.
- For indirect costs, users can select from a wide range of pre-defined cost drivers (e.g., volume, value, machine hours) or create custom drivers to match their organization’s unique allocation strategies.
- For direct costs, users can derive costs from a variety of sources such as purchasing documents, supplier quotes, landed cost calculations, and price lists, enabling accurate calculation of procurement-related costs.
- Cost Plan Execution
- Expense and Driver Aggregation: For indirect costs, the system collects expense amounts from the allocation pool (GL, budget, or manual) and aggregates driver totals (e.g., production volumes, machine hours, purchase quantities) over defined periods. For procurement costs, the system aggregates the price as per the allocation rule definition for a provided time period.
- Cost Calculation: A cost rate is calculated by distributing the allocation pool using the driver value and applied to all entities in the allocation scope or through aggregating procurement costs.
- Roll-up to COGM: Calculated costs are rolled up through the BOM and routing structure to derive the Cost of Goods Manufactured for finished products.
- Analysis: Detailed allocation results are stored, enabling drill-down of individual costs, multi-level cost explosions, valuation impact, and integrated margin analysis.
- Scenario Comparison: Multiple cost plans can be created and their margin impacts compared to identify the most profitable strategy. Cost plans can also help users track actual vs. planned costs over time.
- Integration to Margin Analysis and Margin Comparison Dashboards: Users can analyze historical and current cost data, perform margin analysis, and compare multiple cost plan scenarios across products, geographies, time periods, and business units.
Cost Planning Process Flow
Navigation: Cost Management - SLA > Cost and Profitability Analysis > Cost Planning Tab
Metadata Setup
This is a periodic activity, typically performed a few times a year, or more frequently in dynamic environments, as part of cost planning setup or during major updates.
Step 1: Create Allocation Scope
Define the range of items, resources, or overheads to simulate.
Group entities expected to receive similar cost planning treatment using flexible criteria based on attributes (e.g., product category, resource type).
Specify a unit of measure (UOM) for the scope. All entities in the scope must have UOM conversions defined to enable cost allocations in a common unit.
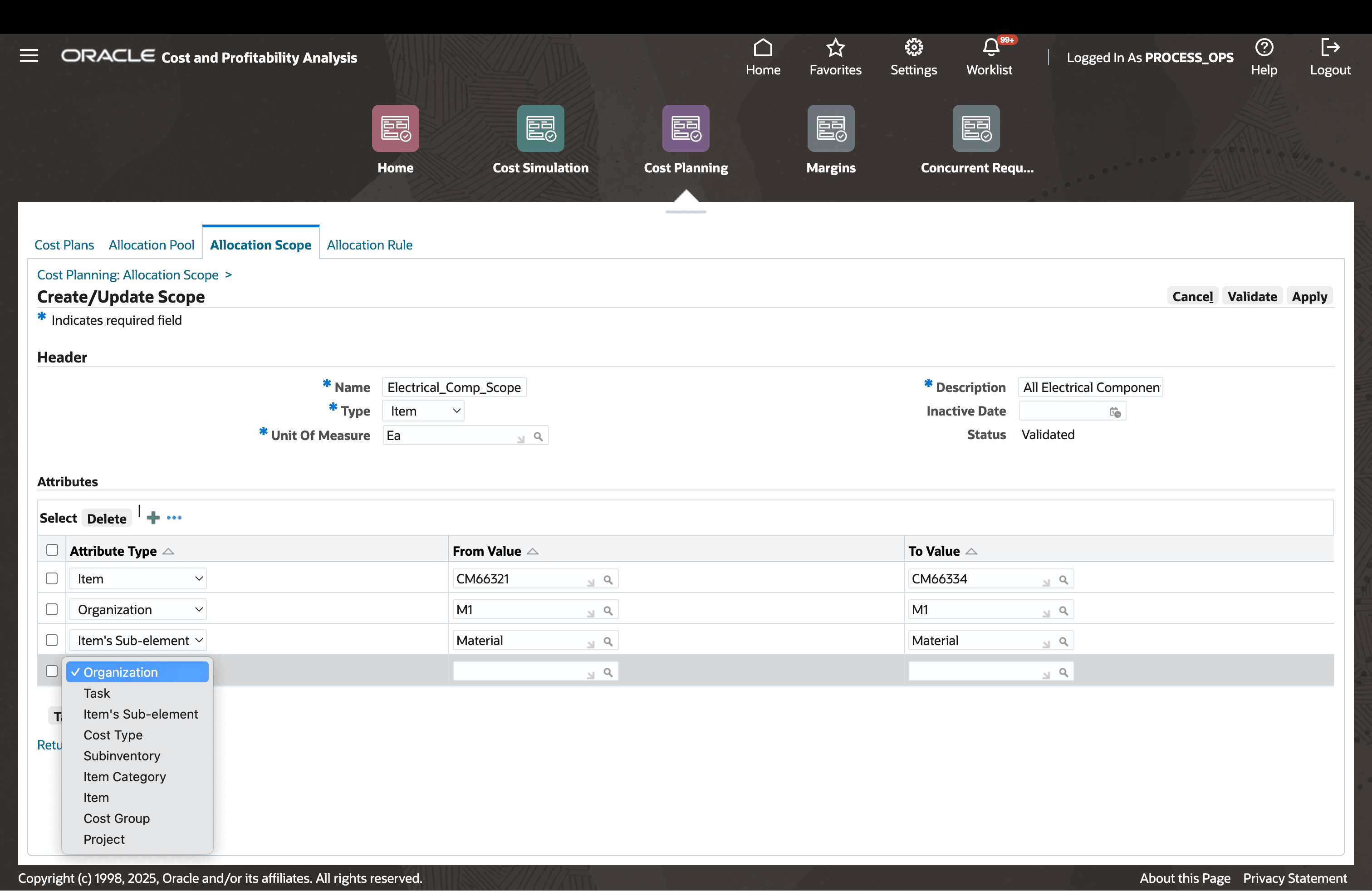
Define Allocation Scope of Type "Item"
Step 2: Create Allocation Pool
For cost allocations, define a list of accounts from which business expenses or budgets will be retrieved (from GL).
Can use historical actuals or planned/budgeted amounts.
If the expense is not in the system, users can manually enter estimated values.
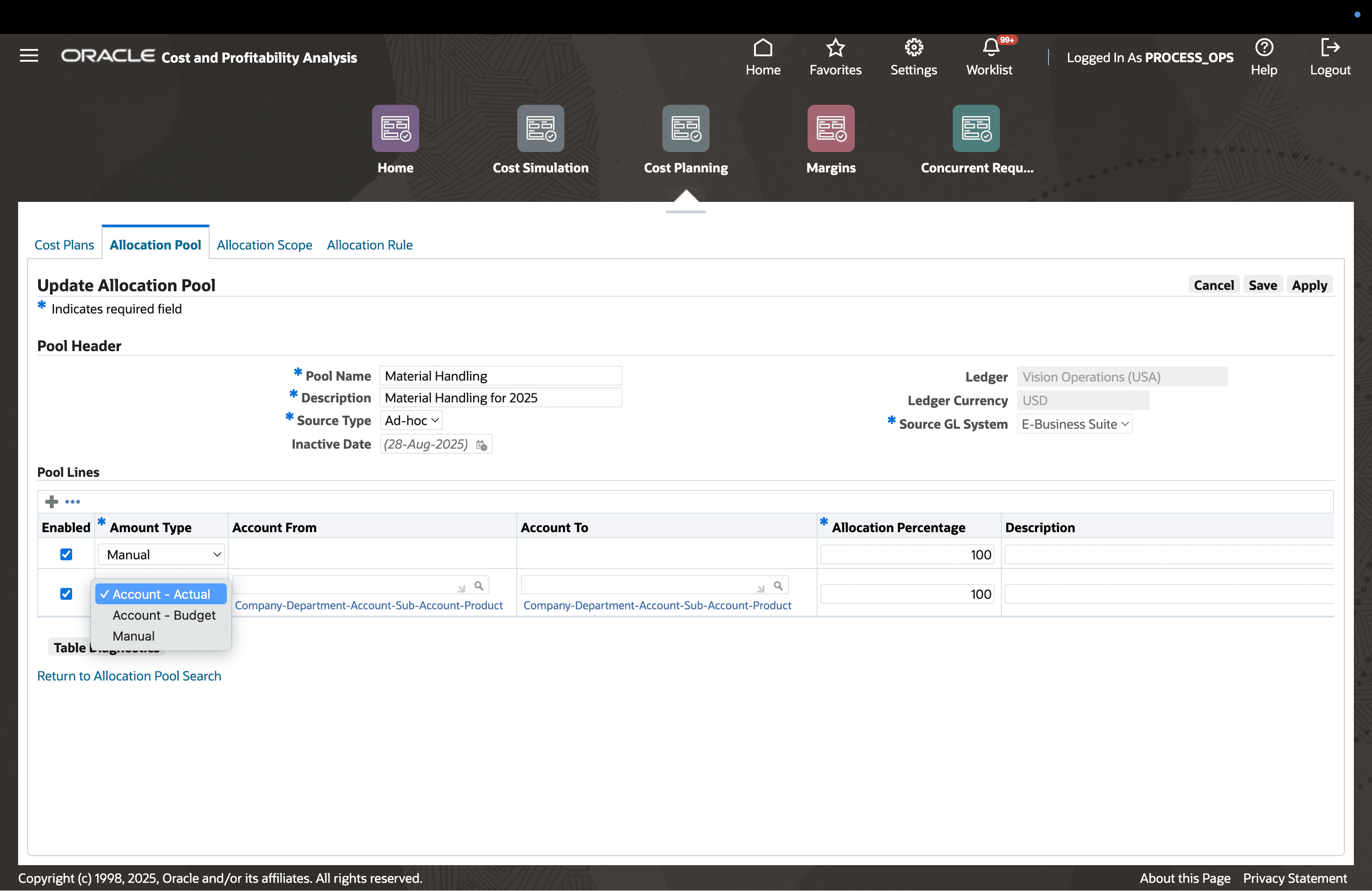
Define Allocation Pool
Step 3: Define Allocation Rules
Allocation rules define how costs are calculated. Allocation pool based allocations distribute business expenses across products, materials, resources or overheads using proportions defined under a driver. Supported driver types are volume, value, contribution margin which are calculated from the ERP data and planned drivers of the same types that users can interface from a third-party system and import into cost management.
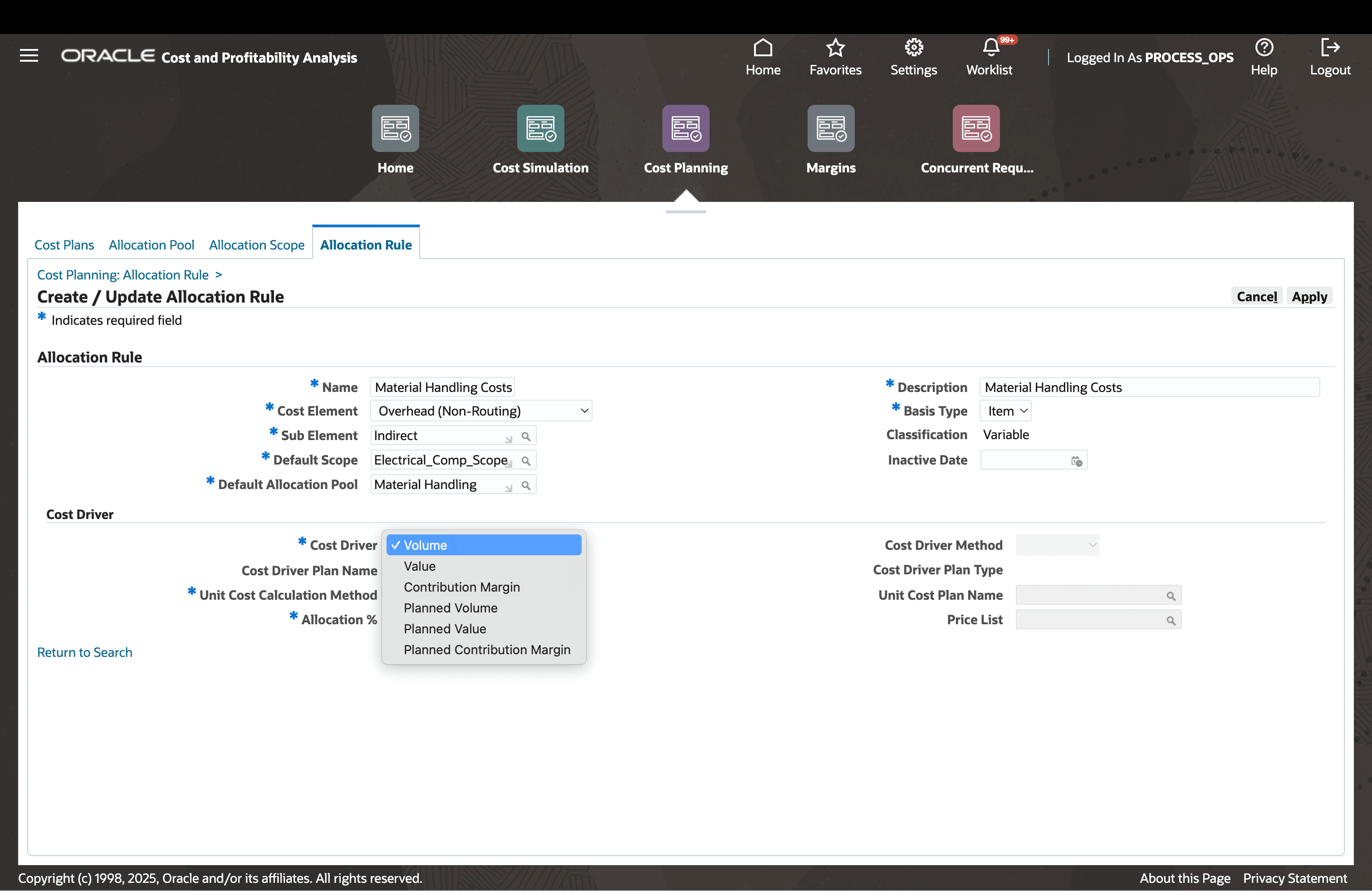
Define Allocation Rules
Procurement-based drivers use purchasing documents to aggregate price information and estimate material costs.
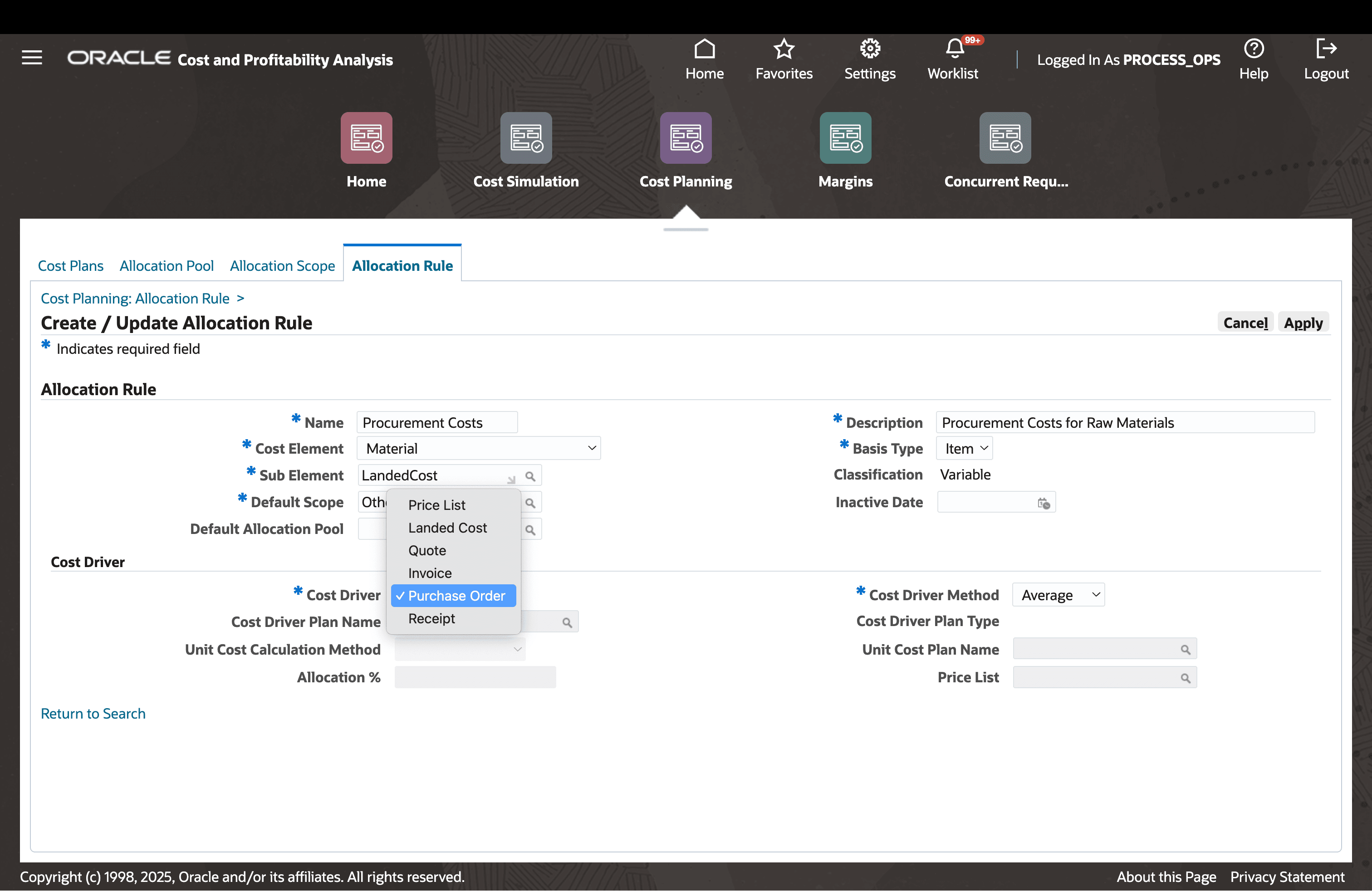
Define Allocation Rules (Procurement Drivers)
Rules include:
- Selection of an Allocation Pool (optional).
- Selection of an Allocation Scope.
- Selection of the Cost Element and Subelement against which the cost will be captured for the cost entity
- Definition of the driver method by which the cost entities will calculate their cost.
Allocation rules are reusable within the same cost plan by varying the pool and/or scope.
Cost Plan Setup: Defining Cost Planning Scenarios
This is a frequent operational activity to plan, revise, and track costs.
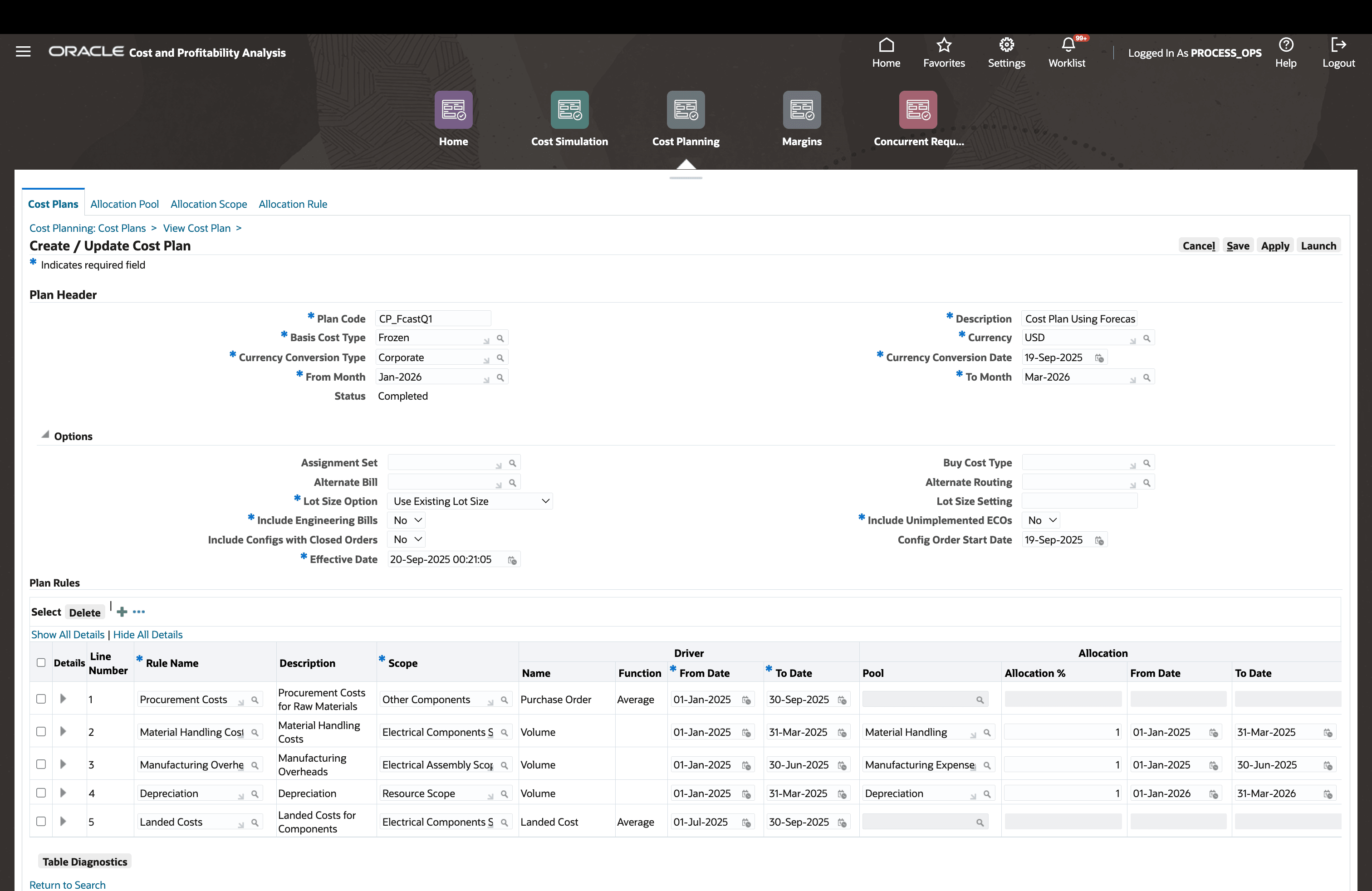
Define Cost Plan
A cost plan consists of
- Cost planning date range - You can plan for a single or multiple periods .
- Basis Cost Type - A cost type that supplies a baseline cost for leaf level entities that you are not replacing with the allocation drivers.
- Currency conversion information for foreign currency values.
- Cost rollup parameters.
- A list of allocation rules.
For each allocation rule line:
- Define the relevant allocation pool period (e.g., retrieve past GL expenses from the first quarter of 2025).
- Define the driver calculation period (e.g., expected component volume in Jul 2025 or average PO prices or landed costs in July 2025).
Cost Plan Review & Analysis
Users can explore results of a cost planning exercise in detail:
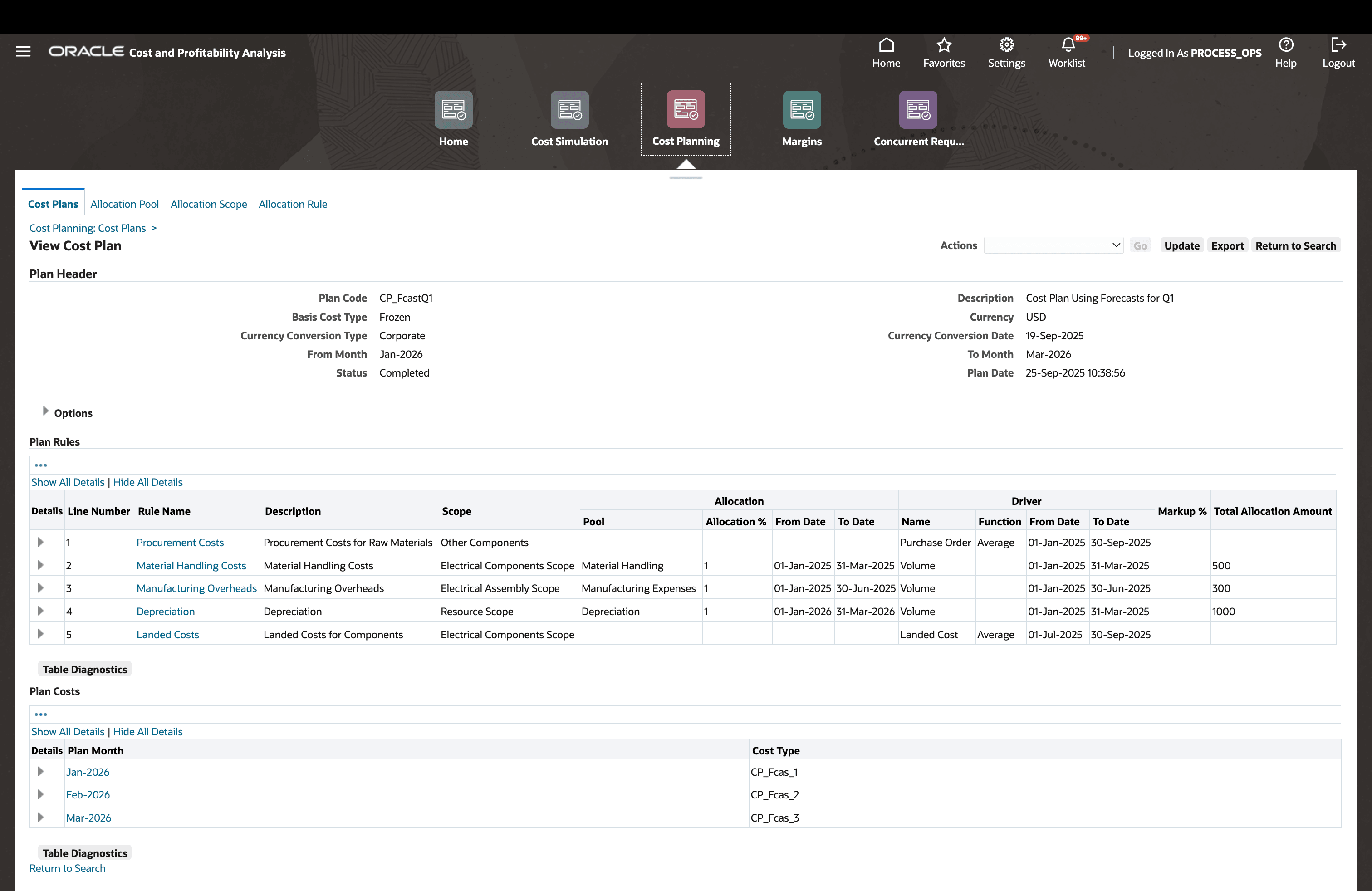
Completed Cost Plan
Review Allocation Details
Click on the rules listed to view granular allocations performed by the system for each allocation rule.
Navigation: View Cost Plan > Click on a rule name under Plan Rules
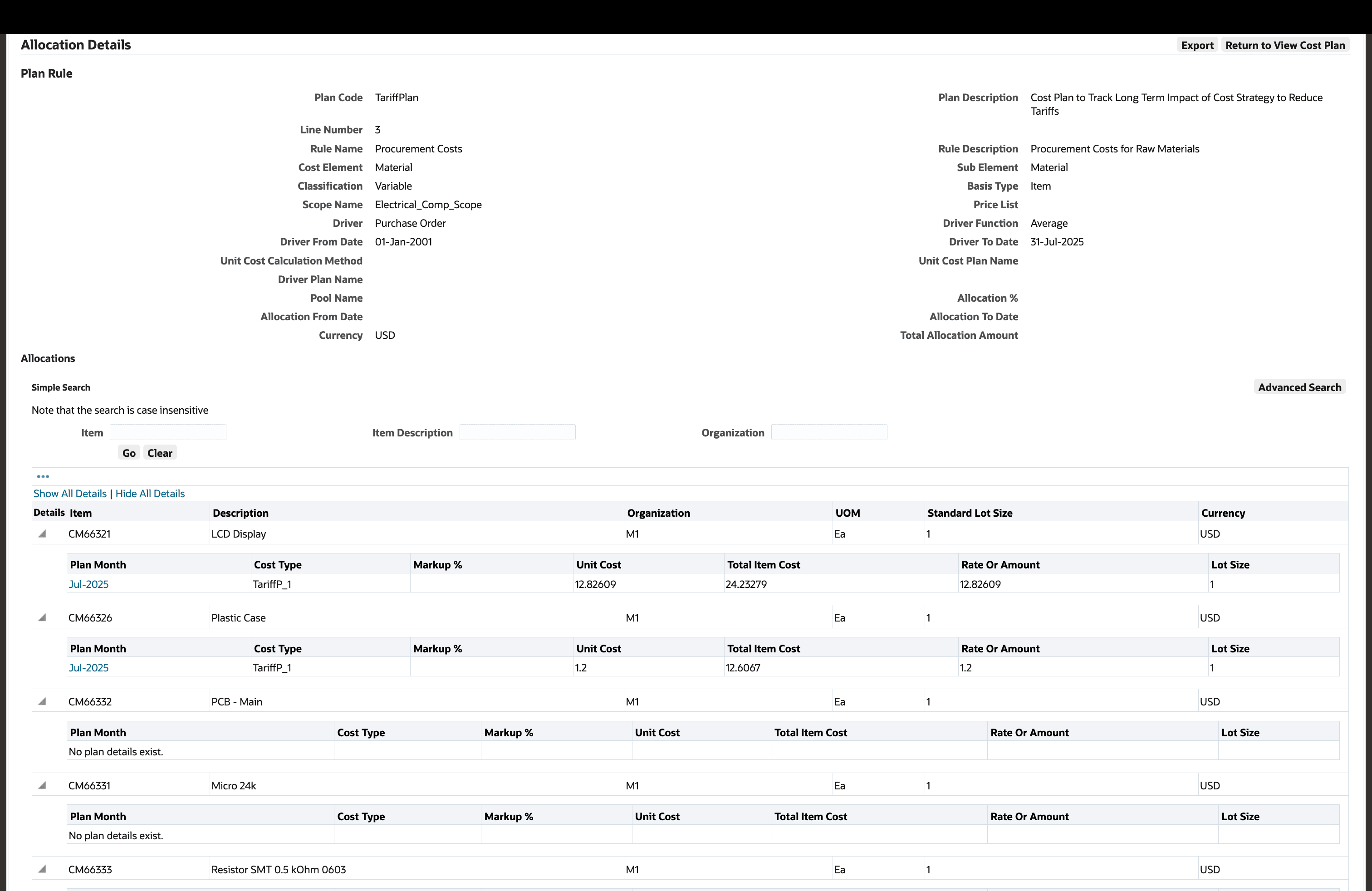
Review the Cost Calculations Done by the Allocation Rule for a Purchasing Driver
Review Plan Impact Summary
Review enterprise wide impact of the cost plan on costs of intermediate and final products.
Navigation: View Cost Plan > Plan Costs > Click on a Plan Month
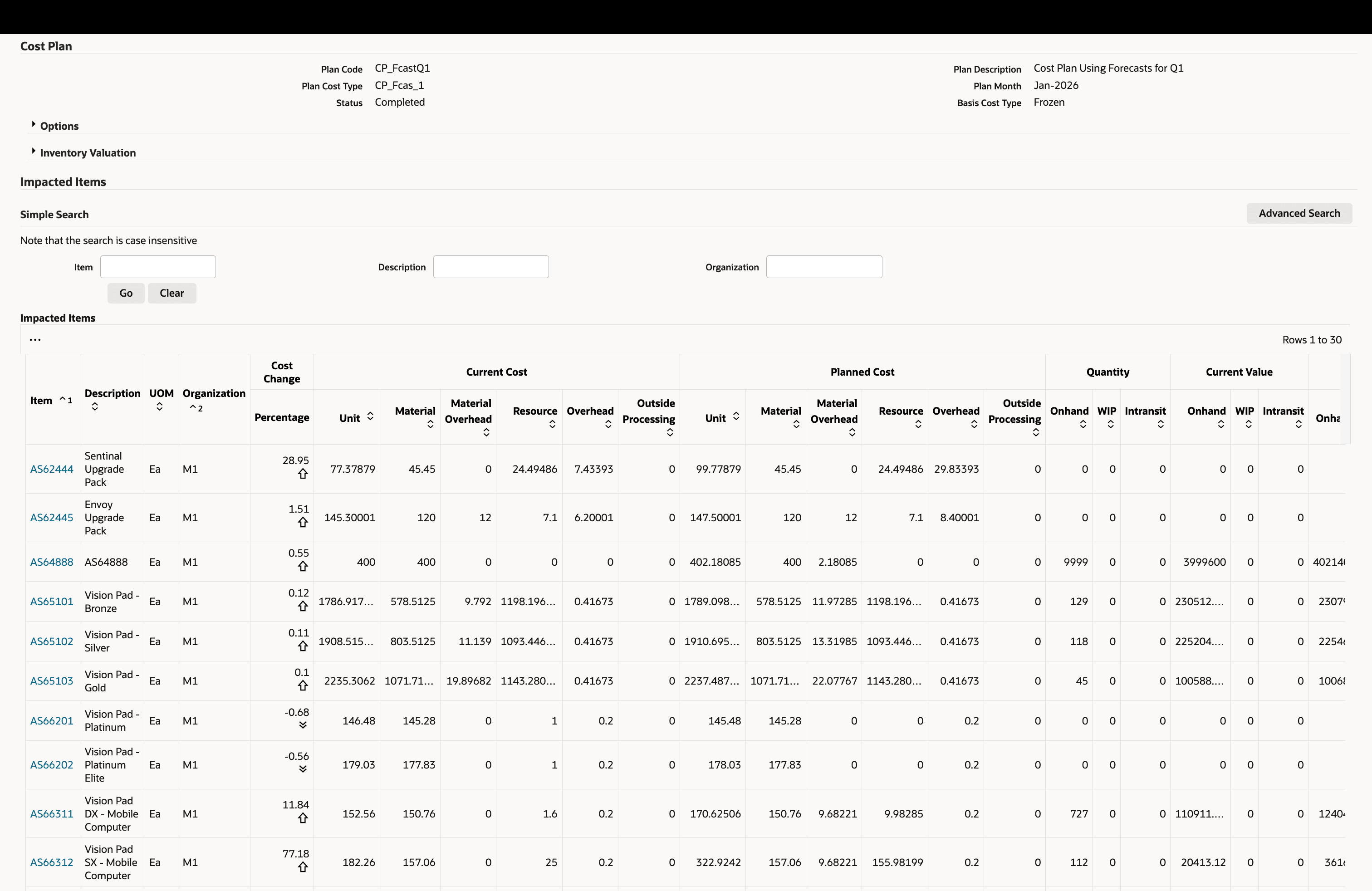
Review Planned Costs
Review Plan Item Cost Structure Detail
Click on an assembly to navigate to its detailed cost structure. Drill into individual cost elements and sub-elements, including a multi-level, indented explosion of the full product cost structure. Users can also export the exploded cost structure for offline review.
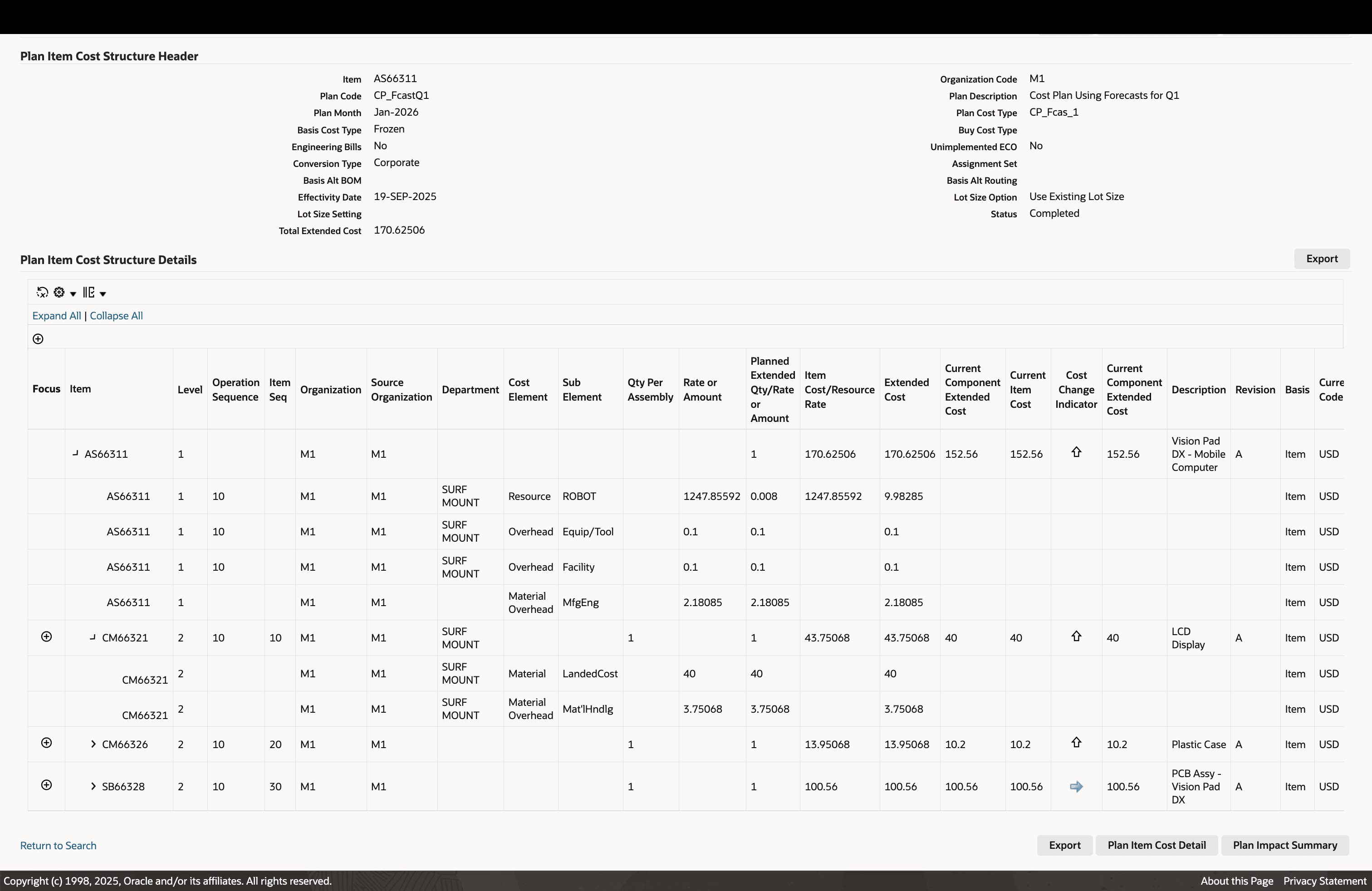
Review Detailed Intended Multi-level Cost Structure of Products
Valuation Impact Analysis
Assess how the planned cost affects inventory valuation and product costing. You can evaluate the impact through the charts as well as by reviewing assembly level impact in the Impacted Items table below.
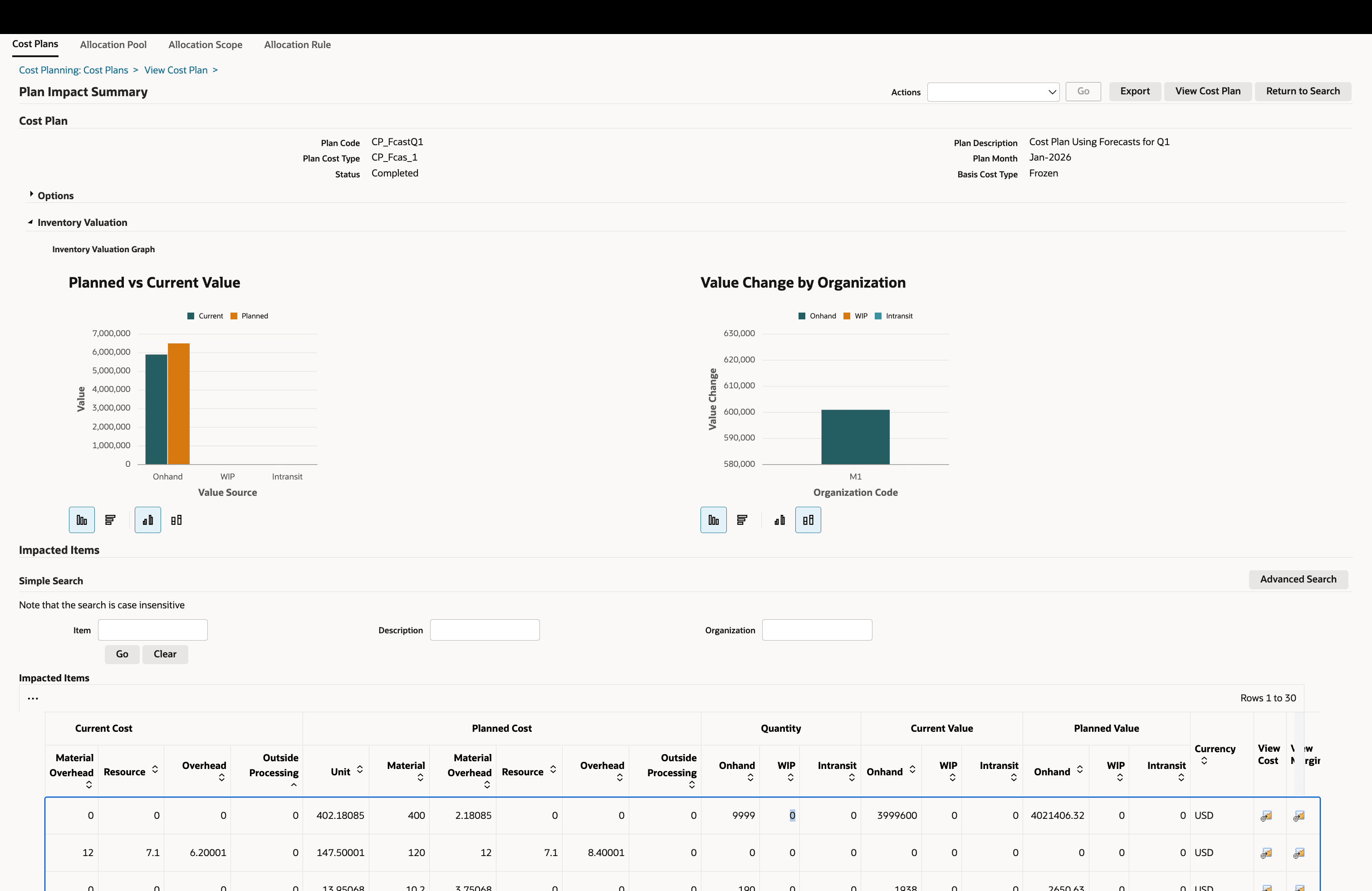
Review Projected Impact to Inventory Valuation
Review the impact to inventory valuation If the cost plan is implemented
Margin Analysis
Analyze product margins across planning periods to evaluate profitability under different scenarios.
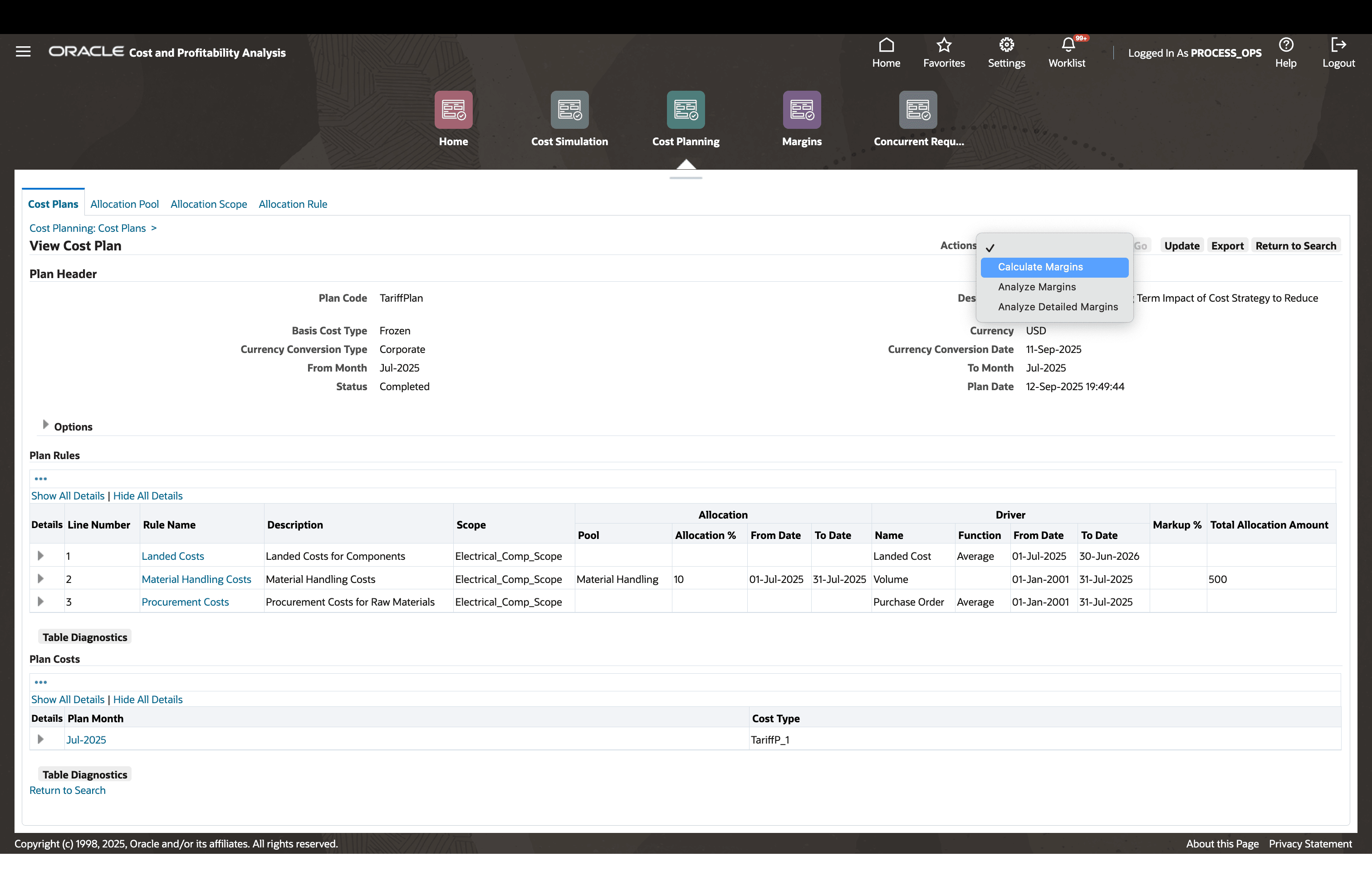
Calculate Gross Margins
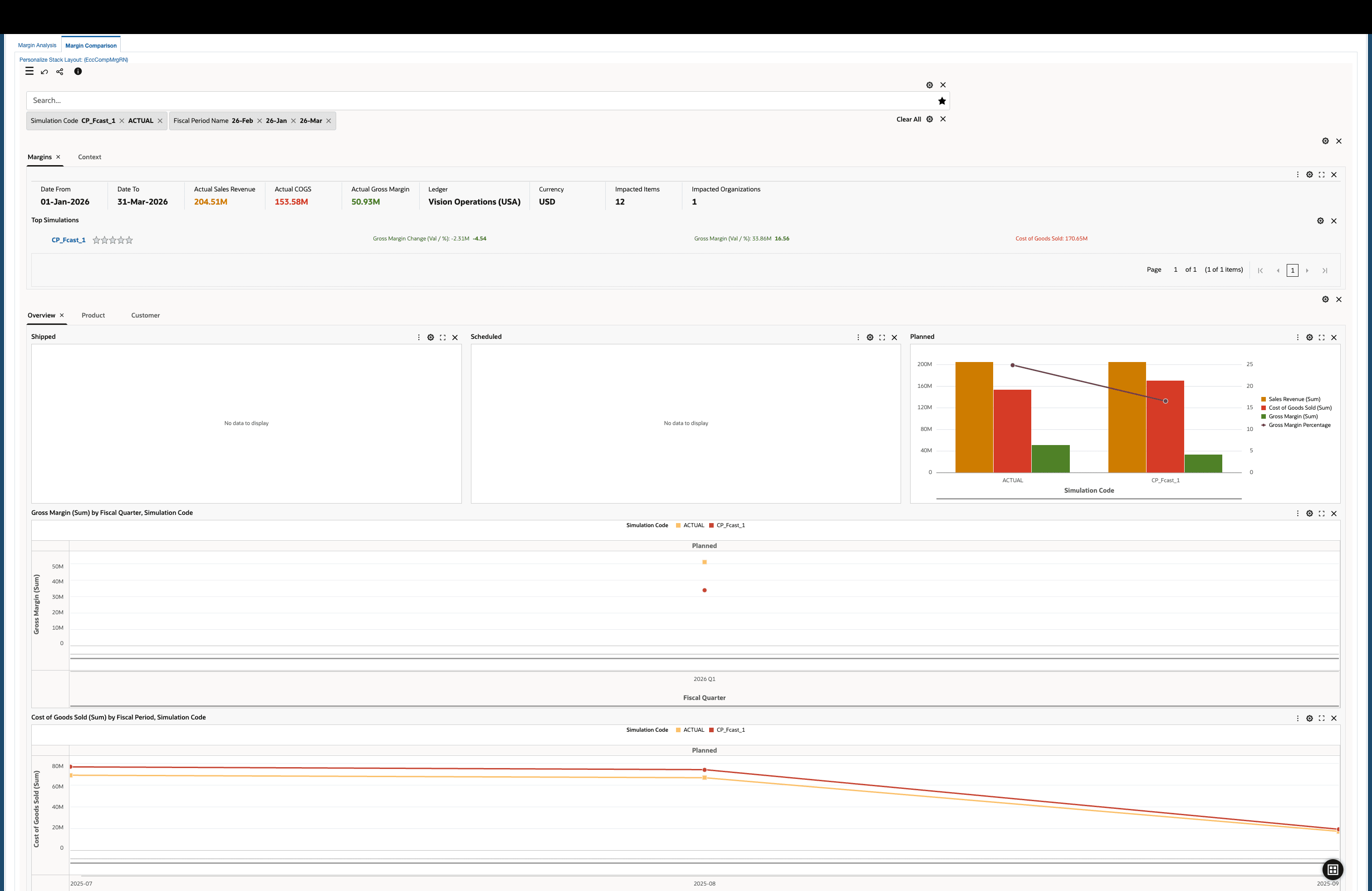
Analyze Margins using the Margin Comparison Dashboard
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips And Considerations
Retrieving cost to simulate from a pre-defined Simulation Criteria
When creating a simulation by retrieving costs from a pre-defined simulation criteria, ensure that the costs exist for the entities in the chosen criteria against the selected basis cost type for the simulation.
Control which products are displayed in the impacted items' list
Define the CMI: Simulation Impact Summary Default Category Set and use the category set to control which items you want displayed on the impacted items' list.
Key Resources
- Oracle E-Business Suite News and Information: oracle.com/ebs
- Oracle E-Business Suite Product Documentation: https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E26401_01/index.htm
- Oracle University: https://www.oracle.com/education
- Oracle Support: https://www.oracle.com/support