


|

|
|
|
|
Configuring Security
This topic includes the following sections:
For general information about configuring WebLogic Integration B2B, see Basic Configuration Tasks in Administering B2B Integration.
Configuring the SSL Protocol and Mutual Authentication
To configure WebLogic Server to use the SSL protocol and mutual authentication, complete the following steps:
Figure 3-1 Choosing a Domain
The Configuration page for WebLogic Server is displayed, shown in the following figure.
Figure 3-2 WebLogic Server Administration Console Configuration Page
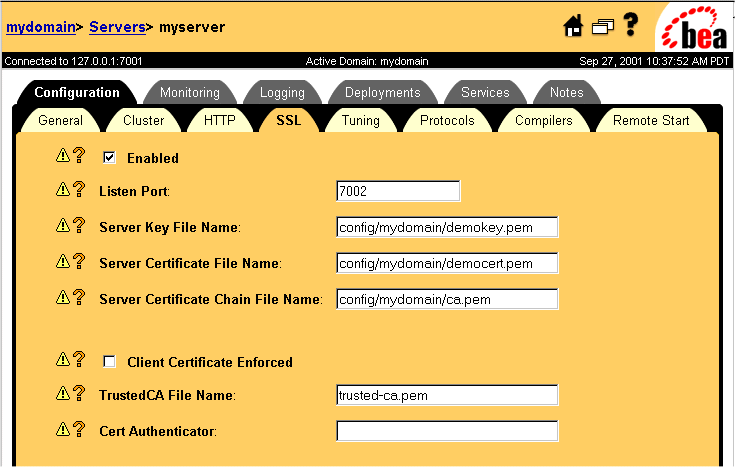
Figure 3-3 SSL Configuration Page
Table 3-1 SSL Configuration Page Fields
Configuring Access Control Lists for WebLogic Integration B2B
The access control list (ACL) for a resource determines whether a user or group can access a WebLogic Integration resource. To define ACLs, you do the following:
For a B2B resource, one or more permissions can be granted.
The ACL on the WebLogic Integration JDBC connection pool that is preset in the sample configuration shipped with WebLogic Integration has the following permissions set for the user wlcSamplesUser: reserve, shrink, and reset.
For complete information about defining ACLs, see "Defining ACLs" in Managing Security in the BEA WebLogic Server Administration Guide.
To set the ACLs on the WebLogic Integration JDBC connection pool in the samples domain:
Figure 3-4 Choosing ACLs in the Navigation Tree
The ACLs that are configured in the WebLogic Server are listed in the Access Control Lists configuration page, as shown in the following figure. Note the entry for the ACL for the WebLogic Integration JDBC connection pool.
Figure 3-5 ACL for the JDBC Connection Pool
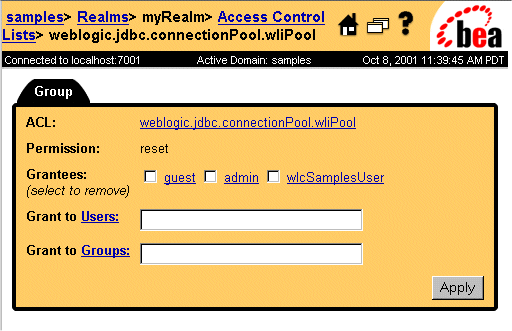
Figure 3-6 Setting Permissions for the WebLogic Integration JDBC Connection Pool
Figure 3-7 ACL Reset Dialog Box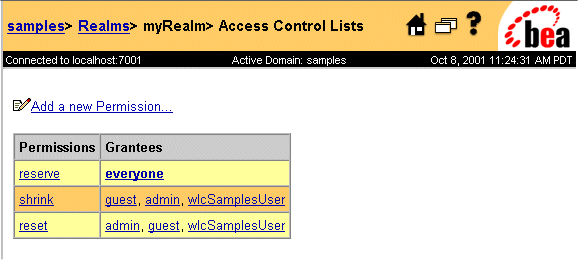
For more information about access control lists, see "Defining ACLs" in Managing Security in the BEA WebLogic Server Administration Guide.
Configuring Security for the WebLogic Integration B2B Engine
The WebLogic Integration repository contains security information about the WebLogic Integration B2B security system and the trading partners that access B2B resources. You can configure repository information either by using the WebLogic Integration B2B Console, or by specifying it in a repository data file that you then import into the repository using the Bulk Loader.
Note: If you use the Bulk Migrator utility to migrate the repository from the 1.0 or 1.0.1 releases of WebLogic Collaborate make sure the user wlcsystem is created and the correct password is included in the Bulk Loader data file. For more information about using the Bulk Migrator utility, see Migrating from WebLogic Collaborate 1.0/1.0.1 to WebLogic Integration 2.1 in Migrating to BEA WebLogic Integration Release 2.1.
For the B2B security system, you need to configure the following as required:
To configure these entities in the B2B security system, complete the following steps:
Figure 3-8 WebLogic Integration B2B Console Main Window
The B2B configuration tabs are displayed, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 3-9 B2B Configuration Tabs
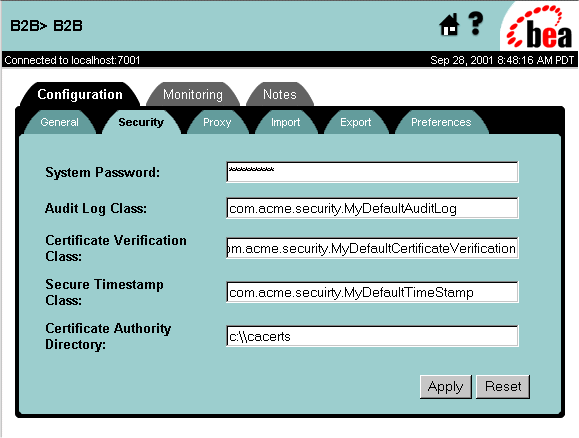
Figure 3-10 WebLogic Integration B2B Security Configuration Page
Table 3-2 Configuring the WebLogic Integration B2B Security System
Configuring Trading Partner Security
Configuring trading partner security involves setting the following for each trading partner:
The following subsections describe how to configure trading partner security for each of these components.
Note: If you use the Bulk Loader to import data into the WebLogic Integration repository, the WebLogic Server users that represent each trading partner configured in the repository are not automatically created. You need to create these WebLogic Server users manually. For more information, see Working with the Bulk Loader in Administering B2B Integration.
Configuring Trading Partner Certificates
WebLogic Integration B2B provides a means to configure the following trading partner certificates.
Table 3-3 Trading Partner Certificates Configured in WebLogic Integration B2B
Note the following general rules about configuring trading partner certificates:
%JAVA_HOME%\bin\java -classic -ms64m -ms64m -classpath %START_WL_CLASSPATH%
-Dbea.home=%BEA_HOME% -Dweblogic.home=%WL_HOME%
-Dweblogic.system.home=%WLC_SAMPLES_HOME% -Dweblogic.Domain=samples
-Dweblogic.management.password=security
-Dcloudscape.system.home=%WLC_SAMPLES_CLOUDSCAPE_HOME% -Dweblogic.Name=myserver
-Djava.security.policy=%WL_HOME%\lib\weblogic.policy
-DKey.certificate-name.password=mypassword weblogic.Server
In the preceding example, certificate-name represents the name of the certificate for which a private key password is being specified, and mypassword represents the password.
To configure trading partner certificates, complete the following steps:
Figure 3-11 Trading Partners Entry in the Navigation Tree
Figure 3-12 Accessing the Trading Partner Configuration Page
Note: In the instructions that follow, we assume that the trading partner has already been created and configured, with the exception of security parameters. For complete details about configuring trading partners in general, see Basic Configuration Tasks in Administering B2B Integration.
Figure 3-14 General Configuration Page for Trading Partner
Figure 3-15 Trading Partner Certificates Configuration Page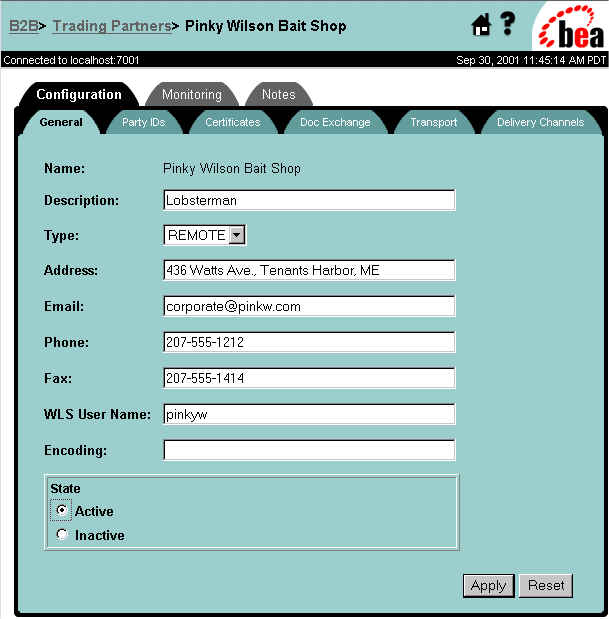
Note: The preceding figure shows configuring a remote trading partner. If the trading partner were local, an additional field would be displayed showing the private key location for the certificate name.
Table 3-4 Configuring Trading Partner Certificates
Notes: When you create a trading partner in WebLogic Integration, a WebLogic Server user is created for that trading partner at run time using the WebLogic Server username that you specify. However, when you delete a trading partner from the WebLogic Integration repository, the corresponding WebLogic Server user is not automatically deleted. When you delete a trading partner, be sure also to manually delete the corresponding WebLogic Server user.
Visit the BEA Developer Center to obtain helpful resources, such as links to sites that provide useful tools for manipulating digital certificates and private keys, which you might find useful in managing WebLogic Integration B2B security. You can reach the BEA Developer Center at the following URL:
http://developer.bea.com/index.jsp
Configuring a Secure Transport
When you configure a transport for a trading partner, you bind the trading partner's transport to a transport security protocol. For example, if a trading partner is configured to use SSL certificates, you must bind that trading partner's transport to a transport protocol that uses SSL. When a secure transport is configured, the client certificate is used for outbound SSL. Because WebLogic Integration allows only one client certificate, there is no need to select the client certificate while configuring a secure transport.
To configure a secure transport for a trading partner, complete the following steps:
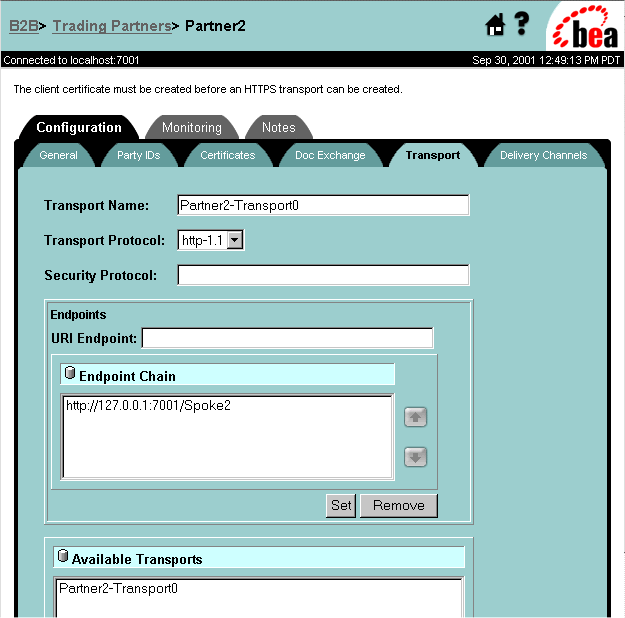
Figure 3-16 Trading Partner Transport Configuration Page
Table 3-5 Configuring the Trading Partner Transport
Configuring a Secure Delivery Channel
When you configure a trading partner's delivery channel, you have the option of making the delivery channel secure by binding it to the secure transport configured in Configuring a Secure Transport.
To configure a secure channel, complete the following steps:
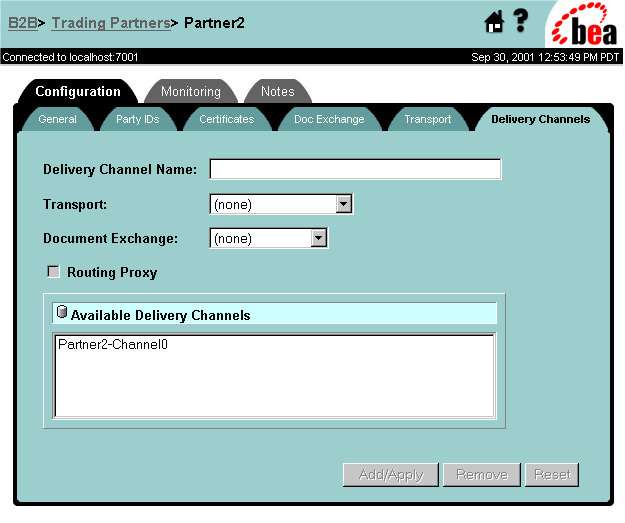
Figure 3-17 Trading Partner Delivery Channels Configuration Page
Table 3-6 Configuring a Trading Partner Delivery Channel
Configuring a Secure Document Exchange
When you configure the trading partner document exchange, you can associate a document exchange with a business protocol binding that provides digital signature support or message encryption. Digital signature support is available with all the business protocols supported in WebLogic Integration; however, message encryption is available only with the RosettaNet protocol.
To enable digital signature or message encryption support, complete the following steps:
Figure 3-18 Trading Partner Document Exchange Configuration Page
Table 3-7 Configuring a Trading Partner Document Exchange
Configuring Message Encryption
As mentioned in Introducing WebLogic Integration B2B Security, the B2B message encryption service encrypts business messages for the business protocols that require it. Currently, message encryption is supported only for the RosettaNet 2.0 protocol.
How WebLogic Integration B2B Message Encryption Works
Data encryption works by using a combination of the sender's certificate, private key, and the recipient's certificate to encode a business message. The message can then be decrypted only by the recipient using the recipient's private key.
Note: The B2B message encryption feature is controlled by licensing (Encryption/Domestic or Encryption/Export), but the decryption of a business message is not. If WebLogic Integration does not have a valid encryption license, the B2B engine disables the encryption service. However, the B2B engine can always decrypt business messages that are received.
The WebLogic Integration Release 2.1 message encryption service supports only the Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption algorithm.
The following figure shows how data encryption is performed using the public and private keys.
Figure 3-19 WebLogic Integration B2B Message Encryption Service
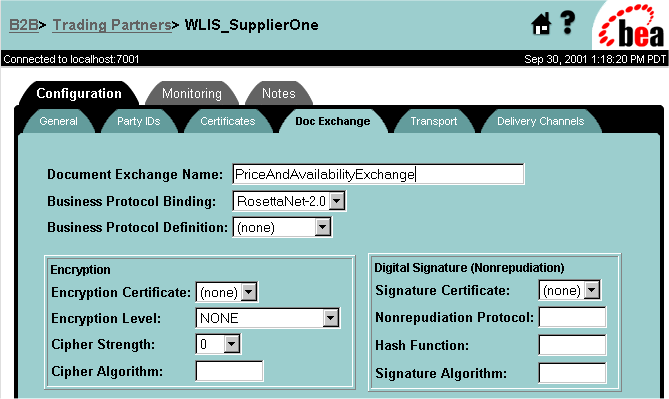
Note: To use message encryption, you must have a valid license for using the encryption service. Configuring Message Encryption To configure message encryption for business messages exchanged by trading partners in a RosettaNet 2.0-based conversation definition, complete the following steps: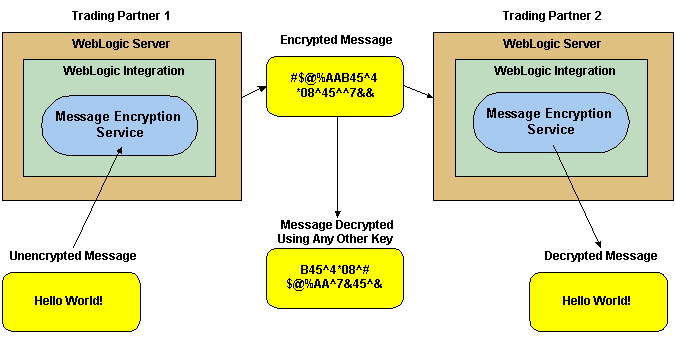
Notice that when you select a RosettaNet business protocol binding on the Doc Exchange configuration page, the Encryption box is displayed in the lower left-hand corner of that configuration page. The following figure shows the Document Exchange configuration page with the Encryption box.
Figure 3-20 Configuration Box for Message Encryption on Doc Exchange Configuration Page
Table 3-8 Message Encryption Configuration Settings
Note that the field labeled Cipher Algorithm is a nonmodifiable information field containing the name of the algorithm. With Release 2.1 of WebLogic Integration, the only value displayed in this field is RSA.
Configuring Digital Signatures for Nonrepudiation
Digital signature support (described in detail in Implementing Nonrepudiation) provides a means to prevent anyone or anything from tampering with the contents of a business message, especially when the business message is in transit between two trading partners. Digital signature support is a requirement for nonrepudiation.
If you are implementing nonrepudiation, you need to configure digital signature support in the B2B engine, which you can do by completing the following steps:
When you choose a signature certificate, notice the data displayed in the nonmodifiable fields that are associated with the signature certificate, as shown in the lower right in the following figure.
Figure 3-21 Configuring Nonrepudiation
These nonmodifiable fields are used for the following purposes.
Customizing the WLCCertAuthenticator Class
The WLCCertAuthenticator class is an implementation of the WebLogic Server CertAuthenticator class. The default implementation of the WLCCertAuthenticator class maps the digital certificate of the trading partner to the corresponding trading partner user defined in the WebLogic Integration repository. You may want to extend this functionality to use mutual authentication for users other than trading partners. For example, you may want to modify the class to map a Web browser or Java client to a WebLogic Server user.
The WLCCertAuthenticator class is invoked by WebLogic Server after an SSL connection between the trading partner and WebLogic Server has been established. The class can extract data from a digital certificate to determine the trading partner name that corresponds to the digital certificate.
The following code example, in which the WebLogic default realm for retrieving users is used, shows how the WLCCertAuthenticator class is customized:
public User authenticate(String userName, Certificate[] certs, boolean ssl)
{
String user = null;
// If not using SSL, return
if (ssl == false)
{
return null;
}
// Verify that the certificate is either a c-hub certificate or a trading partner
// certificate, then return the corresponding WLS user.
if ((user = Security.isValidWLCCertificate(certs))!= null)
{
return realm.getUser(user);
}
// Certificate is not a valid WLC certificate.
// Check here for non-WLC certificate and return the corresponding user.
}
Configuring a Certificate Verification Provider Interface
As explained in Trading Partner Certificate Verification, you use a certificate verification provider to validate a trading partner's digital certificate. If you are using a certificate verification provider (CVP), you need to configure it in the B2B Console, using the steps described in this section.
To configure a CVP:
Figure 3-22 WebLogic Integration B2B System Security Configuration Page

Note: You can load a certificate verification provider via the Bulk Loader. For more information, see Working with the Bulk Loader in Administering B2B Integration.
Configuring WebLogic Integration B2B to Use an Outbound HTTP Proxy Server
If you are using WebLogic Integration in a security-sensitive environment, you may want to use WebLogic Integration behind a proxy server. A proxy server allows trading partners to communicate across intranets or the Internet without compromising security. A proxy server is used to:
When proxy servers are configured on the local network, network traffic (SSL and HTTP) is tunneled through the proxy server to the external network. The following figure illustrates how a proxy server might be used in the WebLogic Integration environment.
Figure 3-23 Proxy Server
To configure a proxy server for WebLogic Integration, complete the following steps: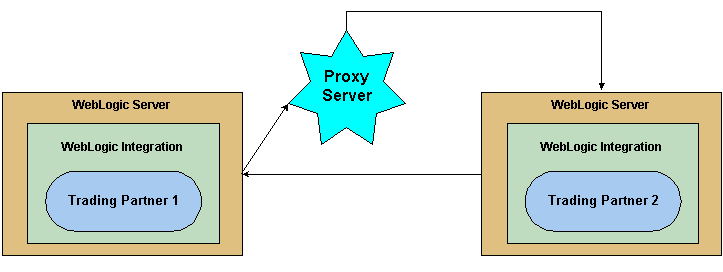
Figure 3-24 Configuration Tabs in the WebLogic Integration B2B Console
Figure 3-25 WebLogic Integration Proxy Server Configuration Page
myproxy.mycompany.com.
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "ssl.proxyHost", "read, write";
permission java.util.PropertyPermission "ssl.proxyPort", "read, write";
Configuring WebLogic Integration with a Webserver and a WebLogic Proxy Plug-In
You can configure WebLogic Integration with a webserver, such as Apache server, that is programmed to service business messages from a remote trading partner. The webserver can provide the following services:
The webserver uses the WebLogic proxy plug-in, which you can configure to provide the following services:
The following figure shows the topology of an environment that uses a webserver, the WebLogic proxy plug-in, and WebLogic Integration.
Figure 3-26 Using a Webserver and the WebLogic Proxy Plug-In
Configuring the Webserver To configure the webserver, see Configuring WebLogic Server Web Components in the BEA WebLogic Server Administration Guide. The following code example provides the segment of httpd.conf (for Apache server) for configuring the proxy plug-in: Note that in WebLogic Server 6.0, the proxy plug-in supports only one-way SSL. Because WebLogic Server hosting WebLogic Integration is configured with mutual authentication, it is important that you do not configure the proxy plug-in with SSL. WebLogic Server User Identity for the Trading Partner The WebLogic Server user identity is optional when you configure the remote trading partner. If a particular WebLogic Integration B2B deployment has stringent security requirements, we recommend the following: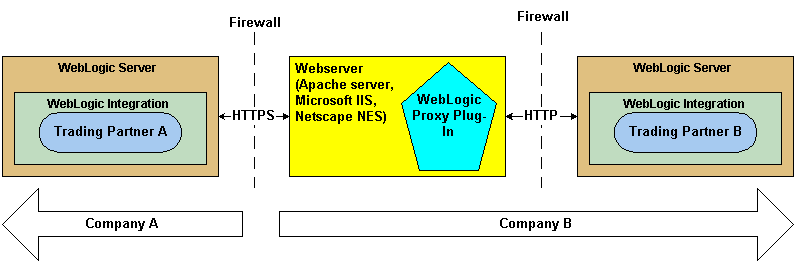
# LoadModule foo_module libexec/mod_foo.so
LoadModule weblogic_module libexec/mod_wl_ssl.<suffix>
<Location /weblogic>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
PathTrim /weblogic
WebLogicHost myhost
WebLogicPort 80
</Location>
Configuring Business Process Management Access to the WebLogic Integration Repository
If you use WebLogic Integration with the business process management component (BPM) of WebLogic Integration, note the following configuration tasks for sharing access to the WebLogic Integration repository.
You can do this by specifying the following ACLs on the WebLogic Server MBeans for the user, where user represents the name of the BPM user:
acl.access.weblogic.admin.mbean.MBeanHome=<user>
acl.lookup.weblogic.admin.mbean.MBeanHome=<user>
For information about configuring ACLs for B2B resources, see Configuring Access Control Lists for WebLogic Integration B2B.

|

|

|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2001 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|