


|

|
|
|
|
Integrating with ALE
This topic describes how to integrate SAP R/3 with SAP application linking and embedding (ALE) technology in the BEA eLink environment. It includes the following main sections:
For information about setting up ALE processing, see the following:
ALE Integration
The following topics provide important conceptual information about integrating with ALE:
Usage Scenarios for ALE Integration
Common ALE integration implementations of eLink Adapter for R/3 ALE include:
Integrating R/3 and Non-R/3 Systems
Figure 2-1 shows how eLink Adapter for R/3 ALE, in conjunction with BEA eLink Data Integration, can be used to integrate R/3 with non-R/3 systems:
Figure 2-1 Integrating R/3 and Non-R/3 Systems

In this scenario, these BEA components provide communication and data transformation services that enable the exchange of IDOC (R/3) and non-IDOC (non-R/3) data between R/3 and non-R/3 systems.
Communicating Among R/3 Logical Systems
Figure 2-2 shows how eLink Platform (called TUXEDO in this and most other diagrams) and eLink Adapter for R/3 ALE can transport IDOCs among R/3 logical systems:
Figure 2-2 Communication Among R/3 Logical Systems
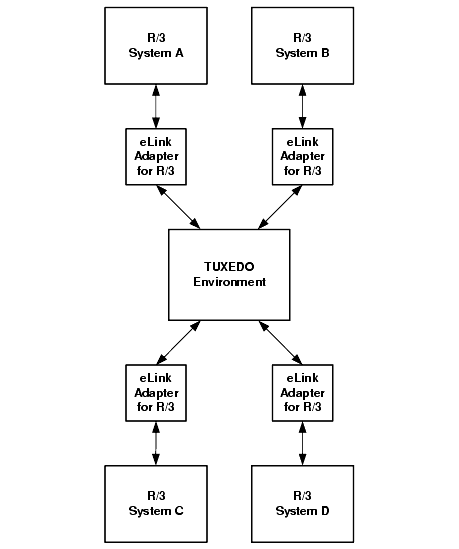
In this scenario, eLink Adapter for R/3 ALE and TUXEDO provide reliable and efficient communication services that enable the transport of IDOC packets between R/3 logical systems, thereby reducing the load on SAP communication services.
Information Flow for ALE Integration
Figure 2-3 shows the information flow for the two main ALE processes: R/3-to-eLink (outbound process) and eLink-to-R/3 (inbound process):
Figure 2-3 Overview of Information Flow for ALE Processing
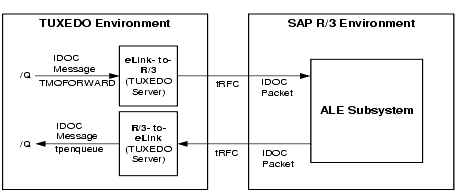
Two key concepts are used in ALE processing:
Intermediate Documents (IDOCs)
In the SAP R/3 environment, an intermediate document (IDOC) is a container for distributing R/3 application data among R/3 logical systems and for exchanging R/3 application data with non-R/3 systems.
In ALE processing, an IDOC consists of two types of records:
Each IDOC is a sequential buffer that contains one control record and one or more data records, as shown in Figure 2-4:
Figure 2-4 Structure of an ALE IDOC
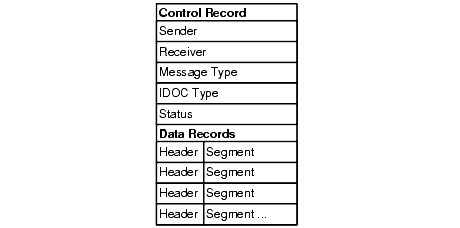
For eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs, eLink-to-R/3 validates the size and structure of control records and data records. For each IDOC, eLink-to-R/3 also verifies that the DOCNUM data in the control record matches the DOCNUM data in associated data records.
An IDOC packet is a message that contains one or more individual IDOCs, as shown in Figure 2-5:
Figure 2-5 Types of IDOC Packets

The R/3 System separately maintains status information about the creation, receipt, and processing of IDOCs. See your SAP R/3 documentation for more information about IDOCs.
In the TUXEDO environment, IDOC packets are transmitted in FML32 messages. These field definitions are specified in the cr3_ale.fml file, as described in FML32 Field Definitions in Introducing BEA eLink Adapter for R/3 ALE.
Transaction IDs (TIDs)
R/3 assigns a unique transaction ID (TID) to each IDOC packet it processes. R/3 uses TIDs to manage transactional integrity:
In the TUXEDO environment, R/3-to-eLink and eLink-to-R/3 monitor TIDs through the use of TID log files. See "Managing Transactional Integrity for eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs" and "Managing Transactional Integrity for R/3-to-eLink IDOCs" for more information.
Processing eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs
The following topics describe how to process eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs using the eLink-to-R/3 server. It includes the following topics:
eLink-to-R/3 must be properly configured before it can process IDOCs. See "Configuring the eLink-to-R/3 Server" in Configuring ALE Integration, for more information.
eLink-to-R/3 Server
eLink-to-R/3 is a TUXEDO server that submits IDOC packets to R/3. eLink-to-R/3 receives each IDOC packet as an FML32 message buffer (forwarded from a TUXEDO queue) and it submits the IDOC packet to R/3 via tRFC. eLink-to-R/3 uses a TID log to track the TIDs associated with IDOC packets to guarantee delivery to R/3 once and only once. The name of the executable for eLink-to-R/3 is cr3alein.
eLink-to-R/3 Services (CR3_SUBMIT and CR3_IDOC_IN)
eLink-to-R/3 provides two services that process eLink-to-R/3 IDOC packets:
|
Service Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CR3_SUBMIT |
Receives an incoming FML32 buffer containing an IDOC packet from a TUXEDO queue; validates the IDOC packet data; obtains a TID from R/3 for the IDOC packet; binds the TID into the IDOC packet; and queues the IDOC message into the CR3_IDOC_IN queue. |
|
CR3_IDOC_IN |
Receives the IDOC packet from the CR3_IDOC_IN queue; encodes the IDOC data for R/3; and submits the IDOC packet to R/3 for processing. |
FML32 Field Definitions for eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs
The eLink-to-R/3 uses the following FML32 field definitions in IDOC messages:
|
Field |
Data Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
CR3_IDOC |
string |
Contains an IDOC packet consisting of one or more IDOCs. |
|
CR3_TARGET_ID |
string |
Contains a data-dependent routing value. Required even if it contains only a dummy value. |
|
CR3_RFC_TID |
string |
Contains the transaction ID (TID) for the IDOC packet. |
|
CR3_IDOC_CONTROL |
string |
Contains one or more control records for the IDOC packet. |
|
CR3_IDOC_DATA |
string |
Contains one or more data records for the IDOC packet. |
These fields are defined in the cr3_ale.fml file, as described in FML32 Field Definitions in Introducing BEA eLink Adapter for R/3 ALE.
Information Flow for eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs
Figure 2-6 shows the information flow for eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs:
Figure 2-6 Information Flow for eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs
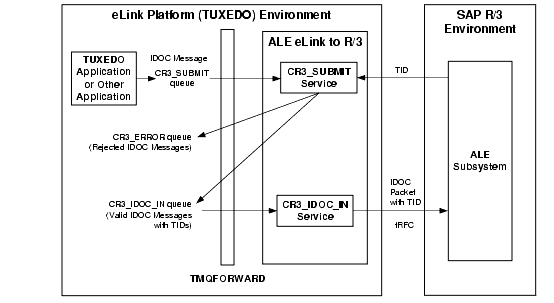
The information flow for eLink-to-R/3 proceeds in the following sequence:
eLink-to-R/3 uses a TID log file to manage transactional integrity. See "Managing Transactional Integrity for R/3-to-eLink IDOCs" later in this section for more information.
Splitting eLink-to-R/3 IDOC Packets
By default, the eLink-to-R/3 server passes an IDOC message containing multiple IDOCs to R/3 in a single packet. You can configure eLink-to-R/3 to split IDOC messages containing multiple IDOCs into individual IDOC messages, each with its own TID. For example, if an IDOC message contains six IDOCs, eLink-to-R/3 can create six separate IDOC packets, each containing a single IDOC and associated with a unique TID. Figure 2-7 shows splitting IDOC packets and queueing them into the CR3_IDOC_IN queue:
Figure 2-7 Splitting eLink-to-R/3 IDOC Packets

Splitting IDOC packets provides additional flexibility for processing eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs. However, this configuration can also increase load on the R/3 System and reduce throughput performance. For example, an IDOC packet containing six IDOCs requires two RFC calls: one to request the TID and another to submit the IDOC packet to R/3. Six IDOC packets containing a single IDOC each, however, requires twelve separate RFC calls: six to request TIDs and six to submit each IDOC packet to R/3.
See "Splitting eLink-to-R/3 IDOC Packets Containing Multiple IDOCs" in Configuring ALE Integration, for instructions.
Managing Transactional Integrity for eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs
The eLink-to-R/3 server manages transactional integrity for eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs to guarantee that it delivers an IDOC packet to R/3 once and only once. R/3 uses the TID to guarantee that it processes the IDOC packet exactly once. If an attempt to submit an IDOC packet to R/3 fails, eLink-to-R/3 retries using the same TID. eLink-to-R/3 uses a TID log file to track the transaction IDs (TIDs) that R/3 assigns to each eLink-to-R/3 IDOC packet. See "Transaction IDs (TIDs)" earlier in this document for an introduction to TIDs.
About the TID Log File Used for eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs
The TID log file used with eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs contains information about TIDs that eLink-to-R/3 has received and processed. Each row in the TID file represents the TID for a separate IDOC packet and contains three fixed-position columns of information:
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Date-Time Stamp |
Date and time at which the state of this TID was last updated in the TID log file. |
|
TID |
TID that R/3 assigned to the IDOC packet. |
|
Status |
One of the following strings:
|
The following example shows a sample TID file for eLink-to-R/3:
Tue Apr 27 14:27:40 1999 0A0201FD03F937262C600004 CONFIRMED
Tue Apr 27 14:29:39 1999 0A0201FD03F937262CD90007 CONFIRMED
Tue Apr 27 14:46:58 1999 0A0201FD03F9372630E8000A CONFIRMED
Tue Apr 27 15:52:30 1999 0A0201FD041637263FC60013 CONFIRMED
The CR3_ALEIN_TID_FILE environment variable specifies the location of the TID log file for eLink-to-R/3. See "Setting Environment Variables for eLink-to-R/3" in Configuring ALE Integration, for more information.
Use the cr3tidmanager program to manage the size and number of entries kept in TID files. See "Configuring the TID File Manager" in Configuring ALE Integration, of this guide.
Processing TIDs with eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs
Figure 2-8 shows how eLink-to-R/3 uses the TID log file to manage transactional integrity for eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs:
Figure 2-8 TID Processing for eLink-to-R/3
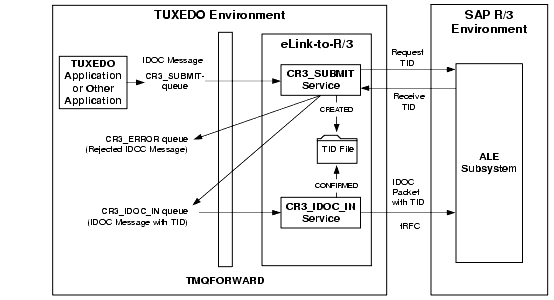
The eLink-to-R/3 IDOC process involves two transaction boundaries:
For the first transaction boundary, the information flow proceeds in the following sequence:
Second Transaction Boundary
For the second transaction boundary, the information flow proceeds in the following sequence:
Handling Problems with eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs
eLink-to-R/3 uses TUXEDO's transaction management capabilities to ensure transactional integrity for eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs. The following table lists problems that can occur with eLink-to-R/3 IDOCs:
|
Problem |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Invalid IDOC structure |
If an IDOC packet fails validation, the CR3_SUBMIT service queues the FML32 message into the CR3_ERROR queue and returns TPSUCCESS to TMQFORWARD. |
|
No CR3_TARGET_ID |
If an IDOC message contains no CR3_TARGET_ID field, the CR3_SUBMIT service queues the FML32 message into the CR3_ERROR queue and returns TPSUCCESS to TMQFORWARD. |
|
TID Not received from R/3 |
If R/3 does not return a TID, CR3_SUBMIT returns TPFAIL to TMQFORWARD, and TMQFORWARD rolls back the transaction. |
|
Send attempt to R/3 failed |
If the CR3_IDOC_IN service does not successfully send the IDOC packet to R/3 (for example, the R/3 System is down), CR3_IDOC_IN returns TPFAIL to TMQFORWARD, and TMQFORWARD rolls back the transaction. The IDOC packet remains in the CR3_IDOC_IN queue until a subsequent send attempt succeeds. |
Note: You must write an application to explicitly unqueue and handle messages in the CR3_ERROR queue.
Processing R/3-to-eLink IDOCs
The following topics describe how to process R/3-to-eLink IDOCs using the R/3-to-eLink server:
The R/3-to-eLink server must be configured properly, before it can process R/3-to-eLink IDOCs. For information about setting up R/3-to-eLink, see Configuration Quick Reference.
R/3-to-eLink Server
R/3-to-eLink is a TUXEDO server that receives IDOC packets from R/3 via transactional RFC (tRFC). R/3-to-eLink encodes each IDOC packet into an FML32 message buffer and queues it into a TUXEDO queue. R/3-to-eLink uses a TID log file to track the IDOC packets that it processes to ensure that it queues an IDOC packet from R/3 once and only once. The name of the executable for R/3-to-eLink is cr3aleout.
R/3-to-eLink uses the following FML32 field definitions in IDOC messages:
|
Field |
Data Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
CR3_IDOC |
string |
Contains a string of one or more IDOCs. |
|
CR3_TARGET_ID |
string |
Data-dependent routing value. |
|
MERCATOR_FV_IN |
string |
Either Y or N. See the BEA eLink Data Integration Option v1.x for more information. |
Information Flow for R/3-to-eLink IDOCs
Figure 2-9 illustrates the information flow for R/3-to-eLink:
Figure 2-9 Information Flow for R/3-to-eLink IDOCs
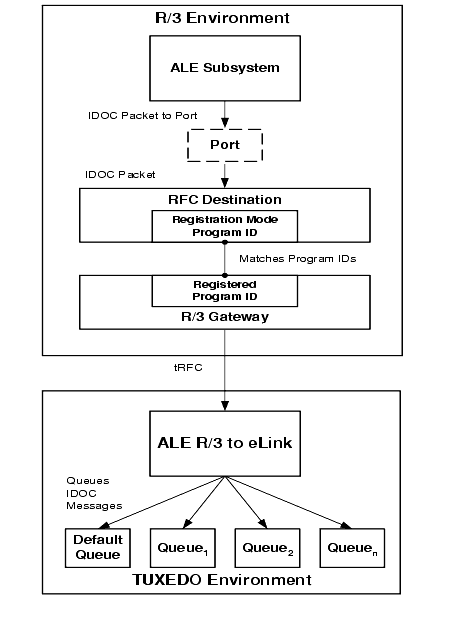
The information flow proceeds in the following sequence:
If the CR3_ALE_DEFAULT_IDOC_SPLIT environment variable is set to "Y," then R/3-to-eLink splits IDOC packets containing multiple IDOCs into separate IDOC messages, each containing a single IDOC. If the CR3_ALE_DEFAULT_IDOC_SPLIT environment variable is set to "N," then R/3-to-eLink does not split IDOC packets. It sends packets to the default queue. This process is described in detail in "Splitting R/3-to-eLink IDOC Packets Into Individual IDOCs."
If the IDOC packets are split (CR3_ALE_DEFAULT_IDOC_SPLIT = "Y"), R/3-to-eLink uses the settings in the environment file to determine the target queue for each IDOC as well as other processing options. See "Queuing R/3-to-eLink IDOCs Into Multiple Queues" for more information.
R/3-to-eLink uses a TID log file to manage transactional integrity. See "Managing Transactional Integrity for R/3-to-eLink IDOCs" later in this topic for more information.
Splitting R/3-to-eLink IDOC Packets Into Individual IDOCs
You can configure R/3-to-eLink to split IDOC packets containing multiple IDOCs into separate IDOC messages, each containing a single IDOC. By default, R/3-to-eLink encodes the entire IDOC packet into a single occurrence of the CR3_IDOC field in the message buffer, then queues the entire IDOC packet into a single message and places it in the default queue, which is defined in the CR3_ALE_DEFAULT_TARGET_ID environment variable. If you set the CR3_ALE_DEFAULT_IDOC_SPLIT environment variable to "Y," however, R/3-to-eLink will split the IDOC packet into individual IDOCs, then queue the individual IDOCs into queues as described in "Queuing R/3-to-eLink IDOCs Into Multiple Queues."
Queuing R/3-to-eLink IDOCs Into Multiple Queues
R/3-to-eLink is configured to use the R/3-to-eLink environment file (cr3aleout.env) so that it can place IDOC messages into different target queues, manage data-dependent routing, and group similar IDOCs into larger IDOCs. R/3-to-eLink makes routing and grouping decisions about individual IDOCs according to two settings specified in an IDOC's control record: the logical system ID of the target R/3 System and the IDOC message type.
If the logical system ID and message type in an individual IDOC's control record (an individual IDOC from the one that has been split) match the logical system ID and message type found in an IDOC section of cr3aleout.env, R/3-to-eLink queues it using the settings specified in the matching IDOC section of cr3aleout.env. If a matching IDOC section cannot be found, R/3-to-eLink will queue it in the default queue. This is shown in Figure 2-10:
Figure 2-10 Splitting IDOC Packets and Queuing IDOCs into Queues
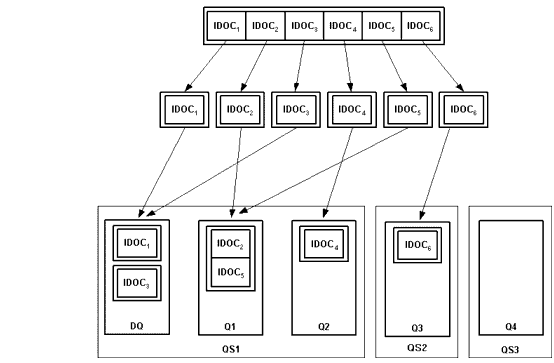
See "Setting Environment Variables for R/3-to-eLink" in Configuring ALE Integration, in this guide for more information about setting the CR3_ALE_DEFAULT_IDOC_SPLIT environment variable.
About the Destination Mapping Variables in the Environment File
The environment file, cr3aleout.env, is used to configure the environment for the R/3-to-eLink server. IDOC types are listed in the CR3_IDOC_LIST environment variable, and specific settings are made for each IDOC type. Each known IDOC type is provided with its own section of the environment file. The destination mapping settings in these sections specify the following information for each IDOC type:
For each outbound R/3-to-eLink IDOC, R/3-to-eLink searches the environment file for the logical system ID of the target R/3 System (RECIEVER_PARTNER_NUMBER) and IDOC message type (MESSAGE_TYPE) specified in the outbound IDOC's control record. If it finds an IDOC section that matches the logical system ID and message type specified in the IDOC's control record, R/3-to-eLink assigns the IDOC to the destination queue space and queue specified in the matching IDOC section of the environment file. R/3-to-eLink also processes the IDOC according to the COMPRESS flag and the Target ID (ROUTING) settings in that section.
Compressing R/3-to-eLink IDOCs
You use the COMPRESS environment variable specified in each IDOC section of the environment file to combine outbound IDOCs with matching combinations of logical system ID and IDOC message type into a single IDOC. For each outbound IDOC whose control record matches an IDOC section with regard to logical system ID and message type. If the COMPRESS variable is set to "Y", then R/3-to-eLink aggregates this IDOC with other matching IDOCs into a single, larger IDOC that it then assigns to the appropriate target queue. If the COMPRESS variable is set to "N", then R/3-to-eLink queues each outbound IDOC separately.
Setting the Data-Dependent Routing Value
You use the Target ID (ROUTING environment variable) specified in each IDOC's section of the environment file to associate an IDOC with a data-dependent routing (DDR) value. For each outbound IDOC whose control record matches an IDOC section with regard to logical system ID and message type, R/3-to-eLink adds the specified ROUTING value to the CR3_TARGET_ID FML32 field of the outbound IDOC. If no matching IDOC section is found in the environment file for that outbound IDOC, then R/3-to-eLink encodes the default DDR value, which is defined in the CR3_ALE_DEFAULT_TARGET_ID environment variable.
See "Setting the Default Data-Dependent Routing Value" in Configuring ALE Integration, in this guide for more information.
Examples of Using Destination Map Settings
The first example shows how the R/3-to-eLink server processes an IDOC packet that contains a single IDOC. Suppose the environment file contains the settings shown in Listing 2-1.
Listing 2-1 Destination Map Settings in a Sample Environment File
CR3_IDOC_LIST=MaterialMaster
[CR3_IDOC=MaterialMaster]
RECIEVER_PARTNER_NUMBER=LOGSYS1
MESSAGE_TYPE=MATMAS
COMPRESS=Y
ROUTING=DDR1
QUEUE_SPACE=QS1
QUEUE_NAME=Q1
The control record in an R/3-to-eLink IDOC named MaterialMaster specifies a target logical ID (RECIEVER_PARTNER_NUMBER) of LOGSYS and a message type (MESSAGE_TYPE) of MATMAS. Figure 2-11 shows how R/3-to-eLink would process this IDOC packet according to the settings in the sample environment file section:
Figure 2-11 Queuing a Single IDOC According to the Environment File

In this scenario, R/3-to-eLink finds that the logical ID and message type specified in the outbound IDOC's control record match the logical ID and message type settings in the MaterialMaster IDOC section of the environment file, so it sends the IDOC message to the Q1 queue in queue space QS1. R/3-to-eLink encodes the specified TargetId value ("DDR1") in the CR3_TARGET_ID FML32 field. Compression does not apply in this case, because the IDOC packet contained only one IDOC.
The second example shows how R/3-to-eLink processes an IDOC packet that contains multiple IDOCs. Suppose the environment file contains the settings shown in Listing 2-2.
Listing 2-2 Complex Destination Map Settings in a Sample Environment File
CR3_IDOC_LIST=MaterialMaster,MaterialMaster2,CustomerMaster,
VendorMaster
[CR3_IDOC=MaterialMaster]
RECIEVER_PARTNER_NUMBER=LOGSYS1
MESSAGE_TYPE=MATMAS
COMPRESS=Y
ROUTING=DDR1
QUEUE_SPACE=QS1
QUEUE_NAME=Q1
[CR3_IDOC=MaterialMaster2]
RECIEVER_PARTNER_NUMBER=LOGSYS2
MESSAGE_TYPE=MATMAS
COMPRESS=Y
ROUTING=DDR2
QUEUE_SPACE=QS1
QUEUE_NAME=Q2
[CR3_IDOC=CustomerMaster]
RECIEVER_PARTNER_NUMBER=LOGSYS3
MESSAGE_TYPE=DEBMAS
COMPRESS=N
ROUTING=DDR3
QUEUE_SPACE=QS2
QUEUE_NAME=Q3
[CR3_IDOC=VendorMaster]
RECIEVER_PARTNER_NUMBER=LOGSYS4
MESSAGE_TYPE=CREMAS
COMPRESS=Y
ROUTING=DDR4
QUEUE_SPACE=QS3
QUEUE_NAME=Q4
An R/3-to-eLink IDOC packet contains six IDOCs with the following settings in the control record of each IDOC, as shown in Table 2-5:
|
IDOC |
LogicalId |
MsgType |
|---|---|---|
|
IDOC1 |
LOGSYS1 |
CREMAS |
|
IDOC2 |
LOGSYS1 |
MATMAS |
|
IDOC3 |
LOGSYS3 |
MATMAS |
|
IDOC4 |
LOGSYS2 |
MATMAS |
|
IDOC5 |
LOGSYS1 |
MATMAS |
|
IDOC6 |
LOGSYS3 |
DEBMAS |
Figure 2-12 shows how R/3-to-eLink would process this IDOC packet according to the settings in the environment file:
Figure 2-12 Queuing Multiple IDOCs According to the Environment File

R/3-to-eLink splits the IDOC packet into individual IDOCs and queues each IDOC in the following manner:
Managing Data-Dependent Routing (DDR)
You can configure the default data-dependent routing (DDR) value that R/3-to-eLink assigns to each IDOC message (in the CR3_TARGET_ID field) that it queues. R/3-to-eLink behaves as follows:
See "Setting the Default Data-Dependent Routing Value" and "Splitting R/3-to-eLink IDOC Packets" in Configuring ALE Integration, in this guide for instructions.
Load Balancing High Volumes of R/3-to-eLink IDOCs
Multiple instances of R/3-to-eLink can register using the same program ID. For deployments that involve high volumes of IDOC packets, you can enhance system performance by balancing the load across multiple instances of R/3-to-eLink. Instances that register under the same program ID must also share the same TID file. Figure 2-13 shows multiple instances of R/3-to-eLink listening for IDOCs on the same program ID and sharing the same TID file:
Figure 2-13 Multiple Instances of R/3-to-eLink Sharing the Same Program ID
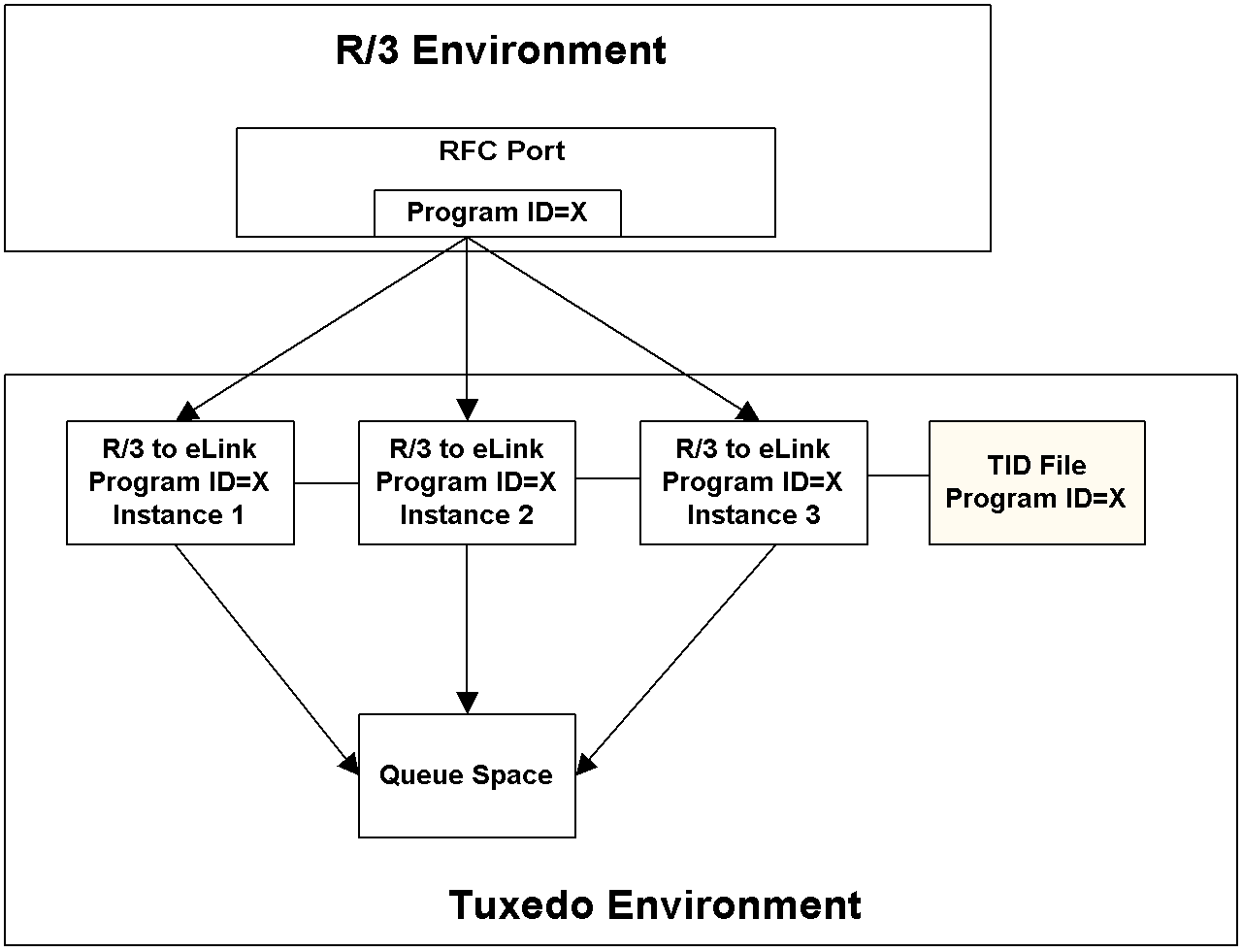
The number of R/3-to-eLink instances should match the anticipated number of IDOC packets that R/3 sends concurrently to port. For example, if R/3 sends five IDOC packets concurrently to port during peak loads, you should load five instances of R/3-to-eLink.
See "Configuring Load Balancing" in Chapter 6, Configuring ALE Integration," in this guide.
Registering Multiple Program IDs
If R/3 is configured to send R/3-to-eLink IDOCs to different program IDs, you can configure the R/3-to-eLink server to handle these IDOCs by running multiple instances of R/3-to-eLink using different program IDs. You must make sure that all instances sharing the same program ID also share the same TID file, and that all instances sharing the same TID file also share the same program ID.
Note: Instances that register under different program IDs must not share the same TID file.
Figure 2-14 shows two groups of instances of R/3-to-eLink, each of which is listening for IDOCs on a shared program ID and sharing the same TID file:
Figure 2-14 Multiple Instances of R/3-to-eLink Using Different Program IDs

See "Configuring Load Balancing for R/3-to-eLink" in Configuring ALE Integration, of this guide.
Managing Transactional Integrity for R/3-to-eLink IDOCs
The R/3-to-eLink server manages transactional integrity for R/3-to-eLink IDOCs to ensure that an IDOC packet has been queued successfully. R/3-to-eLink uses a TID log file to track the transaction IDs (TIDs) associated with the IDOC packets it processes to ensure that it queues an IDOC packet from R/3 exactly once. See "Transaction IDs (TIDs)" later in this topic for an introduction to TIDs.
About the TID Log File Used for R/3-to-eLink IDOCs
R/3-to-eLink uses a TID file to track the IDOC packets it processes to ensure that it queues an IDOC packet once and only once. The R/3 System assigns a TID to each R/3-to-eLink IDOC packet.
The TID file for R/3-to-eLink is a log of all the TIDs that R/3-to-eLink has received and processed. Each row in the TID file represents the TID for a separate IDOC packet and contains three fixed-position columns of information:
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Date-Time Stamp |
Date and time at which the TID log file was last updated. |
|
TID |
TID that R/3 assigned to the IDOC packet. |
|
State |
The processing state. One of the following strings:
|
The following example shows a sample TID file for R/3-to-eLink:
Tue Apr 27 14:27:36 1999 0A0201FD03F937262C5B0001 CONFIRMED
Tue Apr 27 14:29:38 1999 0A0201FD03E937262CD70004 CONFIRMED
Tue Apr 27 14:46:56 1999 0A0201FD03F9372630E60009 CONFIRMED
Tue Apr 27 15:50:21 1999 0A0201FD03E837263F98003F CONFIRMED
The CR3_ALEOUT_TID_FILE environment variable specifies the location of the TID log file for R/3-to-eLink. See "Setting Environment Variables for R/3-to-eLink" in Configuring ALE Integration, in this guide for more information.
Use the cr3tidmanager program to manage the size and number of entries kept in TID files. See "Configuring the TID File Manager" in Configuring ALE Integration, of this guide.
Processing TIDs with R/3-to-eLink IDOCs
Figure 2-15 shows how R/3-to-eLink uses the TID log file to manage transactional integrity for R/3-to-eLink IDOCs:
Figure 2-15 TID Processing for R/3-to-eLink

The information flow proceeds in the following sequence:
Handling Problems with R/3-to-eLink IDOCs
R/3-to-eLink uses TUXEDO's transaction management capabilities to ensure transactional integrity for R/3-to-eLink IDOCs. Figure 2-6 lists problems that can occur with R/3-to-eLink IDOCs:
|
Problem |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Unable to Lock the TID File |
The TID file might be locked by another instance of R/3-to-eLink or the TID File Manager. R/3-to-eLink retries the lock attempt. After a configurable number of retry attempts, R/3-to-eLink returns a lock error to R/3. R/3 then attempts to retry the operation until it succeeds or stops trying. |
|
Unable to Update the TID File |
The file might be corrupted. If R/3-to-eLink can lock the TID file but cannot update it, R/3-to-eLink retries the lock attempt. After a configurable number of retry attempts, R/3-to-eLink returns a lock error to R/3. R/3 then attempts to retry the operation until it succeeds or stops trying. |
|
R/3-to-eLink cannot queue an IDOC message(s) |
One or more target queues might be full. R/3-to-eLink returns an SAP exception to R/3, and R/3 instructs R/3-to-eLink to roll back the transaction. R/3 will subsequently resubmit the IDOC packet to R/3-to-eLink. |

|
|

|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2000 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|