6 Configuring the Domain for a Standalone Agent
- Creating the Database Schema
Ensure that you have created the required schema in your database for your standalone agent. - Creating a Standalone Agent in the Master Repository with ODI Studio
This topic explains how to create a standalone or Java EE agent for a topology. - Configuring the Standalone Domain for the Standalone Agent
Learn how to create a domain for your standalone agent. - Adding Libraries to a Standalone or Standalone Collocated Agent
After configuring a standalone or standalone collocated agent, you can specify additional libraries if required. - Starting a Standalone or Standalone Collocated Agent Using Node Manager
Start Node Manager, then start the standalone or standalone collocated agent. - Starting a Standalone or Standalone Collocated Agent Without Node Manager
Start a standalone or standalone collocated agent without Node Manager, use theagentcommand. - Performing Next Steps
Learn about domain administration and configuration, and other tasks that prepare your Oracle Data Integrator environment for development.
6.1 Creating the Database Schema
Ensure that you have created the required schema in your database for your standalone agent.
Before you can configure the topology for your standalone agent, make sure you have created the necessary schema in your database. See Creating the Master and Work Repository Schemas for instructions.
6.2 Creating a Standalone Agent in the Master Repository with ODI Studio
This topic explains how to create a standalone or Java EE agent for a topology.
A physical agent corresponds to a single standalone agent or a Java EE agent. A physical agent should have a unique name in the topology.
As part of its startup sequence, an agent connects to the Master Repository to see if there is a physical agent defined with its name. If it finds its entry, the agent continues with startup and, once started, it reads all the scheduled jobs of itself from the repository and starts processing.
If there is no physical agent entry for an agent, then the agent startup fails.
To create an agent using ODI Studio, see Creating an Agent in the Master Repository with ODI Studio.
6.3 Configuring the Standalone Domain for the Standalone Agent
Learn how to create a domain for your standalone agent.
For more information on other methods available for domain creation, see Additional Tools for Creating, Extending, and Managing WebLogic Domains.
This topic includes the following t:asks:
- Starting the WebLogic Server Configuration Wizard
The WebLogic Server Configuration Wizard is the tool you use to configure your domain. - Navigating the Configuration Wizard Screen to Create the Domain
Learn how to use the WebLogic Server Configuration Wizard to create a domain.
6.3.1 Starting the WebLogic Server Configuration Wizard
The WebLogic Server Configuration Wizard is the tool you use to configure your domain.
To begin domain configuration, navigate to the ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/common/bin directory and start the WebLogic Server Configuration Wizard.
On UNIX operating systems:
./config.sh
On Microsoft Windows operating systems:
config.cmd
6.3.2 Navigating the Configuration Wizard Screen to Create the Domain
Learn how to use the WebLogic Server Configuration Wizard to create a domain.
To create and configure the domain for the topology:
-
On the Configuration Type screen, select Create a New Domain.
In the Domain Location field, specify your Domain home directory.
It is recommended that you locate your Domain home in accordance with the directory structure summarized in Understanding the Recommended Directory Structure, where the Domain home is located outside the Oracle home directory. This directory structure will help you avoid issues when you need to upgrade or reinstall your software.
Tip:
More information about the Domain home directory can be found in Choosing a Domain Home.
More information about the other options on this screen can be found in Configuration Type.
-
On the Templates screen, select the following template:
Oracle Data Integrator - Standalone Agent
-
On the JDK Selection screen, select the JDK on your system that is certified for use with Oracle Fusion Middleware.
-
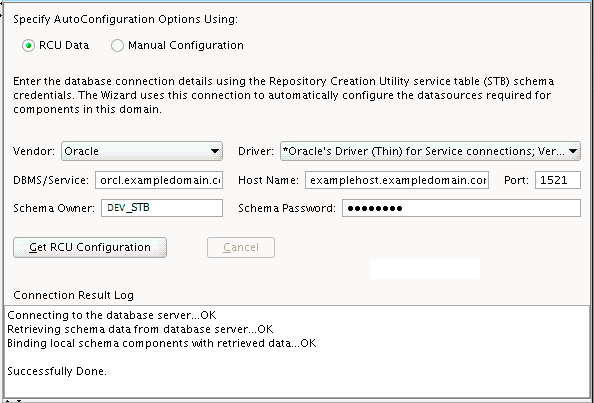
Select RCU Data to activate the fields on this screen. The RCU Data option instructs the Configuration Wizard to connect to the database and Service Table (STB) schema to automatically retrieve schema information for the schemas needed to configure the domain.
Note:
If you choose to select Manual Configuration on this screen, you will have to manually fill in the parameters for your schema on the JDBC Component Schema screen.
After selecting RCU Data, fill in the following fields:
Field Description DBMS/Service
Enter the database DBMS name, or service name if you selected a service type driver.
Host Name
Enter the name of the server hosting the database.
Port
Enter the port number on which the database listens.
Schema Owner
Schema Password
Enter the user name and password for connecting to the database's Service Table schema. This is the schema user name and password that was specified for the Service Table component on the "Schema Passwords" screen in RCU (see Creating the Database Schema).
The default user name is
prefix_STB, whereprefixis the custom prefix that you defined in RCU.Click RCU Data when you are finished specifying the database connection information. The following output in the Connection Result Log indicates that the operation succeeded:
Connecting to the database server...OK Retrieving schema data from database server...OK Binding local schema components with retrieved data...OK Successfully Done.
Tip:
More information about the RCU Data option can be found in Understanding the Service Table Schema.
More information about the other options on this screen can be found in Datasource Defaults.
-
Verify that the values on the JDBC Component Schema screen are correct for all schemas. If you selected RCU Data on the previous screen, the schema table should already be populated appropriately.
Tip:
For high availability environments, see the following sections in High Availability Guide for additional information on configuring data sources for Oracle RAC databases:
More information about the other options on this screen can be found in JDBC Component Schema.
-
Use the JDBC Component Schema Test screen to test the datasource connections you have just configured.
A green check mark in the Status column indicates a successful test. If you encounter any issues, see the error message in the Connection Result Log section of the screen, fix the problem, then try to test the connection again.
Tip:
More information about the other options on this screen can be found in Test Component Schema.
-
Use the System Component screen to create a new ODI system component. Click Add and do the following:
-
Under System Component, you can either use the default ODI component (
OracleDIAgent1) name, or specify a name of your choice. -
Under Component Type, ensure that ODI is selected from the drop-down list.
Tip:
More information about the options on this screen can be found in System Components in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
-
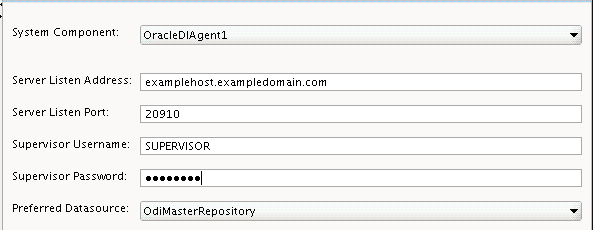
Use the ODI Server Configuration screen to configure access to your ODI server:
Field Description System Component
Select the ODI system component (
OracleDIAgent1).Server Listen Address
Specify the IP address of the server where the ODI server should listen. Do not use "localhost."
Server Listen Port
Enter the port number on which ODI server listens.
Supervisor Username
Specify
SUPERVISORas the user name.Supervisor Password
Specify the Supervisor user password, as specified during schema creation.
Preferred Datasource
Use the default
OdiMasterRepository; do not change this field.Tip:
More information about the options on this screen can be found in ODI Server Configuration.
-
The Node Manager screen can be used to select the type of Node Manager you want to configure, along with the Node Manager credentials.
Select Per Domain as the Node Manager type, then specify the Node Manager credentials. You will be asked for these credentials when starting your system component with the
startComponentcommand.Tip:
More information about the options on this screen can be found in Node Manager.
More information about the types of Node Manager can be found in Node Manager Overview.
-
The Configuration Summary screen contains the detailed configuration information for the domain you are about to create. Review the details of each item on the screen and verify that the information is correct.
You can go back to any previous screen if you need to make any changes, either by using the Back button or by selecting the screen in the navigation pane.
Domain creation will not begin until you click Create.
Tip:
More information about the options on this screen can be found in Configuration Summary.
Click Finish to terminate the Configuration Wizard.
6.4 Adding Libraries to a Standalone or Standalone Collocated Agent
After configuring a standalone or standalone collocated agent, you can specify additional libraries if required.
-
Set the environment variable
ODI_ADDITIONAL_CLASSPATHto locate additional jars before starting the agent. For example:ODI_ADDITIONAL_CLASSPATH=/share/libs/mytool.jar:/share/libs/drivers/mydriver.jar -
Do one the following:
- Copy the additional libraries to the
DOMAIN_HOME/libdirectory. The ODI standalone and standalone collocated agents will automatically add these libaries to the agent’s classpath. - Edit the
DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/components/ODI/Agent Name/bin/instance.sh/cmdcommand to add the libraries to theODI_POST_CLASSPATHvariable.
- Copy the additional libraries to the
6.5 Starting a Standalone or Standalone Collocated Agent Using Node Manager
Start Node Manager, then start the standalone or standalone collocated agent.
Note:
If you have not yet configured the physical agent in the master repository, go to Creating an Agent in the Master Repository with ODI Studio.
- Starting Node Manager
Learn how to start the Node Manager for your domain. - Starting a Standalone or Standalone Collocated Agent
6.5.1 Starting Node Manager
Learn how to start the Node Manager for your domain.
To start your domain Node Manager, go to the DOMAIN_HOME/bin directory.
On UNIX operating systems, start the Node Manager using nohup and nm.out as an example output file:
nohup ./startNodeManager.sh > nm.out&
On Windows operating systems, run:
startNodeManager.cmd
Note:
On Windows operating systems, Oracle recommends configuring Node Manager to run as a startup service. This allows Node Manager to start up automatically each time the system is restarted.
For more information, see Running Node Manager as a Startup Service .
For information about additional Node Manager configuration options, see Administering Node Manager for Oracle WebLogic Server.
6.5.2 Starting a Standalone or Standalone Collocated Agent
To start an ODI standalone agent when using Node Manager:
-
Go to the
DOMAIN_HOME/bindirectory. -
Start the agent:
-
(UNIX)
./startComponent.sh OracleDIAgent1 -
(Windows)
startComponent.cmd OracleDIAgent1
-
-
At the prompt, enter the Administrator password for the domain.
To verify that your agent was started successfully, go to the following URL in your browser:
http://examplehost.exampledomain.com:port/oraclediagent
6.6 Starting a Standalone or Standalone Collocated Agent Without Node Manager
Start a standalone or standalone collocated agent without Node Manager, use the agent command.
To start a standalone agent without Node Manager:
-
Go to the
DOMAIN_HOME/bindirectory. -
Start the agent:
-
(UNIX)
./agent.sh -NAME=OracleDIAgent1 -
(Windows)
agent.cmd -NAME=OracleDIAgent1
where
-NAMEmust be entered in all capital letters, and the name of the agent (in this example,OracleDIAgent1) is case-sensitive. -
6.7 Performing Next Steps
Learn about domain administration and configuration, and other tasks that prepare your Oracle Data Integrator environment for development.
Performing Basic Administrative Tasks contains basic administration tasks. You should familiarize yourself with the tasks described in this section and perform them as needed to verify that your domain is properly configured.
Performing Additional Domain Configuration Tasks contains additional domain configuration tasks that take advantage of additional Oracle Fusion Middleware products and features.
Preparing Oracle Data Integrator for Development contains common tasks to help prepare your Oracle Data Integrator environment for development.
Preparing Your Environment For High Availability contains important tasks to help prepare your environment to move to a highly available environment.