Elastic Pool Operations
When you create an elastic pool in Autonomous AI Database, your instance becomes the pool leader. Instances that you add to an existing pool become pool members. The operations you can perform depend on your role as a leader or member.
Topics:
- Create an Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to create an elastic pool in an existing Autonomous AI Database instance. - Create an Elastic Pool While Provisioning or Cloning an Instance
You can create or join an elastic pool when you provision or clone an Autonomous AI Database instance. - Create a Dedicated Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to create a dedicated elastic pool using an existing Autonomous AI Database instance. - Create a Dedicated Elastic Pool While Provisioning or Cloning an Instance
You can create or join an elastic pool when you provision or clone an Autonomous AI Database instance. - Enable a Dedicated Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to convert an elastic pool into a dedicated elastic pool. - Join an Existing Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to join an existing elastic pool. - Join an Elastic Pool While Provisioning or Cloning an Instance
You can create or join an elastic pool when you provision or clone an Autonomous AI Database instance. - Change the Elastic Pool Shape
Shows the steps for the pool leader to change the elastic pool shape for an existing elastic pool. - Change a Dedicated Elastic Pool Storage
Shows steps to modify the pool storage (TB) of a dedicated elastic pool. - Manage Dedicated Elastic Pool Patching
Shows steps to patch and resume a dedicated elastic pool patching. - List Elastic Pool Members
Shows the steps for the pool leader to list elastic pool members. - Remove Pool Members from an Elastic Pool
As an elastic pool member you can remove yourself from an elastic pool. As an elastic pool leader you can remove pool members from an elastic pool. - As Pool Leader Remove Members from an Elastic Pool
An elastic pool leader can remove pool members from an elastic pool. - Disable a Dedicated Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to disable a dedicated elastic pool. - Terminate an Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to terminate an elastic pool. Only the pool leader can terminate an elastic pool.
Create an Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to create an elastic pool in an existing Autonomous AI Database instance.
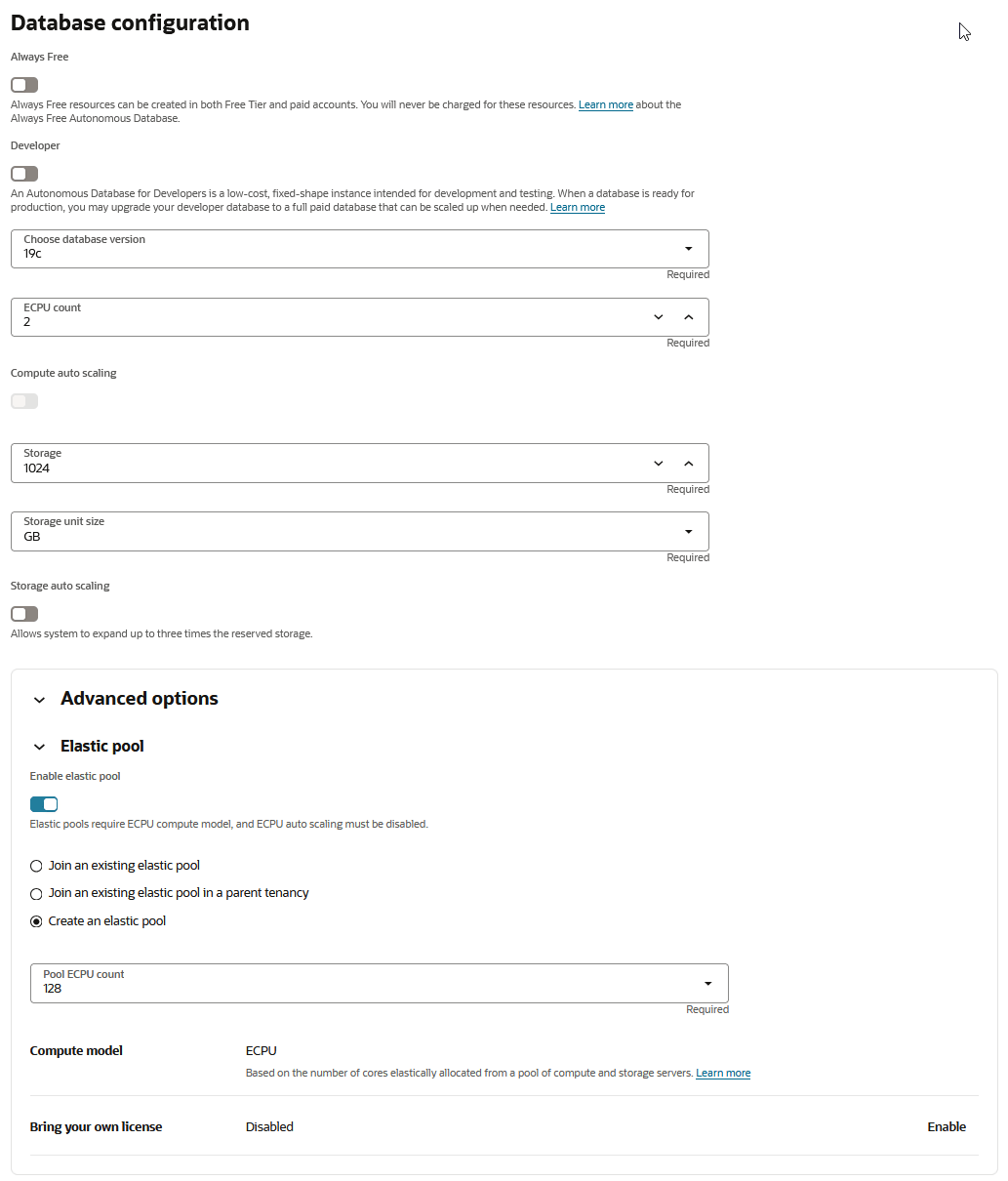
To create an elastic pool the instance must use the ECPU compute model.
-
Open the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console by clicking the
 next to Cloud.
next to Cloud.
-
From the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure left navigation menu click Oracle Database and then click Autonomous AI Database.
-
On the Autonomous AI Databases page select an Autonomous AI Database from the links under the Display name column.
To create an elastic pool:
When you click Apply the Lifecycle state changes to Updating. After the Lifecycle state changes to Available the changes apply immediately.
After you create an elastic pool, click More actions and select Manage resource allocation to display the elastic pool information. In the Manage resource allocation area, the Elastic pool field shows Enabled, the Pool role field shows Leader, and the Pool ECPU count field shows the pool size you selected. It also displays the Total compute capacity and the Available compute capacity fields.
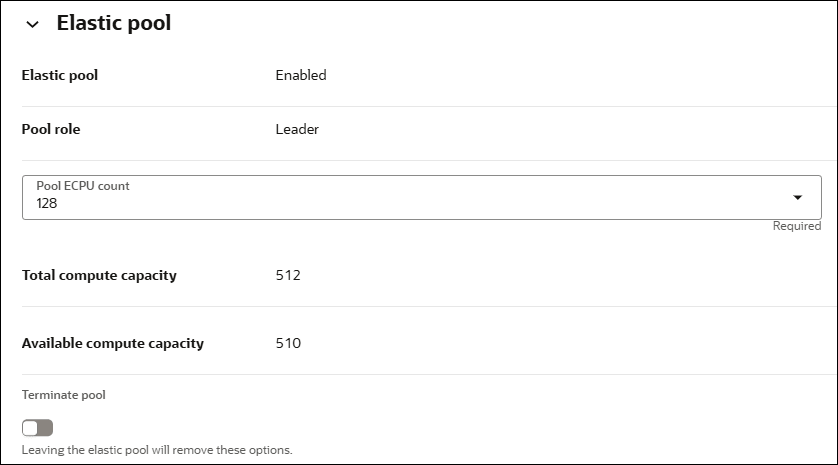
Description of the illustration adb_elastic_pool_leader.png
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Create an Elastic Pool While Provisioning or Cloning an Instance
You can create or join an elastic pool when you provision or clone an Autonomous AI Database instance.
See Provision an Autonomous AI Database Instance for details on how to create an Autonomous AI Database for your workload type using the Create Autonomous AI Database dialog.
See Clone an Autonomous AI Database Instance or Clone an Autonomous AI Database from a Backup for details on cloning.
See Join an Elastic Pool While Provisioning or Cloning an Instance for details on joining an elastic pool while provisioning or cloning.
To create an elastic pool the instance must use the ECPU compute model.
To create an elastic pool while provisioning or cloning:
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Create a Dedicated Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to create a dedicated elastic pool using an existing Autonomous AI Database instance.
To create an elastic pool the instance must use the ECPU compute model.
Once the dedicated elastic pool is created, you can view its details from the Manage resource allocation dialog, after the database lifecycle state changes to Available. In the Elastic pool section, Elastic pool shows Enabled with Pool role as Leader.
You can also see the Pool ECPU count and Pool Storage (TB) values along with the Total compute capacity and the Available compute capacity values.
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Create a Dedicated Elastic Pool While Provisioning or Cloning an Instance
You can create or join an elastic pool when you provision or clone an Autonomous AI Database instance.
To create an elastic pool the instance must use the ECPU compute model.
- Launch the Create Autonomous AI Database or Clone Autonomous AI Database page, depending on whether the database is being provisioned or cloned.
- In the Database configuration section:
- Complete the remaining provisioning or cloning steps, as specified in Provision an Autonomous AI Database Instance, Autonomous AI Database, or Clone an Autonomous AI Database Instance, as appropriate.
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Enable a Dedicated Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to convert an elastic pool into a dedicated elastic pool.
Once the dedicated elastic pool is created, you can view its details from the Manage resource allocation dialog, after the database lifecycle state changes to Available.
In the Elastic pool section, Elastic pool shows enabled with Pool role as Leader.
You can also see Pool ECPU count and Pool Storage (TB) values along with Total compute capacity, Available compute capacity, Total pool storage (TB) and Available pool storage (TB).
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
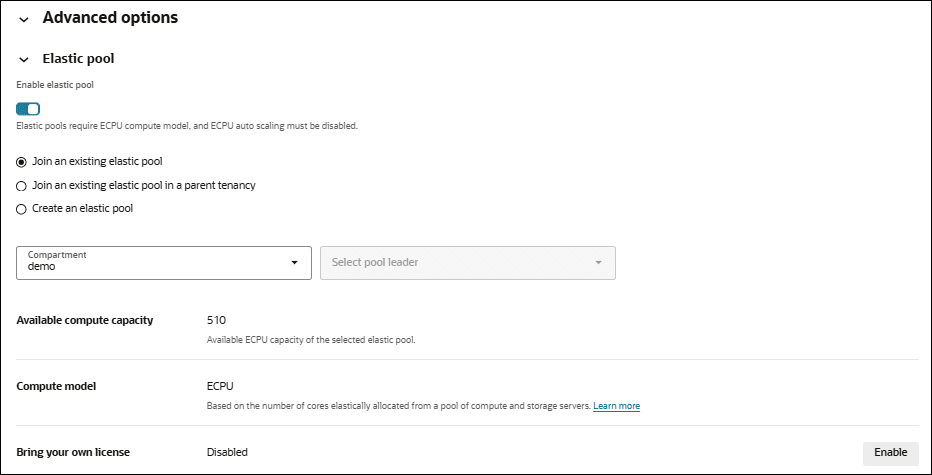
Join an Existing Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to join an existing elastic pool.
To join an elastic pool, the following is required for the Autonomous AI Database instance:
-
The instance must use the ECPU compute model.
See Compute Models in Autonomous AI Database for more information.
-
Auto scaling must be disabled.
-
The instance must not be a member of an elastic pool.
To join an elastic pool:
When you click Apply the Lifecycle state changes to Updating. After the Lifecycle state changes to Available the changes apply immediately.
After you create an elastic pool, click More actions and select Manage resource allocation to see the elastic pool details. In the Manage resource allocations area, under Elastic pool, the Elastic pool field shows Enabled, the Pool role field shows Member, and the Elastic pool leader field shows a link to the pool leader. It also displays the Total compute capacity and the Available compute capacity fields.
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Join an Elastic Pool While Provisioning or Cloning an Instance
You can create or join an elastic pool when you provision or clone an Autonomous AI Database instance.
See Provision an Autonomous AI Database Instance for details on how to create an Autonomous AI Database for your workload type using the Create Autonomous AI Database dialog.
See Clone an Autonomous AI Database Instance or Clone an Autonomous AI Database from a Backup for details on cloning.
See Create an Elastic Pool While Provisioning or Cloning an Instance for details on creating an elastic pool while provisioning or cloning.
To join an elastic pool the instance must use the ECPU compute model.
To join an existing elastic pool while provisioning or cloning:
Complete the remaining provisioning or cloning steps, as specified in Provision an Autonomous AI Database Instance, Clone an Autonomous AI Database Instance, or Clone an Autonomous AI Database from a Backup.
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Change the Elastic Pool Shape
Shows the steps for the pool leader to change the elastic pool shape for an existing elastic pool.
Only a pool leader can modify the pool shape.
To change the shape of an elastic pool (update the pool size):
Decreasing the CPU allocation, Pool ECPU count, to a value that cannot accommodate all the members of the elastic pool is not allowed.
For example, for an elastic pool with a Pool ECPU count of 256 ECPUs and a pool capacity of 1024 ECPUs: If the elastic pool contains eight (8) Autonomous AI Database instances with 80 ECPUs each for a total of 640 ECPUs, the elastic pool leader cannot decrease the Pool ECPU count to 128 ECPUs. In this case, if the pool size were reduced to 128 ECPUs, the pool capacity would be 512 ECPUs, which is less than the total allocation for the pool members (640 ECPUs).
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Change a Dedicated Elastic Pool Storage
Shows steps to modify the pool storage (TB) of a dedicated elastic pool.
Only a pool leader can modify the dedicated elastic pool storage (TB).
- The new value of Pool storage (TB) is not greater than the storage already used by the pool members, while scaling down.
- The new value of Pool storage (TB) is within the tenancy limits.
- The dedicated elastic pool's patching is not in a paused state.
To change a dedicated elastic pool storage:
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Manage Dedicated Elastic Pool Patching
Shows steps to patch and resume a dedicated elastic pool patching.
- Pause the pool's patching for up to four (4) weeks, except for the security patches.
- Resume a previously paused patching for a dedicated elastic pool, at any time from the OCI console. Once resumed, the subsequent patching occurs in your scheduled window.
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
List Elastic Pool Members
Shows the steps for the pool leader to list elastic pool members.
To list elastic pool members:
This shows the list of elastic pool members for the leader Autonomous AI Database instance.
If you click ![]() at the end of a row in the list, you can select an action to perform for
the member. The possible actions are:
at the end of a row in the list, you can select an action to perform for
the member. The possible actions are:
-
View details: Shows the member's Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console
-
Copy OCID: Copies the member's Autonomous AI Database instance OCID.
-
Remove from pool: Brings up a dialog where you can confirm to remove the Autonomous AI Database instance from the pool.
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Remove Pool Members from an Elastic Pool
As an elastic pool member you can remove yourself from an elastic pool. As an elastic pool leader you can remove pool members from an elastic pool.
Perform the following prerequisite steps as necessary:
-
Open the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console by clicking the
 next to Cloud.
next to Cloud.
- From the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure left navigation menu click Oracle Database and then click Autonomous AI Database.
-
On the Autonomous AI Databases page select an Autonomous AI Database from the links under the Display name column.
As a pool member, you can remove your instance from an elastic pool:
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
As Pool Leader Remove Members from an Elastic Pool
An elastic pool leader can remove pool members from an elastic pool.
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Disable a Dedicated Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to disable a dedicated elastic pool.
Once the dedicated elastic pool is disabled, it converts into a traditional elastic pool and you can view its details from the Manage resource allocation dialog, after the database lifecycle state changes to Available.
In the Elastic pool section, Elastic pool shows enabled with Pool role as Leader.
You can also see Pool ECPU count along with Total compute capacity and Available compute capacity
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations
Terminate an Elastic Pool
Shows the steps to terminate an elastic pool. Only the pool leader can terminate an elastic pool.
Terminating an elastic pool is only allowed when there are no pool members in the elastic pool.
-
Open the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console by clicking the
 next to Cloud.
next to Cloud.
- From the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure left navigation menu click Oracle Database and then click Autonomous AI Database.
- On the Autonomous AI Databasees page select the Autonomous AI Database that is the pool leader from the links under the Display Name column.
To terminate an elastic pool:
- On the Autonomous AI Database Details page, click More actions and select Manage resource allocation.
- In the Elastic pool area, select Terminate pool.
- Click Apply to terminate the elastic pool.
When you click Apply, the Lifecycle state changes to Updating. After the Lifecycle state changes to Available the changes apply immediately.
Parent topic: Elastic Pool Operations