Cloud
This topic explains the required steps to connect to Exadata VM Cluster, Exadata Database, and Autonomous AI Database.
- Obtain Exadata Infrastructure Networking Details
- From the Oracle Database@AWS dashboard, select Exadata VM clusters. From the resource list, select the VM cluster name link.
- Expand the Virtual machines section to review details about your virtual machines.
- Select the specific Virtual machine name link of the VM you want to connect.
- Take a note of the Private IP address from the Summary section.
Connect to the Exadata VM Cluster (using SSH)
This topic explains the required steps to create an Amazon EC2 instance within the same VPC as Exadata VM Cluster, generate an SSH key pair and configure connectivity to Exadata VM Cluster through the OCI console.- Create an Amazon EC2 Linux Instance
- Create an Amazon EC2 Linux instance in a VPC peered with an ODB Network where your Exadata VM Cluster resides.
- Assign an Elastic IP ( Public IP) to your Amazon EC2 instance.
- Download and securely store the SSH private key (
.pem) file that is generated during the Amazon EC2 instance creation process.
- Connect to Amazon EC2
- Based on your operating system, complete the following substeps:
- Mac OS:
- Run the following command from your terminal to change your directory to the location where your PEM key is stored:
cd /path/to/your/pem/file - Run the following command from your terminal to modify the permissions of your
.pemfile to restrict access:chmod 400 DemoClient.pemNote
Replace theDemoClient.pemwith your file name before running the command. - Run the following command to use the Elastic IP to connect to Amazon EC2 instance.
ssh -i DemoClient.pem ec2-user@<EC2-Elastic-IP>Note
Replace<EC2-Elastic-IP>with the Elastic IP or public IP of your Amazon EC2 instance before running the command. - Once you log into your Amazon EC2 instance, run the following command on the Amazon EC2.
- Run the following command from your terminal to change your directory to the location where your PEM key is stored:
- Windows:
- Run the following command from your PowerShell or Command Prompt to change your directory to the location where your
.pemfile is stored:cd "C:\path\to\your\pem\file" - Check the permissions. This step is optional.
Note
Windows doesn’t use thechmodcommand. Hoewever, you can ensure that only your user account has access to the PEM file. Right-click the file, select Properties, and then navigate to the Security tab to adjust the permissions. - Run the following
SSHcommand.ssh -i DemoClient.pem ec2-user@<EC2-Elastic-IP>Note
- Replace the
DemoClient.pemwith your file name before running the command. - Replace
<EC2-Elastic-IP>with the Elastic IP or public IP of your Amazon EC2 instance before running the command.
- Replace the
- Once you log into your Amazon EC2 instance, run the following command on the Amazon EC2.
- Run the following command from your PowerShell or Command Prompt to change your directory to the location where your
- Mac OS:
- Based on your operating system, complete the following substeps:
- Connect from Amazon EC2 to Exadata VM Cluster Using SSH
- Copy your Exadata VM Cluster's private key into the Amazon EC2 instance.
- Change your directory to the location where your private key file is copied.
- Run the following command from your terminal to change the permissions of your private key to give only the owner read access and restrict access for all other users and groups.
chmod 400 DemoExadataVm1.pemNote
Replace theDemoExadataVm1.pemwith your file name before running the command. - Run the following command to connect to your VM using the Private IP address of your cluster.
ssh -i ~/DemoExadataVm1.pem <exadata_user>@<Exadata-VM-Private-IP>Note
- Replace
<exadata_user>with your user information that you have for your Exadata before running the command. - Replace
<Exadata-Private-IP>with your Private IP address of Exadata VM Cluster before running the command.
- Replace
- Add a New Rule to the Security Group
- From the AWS console, select the Amazon EC2 service.
- From the Instances section, select the Instances tab.
- From the Instances list, select the Instance ID link, and then select the Security tab.
- Expand the Outbound section, and then select the Outbound rules.
- Select the outbound rule that you are using, and then select the Edit outbound rules button.
- From the Edit outbound rules page, complete the following substeps:
- From the Type dropdown list, select Custom TCP.
- Enter
1521into the Port Range field. - From the Destination dropdown list, select Custom, and then enter your CIDR range
- The Description field is optional. You can enter a description which helps to identify it easier.
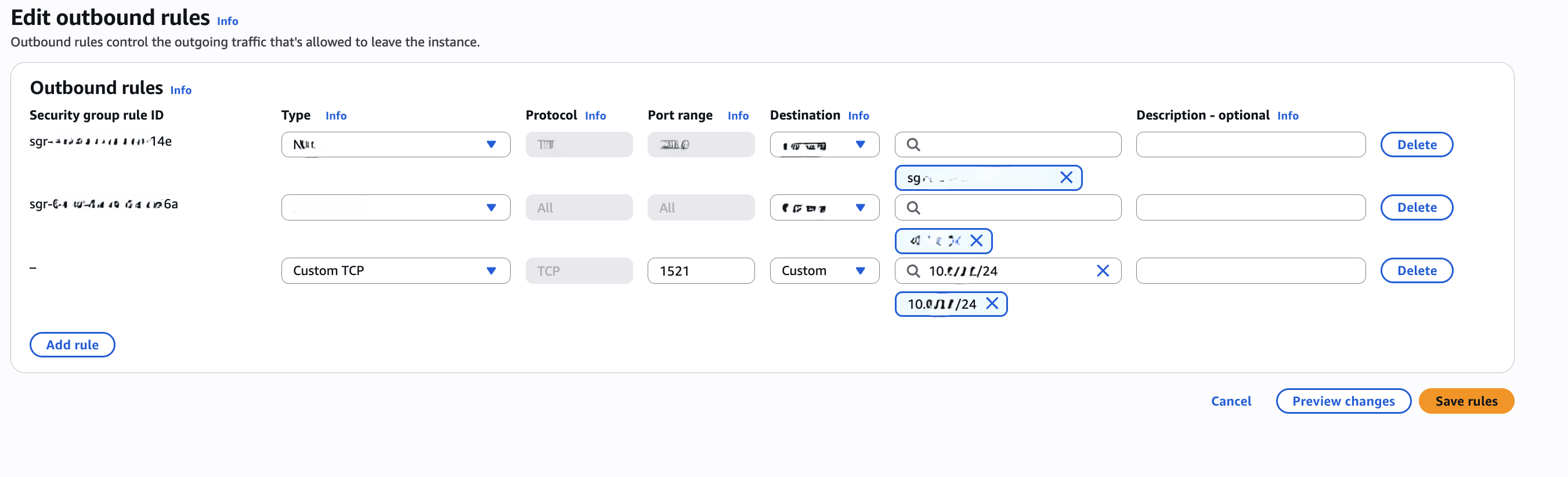
- Review your information, and then select the Save Rules button.
To learn how to add Egress rule for Amazon EC2 windows security group, see Configure security group rules.
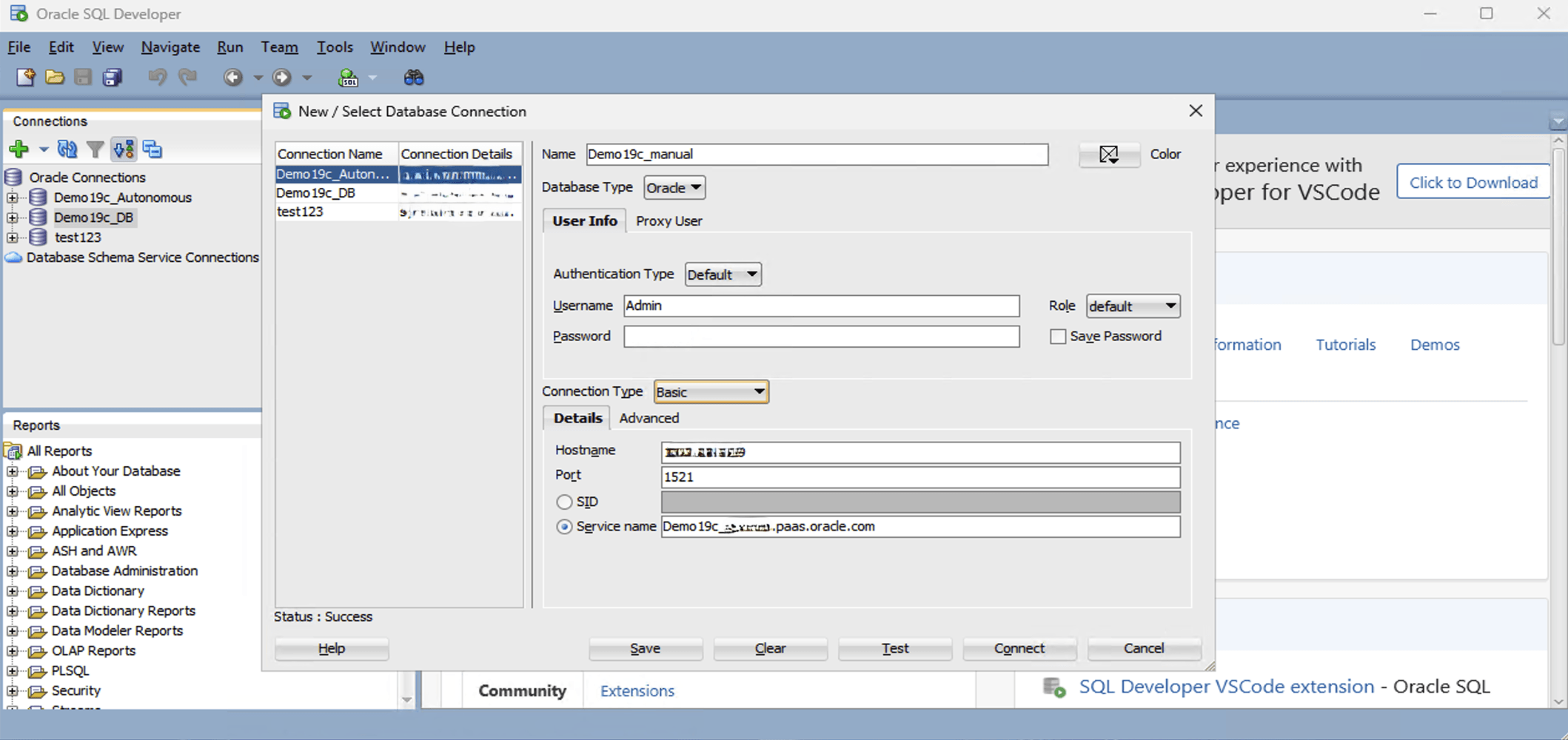
Connect from SQL Developer to Exadata Database- Ensure your Windows EC2 instance can reach the Exadata Database Server
- Test basic connectivity. Since ping won’t work (as it uses ICMP, not TCP), you can use tools like
tnsping, ortelnetto port 1521/1522, or test with SQL*Plus.
- Launch the SQL Developer application and select the + icon to create a new database connection.
- To configure SQL Developer, complete the following substeps:
-
- In the Name field, enter the Name to use for this database connection.
- In the Database Type field, select Oracle.
- In the Username field, enter the name of the user for whom this database connection is being created. For example, you can enter ADMIN.
- In the Password field, enter the password of the user.
- In the Role field, select the default role to assign to the user.
- Select the Save Password checkbox if your security rules allow.
- In the Connection Type field, select the Basic option as your database connection type.
- Enter the Hostname information by providing your Exadata Database private IP address.
- You can enter 1521 as the Port information or provide your listener port.
- Enter a descriptive Service name.
- Select the Test button. The Status at the bottom of the connections list should show Success. If the connection is not successful, the wallet may be out of date or the Exadata Database may not be running.
- Once the connection is successful, select the Save button.
-
- Prerequisites:
- To connect to Autonomous AI Database from SQL Developer, ensure that the EC2 instance has an egress rule allowing outbound traffic on port 1521.
- Download and install SQL Developer on the Amazon EC2 instance.
There are two ways to connect to your Autonomous AI Database:- Using a Wallet import.
- Using manual TNS configuration.
- Using a Wallet Import
- To download the Wallet, complete the following substeps:
- Navigate to the OCI console, select Oracle Database, and then select Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Infrastructure.
- From the left menu, select Autonomous AI Database, and then select your Compartment.
- From the list, select the database that you want to connect.
- Select the Database connection button, and then select the Download wallet button.
- On the Download wallet page, enter a wallet password in the Password field and confirm the password in the Confirm password field.
- Select Download to save the client security credentials zip file. By default the file name is:
Wallet_databasename.zip. You can save this file as any file name you want.
- To transfer the wallet to Amazon EC2, complete the following substeps:
- Upload the
Wallet_<dbname>.zipfile to your Amazon EC2 Windows instance.Note
You can use RDP file copy, WinSCP, Amazon S3, or any other secure method. - Save the file an accessible directory. For example:
C:\ADB_Wallet\
- Upload the
- To extract the wallet, complete the following substeps:
- Right-click the
.zipfile, and then select Extract All. - Make sure that the folder contain the following files:
cwallet.ssoewallet.p12sqlnet.oratnsnames.oratnsnames.oratnsnames_connection_string.txttruststore.jks
- Right-click the
- To review
tnsnames.ora, complete the following substeps:- Launch the
tnsnames.orafile in Notepad. - Note the service names. For example :
<dbname>_high = (description= (address=(protocol=tcps)(port=1522)(host=<adb_host>)) (connect_data=(service_name=<dbname>_high.adb.<region>.oraclecloud.com)) (security=(ssl_server_dn_match=yes)))
These service names (
_low, _medium, _high, _tpurgent) correspond to workload profiles. - Launch the
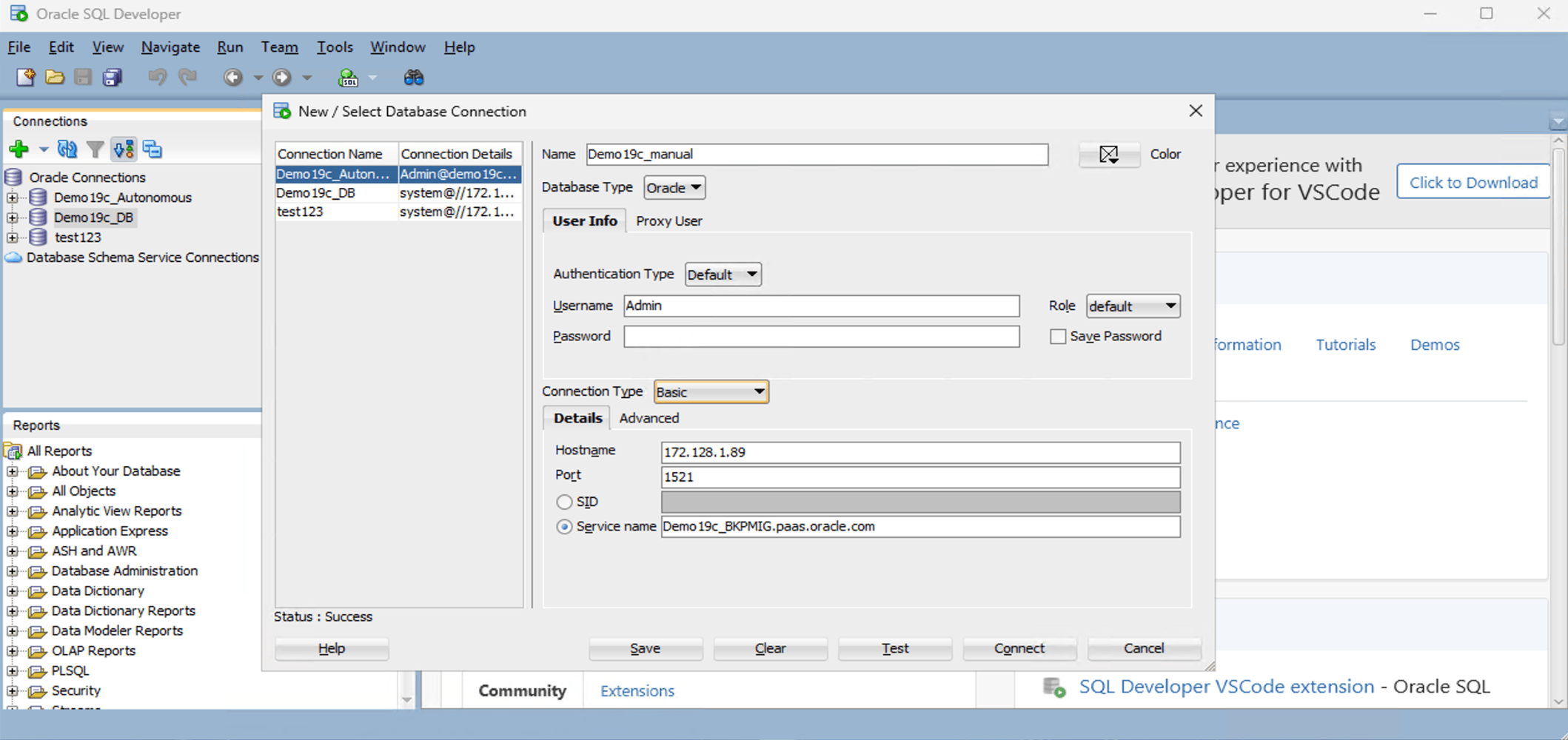
- To configure SQL Developer, complete the following substeps:
-
- In the Name field, enter the Name to use for this database connection.
- In the Database Type field, select Oracle.
- In the Username field, enter the name of the user for whom this database connection is being created. For example, you can enter ADMIN.
- In the Password field, enter the password of the user.
- In the Role field, select the default role to assign to the user.
- Select the Save Password checkbox if your security rules allow.
- In the Connection Type field, select the Cloud Wallet option as your database connection type.
- From the Configuration File dropdown list, select your wallet that you previously downloaded.
- From the Service dropdown list, select your service that you are using.
- Select the Test button to test that the data your provided will allow the specified user to connect to the database.
Note
The Status must show the Success message. If the connection is not successful, it may be because the wallet is out of date or your ADB is not currently running. - When it is complete, select the Save button, and then select the Connect button.
-
- To download the Wallet, complete the following substeps:
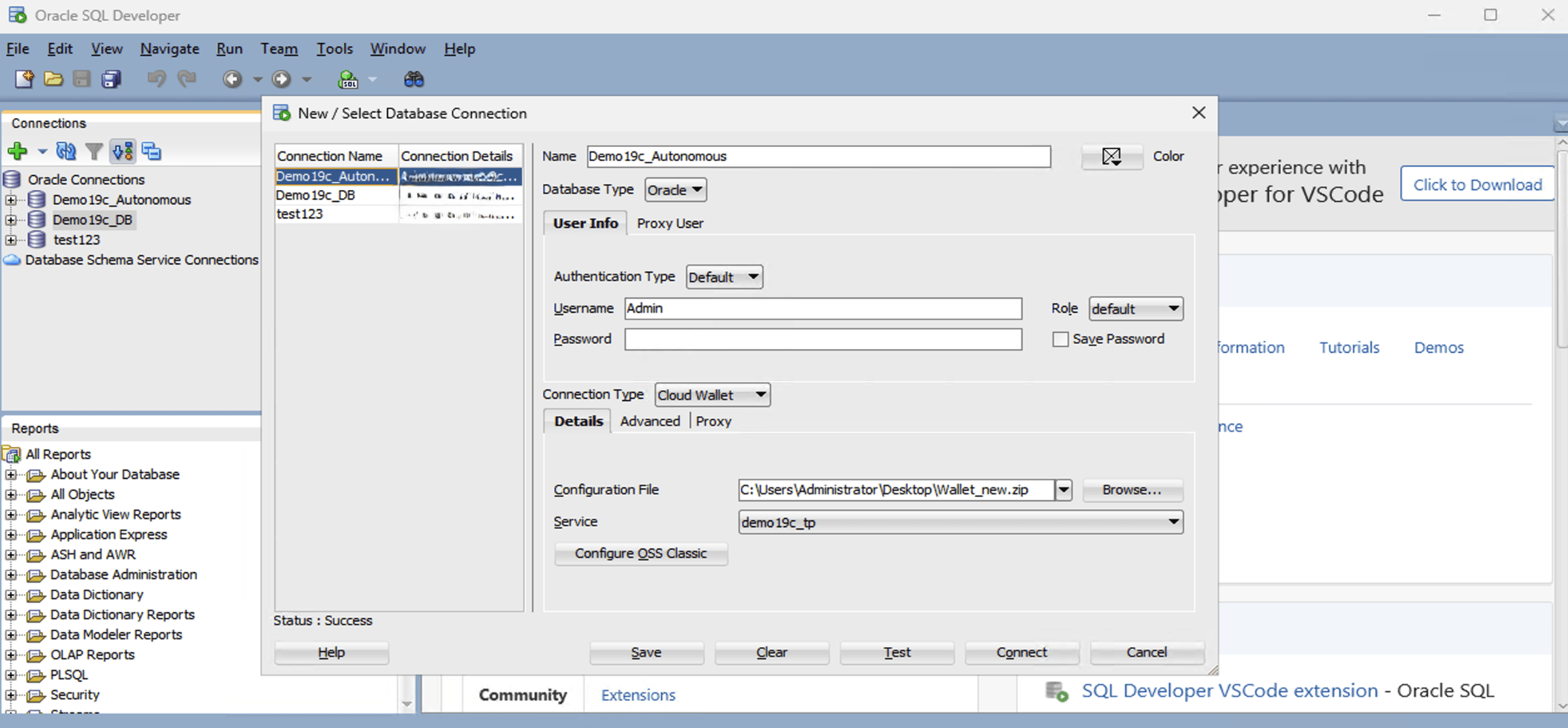
- Using Manual TNS ConfigurationNote
There are prerequisites that must be completed for the manual connection. You need to complete the following:- You must obtain the IP address, and database service name to connect. For more information, see Cloud.
- You must obtain the service name from the
tnsnames.orafile. For more information, see Step 4 in the Using a Wallet Import section.
- Launch the Oracle SQL Developer application, and then select the green plus (+) button .
- To configure your database connection, complete the following substeps:
- In the Name field, enter the Name to use for this database connection.
- In the Database Type field, select Oracle.
- In the Username field, enter the name of the user for whom this database connection is being created. For example, you can enter ADMIN.
- In the Password field, enter the password of the user.
- In the Role field, select the default role to assign to the user.
- Select the Save Password checkbox if your security rules allow.
- In the Connection Type field, select the Basic option as your database connection type.
- From the Details tab, enter your Hostname, Port and Service name.
- Select the Test button to test that the data your provided will allow the specified user to connect to the database.
Note
The Status must show the Success message. If the connection is not successful, it may be because the wallet is out of date or your Exadata is not currently running. - When it is complete, select the Save button, and then select the Connect button.