8 Using Multipathing for Efficient Storage
Multiple paths to storage devices provide connection redundancy, failover capability, load balancing, and improved performance. Device-Mapper Multipath (DM-Multipath) is a multipathing tool that enables you to represent multiple I/O paths between a server and a storage device as a single path.
Device Multipathing Sample Setup
You would typically configure multipathing on a system that can access storage on a Fibre Channel-based storage area network (SAN), or on an iSCSI initiator if redundant network connections exist between the initiator and the target.
Figure 8-1 shows a simple DM-Multipath configuration where two I/O paths are configured between a server and a disk on a SAN-attached storage array:
-
Between host bus adapter
hba1on the server and controllerctrl1on the storage array. -
Between host bus adapter
hba2on the server and controllerctrl2on the storage array.
Figure 8-1 DM-Multipath Mapping of Two Paths to a Disk over a SAN
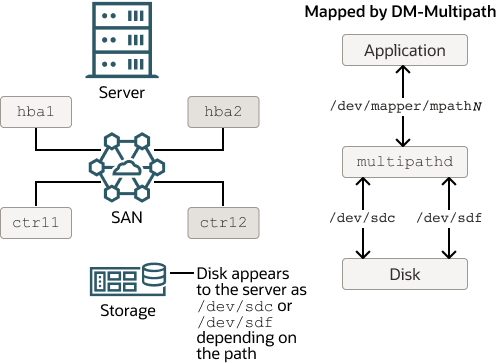
Without DM-Multipath, the system treats each path as being
separate even though both paths connect to the same storage
device. DM-Multipath creates a single multipath device,
/dev/mapper/mpathN
,
that subsumes the underlying devices,
/dev/sdc and /dev/sdf.
The multipathing service (multipathd) handles
I/O from and to a multipathed device in one of the following
ways:
- Active/Active
-
I/O is distributed across all available paths, either by round-robin assignment or dynamic load-balancing.
- Active/Passive (standby failover)
-
I/O uses only one path. If the active path fails, DM-Multipath switches I/O to a standby path. This is the default configuration.
Note:
DM-Multipath can provide failover in the case of path failure, such as in a SAN fabric. Disk media failure must be handled by using either a software or hardware RAID solution.
The naming of multipath devices is managed by multipathing's
user_friendly_names property in the multipath.conf file.
If set to no, then the devices are named based on their World Wide
Identifiers (WWIDs) in /dev/mapper/WWID
. WWIDs are unique to their respective devices.
If the property is set to yes, the devices
are mapped as
/dev/mapper/mpathN
,
where N is the multipath group
number. In addition, you can use the alias
attribute to assign meaningful names to the devices. See
Working With the Multipathing Configuration File.
To check the status of user_friendly_names and other DM-multipath settings,
issue the mpathconf command, for example:
sudo mpathconf
Information similar to the following is displayed:
multipath is enabled find_multipaths is enabled user_friendly_names is enabled dm_multipath modules is loaded multipathd is running
Alternatively, you can view the settings in
/etc/multipath.conf.
You can use the multipath device in
/dev/mapper to reference the storage in the
same way as you would any other physical storage device. For
example, you can configure it as an LVM physical volume, file
system, swap partition, Automatic Storage Management (ASM) disk,
or raw device.
Configuring Multipathing
-
Install the
device-mapper-multipathpackage.sudo dnf install device-mapper-multipath
-
Activate the basic configuration settings of the multipathing feature.
sudo mpathconf --enable --with_multipathd y
This command also creates the
/etc/multipath.conffile. -
(Optional) To know the status of multipathing, type:
sudo mpathconf
-
Edit
/etc/multipath.confas required.For details, see Working With the Multipathing Configuration File.
To display the current multipath configuration, run multipath -ll:
sudo multipath -ll
The command displays output similar to the following, when multipath is configured properly:
mpath1(360000970000292602744533030303730) dm-0 SUN,(StorEdge 3510|T4 size=20G features=‘0’ hwhandler=‘0’ wp=rw |-+- policy=‘round-robin 0’ prio=1 status=active | ‘- 5:0:0:2 sdb 8:16 active ready running ‘-+- policy=‘round-robin 0’ prio=1 status=active ‘- 5:0:0:3 sdc 8:32 active ready running
The sample output shows that
/dev/mapper/mpath1 subsumes two paths
(/dev/sdb and /dev/sdc) to
20 GB of storage in an active/active configuration using
round-robin I/O path selection. The WWID that identifies the
storage is 360000970000292602744533030303730
and the name of the multipath device under
sysfs is dm-0.
For more information, see the mpathconf(8),
multipath(8),
multipathd(8),
multipath.conf(5), and
scsi_id(8) manual pages.
Working With the Multipathing Configuration File
Through the /etc/multipath.conf file, you can add a combination of
definitions that customizes multipathing according to your system environment setup. You can
obtain a commented example configuration from
/usr/share/doc/device-mapper-multipath/multipath.conf.
The /etc/multipath.conf file is divided into the following typical
sections:
-
defaults -
Defines default multipath settings, which can be overridden by settings in the
devicessection. In turn, definitions in thedevicessection can be overridden by settings in themultipathssection. -
blacklist -
Defines devices that are excluded from multipath topology discovery. Excluded devices cannot be subsumed by a multipath device.
The example shows different ways that you can use to exclude devices: by WWID (
wwid) and by device name (devnode). -
blacklist_exceptions -
Defines devices that are included in multipath topology discovery, even if the devices are implicitly or explicitly listed in the
blacklistsection. -
multipaths -
Defines settings for a multipath device that's identified by its WWID.
The
aliasattribute specifies the name of the multipath device as it will appear in/dev/mapperinstead of a name based on either the WWID or the multipath group number. -
devices -
Defines settings for individual types of storage controller. Each controller type is identified by the
vendor,product, and optionalrevisionsettings, which must match the information insysfsfor the device.To add a storage device that DM-Multipath doesn't list as being supported, obtain the vendor, product, and revision information from the
vendor,model, andrevfiles under/sys/block/device_name/device.
The following entries in /etc/multipath.conf
would be appropriate for setting up active/passive multipathing
to an iSCSI LUN with the specified WWID.
defaults {
user_friendly_names yes
uid_attribute ID_SERIAL
}
multipaths {
multipath {
wwid 360000970000292602744533030303730
}
}In this standby failover configuration, I/O continues through a remaining active network interface if a network interface fails on the iSCSI initiator.
Note:
If you edit /etc/multipath.conf, restart
the multipathd service to make it re-read
the file:
sudo systemctl restart multipathd
For more information about configuring entries in
/etc/multipath.conf, refer to the
multipath.conf(5) manual page.