5 Using OpenSCAP to Scan for Vulnerabilities
WARNING:
Oracle Linux 7 is now in Extended Support. See Oracle Linux Extended Support and Oracle Open Source Support Policies for more information.
Migrate applications and data to Oracle Linux 8 or Oracle Linux 9 as soon as possible.
This chapter describes how to use OpenSCAP to scan your Oracle Linux system for security vulnerabilities.
About SCAP
The Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP) provides an automated, standardized methodology for managing system security, including measuring and managing system vulnerability, and evaluating policy compliance against security standards such as the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA). The U.S. government content repository for SCAP standards is the National Vulnerability Database (NVD), which is managed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Oracle Linux provides the following SCAP packages for Oracle Linux 7:
-
openscap-utils -
The
openscap-utilspackage contains command-line tools that use the OpenSCAP library. This package previously included the oscap command-line configuration and vulnerability scanner, but this is now made available separately in theopenscap-scannerpackage. Theopenscap-scannerpackage is installed as a dependency when you install theopenscap-utilspackage. -
openscap-scanner -
Provides the oscap command-line configuration and vulnerability scanner, which can perform compliance checking against SCAP content including the SCAP Security Guide. This is a dependency of the
openscap-utilspackage. The package also includes the oscap-chroot utility that allows you to scan an offline file system within a chroot environment. -
openscap-containers -
The
openscap-containerspackage provides the oscap-docker utility that can be used to scan containers and container images. Note that some dependencies for this package are included in theol7_addonsyum repository. -
openscap -
Provides the OpenSCAP open-source libraries for generating SCAP-compliance documentation. OpenSCAP received SCAP 1.2 certification from NIST in April 2014.
-
scap-security-guide -
Provides system-hardening guidance in SCAP format, including links to government requirements. The guide provides security profiles that you can modify to comply with the security policies that you have established for your site. Starting from version v0.1.46-11.0.2.el7, a stig profile is included in this package to align with the DISA STIG for Oracle Linux 7 V1R1 published at https://public.cyber.mil/stigs/. See Displaying Available Profiles.
Installing the SCAP Packages
Use the yum command to install the SCAP
packages from the
ol7_<arch>_latest
channel on ULN or the ol7_latest repository on
the Oracle Linux yum server:
sudo yum install scap-security-guide
Note that if you intend to install the
openscap-containers package to scan containers
and container images, you must also enable the
ol7_<arch>_addons
channel on ULN or the ol7_addons repository on
the Oracle Linux yum server.
About the oscap Command
The oscap command has the following general syntax:
oscap [options] module operation [operation_options_and_arguments]
For module, oscap supports the following module types:
- cpe
-
Performs operations using a Common Platform Enumeration (CPE) file.
- cve
-
Performs operations using a Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) file.
- cvss
-
Performs operations using a Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) file.
- ds
-
Performs operations using a SCAP Data Stream (DS).
- info
-
Determines a file's type and prints information about the file.
- oval
-
Performs operations using an Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language (OVAL) file.
- xccdf
-
Performs operations using a file in eXtensible Configuration Checklist Description Format (XCCDF).
The info, oval, and xccdf modules are the most generally useful for scanning Oracle Linux systems.
For operation, the value you can specify depends on the module type. The following operations are the most generally useful with the oval and xccdf modules on Oracle Linux systems:
-
evalFor an OVAL file, oscap probes the system, evaluates each definition in the file, and prints the results to the standard output.
For a specified profile in an XCCDF file, oscap tests the system against each rule in the file and prints the results to the standard output.
-
generateFor an OVAL XML results file, generate report converts the specified file to an HTML report.
For an XCCDF file, generate guide outputs a full security guide for a specified profile.
-
validateValidates an OVAL or XCCDF file against an XML schema to check for errors.
For more information, see the oscap(8) manual
page.
Displaying the Available SCAP Information
To display the supported SCAP specifications, any loaded plug-in capabilities, the locations of schema, Common Platform Enumeration (CPE), and probe files, inbuilt CPE names, and supported Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language (OVAL) objects and associated SCAP probes, use the oscap -V command, for example:
oscap -V
OpenSCAP command line tool (oscap) 1.2.10 Copyright 2009--2016 Red Hat Inc., Durham, North Carolina. ==== Supported specifications ==== XCCDF Version: 1.2 OVAL Version: 5.11.1 CPE Version: 2.3 CVSS Version: 2.0 CVE Version: 2.0 Asset Identification Version: 1.1 Asset Reporting Format Version: 1.1 ==== Capabilities added by auto-loaded plugins ==== No plugins have been auto-loaded... ==== Paths ==== Schema files: /usr/share/openscap/schemas Default CPE files: /usr/share/openscap/cpe Probes: /usr/libexec/openscap ==== Inbuilt CPE names ==== Red Hat Enterprise Linux - cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 - cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux:5 Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 - cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux:6 Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 - cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux:7 Community Enterprise Operating System 5 - cpe:/o:centos:centos:5 Community Enterprise Operating System 6 - cpe:/o:centos:centos:6 Community Enterprise Operating System 7 - cpe:/o:centos:centos:7 Scientific Linux 5 - cpe:/o:scientificlinux:scientificlinux:5 Scientific Linux 6 - cpe:/o:scientificlinux:scientificlinux:6 Scientific Linux 7 - cpe:/o:scientificlinux:scientificlinux:7 Fedora 16 - cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:16 Fedora 17 - cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:17 Fedora 18 - cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:18 Fedora 19 - cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:19 Fedora 20 - cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:20 Fedora 21 - cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:21 Fedora 22 - cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:22 Fedora 23 - cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:23 Fedora 24 - cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:24 Fedora 25 - cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:25 SUSE Linux Enterprise all versions - cpe:/o:suse:sle SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 - cpe:/o:suse:sles:10 SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop 10 - cpe:/o:suse:sled:10 SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 - cpe:/o:suse:sles:11 SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop 11 - cpe:/o:suse:sled:11 SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 - cpe:/o:suse:sles:12 SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop 12 - cpe:/o:suse:sled:12 openSUSE 11.4 - cpe:/o:opensuse:opensuse:11.4 openSUSE 13.1 - cpe:/o:opensuse:opensuse:13.1 openSUSE 13.2 - cpe:/o:opensuse:opensuse:13.2 openSUSE 42.1 - cpe:/o:novell:leap:42.1 openSUSE All Versions - cpe:/o:opensuse:opensuse Red Hat Enterprise Linux Optional Productivity Applications - cpe:/a:redhat:rhel_productivity Red Hat Enterprise Linux Optional Productivity Applications 5 - cpe:/a:redhat:rhel_productivity:5 Oracle Linux 5 - cpe:/o:oracle:linux:5 Oracle Linux 6 - cpe:/o:oracle:linux:6 Oracle Linux 7 - cpe:/o:oracle:linux:7 ==== Supported OVAL objects and associated OpenSCAP probes ==== system_info probe_system_info family probe_family filehash probe_filehash environmentvariable probe_environmentvariable textfilecontent54 probe_textfilecontent54 textfilecontent probe_textfilecontent variable probe_variable xmlfilecontent probe_xmlfilecontent environmentvariable58 probe_environmentvariable58 filehash58 probe_filehash58 inetlisteningservers probe_inetlisteningservers rpminfo probe_rpminfo partition probe_partition iflisteners probe_iflisteners rpmverify probe_rpmverify rpmverifyfile probe_rpmverifyfile rpmverifypackage probe_rpmverifypackage selinuxboolean probe_selinuxboolean selinuxsecuritycontext probe_selinuxsecuritycontext systemdunitproperty probe_systemdunitproperty systemdunitdependency probe_systemdunitdependency file probe_file interface probe_interface password probe_password process probe_process runlevel probe_runlevel shadow probe_shadow uname probe_uname xinetd probe_xinetd sysctl probe_sysctl process58 probe_process58 fileextendedattribute probe_fileextendedattribute routingtable probe_routingtable symlink probe_symlink
Displaying Information About a SCAP File
To display information about a SCAP file, use the oscap info command, for example:
oscap info com.oracle.elsa-2017.xml
Document type: OVAL Definitions OVAL version: 5.3 Generated: 2017-06-01T00:00:00 Imported: 2017-06-13T23:12:06
This output shows that the file
com.oracle.elsa-2017.xml is an OVAL definitions
file.
Displaying Available Profiles
You can use the oscap info command to display the profiles that are supported by a checklist file such as the SCAP Security Guide, for example:
oscap info "/usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-ol7-xccdf.xml"
Document type: XCCDF Checklist Checklist version: 1.1 Imported: 2020-04-21T19:46:55 Status: draft Generated: 2020-04-21 Resolved: true Profiles: Title: DISA STIG for Oracle Linux 7 Id: stig Referenced check files: ssg-ol7-oval.xml system: http://oval.mitre.org/XMLSchema/oval-definitions-5 ssg-ol7-ocil.xml system: http://scap.nist.gov/schema/ocil/2 https://linux.oracle.com/security/oval/com.oracle.elsa-all.xml.bz2 system: http://oval.mitre.org/XMLSchema/oval-definitions-5 [vagrant@localhost ~]$
Note:
Other profiles are available and located in a different set of
files, such as ssg-rhel7-* files. For
example, to view other profiles, replace
ssg-ol7-xccdf.xml in the command with
ssg-rhel7-xccdf.xml.
This output shows that ssg-ol7-xccdf.xml
provides the DISA STIG for Oracle Linux 7
(stig). A profile contains generic security
recommendations that apply to all Oracle Linux installations and
additional security recommendations that are specific to the
intended usage of a system.
To obtain information about a specific profile, specify the
--profile option.
oscap info --profile stig /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-ol7-xccdf.xml
Document type: XCCDF Checklist
Profile
Title: DISA STIG for Oracle Linux 7
Id: stig
Description: This profile contains configuration checks that align to
the DISA STIG for Oracle Linux V1R1.This DISA STIG profile can be used to check compliance with the published Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) Security Technical Implementation Guide (STIG) for Oracle Linux. For more information, see https://public.cyber.mil/stigs/.
Note:
Starting from version v0.1.46-11.0.2.el7 the DISA STIG profile and its checklist
definition is deprecated in the ssg-rhel7-xccdf.xml and
ssg-rhel7-ds.xml files . The scap-security-guide package
now provides a profile aligned to DISA STIG for Oracle Linux V1R1 and the profile is
available in the ssg-ol7-xccdf.xml and ssg-ol7-ds.xml
files.
Note that the provided profiles in Oracle Linux 7 might not all be appropriate to your system. However, you can use them to create new profiles that test compliance with your site's security policies.
Validating OVAL and XCCDF Files
To validate an OVAL or XCCDF file against its schema, use the oscap validate command and examine the exit code, for example:
oscap oval validate com.oracle.elsa-2017.xml && echo "ok" || echo "exit code = $? not ok"
ok
oscap xccdf validate /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-ol7-xccdf.xml && echo "ok" || echo "exit code = $? not ok"
ok
An exit code of 0 indicates that the file is valid, 1 indicates an error prevented validation, and 2 indicates that the file is invalid. Error messages are written to the standard error output.
Running a Scan Against a Profile
To scan a system against an XCCDF profile, use the oscap xccdf eval command, for example:
oscap xccdf eval --profile stig \ --results /tmp/`hostname`-ssg-results.xml \ --report /var/www/html/`hostname`-ssg-results.html \ --cpe /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-ol7-cpe-dictionary.xml \ /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-ol7-xccdf.xml
WARNING: This content points out to the remote resources. Use `--fetch-remote-resources' option to download them. WARNING: Skipping https://linux.oracle.com/security/oval/com.oracle.elsa-all.xml.bz2 file which is referenced from XCCDF content Title Remove User Host-Based Authentication Files Rule no_user_host_based_files Result pass Title Remove Host-Based Authentication Files Rule no_host_based_files Result pass Title Uninstall rsh-server Package Rule package_rsh-server_removed Result pass Title Uninstall telnet-server Package Rule package_telnet-server_removed Result pass ...
This example scan performs the scan against the
stig profile of the
ssg-ol7-xccdf.xml checklist using the
ssg-ol7-cpe-dictionary.xml CPE dictionary, and
outputs the XML results and HTML report files to
/tmp and /var/www/html
respectively. Any rule in a profile that results in a
fail potentially requires the system to be
reconfigured.
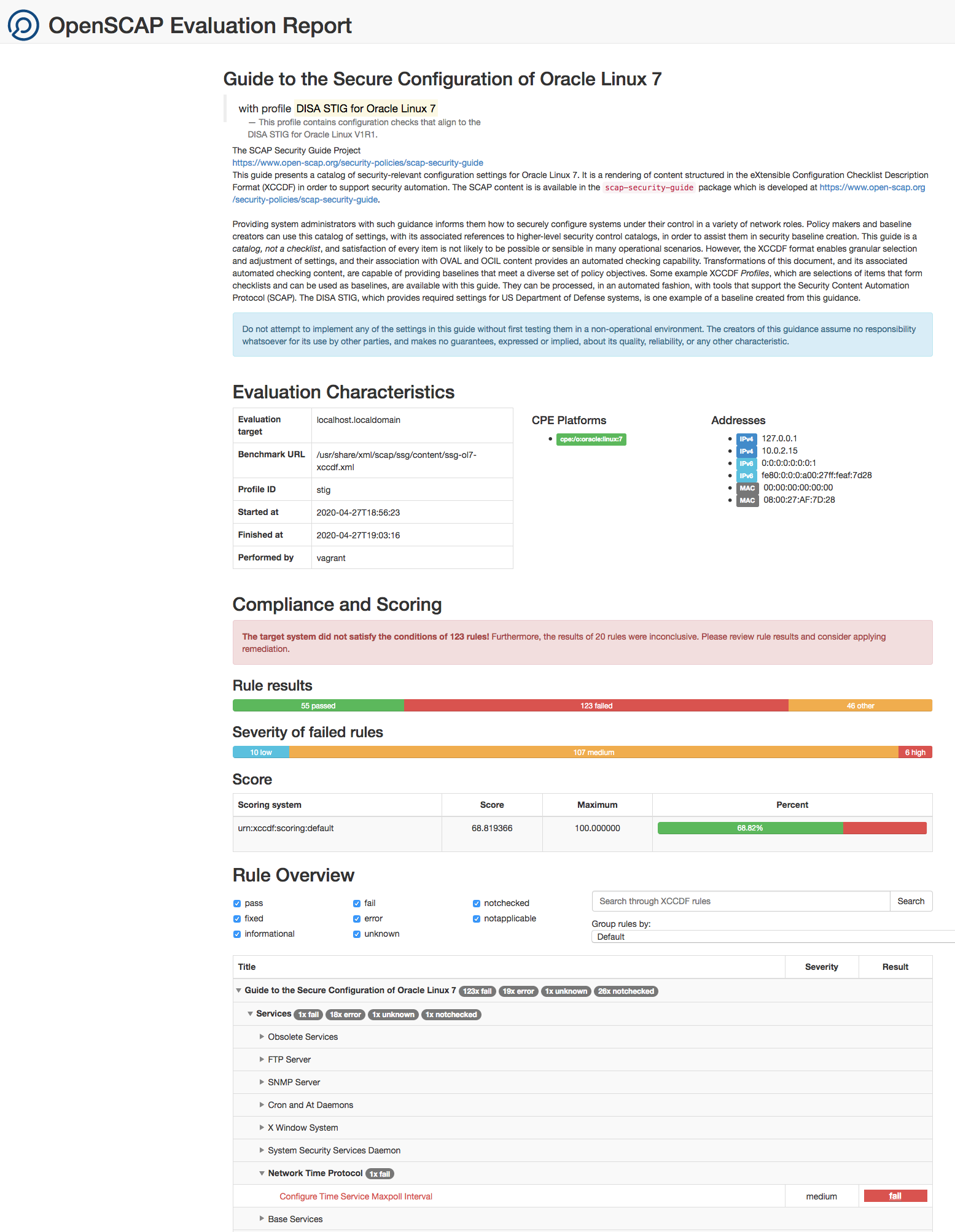
You can view the HTML report in a browser as shown in Figure 5-1.
Figure 5-1 Sample Scan Report
Generating a Full Security Guide
To create a full security guide for a system based on an XCCDF profile, use the oscap xccdf generate guide command, for example:
oscap xccdf generate guide --profile stig \ --cpe /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-ol7-cpe-dictionary.xml \ /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-ol7-xccdf.xml > /var/www/html/security_guide.html
You can view the security guide in a browser as shown in Figure 5-2.
Figure 5-2 Sample Security Guide

Running an OVAL Auditing Scan
Oracle provides OVAL definitions for all errata on ULN. You can use these definitions to ensure that all applicable errata are installed on an Oracle Linux system. For example, Spacewalk allows you to schedule regular auditing scans.
The following OVAL definition files are available:
-
com.oracle.elsa-cve.xmlOVAL definition file for a single ELSA security patch. For example,
com.oracle.elsa-20150377.xmlrelates to ELSA-2015-0377. -
com.oracle.elsa-year.xml.bz2Compressed archive of OVAL definition files for all ELSA patches released in a given year.
-
com.oracle.else-all.xml.bz2Compressed archive of all applicable OVAL definition files for all available ELSA patches.
To download an OVAL definitions file and perform an audit on a system:
-
Use wget or a similar command to download a definitions file from https://linux.oracle.com/security, for example:
wget https://linux.oracle.com/security/oval/com.oracle.elsa-2017.xml.bz2
-
In the definitions file is a compressed
bz2archive, use bzip2 to extract the OVAL definitions file:bzip2 -d com.oracle.elsa-2017.xml.bz2
-
Use oscap oval eval to audit a system using an OVAL definitions file, for example:
oscap oval eval --results /tmp/elsa-results-oval.xml \ --report /var/www/html/elsa-report-oval.html \ /tmp/com.oracle.elsa-2017.xml
Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173580: false Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173579: true Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173576: false Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173575: false Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173574: true Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173567: false Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173566: false Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173565: true Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173539: true Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173538: false Definition oval:com.oracle.elsa:def:20173537: false ... Evaluation done.
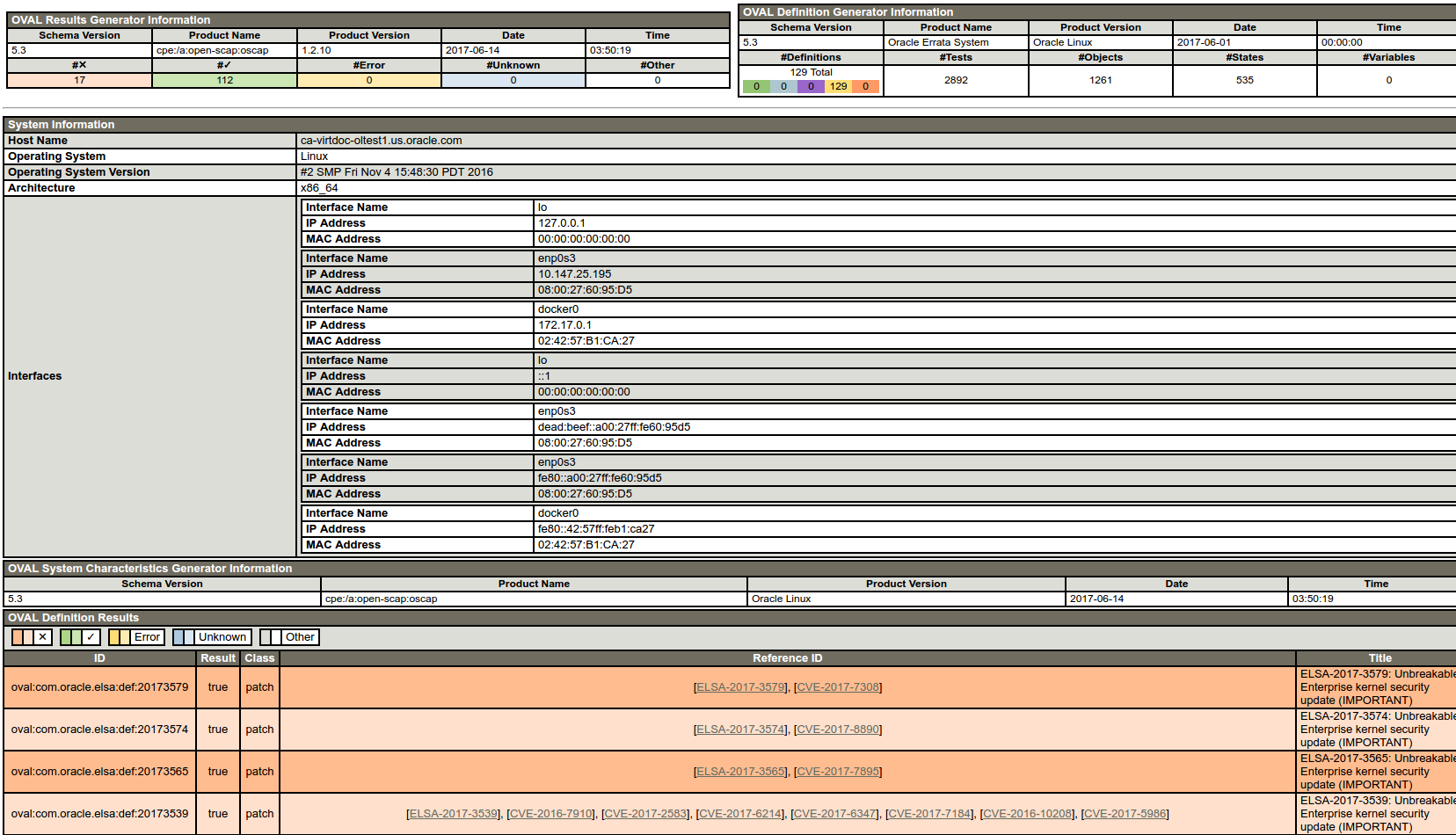
This example scan uses the OVAL definitions in
com.oracle.elsa-2017.xmland outputs the XML results and HTML report files to/tmpand/var/www/htmlrespectively. A result oftruefor a patch means that it has not been applied to a system; a result offalsemeans that it has been applied.If you generate an XML results file but not the HTML report, you can use oscap oval generate report to convert the results file to an HTML report, for example:oscap oval generate report /tmp/elsa-results-oval.xml > /var/www/html/elsa-report-oval.html
You can view the HTML report in a browser as shown in Figure 5-3.
Figure 5-3 Sample OVAL Report
Scanning Containers, Container Images and Offline File Systems
OpenSCAP includes utilities that allow you to scan Docker containers or container images using the oscap-docker command; or to scan offline file systems hosting an operating system using the oscap-chroot command. Note that due to the mechanisms that are used to perform these scans, these tools are only supported in the context of a scan against an Oracle Linux 7 based system.
Scan Container Images and Containers
Scan Docker containers or container images using the oscap-docker command. This tool assesses vulnerabilities in the container or image and checks compliance with security policies similarly to the oscap command. The tool uses offline scanning to perform all assessments and checks by performing a temporary read-only mount of the container or image file system. No changes are made to the container or image and no additional tools are required within the container or image.
To scan an image for vulnerabilities using the appropriate CVE stream for the image variant and to output this information in HTML format, run:
oscap-docker --disable-atomic image-cve ol7-image --report report.html
Note that you must use the --disable-atomic
option when running the command. Atomic containers are not
supported on Oracle Linux.
To scan an image for compliance with a security policy specified in an XCCDF checklist and to output the result in HTML format, run:
oscap-docker --disable-atomic image ol7-image xccdf eval \
--fetch-remote-resources \
--profile <profile> \
--results results.xml \
--report report.html \
--cpe /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-ol7-cpe-dictionary.xml \
/usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-ol7-xccdf.xml
You can change the subcommand from image or
image-cve to container or
container-cve if you would prefer to scan a
specific container. Note that you must use the
--disable-atomic option when running the
command. Atomic containers are not supported on Oracle Linux.
See the oscap-docker(8) manual page for more
information.
Scan Offline File Systems
Use the oscap-chroot command to perform an offline scan of a file system that is mounted at a specified path. This tool can be used for scanning of custom objects that are not supported by oscap-docker, like containers that use an alternate format to Docker or virtual machine disk files. The options for this tool are similar to the oscap command.
For example, to audit a file system mounted at
/mnt audit using an OVAL definitions file,
run:
oscap-chroot /mnt oval eval --results /tmp/elsa-results-oval.xml \ --report elsa-report-oval.html \ /tmp/com.oracle.elsa-2021.xml
See the oscap-chroot(8) manual page for more
information.