11 Managing Instant Messaging and Presence
Configure and manage instant messaging and presence (IMP) for WebCenter Portal.
Always use Fusion Middleware Control or WLST command-line tool to review and configure back-end tools and services for WebCenter Portal. Any changes that you make to these applications, postdeployment, are stored in MDS metadata store as customizations.
Permissions: To perform the tasks in this chapter, you must be granted the WebLogic Server
Adminrole through the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console and theAdministratorrole granted through WebCenter Portal Administration.
For more information about roles and permissions, see Understanding Administrative Operations, Roles, and Tools.
Topics:
Parent topic:Administering Tools and Services
About Instant Messaging and Presence Connections
Instant Messaging and Presence (IMP) lets you see the presence status of other authenticated application users (online, offline, busy, or away), and it provides quick access to interaction options, such as instant messages (IM) and mail.
A single connection to a back-end presence server is required. WebCenter Portal is certified with Microsoft Lync 2010.
Note: Oracle Beehive Server connections are not supported in this release.
You can register the presence server connection for your application through the Fusion Middleware Control Console or using WLST. You must mark a connection as active for IMP to work. You can register additional presence server connections, but only one connection is active at a time. Configuration changes for instant messaging and presence, through Fusion Middleware Control or using WLST, are not dynamic, so you must restart the managed server on which WebCenter Portal is deployed for changes to take effect.
Instant Messaging and Presence Server Prerequisites
This section describes the Microsoft Lync 2010 prerequisites as the presence server for instant messaging and presence.
This section includes the following subsections:
Microsoft Lync - Installation
Refer to the Microsoft Lync 2010 documentation for installation information.
Microsoft Lync - Configuration
To use Microsoft Lync 2010 as the presence server for IMP, you must deploy WebCenter Portal’s Proxy application for Microsoft Lync 2010 in one of the two topologies:
-
Simple Deployment – All components reside on the same box
-
Remote Deployment – The proxy application and Microsoft Lync reside on separate boxes
Microsoft Unified Communications Managed API v2.0 (UCMA) is an endpoint API that allows advanced developers to build server applications that can interact with the Lync environment. In a simple deployment, the UCMA is installed on the same box as Lync. In a remote deployment, the Lync core libraries are installed on the Lync box, and the UCMA is installed on the IIS (proxy) box.
This section includes the following:
Simple Deployment
In a simple topology, install Microsoft Unified Communications Managed API (UCMA) 2.0 on the Lync box. In this topology, WebCenter Portal’s Proxy application is deployed in the Internet Information Services (IIS) server hosted on the Lync box. The proxy application provides web services for interacting with the Lync server, and for sending and receiving information. WebCenter Portal talks to these web services and presents the data.
This section includes the following:
Installing UCMA v2.0
Microsoft Unified Communications Managed API v2.0 (UCMA) is an endpoint API that allows advanced developers to build server applications that can interact with the Lync environment.
In a simple deployment, the UCMA is installed on the same box as Lync. In a remote deployment, the Lync core libraries are installed on the Lync box, and the UCMA is installed on the IIS (proxy) box.
-
Download UCMA v2.0 installation from the following location:
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=9781 -
Download and run the
UcmaSDKWebDownload.msifile.Setup files are extracted to the folder
C:\Microsoft Unified Communications Managed API 2.0 SDK Installer package\amd64 -
Go to the directory (where the files from the previous step were extracted) and run
vcredist_x86.exe.Run-time components of Visual C++ Libraries, required for UCMA APIs, are installed.
-
Go to the directory called
Setupand runUcmaRedist.msi.UCMA 2.0 assemblies in the GAC are installed.
Installing WebCenter Portal’s Proxy Application
-
Extract
owc_ocs2007.zip. The zip file is available in WebCenter Companion Adapters, which you can download from OTN. Navigate to the Downloads page of WebCenter Portal, and download WebCenter Companion Adapters from under the Prerequisites and Recommended Install Process section.A directory named
OCSWebServicesis created. -
Open the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
-
Expand the server node and thenSites in the IIS Manager.
-
Right-click Lync Internal Web Site, and then select Add Application.
-
In the Add Application wizard, enter an alias for the virtual directory in the Alias field, for example
RTC. -
Enter the path to the directory extracted from the
owc_ocs2007.zipfile, and then click OK.For example, if you extracted the zip file in C:\, then enter
C:\OCSWebServices. Alternatively, use the Browse button to navigate to that directory. Click OK. -
Right-click the newly created application and select Edit Permissions to open the Properties dialog.
-
In the Security tab, edit permissions to grant user Everyone read permission.
-
Test the Web service by accessing the website using the following URL format:
http://localhost/lync_internal_web_site/OCSWebService.asmx.where
lync_internal_web_siteis the virtual directory you created for the Oracle RTC Web service.For example:
http://localhost/RTC/OCSWebService.asmx
Remote Deployment
In this topology, WebCenter Portal’s Proxy application is deployed on an IIS server remote to the Lync box. That is, the IIS server and the Lync server are hosted on separate machines.
Because this proxy application is hosted on a remote box, you must set up a trust between the application and the Lync server. This is known as provisioning an application. Provisioning is done through the Application Provisioner utility shipped with Microsoft UCMA v2.0.
Figure 1 provides an overview of the steps (including installing UCMA v2.0) to be performed on different deployment entities.
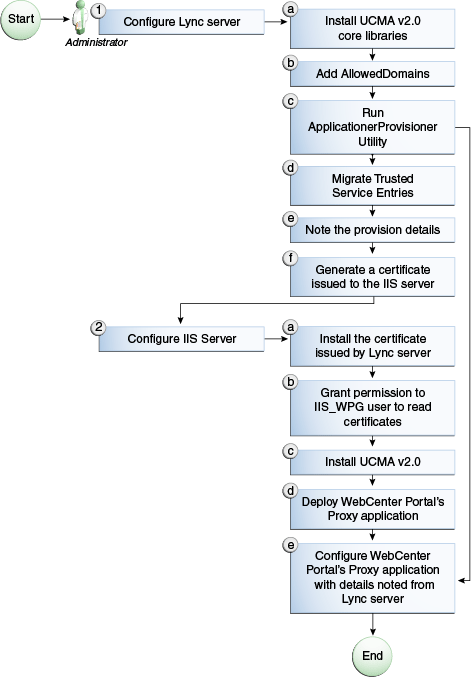
The details of these steps are described in the following sections.
Building Application Provisioner
This section lists the steps Microsoft provides for provisioning other IIS servers to access Lync.
-
Install Visual Studio 2008 on any developer box (not necessarily IIS/Lync).
-
Install UCMA version 2.0 on the same box. The Application Provisioner application comes with the UCMA SDK.
-
Download UCMA v2.0 installation from the following location:
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=9781 -
Download and run the
UcmaSDKWebDownload.msifile.Setup files are extracted to the folder
C:\Microsoft Unified Communications Managed API 2.0 SDK Installer package\amd64 -
Go to the directory where the setup files were extracted and run
vcredist_x86.exe.Run-time components of Visual C++ Libraries, required for UCMA APIs, are installed.
-
Go to the directory called
Setupand runUcmaRedist.msi.UCMA 2.0 assemblies in the GAC are installed.
-
-
Go to the directory
Sample Applications\Collaboration\ApplicationProvisionerunder the location where you installed UCMA Core (for example,C:\Program Files\Microsoft Lync 2010 R2\UCMA SDK 2.0\UCMACore\Sample Applications\Collaboration\ApplicationProvisioner). -
Open the application in Visual Studio 2008 and edit the
Application.csfile as perhttp://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg448038.aspx. -
Build the application using Visual Studio 2008.
This generates the
ApplicationProvisioner.exefile. -
Copy the executable file to the Lync box.
-
See the next step Provisioning WebCenter Portal’s Proxy Application on Lync Server.
Provisioning WebCenter Portal’s Proxy Application on Lync Server
-
Run the
OCSWMIBC.msifile that comes with the Lync setup package.When a UCMA 2.0 application is deployed directly against Lync Server 2010, the SIP domains used in the Lync Server 2010 environment must be added to the Office Communications Server 2007 R2 SIP domain list before you run the
Merge-CsLegacyTopologycmdlet. The application is deployed as if it were being deployed against OCS 2007 R2, then migrated to run against Lync Server 2010. To add the domains, see Adding AllowedDomains Using WBemTest. -
Run the
ApplicationProvisioner.exefile, generated in the previous section.The Application Provisioner dialog appears.
-
In the Application Provisioner dialog, enter
WebCenterProxyApplicationas the name of your application for the Application name, and then click Find or Create. -
In the Create Application Pool dialog, select the pool for your application in the Lync Pool Fqdn list.
-
For Listening port, enter the listening port for your application (for example, 6001).
-
For Application server Fqdn, enter the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the computer on which the application is deployed. (This is the IIS box.)
-
If the application is deployed on two or more computers, then select the Load balanced application checkbox, and for Load balancer Fqdn, enter the FQDN of the load balancer.
The application pool now appears in the Application Provisioner dialog.
-
-
Double-click the server entry.
The View Server dialog appears. Note the information shown there; that is, Server FQDN, port, and GRUU.
-
Migrate the newly-created trusted entry to Lync Server 2010.
See Migrating Trusted Service Entries Using Topology Builder or PowerShell Cmdlets.
-
Create a certificate on the Lync server with the subject name as the Server FQDN noted in the previous step using the Lync Certificate Wizard.
This certificate is used to authorize the requests coming from the IIS server.
-
After the certificate is created, view the certificate.
-
On the Details tab click Copy to File.
The Certificate Export Wizard appears.
-
Export the certificate with the private key to a file.
A
.pfx(Personal Information Exchange) file with the certificate name is created. -
See the next step Adding AllowedDomains Using WBemTest.
Adding AllowedDomains Using WBemTest
-
To start
WBemTest.exe, typeWBemTestin a command prompt window and press Enter. -
In the Windows Management Instrumentation Tester dialog, click Connect.
-
In the Connect dialog, click Connect.
-
In the Windows Management Instrumentation Tester dialog, click Enum Classes.
-
In the Superclass Info dialog, click OK.
-
In the Query Result dialog, scroll down to MSFT_SIPDomainData(), and double-click this entry.
-
In the Object editor for MSFT_SIPDomainData dialog, click Instances.
The Query Result dialog appears, displaying the InstanceIDs for any instances of the MSFT_SIPDomainData WMI class. These entries are the AllowedDomain entries.
-
To add AllowedDomain entries, click Add.
-
In the Instance of MSFT_SIPDomainData dialog, in the Properties listbox, double-click Address.
-
In the Property Editor dialog, select the Not NULL radio button.
-
In the Value text input pane, enter the Lync server domain; for example,
contoso.com, and click Save Property. -
In the Instance of MSFT_SIPDomainData dialog, in the Properties listbox, double-click Authoritative, make sure that the Authoritative property is not Null and is set to
False, and then clickSave Property. -
In the Instance of MSFT_SIPDomainData dialog, in the Properties listbox, double-click Default Domain, make sure that the Default Domain property is not Null and is set to
True, then clickSave Property. -
In the Instance of MSFT_SIPDomainData dialog, click Save Object.
-
Go to the next step Migrating Trusted Service Entries Using Topology Builder or PowerShell Cmdlets.
Migrating Trusted Service Entries Using Topology Builder or PowerShell Cmdlets
To migrate trusted service entries using Microsoft Lync Server 2010 Topology Builder:
-
Launch Microsoft Lync Server 2010, Topology Builder.
-
After the existing topology is loaded, under Action, select Merge 2007 or 2007 R2 Topology.
-
Go through the resulting wizard, keeping the default options.
-
Select Publish Topology and complete the wizard, as in the previous step.
-
After the wizard has finished, check that it completed successfully.
There should be no errors in the user interface.
To migrate trusted service entries using Microsoft Lync Server 2010 PowerShell Cmdlets:
-
From the Start menu, in the Microsoft Lync Server 2010 program group, open Lync Server Management Shell.
-
Run the following PowerShell cmdlet:
Merge-CsLegacyTopology -TopologyXmlFileName D:\output.xml -
Run the following PowerShell cmdlet:
Publish-CsTopology -FileName D:\output.xml
IIS Server Configuration
Because the IIS server hosts WebCenter Portal’s Proxy application in the remote deployment scenario, use the information from the previous section to make it a trusted authority.
-
Install the certificate issued by the Lync server with the private key: Copy the
.pfxfile generated in Provisioning WebCenter Portal’s Proxy Application on Lync Server to the IIS box, and double-click it.The Certificate Import wizard appears.
-
Import the certificate in Personal Folder under LOCAL_MACHINE
-
Make an entry in
C:/WINDOWS/system32/drivers/etc/hostsfor the pool name of the Lync server as follows:<*ip-address-of-lync-box*> <*poolname-of-lync-box*>For example:
10.177.252.146 pool01.example.com -
Because the IIS server hosts WebCenter Portal’s Proxy application, install Microsoft UCMA v2.0 on it.
-
Download UCMA v2.0 installation from the following location:
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=9781 -
Download and run the
UcmaSDKWebDownload.msifile.Setup files are extracted to the folder
C:\Microsoft Unified Communications Managed API 2.0 SDK Installer package\amd64 -
Go to the directory where the setup files were extracted and run
vcredist_x86.exe.Run-time components of Visual C++ Libraries, required for UCMA APIs, are installed.
-
Go to the directory called
Setupand runUcmaRedist.msi.UCMA 2.0 assemblies in the GAC are installed.
-
-
After UCMA is installed, deploy this proxy application on the IIS server.
WebCenter Portal’s Proxy application provides web services for interacting with Lync, and for sending and receiving information. WebCenter Portal talks to these web services and presents the data. For detailed information, see Installing WebCenter Portal’s Proxy Application.
-
Go to the location where WebCenter Portal’s Proxy application was extracted, and open
Web.configand edit theappSettingsXML node to add the values noted in Step 7 in the previous section (Section 12.2.2.2.5, “IIS Server Configuration”).Make sure to set the value for
RemoteDeploymentto true. For example, theappsettingsXML node should look somewhat like this.<appSettings> <add key="ApplicationName" value="WebCenterProxyApplication"/> <add key="RemoteDeployment" value="true"/> <add key="ApplicationFQDN" value="iis.server.com"/> <add key="ApplicationGRUU" value="sip:iis.server.com@EXAMPLE.COM;gruu;opaque=srvr:WebCenterProxyApplication:7mhSo94PlUK-5Q2bKPLyMAAA"/> <add key="ApplicationPort" value="6001"/> </appSettings>
Note: If you see the following exception in the log file:
ErrorCode = -2146893039
FailureReason = NoAuthenticatingAuthority
e.Message = "Unable to perform authentication of credentials."
base {Microsoft.Rtc.Signaling.FailureResponseException} = {"Unable to perform authentication of credentials."}
InnerException = {"NegotiateSecurityAssociation failed, error: \-2146893039"}then add the following entry to Web.config:
<identity impersonate="true" userName="Administrator" password="MyPassword*"/>where username is the administrator’s user name, and password is the administrator’s password.
The trust is established, and WebCenter Portal’s Proxy application can talk to the Lync server.
Microsoft Lync - Security Considerations
You must configure an external application for Microsoft Lync connections so that users can supply credentials to authenticate themselves on the Lync server.
With a secured application, users get presence status. With Lync, if security is required, then Lync should be on a private trusted network.
Lync provides an option for changing external credentials, which works as an alternative to using an external application. A logged-in user can click any Presence tag and select Change Credentials from the menu.
For more information, see Registering Instant Messaging and Presence Servers Using Fusion Middleware Control.
Registering Instant Messaging and Presence Servers
You can register multiple presence server connections with WebCenter Portal, but only one of them is active at a time.
To start using the new (active) presence server you must restart the managed server on which WebCenter Portal is deployed.
This section includes the following subsections:
-
Registering Instant Messaging and Presence Servers Using Fusion Middleware Control
-
Registering Instant Messaging and Presence Servers Using WLST
Registering Instant Messaging and Presence Servers Using Fusion Middleware Control
To register a presence server connection:
-
Log in to Fusion Middleware Control and navigate to the home page for WebCenter Portal.
-
From the WebCenter Portal menu, select Settings > Service Configuration.
-
On the WebCenter Portal Service Configuration page, select Instant Messaging and Presence.
-
To connect to a new presence server, click Add.
-
Enter a unique name for this connection, specify the presence server type, and indicate whether this connection is the active (or default) connection for the application.
Table 11-1 Instant Messaging and Presence Connection - Name
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Connection Name |
Enter a unique name for the connection. The name must be unique (across all connection types) within WebCenter Portal. |
|
Connection Type |
Specify the type of presence server: Note: Microsoft Lync connections use the Microsoft Office Communications Server 2010 connection type. (Oracle Beehive Server connections are not supported in this release.) |
|
Active Connection |
Select to use this connection in WebCenter Portal for instant messaging and presence. While you can register multiple presence server connections for an application, only one connection is used by IMP—the default (or active) connection. |
- Enter connection details for the server hosting instant messaging and presence.
Table 11-2 Instant Messaging and Presence Connection - Connection Details
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Server URL |
Enter the URL of the server hosting instant messaging and presence. For example: |
|
User Domain |
Enter the name of the Active Directory domain (on the Microsoft Office Communications Server) that is associated with this connection. The user domain is mandatory for Lync connections. Refer to Microsoft documentation for details on the user domain. |
|
Pool Name |
Enter the name of the pool that is associated with this connection. The pool name is mandatory. Refer to Microsoft documentation for details on the pool name. |
|
Associated External Application |
Associate the instant messaging and presence server with an external application. External application credential information is used to authenticate users against the instant messaging and presence server. An external application is mandatory. You can select an existing external application from the list, or click Create New to configure a new external application. The external application you configure for instant messaging and presence must use the |
- Enter a timeout in the Advanced Configuration field.
Table 11-3 Instant Messaging and Presence Connection - Advanced Configuration
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Connection Timeout (seconds) |
Specify a suitable timeout for the connection. This is the length of time (in seconds) WebCenter Portal waits for a response from the presence server before issuing a connection timeout message. The default is -1 which means that the default is used. The default is 10 seconds. |
-
Sometimes, additional parameters are required to connect to the presence server.
If additional parameters are required to connect to the presence server, expand Additional Properties and enter details as required.
Table 11-4 Instant Messaging and Presence Connection - Additional Properties
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Add |
Click Add to specify an additional connection parameter:
|
|
Delete |
Click Delete to remove a selected property. Select the correct row before clicking Delete. Note: Deleted rows appear disabled until you click OK. |
-
Click OKto save this connection.
-
To start using the new (active) connection you must restart the managed server on which WebCenter Portal is deployed.
Registering Instant Messaging and Presence Servers Using WLST
Use the WLST command createIMPConnection to create a presence server connection. For command syntax and examples, see createIMPConnection in WebCenter WLST Command Reference Reference.
To configure instant messaging and presence to actively use a new IMP connection, set default=true. For more information, see Choosing the Active Connection for Instant Messaging and Presence Using WLST.
Note: To start using the new (active) connection you must restart the managed server on which WebCenter Portal is deployed.
Choosing the Active Connection for Instant Messaging and Presence
You can register multiple instant messaging and presence server connections with WebCenter Portal, but only one connection is active at a time. The active connection becomes the back-end presence server for WebCenter Portal.
This section includes the following subsections:
-
Choosing the Active Connection for Instant Messaging and Presence Using Fusion Middleware Control
-
Choosing the Active Connection for Instant Messaging and Presence Using WLST
Choosing the Active Connection for Instant Messaging and Presence Using Fusion Middleware Control
To change the active connection:
-
Log in to Fusion Middleware Control and navigate to the home page for WebCenter Portal.
-
From the WebCenter Portal menu, select Settings > Service Configuration.
-
On the WebCenter Portal Services Configuration page, select Instant Messaging and Presence.
The Manage Instant Messaging and Presence Connections table indicates the current active connection, if any.
-
Select the connection you want to make the active (or default) connection, and then click Edit.
-
Select the Active Connection check box.
-
Click OKto update the connection.
-
To start using the new (active) connection, restart the managed server on which WebCenter Portal is deployed.
Choosing the Active Connection for Instant Messaging and Presence Using WLST
Use the WLST command setIMPConnection with default=true to activate an existing presence server connection. For command syntax and examples, see setIMPConnection in WebCenter WLST Command Reference Reference.
To disable a presence server connection, either delete it, make another connection the ‘active connection,’ or use the removeIMPServiceProperty command:
removeIMPServiceProperty('appName='webcenter', property='selected.connection')Using this command, connection details are retained but the connection is no longer named as an active connection. For more information, see removeIMPServiceProperty in WebCenter WLST Command Reference Reference.
Note: To start using this active connection you must restart the managed server on which WebCenter Portal is deployed.
Modifying Instant Messaging and Presence Connection Details
You can modify instant messaging and presence server connection details at any time.
To start using an updated (active) connection you must restart the managed server on which WebCenter Portal is deployed.
This section includes the following subsections:
-
Modifying Instant Messaging and Presence Connections Details Using Fusion Middleware Control
-
Modifying Instant Messaging and Presence Connections Details Using WLST
Modifying Instant Messaging and Presence Connections Details Using Fusion Middleware Control
To update connection details for an instant messaging and presence server:
-
Log in to Fusion Middleware Control and navigate to the home page for WebCenter Portal.
-
From the WebCenter Portal menu, select Settings > Service Configuration.
-
On the WebCenter Portal Service Configuration page, select Instant Messaging and Presence.
-
Select the connection name, and click Edit.
-
Edit connection details, as required.
For detailed parameter information, see Table 2.
-
Click OK to save your changes.
-
To start using the updated (active) connection you must restart the managed server on which WebCenter Portal is deployed.
Modifying Instant Messaging and Presence Connections Details Using WLST
Use the WLST command setIMPConnection to edit presence server connection details. For command syntax and examples, see setIMPConnection in WebCenter WLST Command Reference Reference.
If additional parameters are required to connect to your presence server, then use thesetIMPConnectionProperty command. For more information, see setIMPConnectionProperty in WebCenter WLST Command Reference Reference.
Note: To start using the updated (active) connection you must restart the managed server on which WebCenter Portal is deployed.
Deleting Instant Messaging and Presence Connections
You can delete instant messaging and presence connections at any time, but use caution when deleting the active connection. When you delete the active connection, user presence options are not available, as these require a back-end instant messaging and presence server.
When you delete a connection, consider deleting the external application associated with instant messaging and presence if the application’s sole purpose was to support it. For more information, see Deleting External Application Connections.
This section includes the following subsections:
-
Deleting Instant Messaging and Presence Connections Using Fusion Middleware Control
-
Deleting Instant Messaging and Presence Connections Using WLST
Deleting Instant Messaging and Presence Connections Using Fusion Middleware Control
To delete an instant messaging and presence server connection:
-
Log in to Fusion Middleware Control and navigate to the home page for WebCenter Portal.
-
From the WebCenter Portal menu, select Settings > Service Configuration.
-
On the WebCenter Portal Service Configuration page, select Instant Messaging and Presence.
-
Select the connection name, and click Delete.
-
Restart the managed server on which WebCenter Portal is deployed.
Note: Before restarting the managed server, mark another connection as active; otherwise, Instant Messaging and Presence is disabled.
Deleting Instant Messaging and Presence Connections Using WLST
Use the WLST command deleteConnection to remove a presence server connection. For command syntax and examples, see [deleteConnection](olink:GUID-2FB7920B-6556-46BD-AB93-396C8A4FA0F3) in WebCenter WLST Command Reference Reference.
For information on how to run WLST commands, see Running Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) Commands.
Setting Up Instant Messaging and Presence Defaults
Use the WLST command setIMPServiceProperty to set defaults for IMP:
-
selected.connection: Connection used by instant messaging and presence. -
rtc.cache.time: Cache timeout for instant messaging and presence data. -
resolve.display.name.from.user.profile: Determines what to display if user display names are missing. When set to 0, and display name information is unavailable, only the user name displays in the application. When set to1, and display name information is unavailable, display names are read from user profile data. Setting this option to1impacts performance. The default setting is0.Display names are not mandatory in presence data. If the application does not always provide display names by default and you consider this information important, set
resolve.display.name.from.user.profileto1so that display names always display. -
im.address.resolver.class: Resolver implementation used to map user names to IM addresses and IM addresses to user names. The default setting isoracle.webcenter.collab.rtc.IMPAddressResolverImpl. This implementation looks for IM addresses in the following places and order:-
User Preferences
-
User Credentials
-
User Profiles
-
-
im.address.profile.attribute: User profile attribute used to determine a user’s IM address. The default setting isBUSINESS_EMAIL. Users can change this default withim.address.profile.attribute.
For command syntax and detailed examples, see setIMPServiceProperty in WebCenter WLST Command Reference Reference.
Testing Instant Messaging and Presence Connections
Oracle RTC web services expose a set of web methods that you can invoke to test validity. To verify a connection, try accessing the web service endpoints. The following examples assume the application context path is /RTC:
-
protocol://host/RTC/ApplicationConfigurationService.asmx -
protocol://host/RTC/RTCService.asmx -
protocol://host/RTC/OCSWebService.asmx