Managing Archives, Collections, and Batch Files
This chapter describes how to manage Oracle WebCenter Content Server content archives, collections, and batch files using the Archiver application.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Understanding How the Archiver Works
Archiving Content Server content consists of three elements: the archive itself, a collection, and a batch file. This section describes the structure of the Archiver application and how it uses collections and targets. For an overview of Archiver and how it compares to other archiving tools, see Introduction to Migration Tools and Components.
Archive Structure
An archive is a set of exported content files and their associated batch files. Each archive has its own subdirectory in the collection it belongs to.
CAUTION:
Do not edit any of the files created by Archiver.
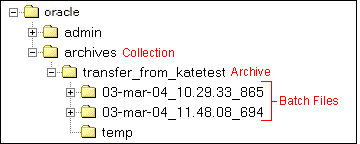
An archive subdirectory includes the following:
| File or Directory | Description |
|---|---|
| Batch file directories | Each batch file has a subdirectory in the archive. The subdirectory name reflects the date and time of the export, with a default format of yy-MMM-dd_HH.mm.ss_SSS. For example, 03-feb-04_15.04.14_174. |
| temp directory | Contains transferred Zip files. |
| archive.hda file | Specifies information about the archive, such as export and import settings, the export query, field and value import maps, archiving history, and so forth. |
| doctypes.hda file | Lists the content types (DocTypes database table) in the source Content Server instance. This file is present only if content types were exported. |
| exports.hda file | Specifies the batch files that are included in the archive. |
| users.hda file | Lists the user attributes (Users database table) in the source Content Server instance. This file is present only if user attributes were exported. |
Collections
This section provides information about collections.
Summary
A collection is a set of archives on a particular Content Server instance.
-
Each instance has a default collection, which is located in the
IntradocDir/archives/directory. Additional collections can be created, but are necessary only in rare situations. For example, you could create a new collection if you want to save disk space by archiving to another system that does not have Content Server on it. -
Collections can be created only through the standalone Archiver application. For details about using the standalone Archiver, see Running Archiver as a Standalone Application.
-
A collection can be removed from a Content Server instance, but this only makes it unavailable from Archiver; the archive and batch files remain until you delete them from the file system.
Note:
Archiver collections are normally compatible between different versions of Content Server instances. One possible exception would be User Configuration information that was archived from a pre-3.0 version Content Server instance. The format of the Users database table changed in version 3.0, so this information might not be compatible between pre- and post-3.0 version Content Server instances.
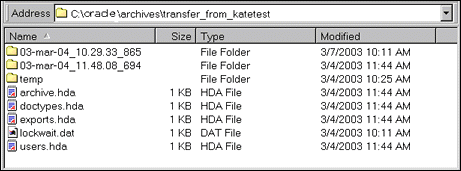
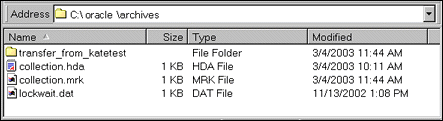
Structure
An archive collection includes the following:
| File or Directory | Description |
|---|---|
collection.hda file |
Specifies the archives that are included in the collection. |
collection.mrk file |
Internal file used by Archiver. |
| Archive directories | Each archive has a subdirectory in the collection. |
Batch Files
This section provides information about batch files.
Summary
A batch file is a text file that contains the file records for archived content items. Batch files describe the metadata for each exported revision.
-
A new batch file subdirectory is created each time an archive is exported.
-
Each batch file contains up to 1000 file records. If an export contains more than 1000 revisions, a new batch file is created.
Note:
Archiver batch files are not the same as the batch files that are used with the Batch Loader application.
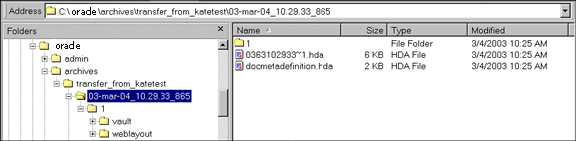
Structure
A batch file subdirectory includes the following:
| File or Directory | Description |
|---|---|
| Content files | A subdirectory named ‘1’ in the batch file directory contains a vault structure that is copied from the source Content Server instance. If web-viewable files are being archived, this subdirectory also contains a weblayout structure. |
| Batch file | Specifies the metadata for each revision that was exported. Batch files are HDA files that are named with a unique number generated by Archiver. For example, 0335150414~1.hda. |
docmetadefinition.hda file |
Lists the custom metadata fields in the source Content Server instance (DocMetaDefinition database table). This file is used by Archiver to create import maps. |
Archive Targets
You can use Archiver to archive the following content:
-
Native files with associated standard metadata values
-
Web-viewable files (
.pdf,.html, and so forth) -
Metadata fields and changes
-
User information fields
-
Security groups (user attributes and settings)
-
User updates
-
Subscription types
-
File formats
-
Document types
-
Content types
-
User attributes (such as user login, full name, password, email address, and so forth)
Note:
Content types and user attributes can be exported and imported manually, but cannot be transferred or archived automatically through replication. Table replication can be used, though, to replicate user information.
CAUTION:
Archiver cannot be used to move or copy data between two instances that share the same Content Server instance name (
IDC_Name). To do so will corrupt the data on the target system.
Using Archive Logs
If you are experiencing Archiver problems, view the Archiver logs for more information.
Summary
The Archiver logs are listed by date and time. They are generated once per day when the first Archiver information status, irrecoverable error, or error occurs.
Click the Archiver Logs link on the Administration page to view information about imports, exports, and replications.
Click the link that appears for the desired log file. A table showing the type, date and time, and description of each action is displayed. It also includes the name of the Content Server instance that created the archive.
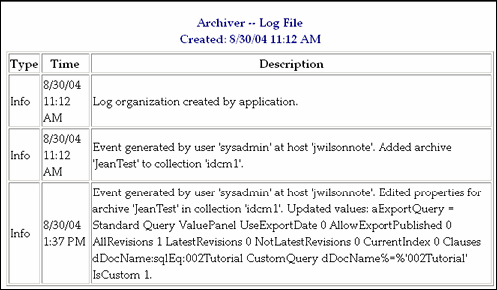
Log Entries
The following types of archiver log entries are generated:
-
Info:Displays basic status information. For example, status information is logged when an export and an import starts and finishes.
-
Error:Displays user and administration errors that occur but do not stop the software from functioning. For example, an error is logged if there is no file information for a content item that you are trying to export.
-
Fatal:Displays errors that stop the software from functioning. For example, an irrecoverable error is logged if the Content Server instance cannot access the database. Check the connection string, user name, and password.
Managing Archives
After archives are created, they can be added to collections and manipulated as a group.
Creating a New Archive
To create a new, undefined archive:
-
Display the Main Archiver window in either standalone or browser mode.
For instructions in using standalone mode, see Running Archiver as a Standalone Application.
-
If necessary, open the collection where you want to create the new archive. For more information, see Opening a Collection.
-
From Edit,select Add.
-
In the Add Archive window, enter the archive name and description. The archive name cannot contain spaces.
-
Click OK.
Copying an Existing Archive
To copy an existing archive to a different directory location:
Note:
This procedure copies the files in an archive. It does not create a new collection or update the collection.hda file if the archive is copied to a collection directory.
-
Display the archiver in standalone mode.
For instructions, see Running Archiver as a Standalone Application.
-
If necessary, open the collection that contains the archive to be copied. For more information, see Opening a Collection.
-
Select the archive to be copied.
-
From Edit,select Copy To.
-
In the Copy Archive window, accept the original archive name, or change the name as necessary.
-
In the Copy Archive To Directory field, enter the directory path where the archive will be copied.
-
Click OK.
The archive files are copied to the specified directory.
Creating a New Archive by Copying
You can copy archives from your system for storage or to your system from another archive if you are using the Archiver standalone version.
To create a new archive in the current collection by copying an existing archive:
-
Display the archiver in standalone mode.
For instructions, see Running Archiver as a Standalone Application.
-
If necessary, open the collection where you want to create the new archive. See Opening a Collection.
-
From Edit,select Add.
-
In the Add Archive window, enter the archive name and description. The archive name cannot contain spaces.
-
Select Copy From.
-
Click Browse.
-
Navigate to and select the desired archive file (archive.hda).
-
Click Open.
-
Click OK.
The archive files are copied to the default archive directory in the local Content Server instance.
Deleting an Archive
To delete an archive from a collection:
-
Open the archive collection.
-
Select the archive to delete in the Current Archives list.
-
From Edit,select Delete. You are prompted to confirm the action.
-
Click OK.
The archive is deleted from the collection.
Running Archiver as a Standalone Application
The following information details how to run Archiver as a standalone application, which is required to create collections.
Running the Archiver in Windows
You can run the archiver in both Windows and Unix.
To run Archiver on a Windows operating system:
-
Select the application from the Windows Start menu, then choose Programs, then Content Server, then instance, then Analyzer. A login window or application window opens.
Note:
It may take several seconds for the login window or the application window to appear, and the window may be hidden by other windows.
-
If required, enter the administrator login name and password, then click OK. The Main Archiver window opens.
Running the Archiver in UNIX
You can run the Archiver in both Unix and Windows.
To run Archiver on a UNIX operating system:
-
Navigate to the
DomainHome/ucm/cs/bin/directory. -
Enter ./archive
-
If required, enter the administrator login name and password.
The Main Archiver window of the application opens.
Managing Collections
Collections are a set of archives and are used to group archives for different archive functions.
Note:
The standalone mode of the Archiver application is required to create new collections or browse the local file system to connect to new collections.
Opening a Collection
To open an existing archive collection:
-
Run Archiver in standalone mode.
For instructions, see Running Archiver as a Standalone Application.
-
From Options,choose Open Archive Collection.
-
Select the collection from the list of existing collections on the Open Archive Collection window (shows the default collection and any other connected collections).
-
To browse to a new collection, use one of these methods:
To select the collection from a shared file system location (standalone Archiver only):
-
Click Browse Local.
-
In the Find Archive Collection Definition File window, navigate to and select the collection HDA file.
-
Click Open.
The Browse to Archiver Collection window opens.
To select the collection from a remote Content Server instance:
-
Click Browse Proxied.
The Browse for Proxied Collection window opens with a list that includes all Content Server instances to which an outgoing provider has been set up.
-
Select the Content Server instance in the Proxied Serverslist.
-
Select the collection in the Collections list.
-
Click OK.
-
Creating a Collection
To create a new archive collection:
Note:
You can create a new collection only on the local Content Server instance using the standalone Archiver.
-
Run Archiver in standalone mode.
For instructions, see Running Archiver as a Standalone Application.
-
From Options,choose Open Archive Collection.
-
In the Open Archiver Collection window, click Browse Local.
-
In the Find Archive Collection Definition File window, navigate to and select the directory where you want to create the new collection.
-
Enter a file name for the new collection (
collection.hdais the default). -
Click Open.
You are prompted to create a collection definition (HDA) file.
-
Click Yes.
-
In the Browse To Archiver Collection window, enter a collection name in the Name field.
-
Collection names cannot contain spaces.
-
Use the same name for a collection and its directory to make navigation easier.
-
-
Enter the directory path for the weblayout and vault directories in the Web Directoryand Vault Directoryfields.
-
Use the same path style as shown in the Location field.
-
To find the directory paths, display the Configuration Information page.
-
-
Click OK.
The new collection is shown in the Open Archive Collection page.
-
Click Open to open the new collection.
Removing a Collection
To remove an archive collection:
Note:
You cannot remove the default collection.
-
From Options, choose Open Archive Collection.
-
In the Open Archive Collection window, select the collection to be removed.
-
Click Remove.
You are prompted to confirm the action.
-
Click OK.
The collection is removed from the Content Server instance. (The collection and archive files remain in the file system, and must be deleted manually.)
Moving the Default Archive Collection
You can change the file system location of the default archive collection by moving the collection and pointing the Content Server instance to the new location. For example, you might want to keep all of your archive data on a separate drive from the program files for easier backup and expansion.
Note:
The default collection is the archives/ directory.
To move the default archive collection:
-
For data safety, close any standalone Archiver applications and stop the Content Server instance.
-
Add the
CollectionLocationconfiguration variable with a specified path to the new location in theDomainHome/ucm/cs/bin/intradoc.cfgfile:CollectionLocation=*path* -
To maintain the previously created archives for the default collection, move the contents of the
archives/directory to the new location you specified in theCollectionLocationsetting. If you do not move the contents, the system will create an empty collection. -
Start the Content Server instance.
Note:
The Content Server instance re-creates the default
Domain_home/ucm/cs/archives/directory when it is restarted, but Archiver defaults to using the collection in the new location.
Managing Batch Files
A batch file describes the metadata for exported revisions. A batch file is created each time Archiver performs an export.
Removing Revisions from a Batch File
To remove individual revisions from a batch file:
-
Open the archive collection.
For instructions, see Opening a Collection.
-
Select the archive in the Current Archives list.
-
In the Main Archiver window, click View Batch Files.
-
In the View Batch files window, select the batch file.
-
Click Edit.
-
In the View Exported Content Items window, use the Filter element and the navigation buttons to display the revision to be deleted.
-
Select the revision to be deleted.
-
Click Delete.
The Status changes to
Deletedfor the selected revision. -
To undo the last deletion, click Undo. To return all deleted revisions to
Archivedstatus, click Refresh. -
Click Applyto delete the specified revisions.
-
Click Close.
Deleting a Batch File
To delete a batch file from an archive:
-
Open the archive collection.
For instructions, see Opening a Collection.
-
Select the archive in the Current Archives list.
-
In the Archiver window General tab, click View Batch Files.
-
In the View Batch Files window, select the batch file to delete.
-
Click Delete.
You are prompted to confirm the action.
-
Click OK.
The batch file is deleted from the archive.
-
Specify whether to replace existing batch files upon export:
-
To delete all existing batch files when the next export is initiated, selectReplace Existing Export Files.
-
To leave existing batch files in place when the next export is initiated, deselectReplace Existing Export Files.
-
-
Specify which files to export:
-
To export the native (vault) and web-viewable (weblayout) files, selectCopy Web Content.
-
To export only the native (vault) files, deselectCopy Web Content.
-
-
Click OK.
The export options are displayed in the Export Options section of the General tab.