Setup Steps
Topics in this section:
- Set up your Kubernetes cluster
- Prepare the environment
- Create a database and the appropriate database services
- Install and configure Oracle HTTP Server in the DMZ
- Configure a front-end load balancer
- Apply operating system changes for Coherence
- Run the Repository Creation Utility to set up your database schemas
- Deploy WebLogic Kubernetes Operator and Oracle SOA Suite
- Configure custom keystore for Oracle SOA Suite domains
- Using Custom Certificates in Oracle HTTP Servers
- Configure redundant persistent volume
- Set front-end addresses
- Enable FAN for GridLink data sources
- Configure ASM
- Configure coredns allocation
- Adjust server’s pods Liveness Probe
Set up your Kubernetes cluster
Prepare the environment for the Kubernetes control plane (Master nodes)
-
Create the L4/TCP listener for the load balancer (LBR).
-
Create the LBR backend pool with the list of control plane nodes that will be added (do not use IPs, always use hostnames).
Note:
We recommend maintaining the values of the followingkube-apibackend pool parameters within the prescribed range to minimize the downtime while restarting the Kubernetes control pane or performing maintenance operations.- Healthcheck interval : Within 1000 milliseconds
- Healthcheck timeout : Within 900 milliseconds
-
Enable the L4 LBR to route to the backend set/pool.
Note:
It is important that this is an L4/TCP listener, not an HTTP/HTTPS listener. -
Make sure that the nodes are in ready state.
-
Create an ssh key (use a common ssh key to enable access from the node executing the setup to the control plane nodes).
-
Allow traffic in intermediate firewalls between control plane nodes and the front-end LBR. Refer to the Kubernetes documentation for the required ports.
- Create the HA cluster with 3 Master and 3 Minion nodes. For Setup refer documentation with Stacked etcd Topology.
Prepare the environment
Configure firewalls and network
- Allow traffic from the load balancer (LBR) to the Oracle HTTP Server (OHS) port that will be configured (7777 by default for OHS).
- Allow traffic from the OHS to the node port that will be configured in the worker nodes for the Administration Server (30701), SOA cluster (30801), and Service Bus cluster (30901).
- Allow traffic from the worker nodes to the control plane front-end
kube-apivirtual server port and also to the front-end Oracle SOA Suite. - Allow traffic from worker nodes to the database listener and ONS port (1521 and 6200 by default, respectively).
You can use the Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle SOA Suite on-premise as a reference.
Load Oracle SOA Suite images on all the worker nodes
Refer Obtain the Oracle SOA Suite Docker image to load the images on each worker node and tag appropriately.
Enable a shared storage location for the persistent volume
A shared storage device must be used from the different worker nodes. This storage hosts the Oracle SOA Suite domain directory. Initially, a single storage location is used to create a persistent volume that will host the Oracle SOA Suite domain. Mount this shared storage (NFS/NAS) from all the worker nodes using the same mount path in all of them.
For example, mount NFS1 (10.10.0.21:/k8nfs) in all the worker nodes to a share directory /k8nfs:
$ grep "k8nfs nfs" /etc/fstab
10.10.0.21:/k8nfs /k8nfs nfs rw,relatime,vers=3,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,mountaddr=10.10.0.21,mountvers=3,mountport=2048,mountproto=udp,local_lock=none,addr=10.10.0.21Later, steps are provided to configure a second storage location for high availability.
Create a database and the appropriate database services
The installation and creation of the RAC database is out of the scope of this document. Once the database is configured, the appropriate services must be created to access the schemas from the middle tier. It is critical that a precise non-default/administration service is created for Oracle SOA Suite. Refer to Preparing the Database for an Enterprise Deployment in the Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle SOA Suite 14.1.2.0.0.
Install and configure Oracle HTTP Server in the DMZ
Follow the steps in the Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle SOA Suite to create two Oracle HTTP Server (OHS) instances in separate nodes from the worker nodes. To configure OHS with the back-end Kubernetes Oracle SOA Suite or Service Bus servers, you must use a port in the range of 30000 - 32767. You will use this port in the Oracle SOA Suite configuration scripts later on.
In this Kubernetes Enterprise Deployment Guide, OHS routes to node ports configured for each separate Oracle SOA Suite/Service Bus cluster in the SOA domain. OHS then routes to these node ports, which redirect to the pertaining server pods. The OHS directive for the configuration must disable DynamicServerList because the node ports are not really WebLogic listeners and it is the node port configuration that maintains an intelligent list of available WebLogic servers. The OHS directive for the soa-infra mount in OHS looks like this:
<Location /soa-infra>
WLSRequest ON
WebLogicCluster workernode1:30801,workernode2:30801,workernode3:30801
</Location>Similarly, the other directives for other paths should reflect similar node port addresses.
Configure a front-end load balancer
You can either use BigIp F5 LBR or any standard LBR, such as CISCO. Refer to the Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle SOA Suite for the required virtual servers: Preparing the Load Balancer and Firewalls for an Enterprise Deployment. The on-premises Enterprise Deployment Guide provides a detailed list of virtual servers/listeners that can be used for optimum isolation of services and traffic. For Kubernetes, at a minimum you should have a virtual server/listener for Oracle SOA Suite using the OHS listeners as back-end pool.
-
Create the load balancer’s L7/https listener.
-
Create a back-end pool with the list of OHS nodes/ports that will be used by Oracle SOA Suite (do not use IPs, always use hostnames).
-
Enable the L7/https listener load balancer to route to the OHS back-end set/pool.
-
Configure the front-end load balancer to route to the OHS pool.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you configure LBR for cookie-based persistence because session persistence is required for some web applications of SOA, such as BPM Worklist (/integration/worklistapp), SOA Composer (/soa/composer) and so on.
Apply operating system changes for Coherence
Coherence requires specific settings to create clusters in a Kubernetes environment. Refer to the steps provided in the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator documentation.
Run the Repository Creation Utility to set up your database schemas
To create the database schemas for Oracle SOA Suite, run the create-rcu-schema.sh script with SOA_PROFILE_TYPE=LARGE. Sample command as below
./create-rcu-schema.sh \
-s SOA1 \
-t soaosb \
-d oracle-db.default.svc.cluster.local:1521/devpdb.k8s \
-n default \
-c oracle-rcu-secret \
-b EBR \
-i soasuite:release-version \
-r SOA_PROFILE_TYPE=LARGE,HEALTHCARE_INTEGRATION=NODeploy WebLogic Kubernetes Operator and Oracle SOA Suite
Follow the steps to Install WebLogic Kubernetes Operator , Prepare the environment for Oracle SOA Suite domains and Create Oracle SOA Suite domain
After successful Oracle SOA Suite domain creation and starting the servers, check the pods and the different services created. Once the Oracle SOA Suite managed servers reach RUNNING state (the pods are ready), check typical Oracle SOA Suite URLs using the front-end load balancer.
Create Nodeport services for Admin Server, SOA cluster and OSB Cluster with
sessionAffinity as ClientIP. Below is the sample Nodeport
Service for soa cluster:
$ cat soa-nodeport.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: soainfra-soa-nodeport-service
namespace: soans
labels:
weblogic.domainUID: soainfra
weblogic.clusterName: soa_cluster
spec:
type: NodePort
sessionAffinity: ClientIP
ports:
- port: 7004
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 7004
nodePort: 30234
selector:
weblogic.domainUID: soainfra
weblogic.clusterName: soa_clusterSOA pods and services deployed and ready:
$ kubectl get all -n soans
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/soaedgdomain-adminserver 1/1 Running 0 47h
pod/soaedgdomain-create-soa-infra-domain-job-6pq9z 0/1 Completed 0 68d
pod/soaedgdomain-soa-server1 1/1 Running 0 2d2h
pod/soaedgdomain-soa-server2 1/1 Running 0 2d2h
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/soaedgdomain-adminserver ClusterIP None <none> 30012/TCP,7001/TCP 2d4h
service/soaedgdomain-adminserver-ext NodePort 10.104.20.22 <none> 30012:30012/TCP,7001:30701/TCP 31d
service/soaedgdomain-cluster-osb-cluster ClusterIP 10.100.97.127 <none> 8002/TCP 68d
service/soaedgdomain-cluster-soa-cluster ClusterIP 10.101.101.113 <none> 7003/TCP 68d
service/soaedgdomain-cluster-soa-cluster-node-port NodePort 10.105.51.223 <none> 7003:30801/TCP 68d
service/soaedgdomain-osb-server1 ClusterIP 10.110.81.153 <none> 8002/TCP 2d4h
service/soaedgdomain-osb-server2 ClusterIP 10.103.220.112 <none> 8002/TCP 2d4h
service/soaedgdomain-osb-server3 ClusterIP 10.97.50.117 <none> 8002/TCP 2d4h
service/soaedgdomain-osb-server4 ClusterIP 10.98.48.247 <none> 8002/TCP 2d4h
service/soaedgdomain-osb-server5 ClusterIP 10.102.137.176 <none> 8002/TCP 2d4h
service/soaedgdomain-soa-server1 ClusterIP None <none> 7003/TCP 2d4h
service/soaedgdomain-soa-server2 ClusterIP None <none> 7003/TCP 2d4h
service/soaedgdomain-soa-server3 ClusterIP 10.105.108.74 <none> 7003/TCP 2d4h
service/soaedgdomain-soa-server4 ClusterIP 10.109.191.102 <none> 7003/TCP 2d4h
service/soaedgdomain-soa-server5 ClusterIP 10.107.2.99 <none> 7003/TCP 2d4h
NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE
job.batch/soaedgdomain-create-soa-infra-domain-job 1/1 4m24s 68dConfigure custom keystore for Oracle SOA Suite domains
Run the the helper script custom-keystore.sh available at
${WORKDIR}/custom-keystore to configure custom keystore for
Oracle SOA Suite domains.
Refer Replacing Demo CA Certificates With Domain CA Signed Certificates.
Using Custom Certificates in Oracle HTTP Servers
Copy the trust.p12 (created with custom-keystore.sh) to the OHS. The following commands are useful to manage keys and wallets in OHS.
Export a certificate from a Java KeyStore (JKS) or PKCS12 keystore file.
$ keytool -export -keystore trust.p12 -storepass trustKeyStorePassword -alias trustcert1 -file trust.crt
Certificate stored in file <trust.crt>Command to create a wallet for OHS
$ orapki wallet create -wallet WLSSLWalletEDG -auto_login -pwd *****
Oracle PKI Tool Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Production
Version 23.0.0.0.0
Copyright (c) 2004, 2024, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Operation is successfully completed.Add trusted certificate to the wallet
$ orapki wallet add -wallet WLSSLWalletEDG -trusted_cert -cert trust.crt -pwd *****
Oracle PKI Tool Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Production
Version 23.0.0.0.0
Copyright (c) 2004, 2024, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Operation is successfully completed.Modify the $WEB_DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/components/OHS/ohs1/mod_wl_ohs.conf to include the appropriate WLSSWallet file (required to route on SSL to the WLS backends) as follows:
# NOTE : This is a template to configure mod_weblogic.
LoadModule weblogic_module "${PRODUCT_HOME}/modules/mod_wl_ohs.so"
# This empty block is needed to save mod_wl related configuration from EM to this file when changes are made at the Base Virtual Host Level
<IfModule weblogic_module>
WLIOTimeoutSecs 900
KeepAliveSecs 290
FileCaching OFF
WLSocketTimeoutSecs 15
ErrorPage http://www.oracle.com/splash/cloud/index.html
WLRetryOnTimeout NONE
WLForwardUriUnparsed On
SecureProxy On
WLSSLWallet "/u02/oracle/config/keystores/WLSSLWalletEDG"
</IfModule>Configure redundant persistent volume
To increase the flexibility in moving Oracle SOA Suite or Service Bus pods around in the Kubernetes cluster, we use node selectors where odd server pods (soa_server1, soa_server3, soa_server5, and so on) are assigned to node selector 1 and even server pods (soa_server2, soa_server4, soa_server6, and so on) are assigned to node selector 2. The resulting configuration is:
Figure 9-2 Configure redundant persistent valume
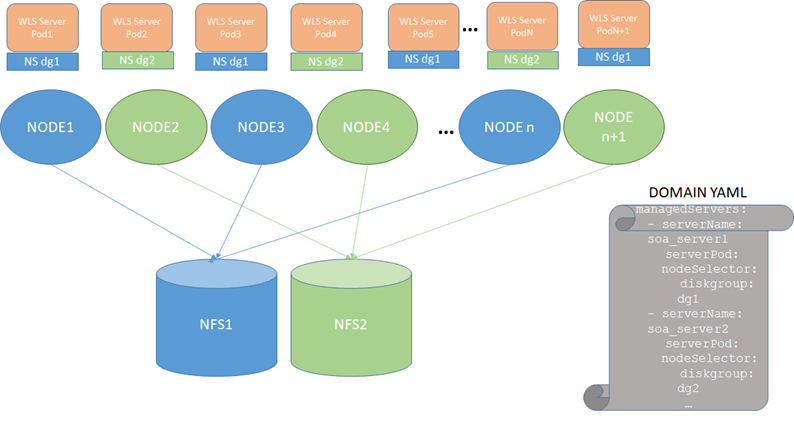
To use this configuration, follow these steps:
-
Stop the Oracle SOA Suite domain. Refer to Scripts to start and stop a domain.
-
Mount NFS1 in all even worker nodes and NFS2 in all odd worker nodes as in the diagram above. For example:
MOUNT ON ODD NODE [opc@olk8-w1 ~]$ grep "k8nfs nfs" /etc/fstab 10.10.0.21:/k8nfs /k8nfs nfs rw,relatime,vers=3,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,mountaddr=10.10.0.21,mountvers=3,mountport=2048,mountproto=udp,local_lock=none,addr=10.10.0.21 MOUNT ON EVEN NODE [opc@olk8-w2 ~]$ grep "k8nfs nfs" /etc/fstab 10.10.0.27:/k8nfs2 /k8nfs nfs rw,relatime,vers=3,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,mountaddr=10.10.0.27,mo untvers=3,mountport=2048,mountproto=udp,local_lock=none,addr=10.10.0.27 MOUNT ON ODD NODE [opc@olk8-w3 ~]$ grep "k8nfs nfs" /etc/fstab 10.10.0.21:/k8nfs /k8nfs nfs rw,relatime,vers=3,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,mountaddr=10.10.0.21,mountvers=3, mountport=2048,mountproto=udp,local_lock=none,addr=10.10.0.21 - Copy the domain mount to an NFS replica, NFS2 (this can be done through a
snapshot or through direct sftp/secure copy).
For example, if the domain is deployed in /k8nfs hosted by NFS1, after stopping the domain, secure copy the data present at /k8nfs on NFS1 to /k8nfs2 on NFS2:
$ cd /k8nfs $ scp -R * user@[NFS2]:/k8nfs2 - Label the odd nodes for NFS1 and the even nodes for NFS2.
For example, add the label diskgroup=dg1 for NFS1 and diskgroup=dg2 for NFS2:
$ kubectl label nodes olk8-w1 diskgroup=dg1 $ kubectl label nodes olk8-w2 diskgroup=dg2 $ kubectl label nodes olk8-w3 diskgroup=dg1Verify the added labels using the following command:
$ kubectl get nodes --show-labelsSample output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION LABELS olk8-m1 Ready master 10d v1.XX.X beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=olk8-m1,kubernetes.io/os=linux,node-role.kubernetes.io/master= olk8-m2 Ready master 10d v1.XX.X beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=olk8-m2,kubernetes.io/os=linux,node-role.kubernetes.io/master= olk8-m3 Ready master 10d v1.XX.X beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=olk8-m3,kubernetes.io/os=linux,node-role.kubernetes.io/master= olk8-w1 Ready <none> 10d v1.XX.X beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,diskgroup=dg1,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=olk8-w1,kubernetes.io/os=linux,name=admin olk8-w2 Ready <none> 10d v1.XX.X beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,diskgroup=dg2,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=olk8-w2,kubernetes.io/os=linux,name=wls1 olk8-w3 Ready <none> 10d v1.XX.X beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,diskgroup=dg1,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=olk8-w3,kubernetes.io/os=linux,name=wls2 - To assign the appropriate selectors in the domain:
- Edit the domain
(domain.yaml). - Alter the managed servers section for all the managed servers configured
in the cluster, sample for soa_server1 and soa_server2 as shown
below:
managedServers: - serverName: soa_server1 serverPod: nodeSelector: diskgroup: dg1 - serverName: soa_server2 serverPod: nodeSelector: diskgroup: dg2 - Apply the domain.yaml
changes:
$ kubectl apply -f domain.yamlNote:
Once this redundant PV configuration is in use, all changes that reside out of the config directory in the domain will need to be copied/synced to the secondary NAS mount manually. The managed servers using NFS2 in the diagram above will replicate only configuration changes that modify files/artifacts under the$DOMAIN_HOME/configdirectory. The rest of changes are NOT copied automatically by the WebLogic infrastructure.For example, if you deploy an
earand specify an upload or stage directory out of theconfigdirectory, theearfiles will NOT be copied by WebLogic).Fileadapter compositeswill place output files in mounts accessible from the pods. The mount point and PV/PVC for the different Oracle SOA Suite server file locations need to be the same, hence a different one from the one used for the$DOMAIN_HOMElocation.For Adapter configuration use a different common shared location which is accessible to all the server pods. Make sure to use different shared location other than $DOMAIN_HOME.
For example create a new NFS share and create the required PV/PVC and update in to the domain yaml so that it will be available to all server pods.
serverPod: volumeMounts: - mountPath: /u01/oracle/user_projects name: weblogic-domain-storage-volume - mountPath: /u01/dev/testing/adapters name: soainfra-adapters-pv-volume volumes: - name: weblogic-domain-storage-volume persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: soainfra-pvc - name: soainfra-adapters-pv-volume persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: soainfra-adapters-pvc
- Edit the domain
Set front-end addresses
For each of the Oracle SOA Suite (soa_cluster) and Service Bus (osb_cluster) clusters, set the appropriate front-end address as follows:
-
Sign in to the WebLogic Remote Console.
-
Navigate to Edit Tree -> environment -> clusters.
-
Click the cluster name.
-
Click the HTTP tab.
-
Enter the Frontend Host and Frontend Port details.
Note:
Note: Set the front-end details for each cluster and for the Administration Server.
Enable FAN for GridLink data sources
Data sources in the default deployment for Oracle SOA Suite on Kubernetes use generic data sources. With ONS auto-registration in 12.2 Database and later, it is only necessary to enable FAN for the data sources to convert to GridLink (GLDS). You can do this by using the WebLogic Administration Console or the following command and restarting the Administration Server and the managed servers:
grep -L fan-enabled $domain_home/config/jdbc/*.xml | xargs sed -i "s/<\/jdbc-data-source>/<jdbc-oracle-params><fan-enabled>true<\/fan-enabled><\/jdbc-oracle-params><\/jdbc-data-source>/g"After the change is applied, verify that all data sources are marked as GridLink Data Sources in the WebLogic Remote Console.
Configure ASM
Refer to the on-premises Enterprise Deployment Guide for steps to configure Automatic Service Migration.
Configure coredns allocation
Note:
This step is applicable to any Kubernetes system usingcoredns regardless of Oracle SOA Suite deployment. However,
the worker node creation is implicit in the setup, hence it is applied in this
context (post Oracle SOA Suite deployment).
Configure replicas for coredns to spawn both control plane and
master plane. If a restore operation is performed on the control plane, worker nodes
may stop working properly. If the coredns lands entirely in the
worker nodes, the control plane may not function correctly if they are brought down
for maintenance. Place at least two coredns pods on the control
plane and another two on the worker nodes. The coredns footprint is
low.
VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
146268 41684 29088 S 0.3 0.1 25:44.04 corednsAccording to CoreDNS documentation, you can estimate the amount of memory required for a CoreDNS instance (using default settings) with the following formula:
MB required (default settings) = (Pods + Services) / 1000 + 54Hence, first label nodes in both control and worker plane.
$ kubectl label nodes olk8-m1 area=dnsarea
$ kubectl label nodes olk8-m2 area=dnsarea
$ kubectl label nodes olk8-m3 area=dnsarea
$ kubectl label nodes olk8-w1 area=dnsarea
$ kubectl label nodes olk8-w2 area=dnsarea
$ kubectl label nodes olk8-w3 area=dnsareaAnd then update the coredns deployment to use topology spread constraints
Note:
Topology spread constraints is beta starting in Kubernetes v1.18First, enable the feature gate in kube-api server and in
kube-scheduler. Then, modify the coredns
deployment for an appropriate spread of pods across worker and control plane
nodes.
The coredns topology spread config details are:
Example for updated coredns deployment yaml:
$ kubectl get deployment coredns -n kube-system -o yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
annotations:
deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: "7"
creationTimestamp: "2021-01-15T13:15:05Z"
generation: 8
labels:
area: dnsarea
k8s-app: kube-dns
managedFields:
- apiVersion: apps/v1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:labels:
.: {}
f:k8s-app: {}
f:spec:
f:progressDeadlineSeconds: {}
f:revisionHistoryLimit: {}
f:selector:
f:matchLabels:
.: {}
f:k8s-app: {}
f:strategy:
f:rollingUpdate:
.: {}
f:maxSurge: {}
f:maxUnavailable: {}
f:type: {}
f:template:
f:metadata:
f:labels:
.: {}
f:k8s-app: {}
f:spec:
f:containers:
k:{"name":"coredns"}:
.: {}
f:args: {}
f:image: {}
f:imagePullPolicy: {}
f:livenessProbe:
.: {}
f:failureThreshold: {}
f:httpGet:
.: {}
f:path: {}
f:port: {}
f:scheme: {}
f:initialDelaySeconds: {}
f:periodSeconds: {}
f:successThreshold: {}
f:timeoutSeconds: {}
f:name: {}
f:ports:
.: {}
k:{"containerPort":53,"protocol":"TCP"}:
.: {}
f:containerPort: {}
f:name: {}
f:protocol: {}
k:{"containerPort":53,"protocol":"UDP"}:
.: {}
f:containerPort: {}
f:name: {}
f:protocol: {}
k:{"containerPort":9153,"protocol":"TCP"}:
.: {}
f:containerPort: {}
f:name: {}
f:protocol: {}
f:readinessProbe:
.: {}
f:failureThreshold: {}
f:httpGet:
.: {}
f:path: {}
f:port: {}
f:scheme: {}
f:periodSeconds: {}
f:successThreshold: {}
f:timeoutSeconds: {}
f:resources:
.: {}
f:limits:
.: {}
f:memory: {}
f:requests:
.: {}
f:cpu: {}
f:memory: {}
f:securityContext:
.: {}
f:allowPrivilegeEscalation: {}
f:capabilities:
.: {}
f:add: {}
f:drop: {}
f:readOnlyRootFilesystem: {}
f:terminationMessagePath: {}
f:terminationMessagePolicy: {}
f:volumeMounts:
.: {}
k:{"mountPath":"/etc/coredns"}:
.: {}
f:mountPath: {}
f:name: {}
f:readOnly: {}
f:dnsPolicy: {}
f:nodeSelector:
.: {}
f:kubernetes.io/os: {}
f:priorityClassName: {}
f:restartPolicy: {}
f:schedulerName: {}
f:securityContext: {}
f:serviceAccount: {}
f:serviceAccountName: {}
f:terminationGracePeriodSeconds: {}
f:tolerations: {}
f:volumes:
.: {}
k:{"name":"config-volume"}:
.: {}
f:configMap:
.: {}
f:defaultMode: {}
f:items: {}
f:name: {}
f:name: {}
manager: kubeadm
operation: Update
time: "2021-01-15T13:15:05Z"
- apiVersion: apps/v1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:labels:
f:area: {}
f:spec:
f:replicas: {}
f:template:
f:metadata:
f:annotations:
.: {}
f:kubectl.kubernetes.io/restartedAt: {}
f:labels:
f:foo: {}
f:spec:
f:topologySpreadConstraints:
.: {}
k:{"topologyKey":"area","whenUnsatisfiable":"DoNotSchedule"}:
.: {}
f:labelSelector:
.: {}
f:matchLabels:
.: {}
f:foo: {}
f:maxSkew: {}
f:topologyKey: {}
f:whenUnsatisfiable: {}
manager: kubectl
operation: Update
time: "2021-01-28T16:00:21Z"
- apiVersion: apps/v1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:annotations:
.: {}
f:deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: {}
f:status:
f:availableReplicas: {}
f:conditions:
.: {}
k:{"type":"Available"}:
.: {}
f:lastTransitionTime: {}
f:lastUpdateTime: {}
f:message: {}
f:reason: {}
f:status: {}
f:type: {}
k:{"type":"Progressing"}:
.: {}
f:lastTransitionTime: {}
f:lastUpdateTime: {}
f:message: {}
f:reason: {}
f:status: {}
f:type: {}
f:observedGeneration: {}
f:readyReplicas: {}
f:replicas: {}
f:updatedReplicas: {}
manager: kube-controller-manager
operation: Update
time: "2021-01-28T16:00:39Z"
name: coredns
namespace: kube-system
resourceVersion: "2520507"
selfLink: /apis/apps/v1/namespaces/kube-system/deployments/coredns
uid: 79d24e61-98f4-434f-b682-132625b04c49
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 4
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: kube-dns
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 25%
maxUnavailable: 1
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/restartedAt: "2021-01-28T15:29:48Z"
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
foo: bar
k8s-app: kube-dns
spec:
containers:
- args:
- -conf
- /etc/coredns/Corefile
image: k8s.gcr.io/coredns:1.6.7
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 5
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 8080
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 60
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 5
name: coredns
ports:
- containerPort: 53
name: dns
protocol: UDP
- containerPort: 53
name: dns-tcp
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 9153
name: metrics
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /ready
port: 8181
scheme: HTTP
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
resources:
limits:
memory: 170Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 70Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
add:
- NET_BIND_SERVICE
drop:
- all
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/coredns
name: config-volume
readOnly: true
dnsPolicy: Default
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
restartPolicy: Always
schedulerName: default-scheduler
securityContext: {}
serviceAccount: coredns
serviceAccountName: coredns
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
tolerations:
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
topologySpreadConstraints:
- labelSelector:
matchLabels:
foo: bar
maxSkew: 1
topologyKey: area
whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule
volumes:
- configMap:
defaultMode: 420
items:
- key: Corefile
path: Corefile
name: coredns
name: config-volume
status:
availableReplicas: 4
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-01-21T19:08:12Z"
lastUpdateTime: "2021-01-21T19:08:12Z"
message: Deployment has minimum availability.
reason: MinimumReplicasAvailable
status: "True"
type: Available
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-01-28T15:29:48Z"
lastUpdateTime: "2021-01-28T16:00:39Z"
message: ReplicaSet "coredns-84b49c57fd" has successfully progressed.
reason: NewReplicaSetAvailable
status: "True"
type: Progressing
observedGeneration: 8
readyReplicas: 4
replicas: 4
updatedReplicas: 4The labels and spread topology changes are:
labels:
foo: bar
k8s-app: kube-dns
topologySpreadConstraints:
- labelSelector:
matchLabels:
foo: bar
maxSkew: 1
topologyKey: area
whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotScheduleThis guarantees an even distribution across the master and worker nodes, so that if the control plane is restored, the worker pods will continue without issues and the other way around.
Sample resulting coredns distribution:
$ kubectl get pods -A -o wide | grep coredns
kube-system coredns-84b49c57fd-4fz4g 1/1 Running 0 166m 10.244.1.20 olk8-m2 <none> <none>
kube-system coredns-84b49c57fd-5mrkw 1/1 Running 0 165m 10.244.4.76 olk8-w2 <none> <none>
kube-system coredns-84b49c57fd-5zm88 1/1 Running 0 165m 10.244.2.17 olk8-m3 <none> <none>
kube-system coredns-84b49c57fd-nqlwb 1/1 Running 0 166m 10.244.4.75 olk8-w2 <none> <none>Adjust server’s pods Liveness Probe
By default, the liveness probe is configured to check liveness every 45
seconds, which might cause requests to be routed to backend pods that are no longer
available during outage scenarios. Recommended to adjust liveness probe values so
that on hard node failures pods are marked as down faster. To configure a more
aggressive probe, edit the domain and change the
serverPods.livenessProbe values to the following:
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 1
initialDelaySeconds: 60
periodSeconds: 40
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 5Refer WebLogic Kubernetes Operator documentation for details on how to customize the liveness probe.