Request-Reply-Callback Message Exchange Patterns
In a request-reply-callback interaction, the Mediator is invoked and sends a response and an asynchronous reply to the initial caller. Depending on the type of routing rule target, the responses, faults, and callbacks are handled as shown in Table 24-6:
Table 24-6 Response When Mediator's WSDL Is a Request Response Callback
| Routing Rule Target Type | Response |
|---|---|
|
Request |
There should be at least one sequential routing rule that returns a response. No callback is sent to the caller if there is no routing rule with a defined callback. |
|
Request Response |
There should be at least one sequential routing rule that returns a response. No callback is sent if there is no routing rule with a defined callback. |
|
Request Response Fault |
There should be at least one sequential routing rule that returns a response. No callback is sent to the caller if there is no routing rule with a defined callback. The fault is forwarded to another target or event. |
|
Request Callback |
There should be at least one sequential routing rule that returns a response. Mediator returns |
|
Request Response Callback |
The response and callback are sent back to the caller. |
|
Request Response Fault Callback |
The response and callback are sent back to the caller. The fault is forwarded to another target or event. |
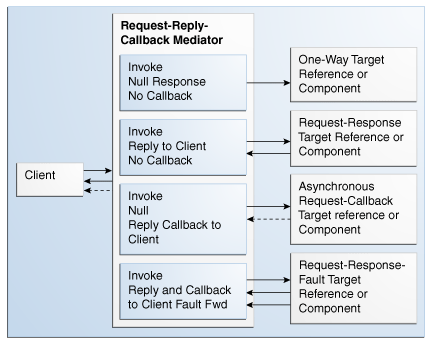
Figure 24-5 illustrates the request-reply-callback message exchange pattern.
Figure 24-5 Request-Reply-Callback Message Exchange Pattern
Description of "Figure 24-5 Request-Reply-Callback Message Exchange Pattern"