31 Monitoring Oracle Healthcare
This chapter includes the following sections:
Introduction to the Audit Trail
You can configure the audit policy to only capture the information you need and ignore the rest. This is done on the Audit Policy page of Oracle Enterprise Manager. See Managing Audit Policies in Securing Applications with Oracle Platform Security Services for more information.
The set of auditable events for each application and component is defined by the audit policy and differs between each application. When you expand the list of events for a component, only those events that can be audited for that component appear in the list. For each event, you can further specify whether to only log successful attempts or failed attempts (currently Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration only logs successful attempts).
When you configure auditing, you can select from the following audit levels:
-
Low: This option selects a subset of events from all auditable components in the audit policy list, including a subset of Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration events. It does not allow custom filters to be created.
-
Medium: This option selects a larger subset of events from all auditable components in the audit policy list, including all Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration events. It does not allow custom filters to be created.
-
Custom: This options lets you select only those components, events, and conditions that you want to audit. This is the recommended level for Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration. You need to select this level in the Oracle Enterprise Manager console to enable auditing.
You can also specify a list of users whose activity is audited regardless of the actions performed or the component used. Auditing occurs for these users no matter what audit level or filters are defined.
Oracle SOA Suite for Healthcare Integration Auditing Options
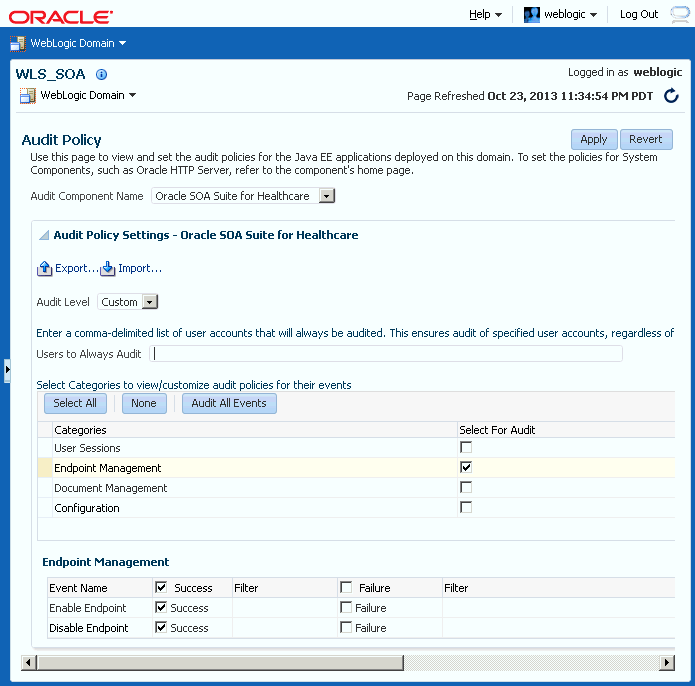
The components and events available for auditing are listed on the Audit Policy page of Oracle Enterprise Manager (Weblogic domain > Security > Audit Policy). To configure the these options, select Oracle SOA Suite for Healthcare from the Audit Component Name list, Custom from the Audit Level list, and click the check boxes adjacent to the events as displayed in Figure 31-1.
Figure 31-1 Healthcare Integration Components on the Audit Policy Page
Description of "Figure 31-1 Healthcare Integration Components on the Audit Policy Page"
Note:
Currently only the SUCCESS events are audited. You should not select FAILURE events.
Currently, the following components and events are supported for audit in Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration (note that additional events appear in the list, but they are not currently logged):
-
User Session
-
User Login
-
User Logout
-
-
Endpoint Management
-
Create Endpoint
-
Enable Endpoint
-
Disable Endpoint
-
Delete Endpoint
-
-
Document Management
-
Create Document Definition
-
Update Document Definition
-
Delete Document Definition
-
Resubmit Message
-
Purge Message
-
Resubmit Message
-
Purge Message
-
Read Payload
-
-
Configuration
-
Import
-
Export
-
Create Internal Delivery Channel
-
Delete Internal Delivery Channel
-
Create Mapset
-
Delete Mapset
-
Oracle B2B Auditing Options
The Oracle B2B components and events available for auditing are listed on the Audit Policy page of Oracle Enterprise Manager. To view or configure the Oracle B2B options, expand the nodes under SOA_B2B.
The available components and events for audit in Oracle B2B include the following:
-
User Session
-
User Login
-
User Logout
-
-
Document Management
-
Create Document Definition
-
Update Document Definition
-
Delete Document Definition
-
Resubmit Message
-
Purge Message
-
Read Payload
-
-
Configuration
-
Import
-
Export
-
Create Batch
-
Delete Batch
-
Update Batch
-
Create Schedule Downtime
-
Delete Schedule Downtime
-
Create Mapset
-
Delete Mapset
-
-
Partner Management
-
Create Trading Partner
-
Delete Trading Partner
-
-
Agreement Management
-
Create Agreement
-
Delete Agreement
-
Edit Agreement
-
Deploy Agreement
-
Activate Agreement
-
Inactivate Agreement
-
Retire Agreement
-
Purge Agreement
-
-
Channel Management
-
Create Delivery Channel
-
Delete Delivery Channel
-
Create Internal Delivery Channel
-
Delete Internal delivery Channel
-
Create Listening Channel
-
Edit Listening Channel
-
Delete Listening Channel
-
-
User Management
-
Add user Roles
-
Remove User Roles
-
Add Supported Document Definition
-
Remove Supported Document Definition
-
Using Filter Conditions for Auditing
For each event, you can define filters for the success condition. Filters use rule-based expressions that are based on the attributes of the event. For most Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration user access auditing, you can use the following attributes in your filter expressions:
-
Host ID
-
Host Network Address
-
Initiator
-
Client IP Address
-
Resource
-
Domain Name
Expressions can include AND and OR operators, as well as a variety of comparison functions, such as equals, starts with, contains, does not equal, and so on.
Configuring the Healthcare Integration Audit Trail
You configure audit policies in Oracle Enterprise Manager by selecting the events or components to include in the audit log. Currently, Oracle B2B components and events are not included in the audit trail.
There are two default configurations, Low and Medium audit levels, that select a predefined subset of components or events. These are not recommended for Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration because they affect all auditable components, not just the components of Oracle SOA Suite for healthcare integration. Selecting either of these options can result in extraneous audit entries and unnecessarily large audit logs. Additionally, these two options do not allow you to define any filters.
The following instructions apply to custom-level audit policy configuration.
To configure auditing for healthcare integration
Viewing User Audit Logs
When an event triggers an audit log entry, the event information is written to the audit log file. The audit log captures the information listed here.
Depending on the type of event that triggered the entry, several of these fields might be empty.
-
Date and time
-
Initiator of the event
-
Event type
-
Event status
-
Message text (indicating what occurred)
-
ECID
-
RID
-
Context fields
-
Session ID
-
Target component type
-
Application name
-
Event category
-
Thread ID
-
Failure code
-
Remote IP address
-
Target
-
Resource
-
Roles
-
Authentication method
-
Reason
You can view the audit log file directly. It is written to the following location:
fmw_home/user_projects/domains/domain_name/servers/managed_server_name/logs/auditlogs/healthcare/audit_1_0.log