22 Enabling AS4-Based Message Exchange
This chapter describes how to enable AS4-based message (typically SOAP-based) exchange between trading partners in Oracle B2B.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Introduction to AS4–Based Message Exchange
Applicability Statement4 (AS4) is a leading standard that aggregates the web service standards to provide necessary transactional features. It standardizes exception handling by defining acknowledgement receipts and error messages, and supports message choreographies. Oracle B2B supports the AS4 protocol in its exchange protocol stack for secure document-agnostic exchange of payloads using web services.
AS4 provides various features such as one-way push, one-way pull, reliability and security over web services. AS4 secures data with authentication, message integrity, non-repudiation of origin, and privacy features.
Exchanging AS4-Based Service Messages with Custom WSDL File
The support for AS4-based messages is available for both inbound and outbound directions. You need to create or use Generic WebService or upload a Web Service Definition Language (WSDL) file that you can customize according to your requirement.
AS4 ebHandler mandates SOAP 1.2, the requirements from BSP 1.1 that depend on SOAP 1.1 would not apply. Similarly, none of the requirements for DESCRIPTION (WSDL) or REGDATA (UDDI) apply here, as these are not used. In the case of SOAP 1.1, the SOAP fault will be received from the service.
It is not necessary to provide a WSDL, because AS4 eliminates WSDL complexity by avoiding the pitfalls of mapping document types and business processes to SOAP operations and actions. The existing Generic WSDL can be used with SOAP 1.2 support.
Exchanging Outbound Messages
From the backend Application (Fabric/AQ/JMS/File/FTP/SFTP) the message will be sent to B2B like other messages. In B2B the Agreement identification will happen based on the From/To/Action and Service or From/To/Doctype and Doc Revision.
Exchanging Inbound Messages
Based on the registered AS4 WS listening channel the trading partner can post the message with appropriate AS4 headers. The user can register an AS4 endpoint using administration -> Listening Channel. The document will be identified based on the user message soap header or normal document identification flow. The message will be processed by AS4 exchange plugin and deliver to the configured backend application.
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ebxml-msg/ebms/v3.0/ns/core/200704/
AS4 exchange plugin also uses WS-HTTP as transport layer. The generic SOAP exchange will use this for identify the exchange. The AS4 Exchange plugin is added much before Generic WS, so if the exchange is identified as AS4 then Generic Exchange will skip the identification layer.
The document identification will be based on the SOAP Header “CollaborationInfo” -> Action/Service combination. The trading partner Identification will be always based on the ebMS 3.0 specification, PartyInfo ->From/To partyId and type combination. There is no specific identifier for AS4, the user can configure custom identifier as part of the administration->types and use the same in partner profile configuration. Default identifier is name and any other Identified like duns. But there is no specific identifier for AS4 (no AS4 Identifier)
Setting up Trading Partners and Hosts
Oracle B2B provides support for AS4 web-service based message exchange with trading partners. This is achieved by having a composite with B2B binding, or AQ, JMS, File, FTP, or SFTP to initiate the payload from the backend application. The same can be sent to the trading partner using AS4.
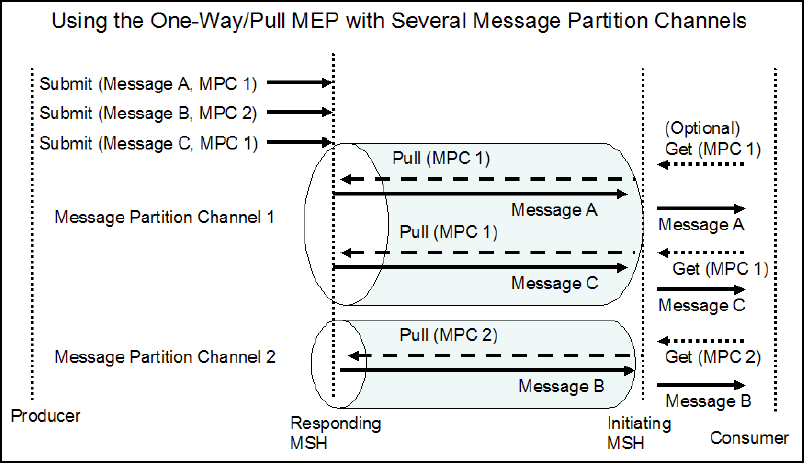
Message Partition Channels
The Message partition channels (MPC) allows for partitioning the flow of the message from sender to receiver into several flows that can be controlled separately and consumed differently.
MPC allows:
-
Setting the transfer priorities: Some messages may be transferred with higher priority than others regardless of the order which they have been submitted.
-
Organizing the inflow of messages on the receiver side: Enables the receiver to dictate each flow in a distinct way.
The following figure shows an example of the MPC work flow for one-way pull transactions.
This can be achieved in Oracle B2B’s existing sequencing mechanism. From the backend application, if the messages are sent with the “MPC” property, then MPC is used as a sequence message target. It is inserted into the appmessage table and sequence manager table. The messages cannot be processed by B2B until the pull message request is received.
Based on the pull message request the corresponding message is picked from the sequence manger table and enqueue into event queue. The message thenpasses through the agreement identification based on the From/To/Action/Service or From/To/Doctype/Docrevision. Based on the agreement configuration, the message is processed and sent to the trading partner as per the delivery channel configuration.
The message prioritization can be handled as part of pull request and response.
Duplicate Message Detection
The duplicate message detection feature provides the ability to detect the message duplication based on the message id. The existing duplicate detection feature is re-used for AS4.
It can be configured as part of the delivery channel. In case of inbound message flow, if the duplicate detection is enabled then the message duplication is identified and a fault message is sent to the message sender.
Example 22-1 Example — Duplicate Message Detection
The following message id is used to detect the message is duplicated or not.
eb:MessageInfo/eb:MessageId.
P-Mode Parameters
B2B supports P-Mode parameters. The parameters relevant to AS4 features are listed here.
Table 22-1 P-Mode Parameters and Descriptions
| P-Mode Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| PMode.ID | Trading Partner profile, the identifier can be configured. |
| PMode.Agreement | The Agreement id will be used to provide th agreement Ref. |
| PMode.MEP | The message exchange pattern(MEP) will be based on the eventName enqueued from backend application. |
| PMode.MEPbinding | The message exchange pattern (MEP) will be based on the eventName enqueued from backend application. The trading partner delivery channel configuration is available. |
| PMode.Initiator.Party | While Enqueue set the From Party will be always a initiator |
| PMode.Initiator.Role | While Enqueue set the ActionName/event Name to set the FromRole |
| PMode.Initiator.Authorization.username | Set the Auth user in OWSM credentials, incase of Basic Authentication |
| PMode.Responder.Party | While Enqueue set the To Party will be always a Responder |
| PMode.Responder.Role | While Enqueue set the ActionName/event Name to set the ToRole |
| PMode.Responder.Authorization.username | Set the Auth user in OWSM credentials, incase of Basic Authentication |
| Protocol.Address | There is no need to configure anything specific to this, as part of delivery channel http will be consider always. |
| Protocol.SOAPVersion | AS4 delivery channel configuration is enough, it will always uses SOAP 1.2 |
| BusinessInfo.Service: | As part of enqueue, set the ActionName/event Name with Service or other wise set as part of Custom Document protocol in case of static service |
| BusinessInfo.Action | As part of enqueue, set the ActionName/event Name with Action or other wise set as part of Custom Document protocol in case of static Action |
| BusinessInfo.Properties[]: | Not Supported to add Properties |
| ErrorHandling.Report.ReceiverErrorsTo | Incase of error/exception B2B will send a exception message to sender |
| ErrorHandling.Report.AsResponse | Incase of error/exception B2B will send a exception message to sender |
| [1].ErrorHandling.Report.ProcessErrorNotifyProducer | The errors will be processed and it will also update request message state to Error. |
| ErrorHandling.Report.DeliveryFailuresNotifyProducer | The errors will not be delivered then the error receipt message will be change the state to Error. |
| Security.WSSVersion | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.X509.Sign | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.X509.Signature.Certificate | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.X509.Signature.HashFunction | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.X509.Signature.Algorithm | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security. X509.Encryption.Encrypt | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.X509.Encryption.Certificate | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.X509.Encryption.Algorithm | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.UsernameToken.username | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.UsernameToken.password | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.UsernameToken.Digest | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.UsernameToken.Created | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.PModeAuthorize | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.SendReceipt | OWSM configuration handles |
| Security.SendReceipt.ReplyPattern | OWSM configuration handles |
Local Policy Attachment
You can attach multiple policies to a delivery channel using LPA (Local Policy Attachment). As part of the delivery channel configuration, you select the OWSM policies and attach to the particular endpoint.
Use-Case Scenarios
Scenarios about exchanging documents between two partners.
Inbound Messaging
The sending and receiving MSH are configured to exchange a particular message type using reliable messaging. The sending MSH sends a signed message of this type.
The expected result is that the receiving MSH returns a synchronous AS4 non-repudiation receipt. The content of the NonRepudiationInformation element in the returned receipt MUST match the Signature of the received message. This can be determined using Message logs, message trackers and/or TCP monitoring tools; the latter requires the to not use TLS.