17 Creating Reports
This chapter describes Oracle B2B reports that provide real-time status on the runtime behavior of deployed data. It discusses business message report, wire message report, application message report, error report, and conversation report.
The chapter includes the following sections:
Introduction to Reports
Use the Reports link to search on data in the runtime repository. The Saved Search function is not available.
The following message types are available for searching:
-
Business messages—See Creating Business Message Reports
-
Wire messages—See Creating Wire Message Reports
-
Application messages—See Creating Application Message Reports
-
Error messages—See Creating Error Reports
-
Conversation messages—See Creating Conversation Reports
Note:
In a cluster environment, if system time stamps are not synchronized for all nodes in the cluster, then you may see message time stamps that look incorrect, but are not. For example, given an unsynchronized, multinode cluster, if an outbound message is received on one node, but the reply is sent from another node, it is possible for a report to show message receipt at 4 a.m., but an acknowledgment sent at 3:55 a.m.
The Monitor User Role
For individuals such as business analysts who create and analyze message reports, Oracle B2B provides a monitor user role that an administrator can assign to trading partner users. This role provides a user with access to only the functionality of the Reports tab of Oracle B2B. A user with the Monitor role cannot see or access the other parts of the interface or see data for other trading partners. See Adding Trading Partner Users, for how to assign the Monitor role.
Purging Messages
From the Business Message tab, use the Purge button to purge one or more messages that display after you search the instance data.
Resubmitting Messages from Oracle B2B
If errors that occur when sending an inbound or outbound message are internal to Oracle B2B, then you can correct the problem and resend the message. For example, if B2B attempts to send a message to an endpoint that is not configured correctly, or if the agreement is not configured correctly, correct the error and use Resubmit for application messages or wire messages.
When messaging errors are because of endpoint Hostname/IPAddress or port change, then the messages are in MSG_WAIT_STACK or MSG_WAIT_TRANSMIT. Correct the Hostname/IPAddress or port of the endpoint and resubmit the first errored message which is in MSG_WAIT_STACK. All the pending messages in the sequence then use the updated Hostname/IPAddress or port of the endpoint and are processed. There is no need to resubmit every error message for the endpoint.
Resubmitting an application message, for an outbound message, replays the message from the time of receipt of the message and goes through agreement lookup, message translation (for EDI) and then finally the delivery is attempted. An application message resubmit is helpful when the agreement settings or document configuration is not as required and the message must be restructured with updated settings.
Resubmitting an application message, for an inbound message, attempts to deliver the message again to the back-end application. Resubmitting is useful when the back-end application is down and the delivery must be retried.
Resubmitting a wire message, for an outbound message, tries to redeliver only the previously processed message. There is no repackaging or other message transformation. This is helpful when the problem was with the delivery endpoint (for example, the partner's server is down and unable to receive the message).
Resubmitting a wire message, for an inbound message, replays the message from the time of receipt from the trading partner. The exchange and document are re-identified and an agreement lookup is done. The processed message is then delivered to the back-end. This is useful when the agreement or document setting are not correct and the message must be translated and validated again.
Note:
For certain documents, the user can set XPath expressions to check for, and thus avoid duplicates. If two messages arrive with the same XPath values, the latter of the messages is marked as duplicate and it errors out.
When you resubmit this errored duplicate message (a wire message resubmit), Oracle B2B processes the message ignoring the fact that it is a duplicate, because the resubmission is done intentionally. So, if you do not want Oracle B2B to process duplicate messages, you should not resubmit those messages.
Note:
If you resubmit an inbound AS2 synchronous wire message, the MDN is generated, but it is not returned to the sender in synchronous mode. This is because the sender is not the one who is initiating the originating message. In this scenario, the MDN message state is in the MSG_COMPLETE state.
Correlation Flow Id Response in B2B During Resubmission
Wire message-based inbound resubmission results in a new correlation flow id. It is treated as new business flow.
Inbound Application resubmission re-uses the correlation information because the B2B business information is not altered.
If you want to retain the correlation information, you can use Application message resubmission; if you are initiating a new flow completely, you can use wire resubmit.
For Outbound Application and Wire resubmission, existing correlation information is re-used as it is the same business flow in the background that is used.
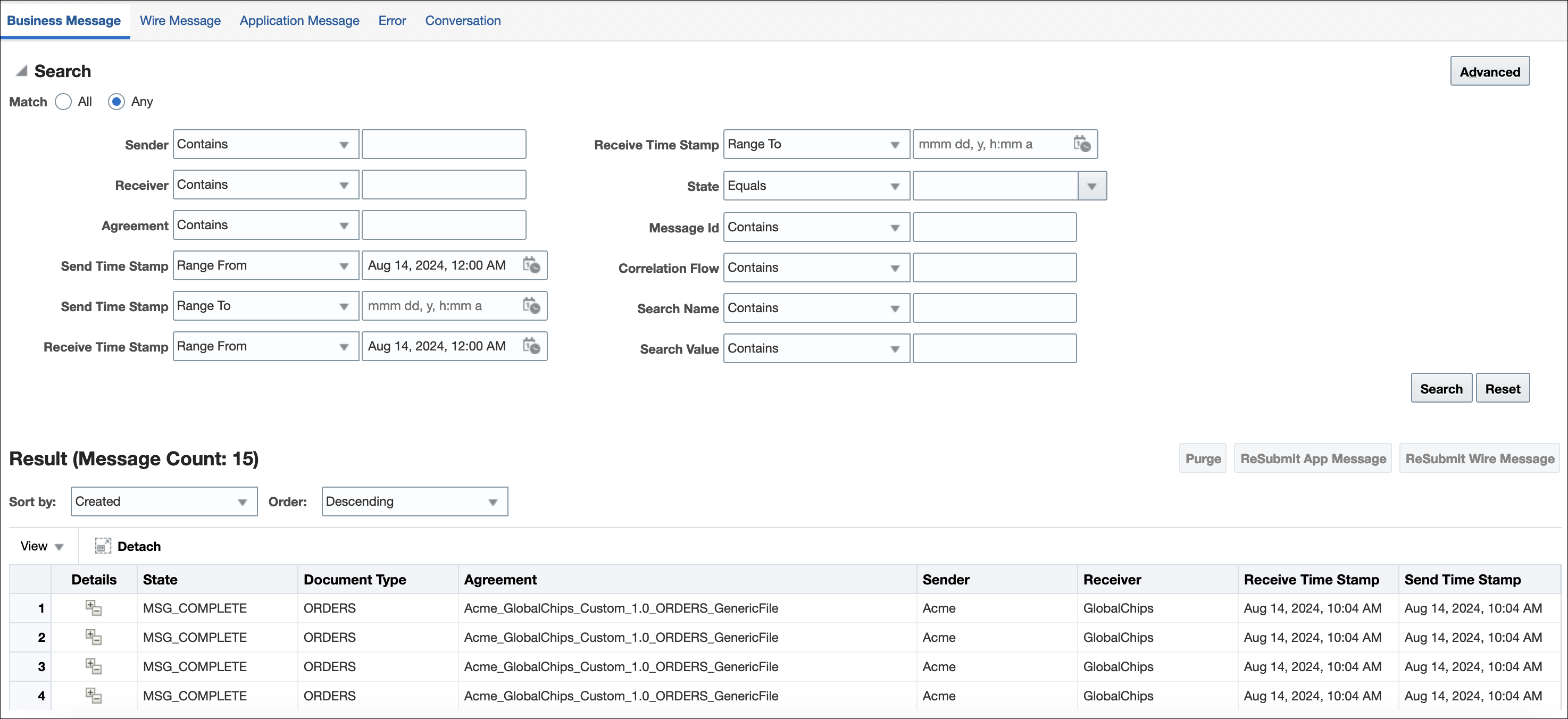
Creating Business Message Reports
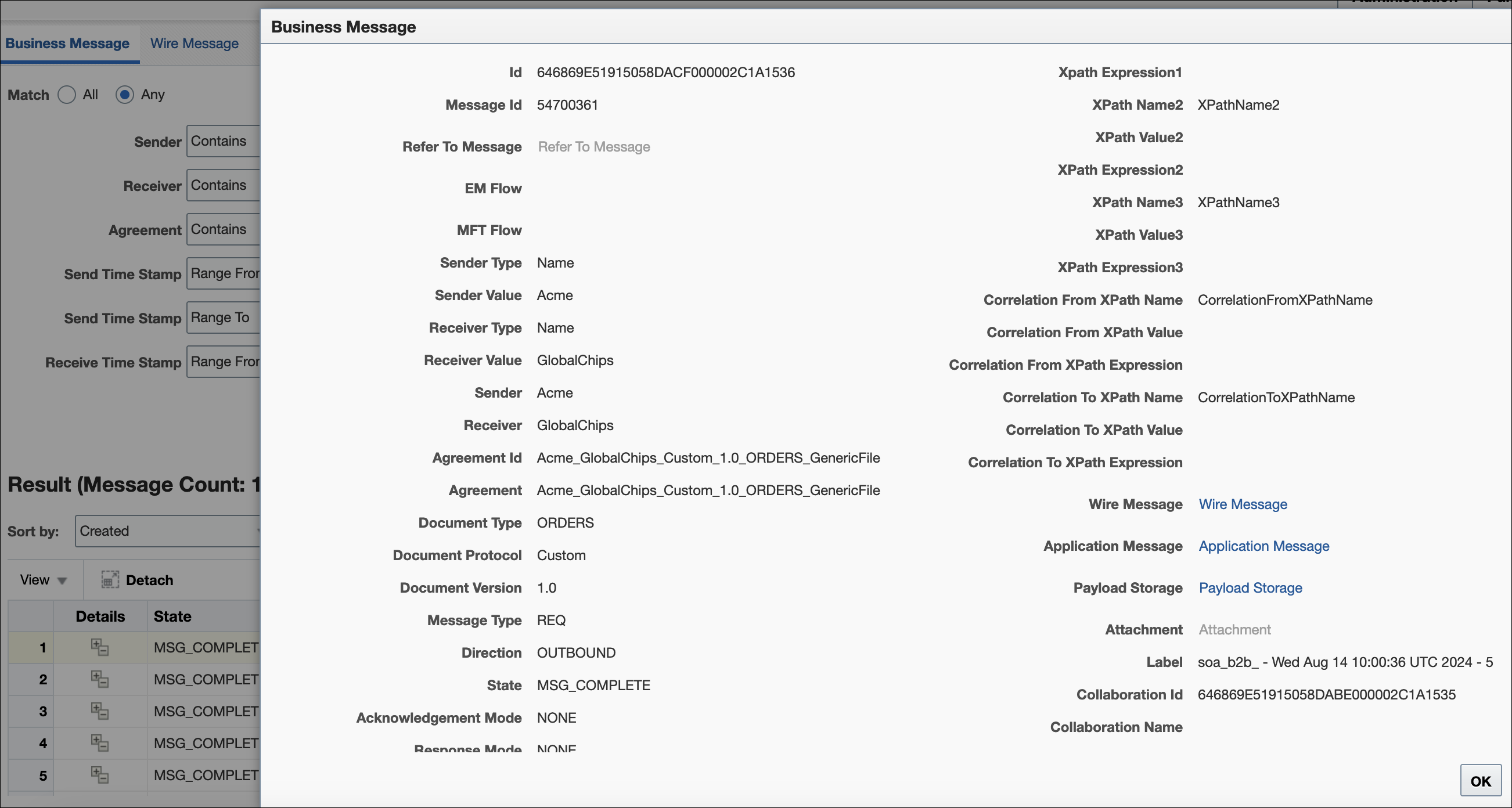
Business message status reports identify business message instance details for a document protocol. These details include the sending and receiving trading partners, the agreement name, the business action, the business message ID, the status, the exchange protocol and document protocol, and message details.
Figure 17-1 shows a business message report.
To create a business message report:
Message State Definition
Table 17-1 provides message state definitions.
Table 17-1 Message State Definitions
| Message | Descriptions |
|---|---|
|
Stable status messages |
- |
|
MSG_COMPLETE |
Business message state after completion of message transfer (and after receiving acknowledgment of the transmission if there is Ack/FA). The wire message state is moved to MSG_COMPLETE state as well. |
|
MSG_WAIT_ACK |
Business message state when an outbound message is sent to trading partner and B2B waits for Ack to be received. |
|
MSG_ERROR |
Business message state after a problem occurs in B2B or a negative acknowledgement is received from the trading partner. Wire message state is moved to MSG_ERROR state as well. |
|
Intermittent status messages |
- |
|
MSG_WAIT_TRANSMIT |
Business message state while B2B is sending message to trading partner. This state is also observed for the messages when they are queued in case of sequencing. |
|
MSG_WAIT_FA |
Business message state when an outbound message is sent to trading partner and B2B waits for Functional Ack to be received. |
|
MSG_SEND_FA |
Business message state when B2B is sending Functional Ack to trading partner. |
|
MSG_WAIT_BATCH |
Business message state while messages are batched up during the interval before batch expiration. After the batch expires, the entire batch of messages are sent out, and business and wire message states move to MSG_COMPLETE (or MSG_ERROR if a problem occurs). |
|
MSG_WAIT_STACK |
Business message state when there is any transport error in case of sequencing. |
|
MSG_WAIT_TA1 |
Business message state while waiting for TA1 Message for EDI-X12. |
|
MSG_SEND_TA1 |
Business message state while sending TA1 Message for EDI-X12. |
|
MSG_CONTINUE_PROCESS |
Business message state when message is being processed in B2B (engine). |
|
MSG_COLLAB_WAIT |
Business message state when message is waiting for Collaboration. |
|
MSG_PROCESS_ACK |
Business message state while processing an Acknowledgement. |
|
MSG_SEND_ACK |
Business message state when an inbound message is received from trading partner and B2B is sending an Acknowledgement. |
|
MSG_SEND_EXP |
Business message state while sending an Exception message. |
|
MSG_PROCESS_EXP |
Business message state while Processing an Exception Message |
|
MSG_INVALD |
This state is the default/first state when the message processing begins in B2B. This state should not be encountered while monitoring the Message states in B2B. |
|
MSG_ABORTED |
The message has been aborted. |
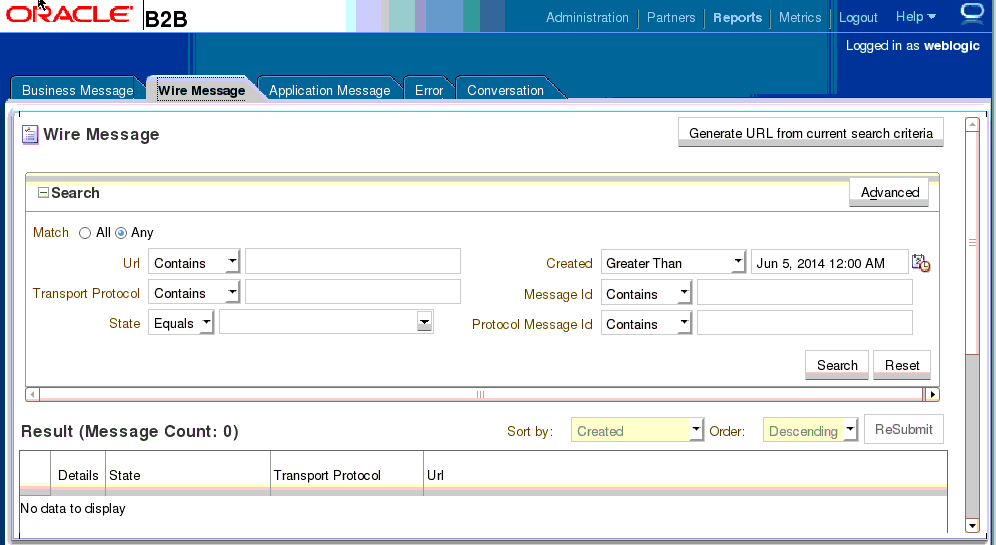
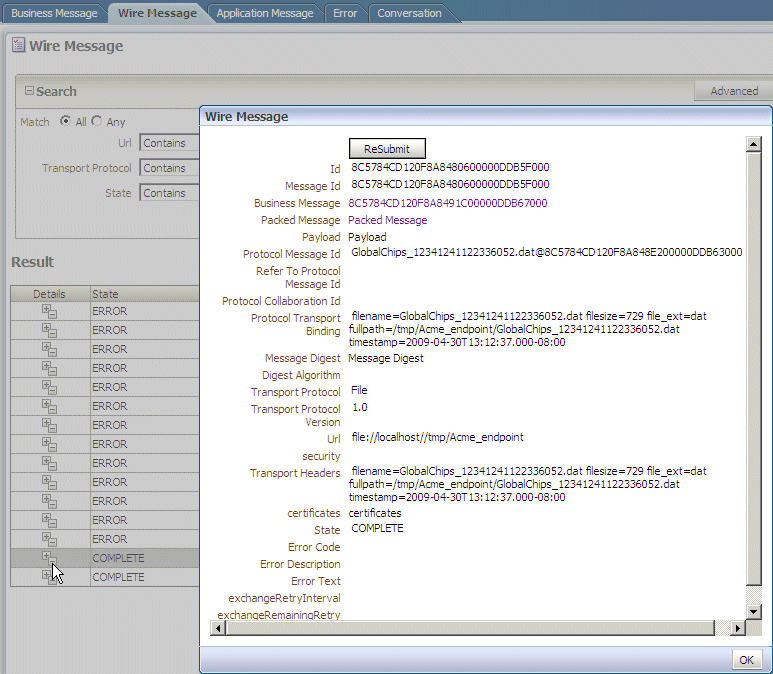
Creating Wire Message Reports
Figure 17-3 shows a wire message report.
See Table 17-1 for a list of applicable message states.
To create a wire message report:
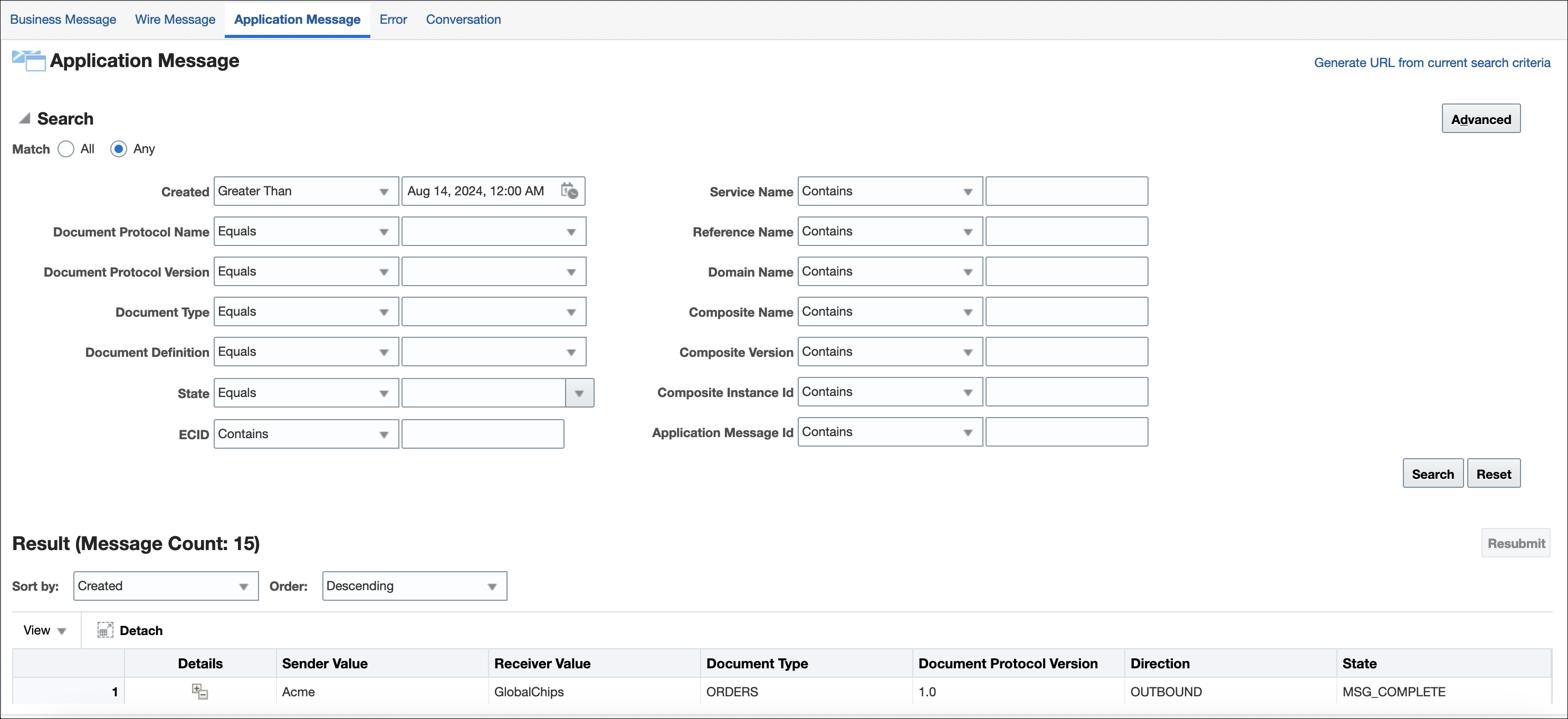
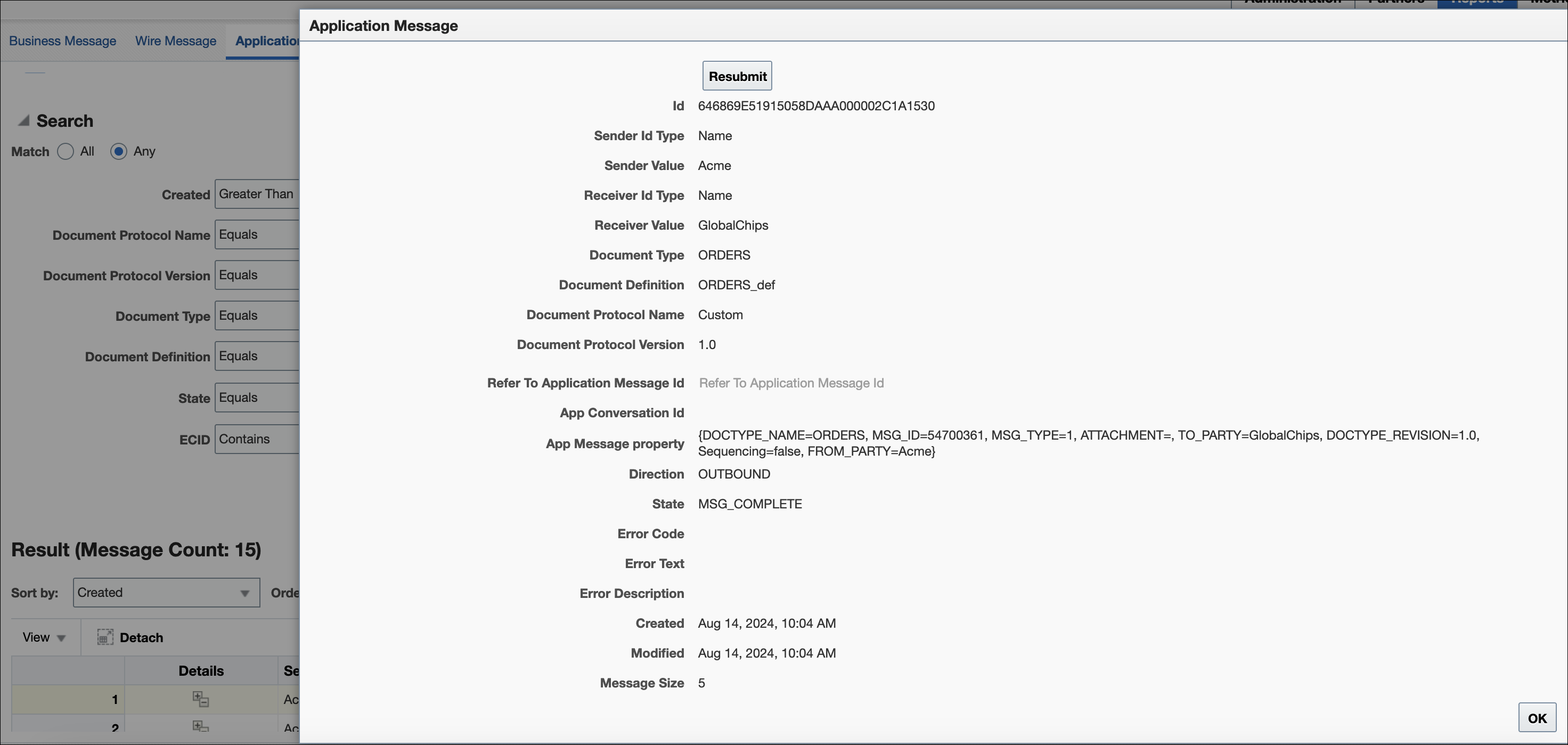
Creating Application Message Reports
This report provides information related to the SOA Composite—the name, version, and so on, if a back-end composite application sent or received the message.
Figure 17-5 shows an application message report.
See Table 17-1 for a list of applicable message states.
To create an application message report:
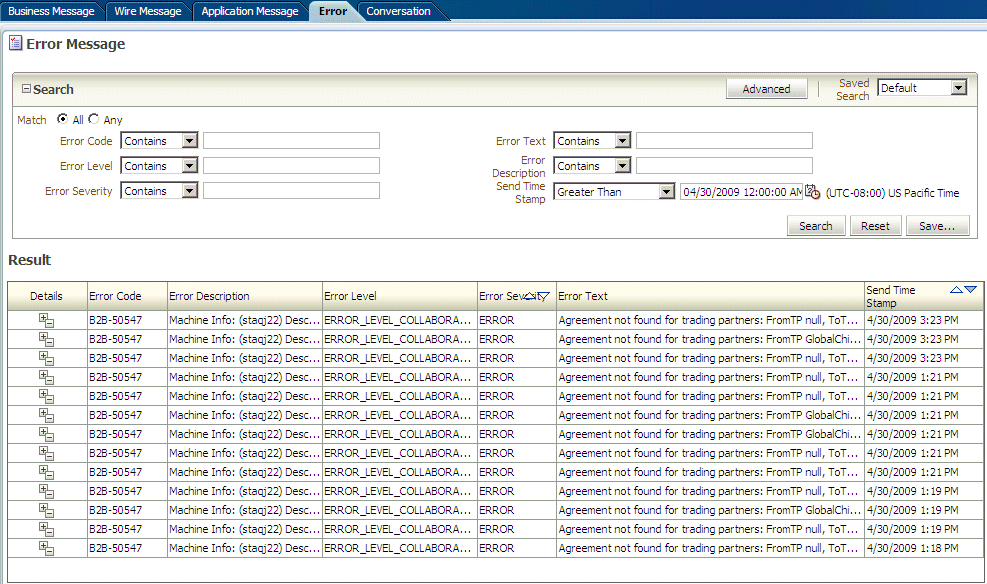
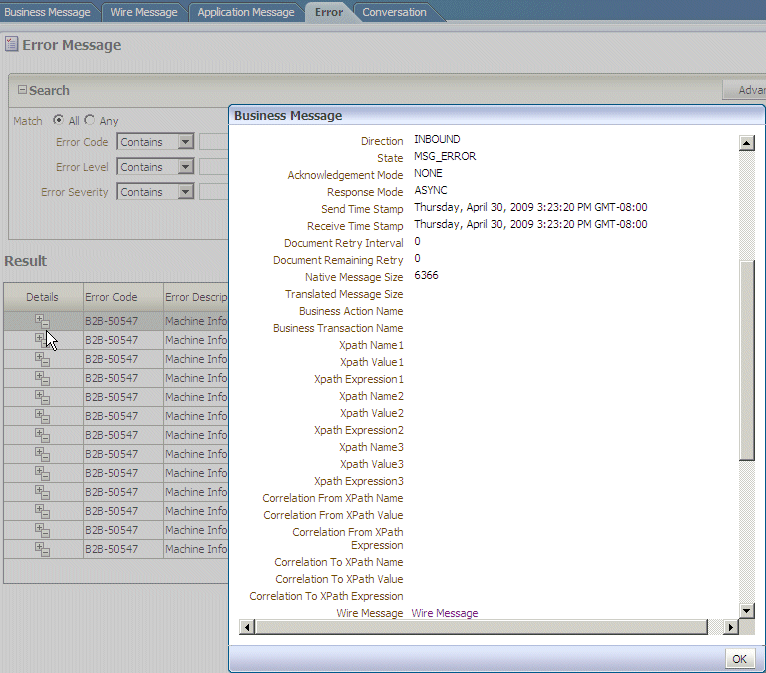
Creating Error Reports
Error status reports provide error message details. These details include the error code, error text, business message identification, message date, and message details.
Figure 17-7 shows an error report.
To create an error report:
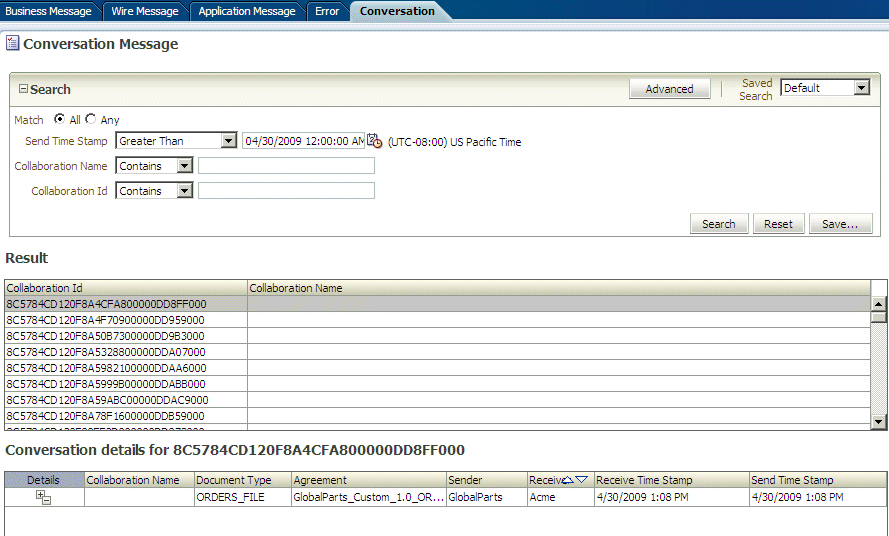
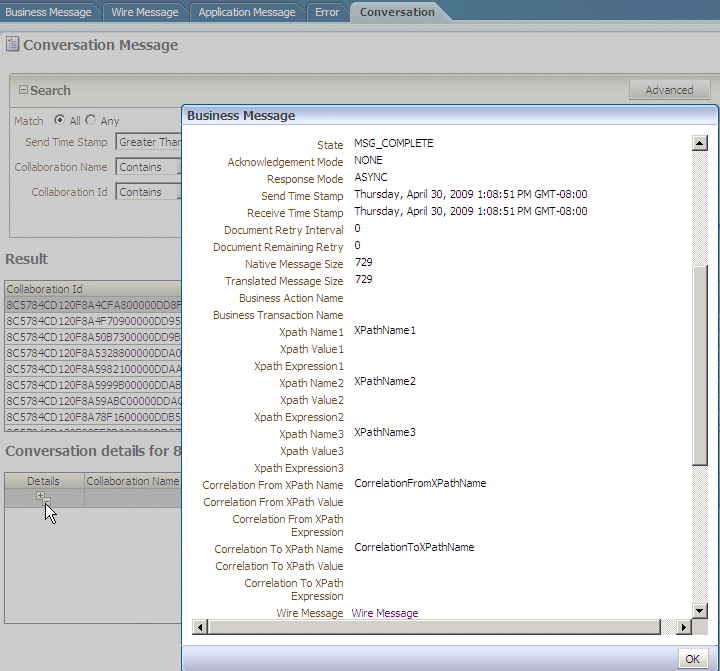
Creating Conversation Reports
A conversation message results when the correlation XPath is set in a document definition to correlate messages. A correlation message also shows messages that are correlated automatically.
For example, an AS2 message and its acknowledgment (MDN) are automatically correlated as part of a conversation. In RosettaNet, request and response messages are also correlated, in addition to the acknowledgments sent and received. These related messages are displayed on the Conversation tab.
Figure 17-9 shows a conversation report.
To create a conversation report: