8 Using Document Protocols
This chapter describes the different document protocols supported by Oracle B2B such as EDI EDIFACT, EDI X12, HL7, RosettaNet, and so on.
This chapter includes the following sections:
For related information, see the following:
8.1 Using the Custom Document Protocol
Oracle B2B document protocols define the document type of the message payload.
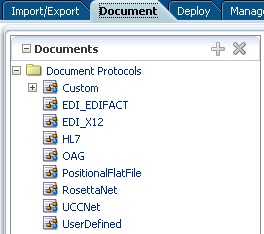
Document protocols are shown in Figure 8-1.
You can define nearly any protocol by using the Custom protocol and the many guideline documents in Oracle B2B Document Editor.
Oracle B2B supports custom document protocols to create documents needed for proprietary transactions. With XML messages, you have the advantage of schema enforcement (XSDs).
With non-XML messages, you can create trading partner agreements for specific message types.
When creating a Custom document, you specify rules to identify the incoming document. For XML documents, specify an XPath expression and a value, which is the expected result of the expression.
For non-XML documents such as a flat file, you can specify start and end positions or a document routing ID.
Document Version Parameters
No parameters need to be set when you create the document version for a Custom document.
Document Type Parameters
When you create a Custom document type, you can set ebXML messaging service (ebMS) parameters to identify the ebXML document. Figure 8-2 shows the document type parameters for a Custom document.
Figure 8-2 Document Type Parameters for a Custom Document
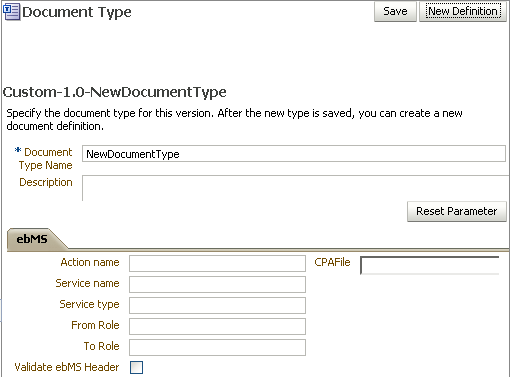
Description of "Figure 8-2 Document Type Parameters for a Custom Document"
Table 8-1 describes the document type parameters for a Custom document.
Table 8-1 Document Type Parameters for a Custom Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
ebMS Tab |
- |
|
Action name |
The action name for the ebXML header, which is also an identification criteria for inbound and outbound messages. ebMS documents require an action name to avoid runtime errors. |
|
Service name |
The service name for the ebXML header, which is also an identification criteria for inbound messages. ebMS documents require a service name to avoid runtime errors. |
|
Service type |
The service type for the ebXML header, which is also an identification criteria for inbound messages. ebMS documents require a service type to avoid runtime errors. |
|
From Role |
The trading partner that sends the message. A value provided here overrides the Identifiers values supplied on the Profile tab. |
|
To Role |
The trading partner that receives the message. A value provided here overrides the Identifiers values supplied on the Profile tab. |
|
Validate ebMS Header |
When selected, validates inbound ebMS header from role to role. |
|
CPA File |
CPA file |
Document Definition Parameters
When you create a Custom document definition, select the file type—XML or Flat—and set parameters in the tabbed areas. Figure 8-3 shows the document definition parameters for an XML-type Custom document.
Figure 8-3 Document Definition Parameters for an XML-Type Custom Document
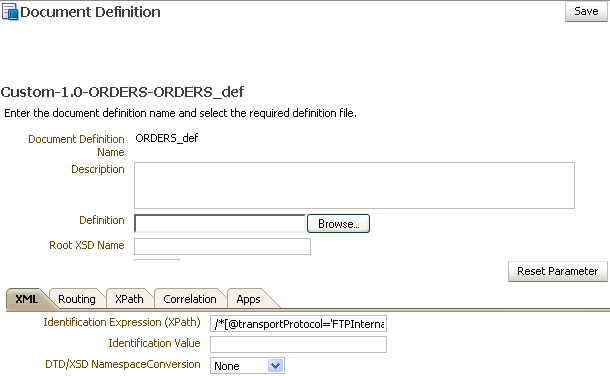
Description of "Figure 8-3 Document Definition Parameters for an XML-Type Custom Document"
Figure 8-4 shows the document definition parameters for a flat-file Custom document.
Figure 8-4 Document Definition Parameters for a Flat-FIle Custom Document
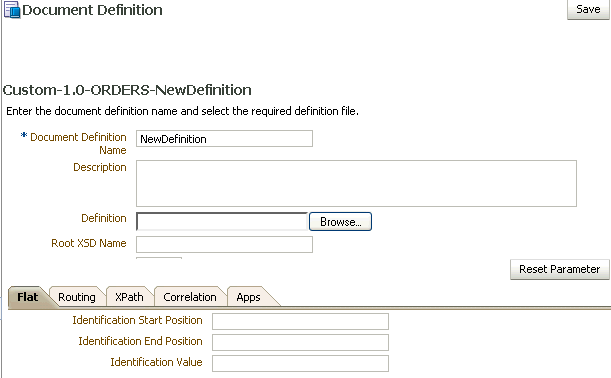
Description of "Figure 8-4 Document Definition Parameters for a Flat-FIle Custom Document"
Table 8-2 describes the document definition parameters for a Custom document.
Table 8-2 Document Definition Parameters for a Custom Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
XML Tab |
(Available if XML is selected from Identification Type) |
|
Identification Expression (XPath) |
Locates a node in the XML payload |
|
Identification Value |
Provides the value to match in the node identified by the Identification Expression. If the values match, then the document is successfully identified. If the value is left blank, then Oracle B2B checks for the existence of the node and the document is successfully identified. |
|
DTD/XSD NamespaceConversion |
Select from None, Both, Inbound, or Outbound. |
|
Routing Tab |
- |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application |
|
XPath Tab |
For more information, see How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document |
|
XPath Name1 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Expression1 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload (see Note below table) |
|
XPath Name2 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Expression2 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload (see Note below table) |
|
XPath Name3 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Expression3 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload (see Note below table) |
|
Correlation Tab |
- |
|
Correlation From XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for initiating the correlation. |
|
Correlation From XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload to initiate the correlation. (see Note below table) |
|
Correlation To XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload for the correlation. (see Note below table) |
|
Flat Tab |
- |
|
Identification Start Position |
Used in combination with the end position to retrieve a value from the payload between the start and end positions |
|
Identification End Position |
Used in combination with the start position to retrieve a value from the payload between the start and end positions |
|
Identification Value |
A value between the start and end positions |
|
Apps Tab |
- |
|
Document |
The name of the internal application document. |
|
Action |
A sub-classification within the document. |
|
XSLTFile |
The name of the XSLT file. |
Note:
When using EDI documents which have default namespace, the usage of
//*[local-name()='...']
can be used, but the more common usage
//Segment-TH/Field-101-A1/text()
cannot be used.
8.1.1 How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document
The XPath expression identifies a Custom XML document. You configure the XPath expression when you specify the document type parameters.
The options when configuring an XPath expression are:
8.1.1.1 Option 1: Specify the XPath and the Matching Value
Assume that the transaction ID is 12345. Set the parameters as follows:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
|
Identification Value |
12345 |
|
Identification Expression |
//*[local-name() = 'TransactionID']/text() |
Oracle B2B compares the value of Identification Expression in the payload to the value specified in Identification Value. If the values match, then the document is identified successfully and the corresponding document type and document protocol version are used to identify the agreement. Example 8-1 shows an excerpt of the XML payload for this option.
Example 8-1 Specify the XPath and the Matching Value
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Message xmlns:ns1="http://www.example1.org" xmlns:ns2="http://www.example2.org"
xmlns="http://www.example3.org"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:ns="http://www.example4.org">
<MessageHeader>
<Source>201944019</Source>
<Destination>205704856</Destination>
<TransactionID>123456</TransactionID>
<Version>1-0-0</Version>
</MessageHeader>
<Body>
<ns:Case xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.example4.org" ns1:caseCategoryID="1">
<ns1:OfficialProvisionNumber>String</ns1:OfficialProvisionNumber>
</ns:Case>
</Body>
</Message>8.1.1.2 Option 2: Check for the Existence of a Node
Assume that you are checking for the existence of a node called registerCommand. Set the parameters as follows:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
|
Identification Value |
Leave blank. |
|
Identification Expression |
/*[local-name()='envelope']/body/transaction/command/*[local-name()='registerCommand'] |
When the Identification Value field is left blank, Oracle B2B checks for the node identified in Identification Expression. If a node in the payload matches, then the document is identified successfully. Example 8-2 shows an excerpt of the XML payload for this option.
Example 8-2 Check for the Existence of a Node
<uccnet:envelope xmins:eanucc="http://www.ean-ucc.org/schemas/1.3/eanucc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:uccnet="http://www.uccnet.org/schemas/2.2/uccnet"
communicationVersion="2.2"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.uccnet.org/schemas/2.2/uccnet
http://www.testregistry.net/xmlschema/uccnet/2.2/Envelope.xsd">
<messageHeader>
<messageIdentifier>
<value>791:1_EB3CDC749A1F2BABE03014906CC4605A</value>
</messageIdentifier>
<userId>oraclesupXSD</userId>
<representingParty>
<gin>0060974050142</gin>
</representingParty>
</messageHeader>
<body>
<transaction>
<entityIdentification>
<uniqueCreatorIdentification>856</uniqueCreatorIdentification>
<globalLocationNumber>
<gin>0060974050142</gin>
</globalLocationNumber>
</entityIdentification>
<command>
<uccnet:registerCommand>
<registerCommandHeader type="ADD" />
</uccnet:registerCommand>
</command>
</transaction>
</body>
</uccnet:envelope>8.1.1.3 Option 3: Check the Value of an Attribute
Assume that the value of the country attribute is US. Set the parameters as follows:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
|
Identification Value |
US |
|
Identification Expression |
//*/@country |
Oracle B2B compares the value of the country attribute to the value set for Identification Value. If the values match, then the document is identified successfully. Example 8-3 shows an excerpt of the XML payload for this option.
Example 8-3 Check the Value of an Attribute
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252" ?>
<MyAddress country="US" xmlns="http://www.example.org"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="PO.xsd">
<name>B2B Buyer</name>
<street>100 Oracle Parkway</street>
<city>Redwood City</city>
<state>CA</state>
<zip>94065</zip>
</MyAddress>8.2 Using the EDI EDIFACT Document Protocol
Oracle B2B supports message exchanges using UN/EDIFACT, the United Nations Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce and Transport. These standards prescribe the formats, character sets, and data elements used in purchase orders and invoices.
Oracle B2B supports all versions and document types of EDI EDIFACT, although for some of the newer versions you may need to add the interchange and group guidelines while creating the document version. Table 8-3 lists a few of the transaction sets supported in Oracle B2B.
Table 8-3 Examples of EDI EDIFACT Transaction Sets Supported in Oracle B2B
| Set | Description | Version |
|---|---|---|
|
ORDERS |
Purchase Order Message |
D98A |
|
ORDRSP |
Purchase Order Response Message |
D98A |
|
CONTRL |
Syntax and Service Report Message |
D3 |
For information about the organization that created and maintains the UN/EDIFACT standards, go to http://www.unece.org.
Document Version Parameters
When you create an EDI EDIFACT document version, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-5 shows document version parameters for an EDI EDIFACT document.
Figure 8-5 Document Version Parameters for an EDI EDIFACT Document
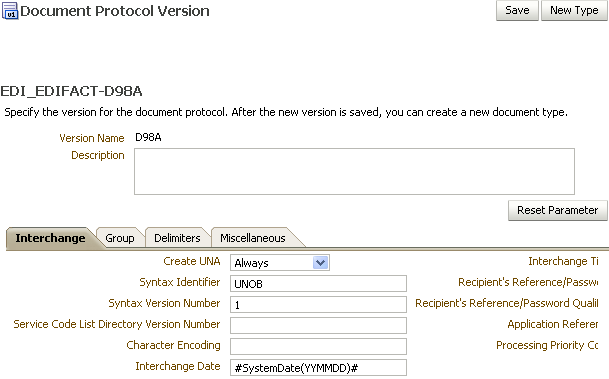
Description of "Figure 8-5 Document Version Parameters for an EDI EDIFACT Document"
Table 8-4 describes the document version parameters for an EDI EDIFACT document.
Table 8-4 Document Version Parameters for an EDI EDIFACT Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Interchange Tab |
- |
|
Create UNA |
Select from always, never, or delimiter-based. If delimiter-based is selected, then UNA is created if the specified delimiters are different from the EDIFACT default value. The Never option does not generate UNA for outbound EDIFACT documents, even if nondefault delimiters are used. The Never option for inbound messages cannot work for B2B if an EDIFACT document is received without UNA and with nondefault delimiters. |
|
Syntax Identifier |
Coded identification of the agency controlling syntax and syntax level used in an interchange. EDI position UNB 010 010 S001 0001. The value UNOB is supplied. |
|
Syntax Version Number |
Version number of the syntax identified in the syntax identifier (0001). EDI position UNB 010 020 S001 0002. The value 1 is supplied. |
|
Service Code List Directory Version Number |
Version number of the service code list directory. EDI position UNB 010 030 S001 0030. |
|
Character Encoding |
Coded identification of the character encoding used in the interchange. To be used as specified in the partners' interchange agreement, for the purpose of identifying the character repertoire encoding technique used in the interchange (when the default encoding defined by the character repertoire's associated character set specification is not used). EDI position UNB 010 040 S001 0133. |
|
Interchange Date |
Local date when an interchange or a group was prepared. EDI position UNB 030 010 S004 0017. The value #SystemDate(YYMMDD)# is supplied. |
|
Interchange Time |
Local time of day when an interchange or a group was prepared. EDI position UNB 030 020 S004 0019. The value #SystemTime(HHMM)# is supplied. |
|
Recipient's Reference/Password |
Reference or password to the recipient's system or to a third-party network as specified in the partners' interchange agreement. To be used as specified in the partners' interchange agreement. It may be qualified by data element 0025. EDI position UNB 060 010 S005 0022. |
|
Recipient's Reference/Password Qualifier |
Qualifier for the recipient's reference or password. To be used as specified in the partners' interchange agreement. EDI position UNB 060 020 S005 0025. |
|
Application Reference |
Identification of the application area assigned by the sender, to which the messages in the interchange relate; for example, the message type, if all the messages in the interchange are of the same type. Identification of the application area (for example, accounting, purchasing) or of the message type, as applicable. EDI position UNB 070. |
|
Processing Priority Code |
Code determined by the sender requesting processing priority for the interchange. To be used as specified in the partners' interchange agreement. EDI position UNB 080. |
|
Interchange Agreement Identifier |
Identification by name or code of the type of agreement under which the interchange takes place. Name or code to be specified in the partners' interchange agreement. EDI position UNB 100. |
|
Test Indicator |
Indication that the structural level containing the test indicator is a test. EDI position UNB 110. |
|
Interchange ecs File |
Use the Browse button to find an ecs file to override the standard file. If not provided, the B2B-provided default file (interchange ecs file of the syntax version number, UNB 010 020) is used. |
|
Group Tab |
- |
|
Create Functional Group |
Indication of function group (UNG) creation. The value TRUE is supplied. |
|
Date of Group Preparation |
Local date when an interchange or a group was prepared. EDI position UNG 040 010. The system date stamp is supplied. |
|
Time of Group Preparation |
Local time of day when an interchange or a group was prepared. EDI position UNG 040 020. The system time stamp is supplied. |
|
Controlling Agency |
Code identifying a controlling agency. EDI position UNG 070 010. The value UN is supplied. |
|
Group Association Assigned Code |
Code assigned by the association responsible for the design and maintenance of the message type cafterrned that further identifies the message. EDI position UNG 070 030. |
|
Application Password |
Password to the recipient's division, department or sectional application system/process. EDI position UNG 080. |
|
Group ecs File |
Use the Browse button to find an ecs file to override the standard file. If not provided, the B2B-provided default file is used. |
|
Delimiters Tab |
A delimiter is characterized by two levels of separators and a terminator assigned by the sender. Delimiters are also called service characters, data delimiters, or message delimiters. They are specified in the interchange header and cannot be used in a data element value elsewhere in the interchange. In an EDI file, the segment delimiter, the element delimiter, and the subelement delimiter are used. Click Select Hexadecimal Characters next to any of the delimiter fields to provide values. Note: Make sure that none of the delimiters are configured to be characters that are expected in the payload, or the payload may be altered or corrupted. |
|
Segment Delimiter |
EDIFACT segment delimiter. The value 0x27 is supplied. |
|
Element Delimiter |
EDIFACT element delimiter. The value 0x2b is supplied. |
|
Subelement Delimiter |
EDIFACT subelement delimiter. The value 0x3a is supplied. |
|
Decimal Separator |
EDIFACT decimal separator. The value 0x2e is supplied. |
|
Release Character |
EDIFACT release character. The value 0x3f is supplied. |
|
Replacement Character |
EDIFACT replacement character. The value 0x7c is supplied. |
|
Repeating Separator |
EDIFACT repeating separator. The value 0x2a is supplied. |
|
Miscellaneous Tab |
- |
|
Check Duplicate Control Number |
When this property is selected (set to true), messages with duplicate interchange control numbers are rejected, meaning that the state of the incoming message is set to ERROR. In this case, when Oracle B2B receives a duplicate message (a message with a duplicate control number), it sends back a negative CONTRL message with Action code (UCI 0083) set to |
|
Ignore Envelope Parameters |
Use this option to provide a list of envelope elements, separated by commas, to be ignored during look-up validation. The possible values depend on the identifiers used in the agreement. Possible values include InterchangeSenderID, InterchangeReceiverID, GroupReceiverID, GroupSenderID, TransactionAssociationAssignedCode, InterchangeReceiverQual, InterchangeSenderQual, and InterchangeControlVersion. |
Document Type Parameters
When you create an EDI EDIFACT document type, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-6 shows the document type parameters for an EDI EDIFACT document.
Figure 8-6 Document Type Parameters for an EDI EDIFACT Document
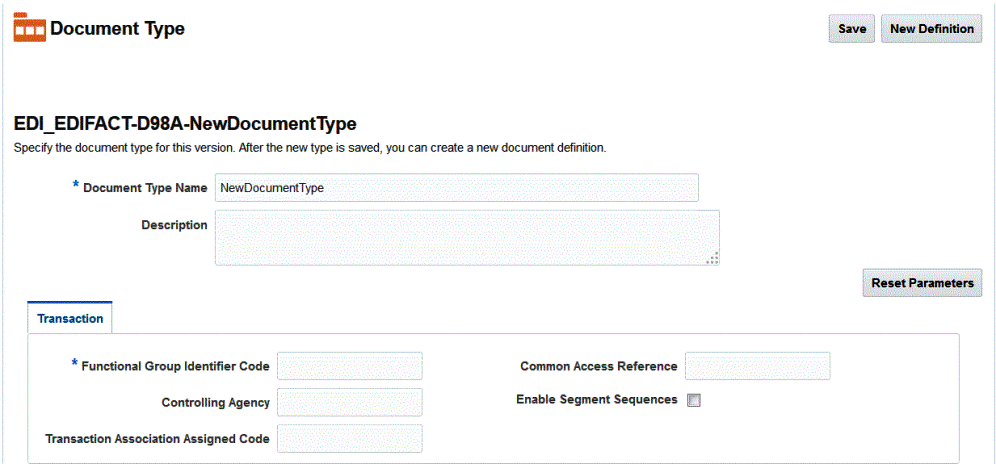
Description of "Figure 8-6 Document Type Parameters for an EDI EDIFACT Document"
Table 8-5 describes the document type parameters for an EDI EDIFACT document.
Table 8-5 Document Type Parameters for an EDI EDIFACT Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Transaction Tab |
- |
|
*Functional Group Identifier Code |
Code identifying one type of message in a functional group. EDI position UNG 010 0038. Required. |
|
Controlling Agency |
Code identifying the agency controlling the specification, maintenance and publication of the message type. EDI position UNH 020 040 S009 0051. |
|
Transaction Association Assigned Code |
Code, assigned by the association responsible for the design and maintenance of the message type cafterrned, which further identifies the message. EDI position UNH 020 050 S009 0057. |
|
Common Access Reference |
Reference serving as a key to relate all subsequent transfers of data to the same business case or file. EDI position UNH 030 0068. |
|
Enable Segment Sequences |
When this property is set to true, outbound UN/EDIFACT messages includes segment sequences (Segment Name: Sequence Number) in the outbound translated message. If this is set to false (default), then Oracle B2B does not generate any segment sequence numbers. |
Document Definition Parameters
When you create an EDI EDIFACT document definition, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-7 shows document definition parameters for an EDI EDIFACT document.
Figure 8-7 Document Definition Parameters for an EDI EDIFACT Document
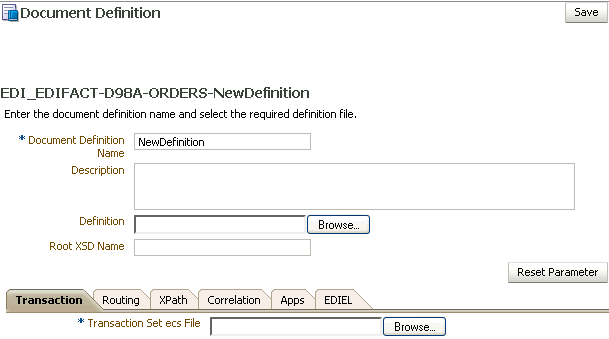
Description of "Figure 8-7 Document Definition Parameters for an EDI EDIFACT Document"
Table 8-6 describes the document definition parameters for an EDI EDIFACT document.
Table 8-6 Document Definition Parameters for an EDI EDIFACT Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Transaction Tab |
- |
|
*Transaction Set ecs File |
Use the Browse button to select the ecs file. |
|
Routing Tab |
- |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application. |
|
XPath Tab |
For more information, see How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document. |
|
XPath Name1 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression1 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name2 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression2 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name3 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression3 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
Correlation Tab |
- |
|
Correlation From XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for initiating the correlation. |
|
Correlation From XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload to initiate the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload for the correlation. |
|
Apps Tab |
- |
|
Document |
The name of the internal application document. |
|
Action |
A sub-classification within the document. |
|
XSLTFile |
The name of the XSLT file. |
|
EDIEL Tab |
- |
|
FA Assoc Assigned Code |
Code for the functional acknowledgment. |
|
FA Action Coded |
Set this to a value of |
|
FA Message Version Number |
Version number for the functional acknowledgment. |
|
FA Message Release Number |
Release number for the functional acknowledgment. |
|
Remove FA Segments |
Remove functional acknowledgment segments. |
|
Map Application Reference |
Maps the |
8.3 Using the EDI X12 Document Protocol
Oracle B2B supports message exchanges using American National Standards Institute (ANSI) X12. These standards prescribe the formats, character sets, and data elements used in documents such as purchase orders and invoices.
Oracle B2B supports all versions and document types of EDI X12, although for some of the newer versions you may need to add the interchange and group guidelines while creating the document version. Table 8-7 lists a few of the transaction sets supported in Oracle B2B.
Table 8-7 Examples of EDI X12 Transaction Sets Supported in Oracle B2B
| Set | Description | Version |
|---|---|---|
|
850 |
Purchase Order |
4010 |
|
855 |
Purchase Order Acknowledgment |
4010 |
|
997 |
Functional Acknowledgment |
4010 |
|
999 |
Functional Acknowledgment |
HIPAA versions |
|
TA1 |
Interchange acknowledgment |
All X12 and HIPAA versions |
For information about the organization that created and maintains the ANSI X12 standards, go to http://www.ansi.org.
Document Version Parameters
When you create an EDI X12 document version, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-8 shows document version parameters for an EDI X12 document.
Figure 8-8 Document Version Parameters for an EDI X12 Document
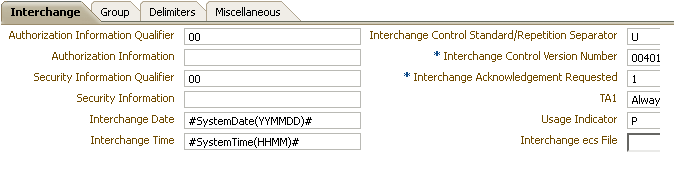
Description of "Figure 8-8 Document Version Parameters for an EDI X12 Document"
Table 8-8 describes the document version parameters for an EDI X12 document.
Table 8-8 Document Version Parameters for an EDI X12 Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Interchange Tab |
- |
|
Authorization Information Qualifier |
Code to identify the type of information in the authorization information. EDI position ISA 01. The value 00 is supplied. |
|
Authorization Information |
Information used for additional identification or authorization of the sender or the data in the interchange. The authorization information qualifier sets the type of information. EDI position ISA 02. |
|
Security Information Qualifier |
Code to identify the type of information in the security information. EDI position ISA 03. The value 00 is supplied. |
|
Security Information |
Information used to identify the security information about the interchange sender or the data in the interchange. The security information qualifier sets the type of information. EDI position ISA 04. |
|
Interchange Date |
Date of the interchange. EDI position ISA 09. The system date stamp is supplied ( |
|
Interchange Time |
Time of the interchange. EDI position ISA 10.The system time stamp is supplied ( |
|
Interchange Control Standard/Repetition Separator |
Code to identify the agency responsible for the control standard used by the message that is enclosed by the interchange header and trailer. EDI position is ISA 11. The value U is supplied. |
|
*Interchange Control Version Number |
Code specifying the version number of the interchange control segments. EDI position ISA 12. The value 00401 is supplied. |
|
*Interchange acknowledgment Requested |
Code specifying whether the trading partner has requested an interchange acknowledgment. |
|
TA1 |
Specifies when Oracle B2B expects a TA1 acknowledgment from the trading partner. |
|
Usage Indicator |
Code to indicate whether data enclosed by this interchange envelope is in test or production. EDI position ISA 15. The value P, for production, is supplied. |
|
Interchange ecs File |
Use the Browse button to find an ecs file to override the standard file. If not provided, the B2B-provided default file (interchange ecs file of the interchange control version, ISA 12) is used. |
|
Group Tab |
- |
|
Functional Group Date |
Date sender generated a functional group of transaction sets. EDI position GS 04. The system date stamp is supplied ( |
|
Functional Group Time |
Time when the sender generated a functional group of transaction sets (local time at sender's location). EDI position GS 05.The system time stamp is supplied ( |
|
Responsible Agency Code |
Code used in conjunction with data element 480 to identify the issuer of the standard. EDI position GS 06. The value X is supplied. |
|
Version/Release/Industry Identifier Code |
Code indicating the version, release, subrelease, and industry identifier of the EDI standard being used, including the GS and GE segments; if the code in DE455 in GS segment is X, then in DE 480 positions 1-3 are the version number; positions 4-6 are the release and subrelease, level of the version; and positions 7-12 are the industry or trade association identifiers (optionally assigned by user); if the code in DE455 in GS segment is T, then other formats are allowed. |
|
Group ecs File |
Use the Browse button to find an ecs file to override the standard file. If not provided, the B2B-provided default file (group ecs file of EDI X12 version) is used. |
|
Delimiters Tab |
Click Select Hexadecimal Characters next to any of the delimiter fields to provide values. See Table 8-4 for more about delimiters. Note: Make sure that none of the delimiters are configured to be characters that are expected in the payload, or the payload may be altered or corrupted. |
|
Segment Delimiter |
The value 0x7e is supplied. |
|
Element Delimiter |
The value 0x2a is supplied. |
|
Subelement Delimiter |
The value 0x5c is supplied. |
|
Decimal Separator |
The value 0x2e is supplied. |
|
Replacement Character |
The value 0x7c is supplied. |
|
Repeating Separator |
The value 0x5e is supplied. |
|
Miscellaneous Tab |
- |
|
Check Duplicate Control Number |
When this property is selected (set to true), messages with duplicate interchange control numbers are rejected, meaning that the state of the incoming message is set to ERROR. |
|
Ignore Envelope Parameters |
Use this option to provide a list of envelope elements, separated by commas, to be ignored during look-up validation. The possible values depend on the identifiers used in the agreement. Possible values include InterchangeSenderID, InterchangeReceiverID, GroupReceiverID, GroupSenderID, TransactionAssociationAssignedCode, InterchangeReceiverQual, InterchangeSenderQual, and InterchangeControlVersion. |
Document Type Parameters
When you create an EDI X12 document type, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-9 shows the document type parameters for an EDI X12 document.
Figure 8-9 Document Type Parameters for an EDI X12 Document
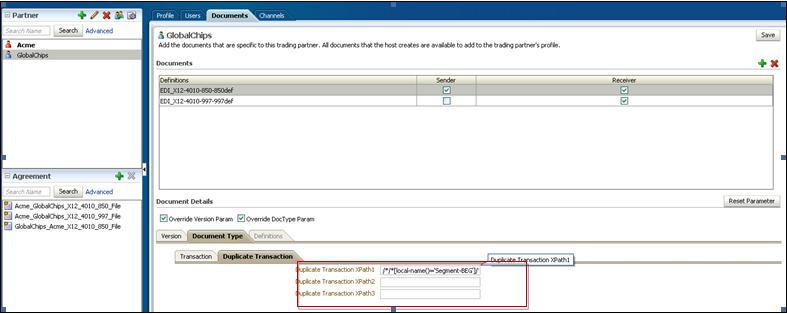
Description of "Figure 8-9 Document Type Parameters for an EDI X12 Document"
Table 8-9 describes the document type parameters for an EDI X12 document.
Table 8-9 Document Type Parameters for an EDI X12 Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Transaction Tab |
- |
|
Functional Group Identifier Code |
Uniquely identifies a transaction set GS 01. Required. |
|
Implementation Convention Reference |
Reference assigned to identify Implementation Convention. EDI position ST 03. |
|
Transaction Purpose Code |
Code identifying the purpose of the transaction set. EDI position BEG/BGN 01. |
|
Functional Acknowledgment Transaction |
Functional Acknowledgment (997 or 999) By default, it is 997. This field can be used for non default Functional Acknowledgment such as 999. |
|
Functional Acknowledgment Transaction Version |
If this field is not set, the default version is the version of the original transaction. This field is used in conjunction with Functional Acknowledgment Transaction field, that is, when 999 is set for Functional Acknowledgment Transaction, the version can be set to 5010X231 (as an example) in this field. |
|
Functional Acknowledgment On Error Only checkbox |
Check this box if you want to generate Functional Acknowledgment in case of original message error (perhaps due to validation error) whereas no Functional Acknowledgment is generated for positive cases (that is, no errors). By default, this box is unchecked, that is. Functional Acknowledgment is generated in both positive and error cases when Functional Acknowledgement is requested in the Trading Partner Agreement (TPA) (that is, Functional Ack is checked in TPA). |
|
Duplicate Transaction Tab |
This feature enables you to detect the duplicate transactions by considering specific content in the payload (such as Purchase Order number and invoice number).This is achieved by providing the XPath for the specific tag of the payload. The three XPath fields provide the flexibility to arrive at the uniqueness criteria with multiple values of the payload.For inbound, this adds an additional check during the Oracle B2B inbound message processing to check duplicate control numbers. The XPath-based duplicate check is done after the control number check. Note: You cannot specify the second/third XPath without specifying the first XPath |
|
HIPAA Tab |
This feature allows you to specify the different level of severity (Default, Validate, Warning, Information, Ignore) for each of the SNIP Type 1-7. For example, if you want to validate HIPAA Syntax only, you can set severity for Type 3-7 to Ignore |
|
Default |
Validate all data and will report the error. |
|
Warning |
Indicates that problems exist with the data, but the data can continue to be processed. In the case of a production environment such as XEngine, it indicates that the error will be noted on the acknowledgement document, but the data will get passed to the next step in the work flow. |
|
Information |
Indicates that the data check reported a message that should be noted. In the case of a production environment such as XEngine, it indicates that no error will be noted on acknowledgement document and the data will get passed to the next step in the work flow. |
|
Ignore |
Indicates that any data check message will be suppressed and it will be treated in the same manner as clean data. In a production environment such as XEngine, it indicates that no error will be noted on the error report or acknowledgement document and the data will get passed to the next step in the work flow document. |
|
Validate |
Set the validation to the normal mode so that XEngine can provide error if error is found. |
Document Definition Parameters
When you create an EDI X12 document definition, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-10 shows document definition parameters for an EDI X12 document.
Figure 8-10 Document Definition Parameters for an EDI X12 Document
Description of "Figure 8-10 Document Definition Parameters for an EDI X12 Document"
Table 8-10 describes the document definition parameters for an EDI X12 document.
Table 8-10 Document Definition Parameters for an EDI X12 Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Transaction Tab |
- |
|
Transaction Set ecs File |
Use the Browse button to select the ecs file. |
|
Routing Tab |
- |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application |
|
XPath Tab |
For more information, see How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document |
|
XPath Name1 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Expression1 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Name2 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Expression2 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Name3 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
XPath Expression3 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload |
|
Correlation Tab |
- |
|
Correlation From XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for initiating the correlation. |
|
Correlation From XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload to initiate the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload for the correlation. |
|
Apps Tab |
- |
|
Document |
The name of the internal application document. |
|
Action |
A sub-classification within the document. |
|
XSLTFile |
The name of the XSLT file. |
Note:
For information about behavior and limitations when the b2b.FAHandledByB2B property is set to false, see Setting B2B Configuration Properties in Fusion Middleware Control.
8.3.1 Generating acknowledgment for EDI X12 Documents
An EDI-X12 document that is received from a trading partner can be acknowledged in the following ways:
-
By sending 997, which is Functional acknowledgment
-
By sending 999, which is Implementation acknowledgment
Even though the usage of the both document are similar, the 997 acknowledgment can be used to verify the syntactical correctness of the document. On the other hand, the 999 acknowledgment indicates the relational analysis of the control structure as well.
In the case of 997 generation for X12 version 5010 and higher, the following additional elements (optional) are generated:
<Element-480>005010</Element-480> <Element-1705>Implementation Convention Reference</Element-1705>
In addition, Oracle B2B also validates the 997/999 acknowledgments during the translation to native against the default preseeded 997/999 definition. So while implementing the solutions using Oracle B2B, it is a suggested practice to use 999 for the version 5010 or above.
8.3.1.1 Handling Duplicate Functional Acknowledgments in X12
An inbound duplicate functional acknowledgments (997/999) is put in the MSG_ERROR state with the following error details when Check Duplicate Control Number is enabled (selected) in the Miscellaneous tab of the Document Protocol Version, such as - 4010, which could be under Document EDI_X12:
Error Code: B2B-50081
Error Description: Duplicate Functional Acknowledgment
Error Level ERROR_LEVEL_COLLABORATION
Error Severity ERROR
Error Text Duplicate FA
If an inbound duplicate Functional Acknowledgment (997 or 999) enters into the Oracle B2B system and "Check Duplicate Control Number" is not enabled, then the Functional Acknowledgment is not be treated as a duplicate.
8.4 Using the HL7 Document Protocol
Note:
While HL7 BATCH and FILE envelopes are supported, batching is not supported in this release.
The HL7 protocol is not supported over MLLP. As a best practice, use HL7 with a Healthcare installation only.
For information about the organization that created and maintains the HL7 standards, go to http://www.hl7.org.
Document Version Parameters
When you create an HL7 document version, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-11 shows document version parameters for an HL7 document.
Figure 8-11 Document Version Parameters for an HL7 Document
Description of "Figure 8-11 Document Version Parameters for an HL7 Document"
Table 8-11 describes the document version parameters for an HL7 document.
Table 8-11 Document Version Parameters for an HL7 Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Message Header Tab |
- |
|
Security |
In some applications of HL7, this field is used to implement security features. |
|
Processing ID |
MSH.11 - This field is used to decide whether to process the message as defined in HL7 Application (level 7) processing rules. The first component defines whether the message is part of a production, training, or debugging system (refer to HL7 table 0103 - Processing ID for valid values). The second component defines whether the message is part of an archival process or an initial load (refer to HL7 table 0207 - Processing mode for valid values). This allows different priorities to be given to different processing modes. |
|
Accept acknowledgment Type |
Sets the conditions under which application acknowledgments are required to be returned in response to the message. The value AL (always) is supplied. B2B checks the payload (MSH.15) of an incoming message to see if an ACK has to be generated. In some HL7 Systems, MSH.15 is not sent in the payload at all and it is expected that an ACK is still sent. |
|
Application Acknowledgment Type |
MSH.16. The value AL (always) is supplied. |
|
Country Code |
Sets the country of origin for the message. The value US is supplied. |
|
Character Set |
Sets the character set for the entire message. The value ASCII is supplied. |
|
Internationalization Code Identifier |
MSH.19 |
|
Internationalization Code Text |
MSH.19 |
|
Internationalization Coding System Name |
MSH.19 |
|
Internationalization Code Alternate Identifier |
MSH.19 |
|
Internationalization Code Alternate Text |
MSH.19 |
|
Internationalization Code Alternate Coding System Name |
MSH.19 |
|
International Version Identifier |
MSH.12 |
|
International Version ID Text |
MSH.12 |
|
International Version ID Coding System Name |
MSH.12 |
|
International Version ID Alternate Identifier |
MSH.12 |
|
International Version ID Alternate Text |
MSH.12 |
|
International Version ID Alternate Coding System Name |
MSH.12 |
|
Batch Header Tab |
- |
|
Create Batch Header |
Check the box to create batch headers. |
|
Batch Header ecs File |
Use the Browse button to find an ecs file to override the standard file. If not provided, the B2B-provided default file is used. |
|
Batch Security |
BHS.8 |
|
Batch Date |
BHS.7. The system date-time stamp is supplied ( |
|
File Header Tab |
- |
|
Create File Header |
Check the box to enable. |
|
File Header ecs File |
Use the Browse button to find an ecs file to override the standard file. If not provided, the B2B-provided default file is used. |
|
File Security |
FHS.8 |
|
File Date |
FHS.7. The system date-time stamp is supplied ( |
|
Delimiters Tab |
Click Select Hexadecimal Characters next to any of the delimiter fields to provide values. See Table 8-4 for more about delimiters. |
|
Element Delimiter |
A single character that follows the segment identifier and separates each data element in a segment except the last. The value 0x7c is supplied. |
|
Escape Character |
The value 0x5c is supplied. |
|
Repeating Separator |
A service character used to separate adjacent occurrences of a repeating data element, or to separate multiple occurrences of a field.The value 0x7e is supplied. |
|
Segment Delimiter |
A syntax character indicating the end of a segment (a logical grouping of data fields) within a message. The value 0x0d is supplied. |
|
Subcomponent Delimiter |
The value 0x26 is supplied. |
|
Subelement Delimiter |
The value 0x5e is supplied. |
|
Miscellaneous Tab |
- |
|
Ignore Envelope Parameters |
Use this option to provide a list of envelope elements, separated by commas, to be ignored during look-up validation. The possible values depend on the identifiers used in the agreement. For an HL7 agreement, the possible values include MessageSendingApp, MessageReceivingApp, MessageSendingFacility, and MessageReceivingFacility. |
Document Type Parameters
When you create an HL7 document type, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-12 shows the document type parameters for an HL7 document.
Figure 8-12 Document Type Parameters for an HL7 Document
Description of "Figure 8-12 Document Type Parameters for an HL7 Document"
Table 8-12 describes the document type parameters for an HL7 document.
Table 8-12 Document Type Parameters for an HL7 Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Transaction Tab |
- |
|
HL7 Generic ACK |
If selected, Oracle B2B sends a generic ACK immediately upon receiving an HL7 message. Note: The HL7 standard does not specify any Ack generation rules for the errors on file or batch header - only for the message. Oracle B2B does not generate acks for file and batch header errors for HL7 inbound messages (only error reports are generated). |
|
Map ACK Control ID |
Select to enable mapping the MSH.10 of the business message to the MSH.10 of the acknowledgment. Note: This Map ACK Control ID parameter is for the functional ACK. |
|
Accept acknowledgment |
A functional acknowledgment is generated when MSH.15 has no value. Select None to take no action. Acknowledgment generation is dependent on the value in MSH.15 of the business message. Select AL (always) to generate the acknowledgment under any conditions. Select ER (error/reject) to generate the acknowledgment when the message errors or is rejected. Select SU (successful completion) to generate the acknowledgment when the message is successfully processed. |
Document Definition Parameters
When you create an HL7 document definition, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-13 shows document definition parameters for an HL7 document.
Figure 8-13 Document Definition Parameters for an HL7 Document
Description of "Figure 8-13 Document Definition Parameters for an HL7 Document"
Table 8-13 describes the document definition parameters for an HL7 document.
Table 8-13 Document Definition Parameters for an HL7 Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Transaction Tab |
- |
|
*Transaction Set ecs File |
Use the Browse button to find the ecs file. |
|
Routing Tab |
- |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application. |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application |
|
XPath Tab |
For more information, see How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document. |
|
XPath Name1 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression1 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name2 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression2 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name3 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression3 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
Correlation Tab |
- |
|
Correlation From XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for initiating the correlation. |
|
Correlation From XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload to initiate the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload for the correlation. |
|
Apps Tab |
- |
|
Document |
The name of the internal application document. |
|
Action |
A sub-classification within the document. |
|
XSLTFile |
The name of the XSLT file. |
About Using HL7
-
No business message is produced for an HL7 immediate acknowledgment (transport-level acknowledgment). When using AS2, you see one acknowledgment business message for MDN (transport-level acknowledgment), and for ebMS, you see one acknowledgment business message in the business message report. In summary, because immediate acknowledgments are sent at the transport level, the entry is available only in the wire message report and not in the business message report.
-
Negative acknowledgment messages indicating errors in an HL7 exchange may be truncated because of the 80-character length limitation in HL7 versions 2.1 through 2.5.
8.5 Using the OAG Document Protocol
Oracle B2B implements Open Applications Group (OAG) standards, a robust XML standard used across many industries. This standard defines messages as business object documents (BODs).
For information about the organization that created and maintains the OAG standards, go to http://www.oagi.org.
Document Version Parameters
No parameters need to be set when you create the document version for an OAG document.
Document Type Parameters
When you create an OAG document type, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-14 shows the document type parameters for an OAG document.
Figure 8-14 Document Type Parameters for an OAG Document
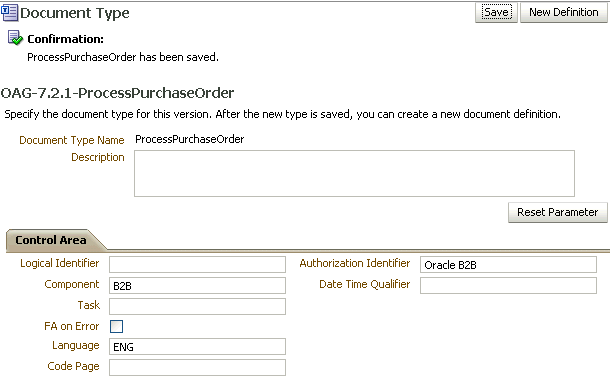
Description of "Figure 8-14 Document Type Parameters for an OAG Document"
Table 8-14 describes the document type parameters for an OAG document.
Table 8-14 Document Type Parameters for an OAG Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Control Area Tab |
- |
|
Logical Identifier |
Logical Identifier |
|
Component |
Component |
|
Task |
Task |
|
FA on Error |
When enabled, CONFIRMATION flag is set to 1. |
|
Language |
Language |
|
Code Page |
Code Page |
|
Authorization Identifier |
Authorization Identifier |
|
Date Time Qualifier |
Date Time Qualifier attribute |
Document Definition Parameters
When you create an OAG document definition, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-15 shows document definition parameters for an OAG document.
Figure 8-15 Document Definition Parameters for an OAG Document
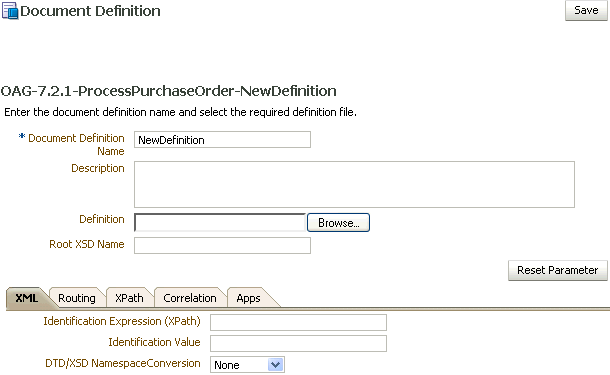
Description of "Figure 8-15 Document Definition Parameters for an OAG Document"
Table 8-15 describes the document definition parameters for an OAG document.
Table 8-15 Document Definition Parameters for an OAG Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
XML Tab |
- |
|
Identification Expression (XPath) |
Locates a node in the XML payload. |
|
Identification Value |
Provides the value to match in the node identified by the identification expression. If the values match, then the document is successfully identified. If the value is left blank, then Oracle B2B checks for the existence of the node and the document is successfully identified. |
|
DTD/XSD Namespace Conversion |
Select from None, Both, Inbound, or Outbound. |
|
Routing Tab |
- |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application. |
|
XPath Tab |
For more information, see How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document. |
|
XPath Name1 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression1 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name2 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression2 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name3 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression3 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
Correlation Tab |
- |
|
Correlation From XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for initiating the correlation. |
|
Correlation From XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload to initiate the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload for the correlation. |
|
Apps Tab |
- |
|
Document |
The name of the internal application document. |
|
Action |
A sub-classification within the document. |
|
XSLTFile |
The name of the XSLT file. |
8.6 Using the Positional Flat File Document Protocol
Oracle B2B supports message exchange for positional flat files, for example, NCPDP Telecom documents and SAP iDocs (intermediate documents (text files) used with SAP applications). This adds capabilities beyond handling XML files and traditional EDI files based on various XML and EDI standards.
Note:
Oracle B2B supports NCPDP documents that are used in the Insurance industry. The two widely used NCPDP documents are:
-
Post Adjudication History File: used for large detailed records
-
Post Adjudication Utilization File: used for small utilization records
Oracle B2B implements NCPDP documents through positional flat files.
Document Version Parameters
No parameters need to be set when you create the document version for a positional flat file.
Document Type Parameters
No parameters need to be set when you create the document type for a positional flat file.
Document Definition Parameters
When you create a document definition for a positional flat file, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-16 shows document definition parameters for a positional flat file.
Note:
Shift-JIS encoding is not supported for Positional Flat File documents. If the b2b.encoding is Shift-JIS and there are multi-byte characters in the payload, a B2B-51507: Payload validation error appears in the B2B report UI. Set the b2b.encoding to UTF-8 and use a valid UTF-8 payload.
A B2B-51507: Payload validation error also appears in the B2B report UI if an internal ftp channel is used for outbound PFF documents, the b2b.encoding is different from payload.encoding&internal.ftp encoding, and there are multibyte characters in the payload.
The field Field-VSART_BEZ string length is counted by bytes when payload.encoding is EUC-KR while it is counted by characters in other encodings, such as UTF-8, ISO-8859-1, Big5, and GBK. Increase the maximum length in the schema document if the payload is in EUC-KR when encountering the error The data element is too long in B2B reports.
Figure 8-16 Document Definition Parameters for a Positional Flat File (including SAP iDocs)
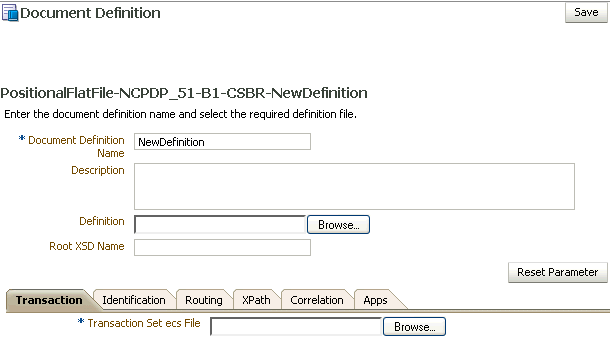
Description of "Figure 8-16 Document Definition Parameters for a Positional Flat File (including SAP iDocs)"
Table 8-16 describes the document definition parameters for a positional flat file.
Table 8-16 Document Definition Parameters for a Positional Flat File
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Transaction Tab |
- |
|
*Transaction Set ecs File |
Use the Browse button to find the ecs file. |
|
Identification Tab |
- |
|
Identification Value |
Not applicable. |
|
Identification Start Position |
Used in combination with the end position to retrieve a value from the payload between the start and end positions. |
|
Identification End Position |
Used in combination with the start position to retrieve a value from the payload between the start and end positions. |
|
Routing Tab |
- |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application. |
|
XPath Tab |
For more information, see How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document. |
|
XPath Name1 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression1 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name2 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression2 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name3 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression3 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
Correlation Tab |
- |
|
Correlation From XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for initiating the correlation. |
|
Correlation From XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload to initiate the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload for the correlation. |
|
Apps Tab |
- |
|
Document |
The name of the internal application document. |
|
Action |
A sub-classification within the document. |
|
XSLTFile |
The name of the XSLT file. |
8.7 Using the RosettaNet Document Protocol
A RosettaNet DTD, when used with Oracle B2B in a SOA composite application, must be converted to an XSD. An AQ Adapter added to the composite application can convert the inbound DTD to an XSD and manipulate the data as needed. Likewise, the AQ Adapter can convert the outbound XSD to a DTD for Oracle B2B to send the message out.
RosettaNet standards are specified by using of the RosettaNet Partner Interface Process (PIP), RosettaNet Dictionaries, and RNIF. Oracle B2B supports all PIPs. (The RosettaNet Technical Dictionary is not supported in Oracle B2B.)
8.7.1 PIPs
A PIP is an XML-based dialog that defines the business processes between trading partners. It defines the structure, sequence of steps, roles (buyer and seller) activities, data elements, values, and value types for each business document message exchanged between trading partners.
Using PIP 3A4 as an example, you can see how a PIP defines a dialog between trading partners, as shown in Figure 8-17.
Figure 8-17 PIP 3A4 Message Exchange Between Buyer and Seller
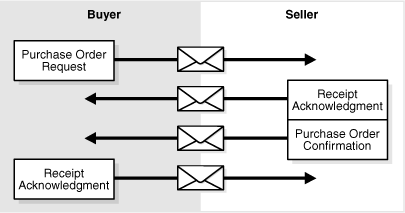
Description of "Figure 8-17 PIP 3A4 Message Exchange Between Buyer and Seller"
A PIP sequence combines a cluster, segment, and type. The PIP sequence 3A4, for example, encodes the information shown in Table 8-17.
Table 8-17 PIP 3A4 Breakdown
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
3 |
Order manage cluster, with which trading partners can:
|
|
3A |
Quote and order entry segment. |
|
3A4 |
Specific PIP type, which supports:
|
Document Version Parameters
No parameters need to be set when you create the document version for a RosettaNet document.
Document Type Parameters
When you create a RosettaNet document type, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-18 shows document type parameters for a RosettaNet document.
Figure 8-18 Document Type Parameters for a RosettaNet Document
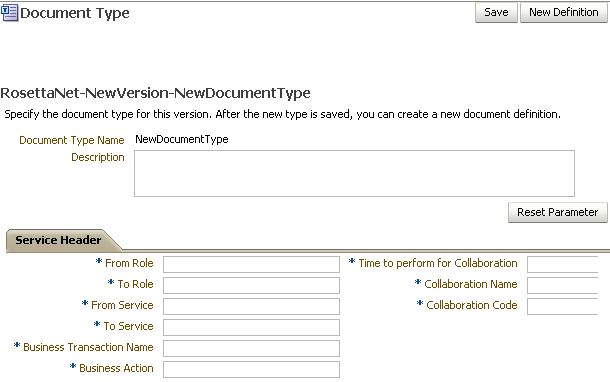
Description of "Figure 8-18 Document Type Parameters for a RosettaNet Document"
Table 8-18 describes document type parameters for a RosettaNet document.
Table 8-18 Document Type Parameters for a RosettaNet Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Service Header Tab |
- |
|
*From Role |
The trading partner that sends the message (in Partner Role Description of the PIP). |
|
*To Role |
The trading partner that receives the message (the role the trading partner receiving the message plays in the PIP). |
|
*From Service |
The service that sends the message. |
|
*To Service |
The service to which the message is sent. |
|
*Business Transaction Name |
The name of the business transaction is required. |
|
*Business Action |
The name of the business action is required. The value must be consistent with the Global Business Action Code. |
|
*Time to Perform for Collaboration |
The time to perform the business action is required. |
|
*Collaboration Name |
The RosettaNet collaboration name signifies the business transaction between trading partners (the roles as buyer and seller) depending on a common transaction. Required. |
|
*Collaboration Code |
The textual form of the abbreviated collaboration name. Required. |
Document Definition Parameters
When you create a RosettaNet document definition, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-19 shows the document definition parameters for a RosettaNet document.
Figure 8-19 Document Definition Parameters for a RosettaNet Document
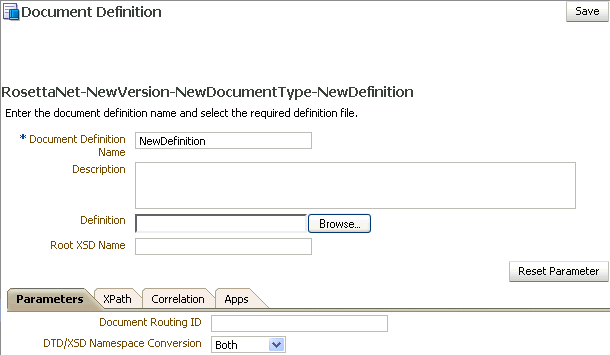
Description of "Figure 8-19 Document Definition Parameters for a RosettaNet Document"
Table 8-19 describes the document definition parameters for a RosettaNet document.
Table 8-19 Document Definition Parameters for a RosettaNet Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Parameters Tab |
- |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application. |
|
DTD/XSD Namespace Conversion |
A converted document can optionally replace the original RosettaNet document. Select Both to replace the RosettaNet document with the converted document for both the inbound and outbound messages. Select Inbound to replace the RosettaNet document with the converted document for the inbound message. Select Outbound to replace the RosettaNet document with the converted document for the outbound message. Select None for no replacement. None passes the DTD instance as-is. Inbound converts the instance DTD to XSD. Outbound converts the instance XSD to DTD. Both convert both inbound and outbound formats. |
|
XPath Tab |
For more information, see How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document. |
|
XPath Name1 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression1 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name2 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression2 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name3 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression3 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
Correlation Tab |
Correlation is required for a two-action PIP, for example, a 3A4. |
|
Correlation From XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for initiating the correlation. For example, |
|
Correlation From XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload to initiate the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for the correlation. Correlation-to represents the other message that takes part in the correlation. For example, |
|
Correlation To XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload for the correlation. |
|
Apps Tab |
- |
|
Document |
The name of the internal application document. |
|
Action |
A sub-classification within the document. |
|
XSLTFile |
The name of the XSLT file. |
8.7.2 Using the partnerDefinedPIPPayloadBindingId and LocationId Service Header Parameters
Oracle B2B provides support for the following Service Header parameters:
-
partnerDefinedPIPPayloadBindingID
-
LocationID
Configuring partnerDefinedPIPPayloadBindingID
You can configure the partnerDefinedPIPPayloadBindingID parameter by using the Service Header section under DocumentType in the Oracle B2B console.
Configuring locationID
To configure Rosettanet sender and receiver LocationID using the Oracle B2B console:
8.7.3 RosettaNet Validation
RosettaNet validation compares the elements in RosettaNet XML-format business documents to the requirements specified in the RosettaNet Message Guideline specification to determine their validity. This specification defines requirements for details such as element data types, element lengths, element value lists, and element cardinality. PIPs that require RosettaNet dictionary validation are also validated when a dictionary is present.The minimum validation-level requirements on the sections of a RosettaNet XML-format business document are as follows. These requirements cover the preamble, delivery header, service header, and service content sections of a document. Documents not following one or more of these requirements are identified as invalid.
- The XML-format business document requires compliance with its DTD.
- Elements with data types, lengths, or both that are specified in the RosettaNet Message Guideline specification require validation against this specification.
- An element's list of values specified in the entity instance list in the corresponding RosettaNet Message Guideline specification requires validation against this specification.
- If the Message Guideline specification defines the cardinality specification of an element differently from the corresponding DTD specification, the Message Guideline specification takes precedence.
- If a PIP requires dictionary validation, and a dictionary is included, the service content requires validation against the dictionary as a part of action performance.
- Cross-tag validation is based on message guidelines.
8.8 Using the UCCNet Document Protocol
Oracle B2B implements UCCNet, which enables trading partners—typically retailers and suppliers in the retail and consumer goods industries—to exchange documents with UCCNet.
The UCCNet document types supported in Oracle B2B are list below.
-
registerCommand
-
confirmCommand
-
linkCommand
-
checkComplianceCommand
-
documentCommand
-
documentIdentificationCommand
-
notificationStateCommand
-
queryCommand
-
registerLinkCommand
-
publicationCommand
-
publishCommand
-
catalogueItemMaintenanceCommand
-
priceCommand
-
validateCommand
-
registerOwnershipCommand
-
subscriptionCommand
-
notifyCommand
-
response
For information about the organization that created and maintains the UCCNet standards, go to http://www.1sync.org.
Document Version Parameters
No parameters need to be set when you create the document version for a UCCNet document.
Document Type Parameters
No parameters need to be set when you create the document type for a UCCNet document.
Document Definition Parameters
When you create a UCCNet document definition, you can set various parameters. Figure 8-20 shows document definition parameters for a UCCNet document.
Figure 8-20 Document Definition Parameters for a UCCNet Document
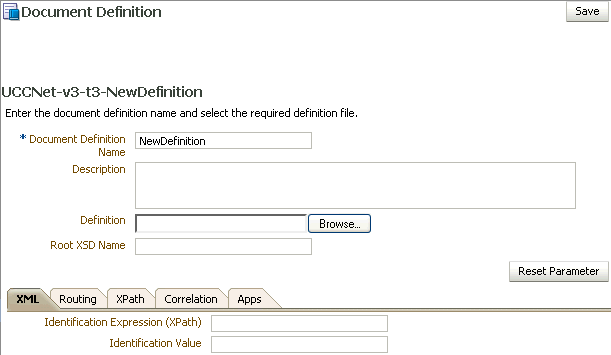
Description of "Figure 8-20 Document Definition Parameters for a UCCNet Document"
Table 8-20 describes the document definition parameters for a UCCNet document.
Table 8-20 Document Definition Parameters for a UCCnet Document
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
XML Tab |
The following parameters are on the XML tab. |
|
Identification Expression (XPath) |
Locates a node in the XML payload |
|
Identification Value |
Provides the value to match in the node identified by the Identification Expression. If the values match, then the document is successfully identified. If the value is left blank, then Oracle B2B checks for the existence of the node and the document is successfully identified. |
|
Routing Tab |
The following parameters are on the Routing tab. |
|
Document Routing ID |
Sets the consumer name to the back-end application. |
|
XPath Tab |
For more information, see How to Configure the XPath Expression for a Custom XML Document. |
|
XPath Name1 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression1 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name2 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression2 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Name3 |
The XML XPath name for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
XPath Expression3 |
The XML XPath expression for retrieving the value from the payload. |
|
Correlation Tab |
The following parameters are on the Correlation tab. |
|
Correlation From XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for initiating the correlation. |
|
Correlation From XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload to initiate the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Name |
The name of the correlation property for the correlation. |
|
Correlation To XPath Expression |
The XML XPath for retrieving the value from the payload for the correlation. |
|
Apps Tab |
The following parameters are on the Apps tab. |
|
Document |
The name of the internal application document. |
|
Action |
A sub-classification within the document. |
|
XSLTFile |
The name of the XSLT file. |
8.8.1 Creating a 1Sync Document
The 1Sync document protocol helps in the data synchronization between seller and buyer, which enables the transfer of product and location information with the continuous synchronization of the data over time.
Use the Custom document protocol or the UCCNet document protocol to create a 1Sync XML document.
Note:
The GS-1 organization has changed the standard name from UCCNet to 1Sync. Use either the seeded UCCNet document protocol or create a new Custom document protocol, 1Sync, as illustrated in the figure. The functionality is the same.
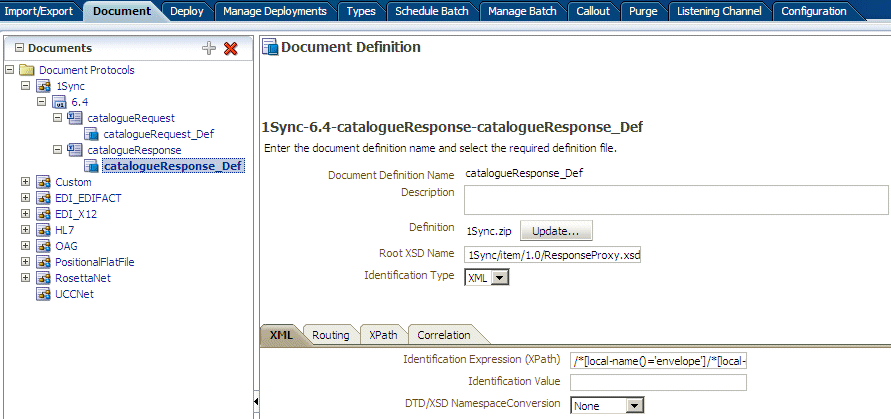
Figure 8-21 shows a document definition for a 1Sync document, using the Custom document protocol.
You can correlate 1Sync request and response messages as follows:
-
Use the document routing ID on the Routing tab. The routing ID 1Sync_64_catalogueRequest is shown Figure 8-22.
Figure 8-22 The Routing Tab for a 1Sync Document Definition
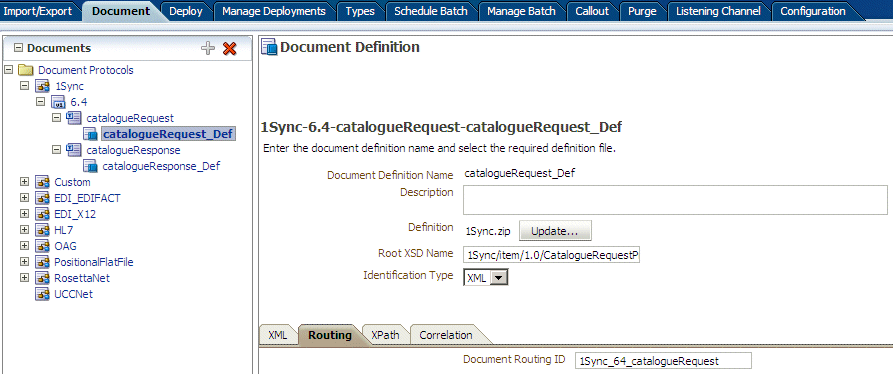
Description of "Figure 8-22 The Routing Tab for a 1Sync Document Definition" -
Use correlation parameters on the Correlation tab. The following parameters and values are shown in Figure 8-23.
-
Correlation From XPath Name:
From_catalogueRequest_messageId -
Correlation From XPath Expression:
/*[local-name()='envelope']/*[local-name()='header']/*[local-name()='messageId']This value matches the correlationFrom value in the payload.
Figure 8-23 The Correlation Tab for a 1Sync Document Definition
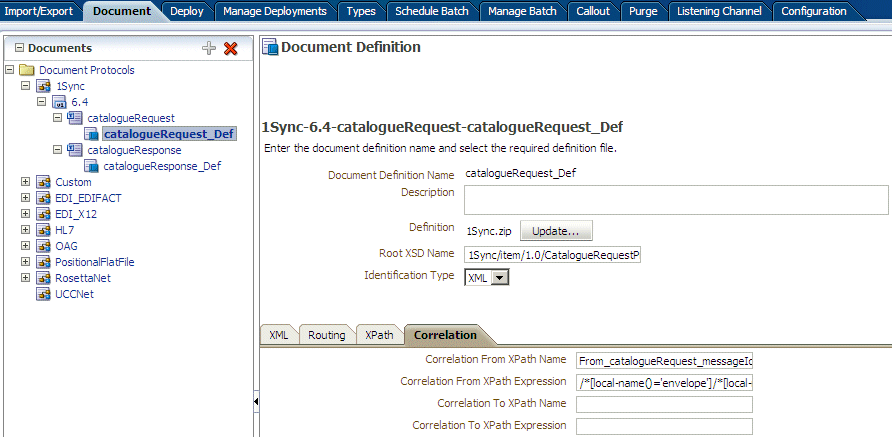
Description of "Figure 8-23 The Correlation Tab for a 1Sync Document Definition"
-
For more information, see Using the Custom Document Protocol.
8.9 Changing Document Details
For more information, see Restricting Access to Document Types.
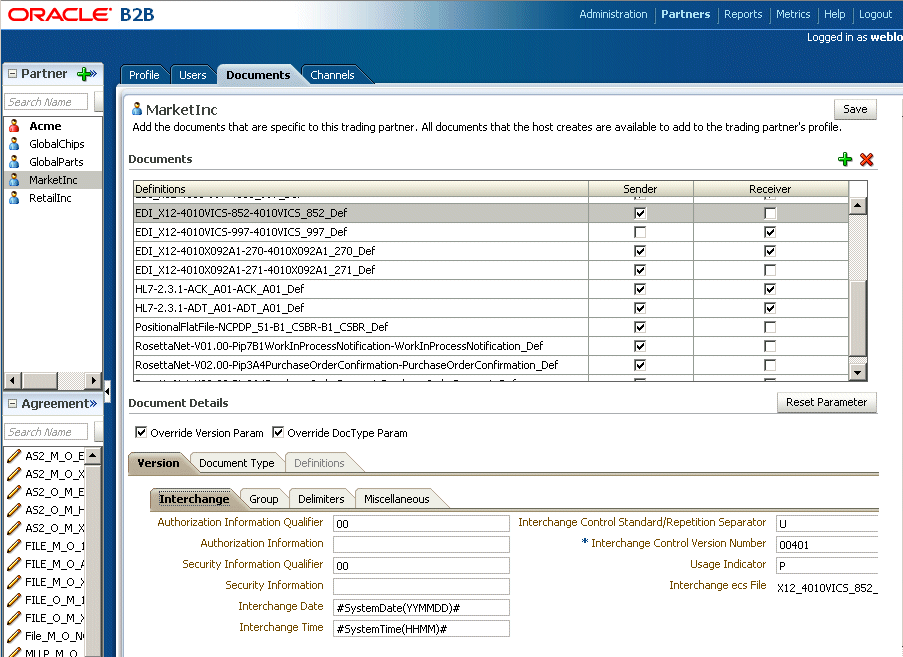
Figure 8-24 shows the Version tab in the Document Details section, where parameters for the document protocol version can be changed.
Delimiters, and parameters such as Interchange Control Version Number, Interchange Date, and Interchange Time are typically changed for different remote trading partners.
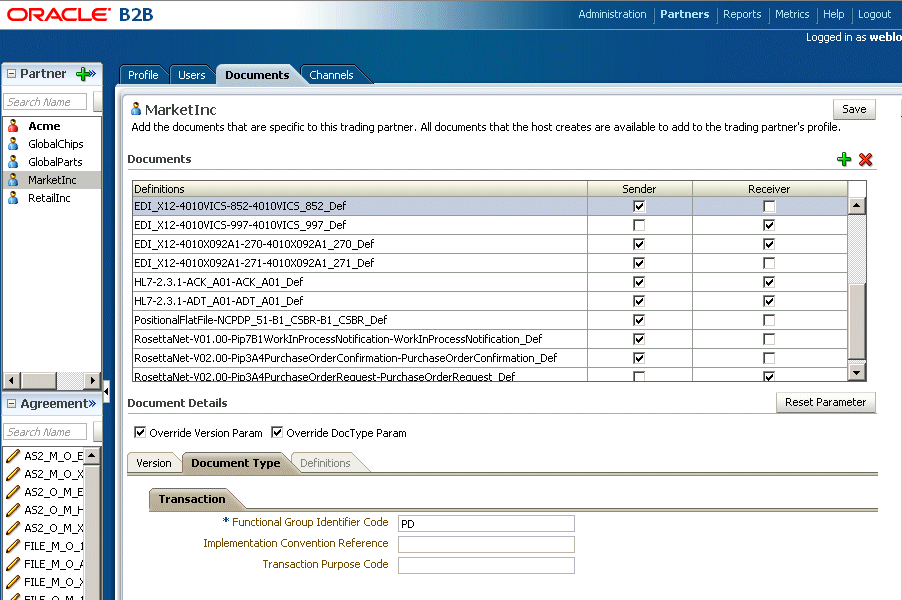
Figure 8-25 shows the Document Type tab, where parameters for the document type can be changed.
Use the Override Version Param and Override DocType Param parameters to indicate that override values are provided. Document type parameter values set for a remote trading partner take precedence over the default document type parameter values set for the document definition when the document was created on the Administration > Document tab.
To override document details:
8.9.1 Changing Document Definitions After Deploying an Agreement
Changes to a document definition after an agreement is deployed are not reflected in the trading partner's profile. Use the Document Details area on the Partners > Documents tab to change document protocol version and document type parameters. Then redeploy the agreement.
8.9.2 Changing Document Definitions After Importing Metadata
If you import B2B metadata and then change the document from the Administration > Document tab, then you must also make the same changes to the supported document definition for the host and remote trading partners from the Partners > Documents tab. Use the Version, Document Type, and Definitions tabs under Document Details to make the changes.
8.10 Using Document Routing IDs
This is useful if you have many different document definitions, but you want them to be handled the same way. The WSDL uses the document routing ID instead of the document definitions. In a SOA composite application, the B2B Configuration Wizard provides an option to use the document routing ID instead of selecting a document definition, as shown in Figure 8-26.
Figure 8-26 Document Routing ID Option in Oracle JDeveloper
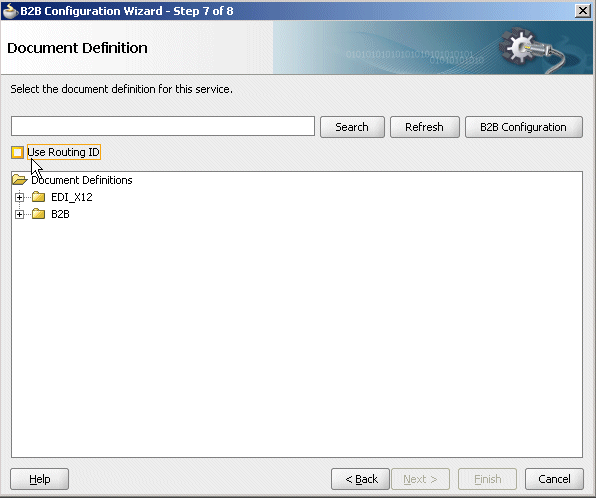
Description of "Figure 8-26 Document Routing ID Option in Oracle JDeveloper"
When using AQ, if you set the routing ID value instead of using the default b2buser, then do not set it to a numeric value. Use a combination of alphabetic and numeric values.