19 Managing Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entries
This chapter includes the following sections:
Introduction to Managing Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entries
You can define attribute uniqueness across an entire directory, across one subtree, and across one object class. You can implement attribute uniqueness by creating an attribute uniqueness constraint entry.
The following sections explain this further:
Attribute Uniqueness Scope
You can define attribute uniqueness across an entire directory, across one subtree, and across one object class.
-
Across the entire directory
For example, to ensure that every entry in your directory that includes a
mailattribute has a unique value for that attribute, you create an instance of attribute uniqueness associated withmail. -
Across one subtree for each attribute
For example, suppose that MyCompany hosts the directories for SubscriberCompany1 and SubscriberCompany2. You can choose to enforce attribute uniqueness in SubscriberCompany1 only.
-
Across one object class
For example, suppose that
IDis an attribute in both themachineobject class and thepersonobject class. If attribute uniqueness is enabled, then the directory server prevents you from adding either two machines or two people with the sameID. You can, however, add amachineIDattribute that has the same value as an existingpersonIDattribute. Similarly, you can add apersonIDattribute that has the same value as an existingmachineIDattribute.
Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entries
Attribute uniqueness constraint entries are stored under cn=unique,cn=Common,cn=Products,cn=OracleContext.
To implement attribute uniqueness, you create an attribute uniqueness constraint entry in which you provide values for the attributes shown in Table 19-1.
Table 19-1 Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entry
| Attribute Name | Mandatory? | Valid Value | Default Value | Default Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Yes |
Any string |
N/A |
N/A |
|
|
No |
One of the following:
|
|
Searches the entire directory |
|
|
No |
Either |
|
Disables attribute uniqueness |
|
|
No |
Any string |
|
Searches the entire directory |
|
|
No |
Any string |
|
Searches all object classes |
Attribute Uniqueness Constraint in Oracle Internet Directory Replication Environment
When an attribute uniqueness constraint is present in the Oracle Internet Directory replication environment, be careful about configuring the attribute uniqueness constraints on each server.
This section contains these topics:
Attribute Uniqueness Constraint in Simple Replication Environment
When attribute uniqueness constraint is present in Oracle Internet Directory simple replication environment:
Because all modifications by client applications are performed on the supplier server, the attribute uniqueness constraint should be enabled on that server. It is not necessary to enable the attribute uniqueness constraint on the consumer server. Enabling the attribute uniqueness constraint on the consumer server does not prevent the directory server from operating correctly, but it can cause a performance degradation.
Attribute Uniqueness Constraint in Multimaster Replication Environment
When attribute uniqueness constraint is present in Oracle Internet Directory multimaster replication environment:
In a multimaster replication scenario, nodes serve as both suppliers and consumers of the same replica. Multimaster replication uses a loosely consistent replication model.
Enabling an attribute uniqueness constraint on one of the servers does not ensure that attribute values are unique across both masters at any given time. Enabling an attribute uniqueness constraint on only one server can cause inconsistencies in the data held on each replica.
The attribute uniqueness constraint must be enabled on both masters. However, there may still be an inconsistent state. For example, in both masters we can successfully modify entries to the same attribute value. However, when the changes are later replicated to the other node, the conflict becomes apparent. You must take this type of conflict resolution into consideration as well, deciding whether conflict resolution should be the replication server's responsibility.
Support of LDAP Tools for Attribute Uniqueness
When you use the LDAP tools, the attribute uniqueness feature prevents duplication of attribute values, both when adding and modifying them. For example, it prevents you from assigning to a new employee an identifier already assigned to another employee. Instead, the directory server terminates the operation and returns an error message.
Note:
The LDAP tools support attribute uniqueness. The bulk tools does not support attribute uniqueness.
When you have created the entry and specified the attributes, before it performs an operation, the directory server:
-
Uses the attribute uniqueness constraint to check all update operations
-
Determines whether the operation applies to a monitored attribute, subtree, or object class
If an operation applies to a monitored attribute, suffix, or object class, and would cause two entries to have the same attribute value, then the directory server terminates the operation and returns a constraint violation error message to the client.
Note:
The attribute uniqueness feature works on indexed attributes only.
Duplicate Attribute Values
In earlier releases, if duplicate attribute values existed in the directory before attribute uniqueness was enabled, Oracle Internet Directory server did not report an error for these duplicate values.
During an upgrade to Oracle Internet Directory 14c (14.1.2.1.0), data is copied to the attr_uniqueness table. During this upgrade process, duplicate values are copied the attr_uniqueness_log table and not to the attr_uniqueness table.
After a fresh installation of Oracle Internet Directory, when the attribute uniqueness is enabled existing data can also have duplicate values.
Cleaning Up Duplicate Attribute Values
You need to determine and clean up duplicate attribute values.
Follow these steps:
Specifying Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entries
Attribute uniqueness constraint entries are stored under cn=unique,cn=Common,cn=Products,cn=OracleContext.
To understand the examples in this section, refer to Figure 19-1.
Figure 19-1 Example of a Directory Information Tree
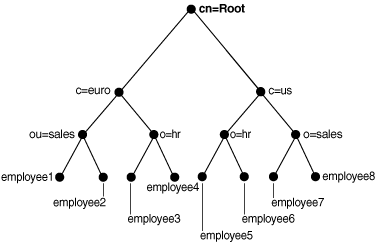
Description of "Figure 19-1 Example of a Directory Information Tree"
This section describes and gives examples of rules you follow when creating attribute uniqueness constraints. It contains these topics:
-
Specifying Multiple Attribute Names in an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint
-
Specifying Multiple Subtrees in an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint
-
Specifying Multiple Scopes in an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint
-
Specifying Multiple Object Classes in an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint
-
Specifying Multiple Subtrees, Scopes, and Object Classes in an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint
Specifying Multiple Attribute Names in an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint
When multiple attribute uniqueness constraints have different values in orcluniqueattrname, their effects are independent of each other.
For example, suppose that a user defines two attribute uniqueness constraints as follows:
Constraint1:
orcluniqueattrname: employee_id
Constraint2:
orcluniqueattrname: email_id
In this example, Constraint1 and Constraint2 enforce uniqueness on the specified attribute within their own attribute uniqueness scopes. Constraint1 and Constraint2 are independent of each other.
Specifying Multiple Subtrees in an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint
When multiple attribute uniqueness constraints have the same values in orcluniqueattrname, orcluniquescope and orcluniqueobjectclass, but different values in orcluniquesubtree, the subtree scopes specified by those attribute uniqueness constraints are checked individually.
For example, refer to Figure 19-1. Suppose that a user defines two attribute uniqueness constraints as follows:
Constraint1:
orcluniqueattrname: employee_id orcluniquesubtree: o=sales, c=us, cn=root orcluniquescope: onelevel
Constraint2:
orcluniqueattrname: employee_id orcluniquesubtree: o=hr, c=euro, cn=root orcluniquescope: onelevel
In this example, the attribute uniqueness on employee_id is enforced against all entries under subtree o=sales,c=us,cn=root. Attribute uniqueness on employee_id is also enforced against all entries under o=hr,c=euro,cn=root independent of the entries under the subtree o=sales,c=us,cn=root—that is, the directory server enforces the unique value of the employee_id attribute for employee3 and employee4. Unique employee_id is enforced for employee7 and employee8 as well while employee7 could have the same employee_id as employee4.
Specifying Multiple Scopes in an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint
When multiple attribute uniqueness constraints have the same values in orcluniqueattrname, orcluniquesubtree and orcluniqueobjectclass, but different values in orcluniquescope, the attribute uniqueness constraint with the largest search scope takes effect.
For example, referring to Figure 19-1, suppose that a user defines two attribute uniqueness constraints as follows:
Constraint1:
orcluniqueattrname: employee_id orcluniquesubtree: c=us, cn=root orcluniquescope: onelevel
Constraint2:
orcluniqueattrname: employee_id orcluniquesubtree: c=us, cn=root orcluniquescope: sub
In this example, the attribute uniqueness on employee_id is enforced against all entries under the subtree c=us,cn=root and the entry c=us,cn=root itself. Note that this is the same as if the user had defined only Constraint2.
Specifying Multiple Object Classes in an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint
When multiple attribute uniqueness constraints have the same values in orcluniqueattrname, orcluniquesubtree, and orcluniquescope, but different values in orcluniqueobjectclass, then the union of attributes belonging to those object classes is checked.
For example, look at Figure 19-1. Suppose that a user defines two attribute uniqueness constraints as follows:
Constraint1:
orcluniqueattrname: employee_id orcluniquesubtree: c=us, cn=root orcluniqueobjectclass: person
Constraint2:
orcluniqueattrname: employee_id orcluniquesubtree: c=us, cn=root
In this example, the attribute uniqueness on employee_id is enforced against all entries under the subtree c=us,cn=root and the entry c=us,cn=root itself, no matter what object class those entries belong to. Note that Constraint2 specifies no orcluniqueobjectclass attribute, which is the same as specifying all object classes.
Specifying Multiple Subtrees, Scopes, and Object Classes in an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint
When multiple attribute uniqueness constraints have the same values in orcluniqueattrname, but different values in orcluniquesubtree, orcluniquescope, and orcluniqueobjectclass, the entries that belong to the attribute uniqueness scopes of different constraints are checked individually.
For example, referring to Figure 19-1, suppose that a user defines two attribute uniqueness constraints as follows:
Constraint1:
orcluniqueattrname: employee_id orcluniquesubtree: o=sales, c=us, cn=root orcluniquescope: onelevel orcluniqueobjectclass: person
Constraint2:
orcluniqueattrname: employee_id orcluniquesubtree: c=euro, cn=root orcluniquescope: sub orcluniqueobjectclass: organization
In this example, the attribute uniqueness on employee_id is enforced against each of the following independent of each other:
-
All entries one level under the entry
o=sales,c=us,cn=rootwith the object classperson -
All entries under subtree
c=euro,cn=rootand the entryc=euro,cn=rootitself with the object classorganization
Managing an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entry by Using ODSM
You can manage an attribute uniqueness constraint policy by using Oracle Directory Services Manager (ODSM).
The following sections explain this further:
Creating an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entry by Using ODSM
Using ODSM, you can create an attribute uniqueness constraint entry.
To create an attribute uniqueness constraint entry by using ODSM:
- Invoke Oracle Directory Services Manager and connect to the Oracle Internet Directory server as described in Invoking Oracle Directory Services Manager.
- Select Advanced from the task selection bar.
- Expand Attribute Uniqueness in the left pane.
- On the toolbar, choose the Create an attribute uniqueness constraint icon. This displays the New Constraint window.
- In the New Constraint dialog box, enter values in the text fields and select the Unique Attribute Scope. You can click Browse to select the Unique Attribute Subtree.
- If you want to enable the constraint now, click Enable Unique Attribute.
- Choose OK. The entry you just created appears in the list of attribute uniqueness constraint entries in the left panel.
- Click Apply to apply this constraint or Revert to revert to the state before you created the new entry.
Modifying an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entry by Using ODSM
Using ODSM, you can modify an attribute uniqueness constraint.
To modify an attribute uniqueness constraint entry by using ODSM:
- Invoke Oracle Directory Services Manager and connect to the Oracle Internet Directory server as described in Invoking Oracle Directory Services Manager.
- Select Advanced from the task selection bar.
- Expand Attribute Uniqueness in the left pane.
- Select an existing uniqueness constraint. This displays the General tab of the Attribute Uniqueness Constraint window.
- Enter or modify values.
- If you want to enable the constraint now, click Enable Unique Attribute.
- Click Apply to apply this change or Revert to revert to the state before you modified the entry.
Deleting an Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entry by Using ODSM
You can delete an attribute uniqueness constraint entry by using ODSM.
To delete an attribute uniqueness constraint policy:
- Invoke Oracle Directory Services Manager and connect to the Oracle Internet Directory server as described in Invoking Oracle Directory Services Manager.
- Select Advanced from the task selection bar.
- Expand Attribute Uniqueness in the left pane.
- In the left panel, select the attribute uniqueness constraint entry you want to delete.
- Choose the Delete icon, then, when prompted, confirm the deletion. The entry you deleted no longer appears in the list of attribute uniqueness constraint entries in the left panel.
- Click Apply to apply this change or Revert to revert to the state before you deleted the entry.
Managing Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entries by Using the Command Line
You can manage an attribute uniqueness constraint policy by using the command line.
The following sections explain this further:
-
Creating Attribute Uniqueness Across a Directory by Using Command-Line
-
Specifying Uniqueness Constraint for an Attribute by Using Command-Line
-
Creating Attribute Uniqueness Across One Subtree by Using Command-Line
-
Creating Attribute Uniqueness Across One Object Class by Using Command-Line
-
Modifying Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entries by Using Command-Line
-
Deleting Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entries by Using Command-Line
-
Enabling and Disabling Attribute Uniqueness by Using Command-Line
Creating Attribute Uniqueness Across a Directory by Using Command-Line
To create an instance of attribute uniqueness across an entire directory, specify an attribute name for which you want to enforce value uniqueness.
For example, to make employee identifiers unique for all US employees at MyCompany, you would follow these steps:
Specifying Uniqueness Constraint for an Attribute by Using Command-Line
Using Command-Line you can specify uniqueness constraint for an attribute.
The following LDIF file, uniquenessConstraint.ldif, specifies a uniqueness constraint for the orclcommonusernickname attribute:
# Use this LDIF file to set up a uniqueness constraint on the nickname # attribute within the user search base. # Before running the script, change the following parameters in the LDIF file. # <userid_attribute> - Specify the name of the attribute that holds the user # id. This value should be the same as the orclcommonusernickname attribute # configured for the realm.# <dn _f_user_serach_base> - Specify the user search base in which the # uniqueness constraint should be enforced. # dn: cn=<userid_attribute> ,cn=unique,cn=common,cn=Products, cn=OracleContext changetype: add objectclass: orclUniqueConfig orcluniqueattrname: <userid _ttribute> orcluniquesubtree: <dn_of_user_search_base> orcluniqueenable:1
Creating Attribute Uniqueness Across One Subtree by Using Command-Line
To create an instance of attribute uniqueness across one or more subtrees, specify:
-
An attribute name for which you want to enforce value uniqueness
-
Subtree locations under which you want the uniqueness constraint to be enforced
For example, suppose that MyCompany hosts the directories for SubscriberCompany1 and SubscriberCompany2, and you want to enforce the uniqueness of the employee identifier attribute in SubscriberCompany1 only. When you add an entry such as uid=dlin,ou=people,o=SubscriberCompany1,dc=MyCompany, dc=com, you must enforce uniqueness only in the o=SubscriberCompany1,dc=MyCompany,dc=com subtree. Do this by listing the DN of the subtree explicitly in the attribute uniqueness constraint configuration.
In this case, the LDIF file would look like this:
dn: cn=constraint1, cn=unique, cn=common, cn=products, cn=oraclecontext objectclass: orclUniqueConfig orcluniqueattrname: employeenumber orcluniquesubtree: o=SubscriberCompany1,dc=MyCompany, dc=com
Creating Attribute Uniqueness Across One Object Class by Using Command-Line
To create an instance of attribute uniqueness across one object class, you need to specify an attribute name for which you want to enforce value uniqueness and an object class name.
In this case, the LDIF file would look like this:
dn: cn=constraint1, cn=unique, cn=common, cn=products, cn=oraclecontext objectclass: orclUniqueConfig orcluniqueattrname: employeenumber orcluniqueobjectclass: person
Use ldapadd to add the entry.
ldapadd -D "cn=orcladmin" -q -p port -D user -f file_name
Modifying Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entries by Using Command-Line
To modify an attribute uniqueness entry, use create an LDIF file for the entry, then use ldapmodify to upload it into the directory.
For example, suppose there is an existing attribute uniqueness constraint entry:
dn: cn=constraint1, cn=unique, cn=common, cn=products, cn=oraclecontext objectclass: orclUniqueConfig orcluniqueattrname: employeenumber orcluniquesubtree: o=MyCompany, c=US orcluniqueobjectclass: person
To enforce the constraint against c=US, instead of o=MyCompany, you would perform these steps:
Deleting Attribute Uniqueness Constraint Entries by Using Command-Line
Use the ldapdelete command-line tool to delete an attribute uniqueness constraint policy.
Enabling and Disabling Attribute Uniqueness by Using Command-Line
You can enable or disable attribute uniqueness for an existing attribute uniqueness constraint entry.
To enable attribute uniqueness for an existing attribute uniqueness constraint entry:
-
Set the
orcluniqueenableattribute to1by usingldapmodify. -
Restart the directory server to enable the policy.
To disable attribute uniqueness:
- Set the
orcluniqueenableattribute to0by using ldapmodify. - Restart the directory server to disable the policy.