2 Developing Provisioning Processes
Process definitions consist of tasks. Process tasks represent the steps that you must complete to fulfill the purpose of a process. For example, in a provisioning process, tasks are used to enable a user or organization to access the target resource.
This chapter describes process management by using the Process Definition form of the Design Console. It contains the following topics:
2.1 Process Definition Form
The Process Definition form is used to create and manage the provisioning processes that are associated with resource objects.
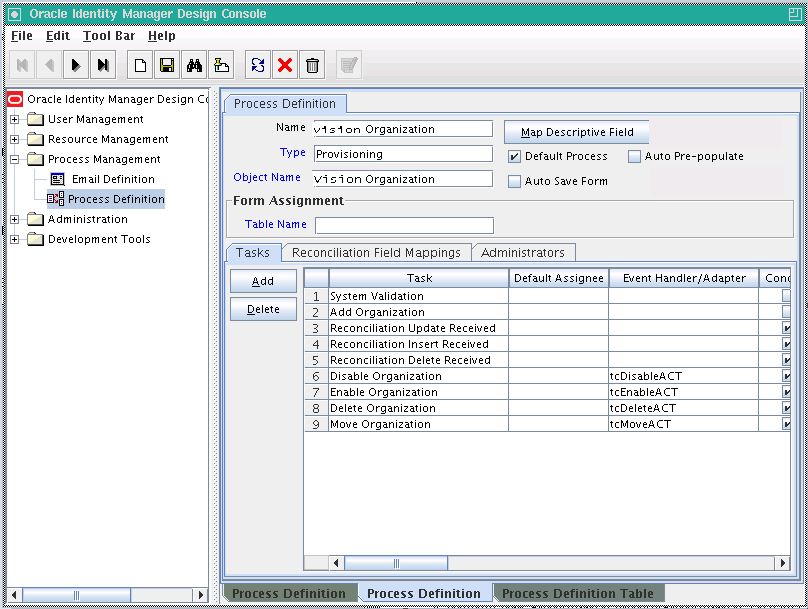
The Process Definition form shown in Figure 2-1 is in the Process Management folder.
In Figure 2-1, the Vision Organization provisioning process is created and assigned to the resource object of the same name.
Note:
Not all the form columns are captured in Figure 2-1; additional field columns extend on the right of the Tasks table.
2.2 Fields of the Process Definition Form
The fields of the Process Definition form represent the attributes of the provisioning processes that are associated with resource objects.
Table 2-1 describes the fields of the Process Definition form.
Table 2-1 Fields of the Process Definition Form
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
The name of the process. |
|
Type |
The classification type of the process definition. |
|
Object Name |
The name of the resource object to which the process will be assigned. |
|
Map Descriptive Field |
Click this button to select a field that will be used as an identifier of the process definition after an instance is assigned to a resource object. |
|
Render Workflow |
Click this button to start a Web browser and display the current workflow definition by using the Workflow Renderer tool. |
|
Default Process |
This check box determines if the current process is the default provisioning process for the resource object with which it is associated. Select the check box to set the process as the default provisioning process for the resource object to which it is assigned. If you deselect the check box, the process will not be the default. It will only be invoked if a process selection rule causes it to be chosen. |
|
Auto Save Form |
This check box designates whether Oracle Identity Manager suppresses the display of the custom form associated with this provisioning process or display it and allow a user to supply it with data each time the process is instantiated. Select this check box to automatically save the data in the custom process form without displaying the form. If you select this check box, you must supply either system-defined data or ensure that an adapter is configured to populate the form with the required data because the user will not be able to access the form. Deselect this check box to display the custom process form and allow users to enter data into its fields. |
|
Auto Pre-Populate |
This check box designates whether the fields of a custom form are populated by Oracle Identity Manager or a user. Two types of forms are affected:
If the Auto Pre-Populate check box is selected, when the associated custom form is displayed, the fields that have prepopulate adapters attached to them will be populated by Oracle Identity Manager. When this check box is deselected, a user must populate these fields by clicking the Pre-Populate button on the toolbar or by manually entering the data. Note: This setting does not control the triggering of the prepopulate adapter. It only determines if the contents resulting from the execution of the adapter are displayed in the associated form field(s) because of Oracle Identity Manager or a user. For more information about prepopulate adapters, see Working with Prepopulate Adapters. Note: This check box is only relevant if you have created a process form that is to be associated with the process and prepopulate adapters are used with that form. |
|
Table Name |
The name of the table that represents the form that is associated with the process definition. |
2.3 Creating a Process Definition
Process definitions are created by using the Process Definition from, which is in the Process Management folder of the Design Console.
To create a process definition:
2.4 Tabs on the Process Definition Form
After you start the Process Definition form and create a process definition, the tabs of this form become functional, namely the Tasks tab and the Reconciliation Field Mappings tab..
The Process Definition form contains the following tabs:
2.4.1 The Tasks Tab
The Tasks tab is used to create, modify, and remove process tasks.
The Tasks tab of the Process Definition form is described in the following sections:
2.4.1.1 About the Tasks Tab
You use the Tasks tab to:
-
Create and modify the process tasks that comprise the current process definition
-
Remove a process task from the process definition (when it is no longer valid)
Figure 2-2 displays the Tasks tab of the Process Definition form.
Figure 2-2 Tasks Tab of the Process Definition Form
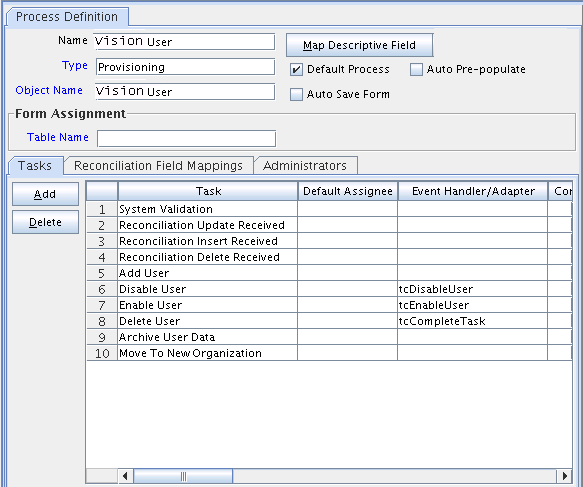
Description of "Figure 2-2 Tasks Tab of the Process Definition Form"
Note:
See Modifying Process Tasks for information about editing process tasks
2.4.1.2 Adding a Process Task
Process tasks represent the steps that you must complete in a process.
To add a process task:
2.4.1.3 Editing a Process Task
For instructions about how to edit and set process tasks, see Modifying Process Tasks.
2.4.2 The Reconciliation Field Mappings Tab
The Reconciliation Field Mappings tab is used to define a relationship between data elements in a target system or trusted source and fields in Oracle Identity Manager.
The Reconciliation Field Mappings tab is described in the following sections:
2.4.2.1 About the Reconciliation Field Mappings Tab
You use the Reconciliation Field Mappings tab shown in Figure 2-3 to define a relationship between data elements in a target system or trusted source and fields in Oracle Identity Manager.
Figure 2-3 Reconciliation Field Mappings Tab of the Process Definition Form
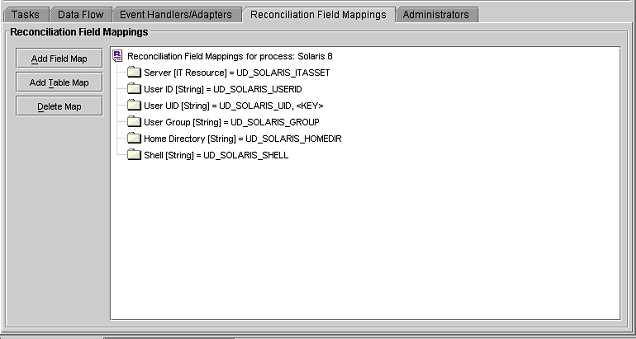
Description of "Figure 2-3 Reconciliation Field Mappings Tab of the Process Definition Form "
Only fields that you define in the Reconciliation Fields tab of the associated resource are available for mapping. Using a reconciliation event, these mappings determine which fields in Oracle Identity Manager to populate with information from the target system. For target resources (not trusted sources), you can use this tab to indicate which fields are key fields. Key fields determine the values that must be same on the process form and the reconciliation event to generate a match on the Processes Matched Tree tab of the Reconciliation Manager form.
For each mapping, the following information is displayed:
-
Name of the field, as defined on the Reconciliation Fields tab of the associated resource, on the target system or trusted source that is to be reconciled with data in Oracle Identity Manager.
-
Data type associated with the field, as defined on the Reconciliation Fields tab of the associated resource.
Possible values are Multi-Valued, String, Number, Date, and IT resource.
Note:
The IT Resource must be marked as a key field.
-
For trusted sources: For user discovery, mapping of the data in the trusted source field to the name of a field on the users form, or for organization discovery, mapping of the data in the trusted source field to the name of a field on the Oracle Identity Manager Organizations form.
If you are performing user and organization discovery with a trusted source, organization discovery must be conducted first.
-
For target resources: The name of the field on the resource's custom (provisioning) process form to which the data in the target resources field is to be mapped.
-
For target resources: Indicator designating if the field is a key field in the reconciliation for this target resource.
For provisioning processes to match a reconciliation event data, the key field values in their process forms must be the same as those in the reconciliation event.
Note:
Oracle recommends configuring both the entitlement attribute and the key attribute for the child data in reconciliation field mappings to enable effective duplicate entitlement or child data validation. See Duplicate Validation for Entitlements or Child Data in Administering Oracle Identity Governance for information about duplicate validation for entitlements or child data.
2.4.2.2 User Account Status Reconciliation
To configure user account status reconciliation, you must do the following:
-
For trusted sources: You must create a reconciliation field, for example,
Status, in the corresponding trusted resource object, which denotes the status of the user in the target. The value of this field must be eitherActiveorDisabled. This reconciliation field must be mapped to the user attributestatusin the corresponding process definition. -
For target resources: You must create a reconciliation field, for example,
Status, in the corresponding resource object, which denotes the status of the resource in the target. This reconciliation field must be mapped to the process attributeOIM_OBJECT_STATUSin the corresponding process definition. The following statuses are supported for target resource reconciliation:-
Revoked
-
Provisioned
-
Ready
-
Provide Information
-
Enabled
-
None
-
Waiting
-
Provisioning
-
Disabled
-
2.4.2.3 Mapping a Target Resource Field to Oracle Identity Governance
You can map the fields on a target resource or trusted source, as defined on the Reconciliation Fields tab of the associated resource definition, to applicable fields in Oracle Identity Manager. These mappings determine the fields that must be updated in Oracle Identity Manager in a reconciliation event. These mappings occur when you click one of the following on the Reconciliation Manager form:
-
The Create User or Create Organization button
-
The Link button on the Matched Users or Matched Organizations tab
-
The Establish Link button on the Processes Matched Tree tab
For user discovery on a trusted source, you define the fields to be mapped from the User resource to fields in the User provisioning process. The fields (that is, the user attributes) to which you will map your trusted source fields are derived from the Users form.
For organization discovery on a trusted source, you define fields to be mapped from the Oracle Identity Manager Organization resource to fields in the Oracle Identity Manager Organization provisioning process. The fields (that is, the organization attributes) to which you will map your trusted source fields are derived from the Organizations form.
After you have accessed the provisioning process definition for the associated resource and selected the Reconciliation Field Mappings tab, use one of the two procedures described in the following sections.
2.5 Modifying Process Tasks
To modify a process task for a process definition, double-click its row heading. The Editing Task window is displayed, containing additional information about the process task.
The Editing Task window contains the following tabs:
Note:
You must not modify the Xellerate Users process definition.
2.5.1 The General Tab
The General tab of the Editing Task window is used to set high-level information for the task that you modify.
The General tab is described in the following sections:
2.5.1.1 About the General Tab
You use the General tab of the Editing Task window to set high-level information for the task that you want to modify. For this example, the Create User task is used to create a user in the Solaris environment.
2.5.1.2 Fields of the General Tab
Table 2-2 describes the fields of the General tab.
Table 2-2 Fields of the General Tab
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Task Name |
The name of the process task. |
|
Task Description |
Explanatory information about the process task. |
|
Duration |
The expected completion time of the current process task in days, hours, and minutes. |
|
Conditional |
This check box determines if a condition is met to add the current process task to the process. Select this check box to prevent the process task from being added to the process unless a condition has been met. Clear this check box to not require the condition to be met for the process task to be added to the process. |
|
Required for Completion |
This check box determines if the current process task must be completed for the process to be completed. Select this check box to require the process task to have a status of Completed before the process can be completed. Deselect this check box to ensure that the status of the process task does not affect the completion status of the process. |
|
Constant Duration |
Not applicable |
|
Task Effect |
From this box, select the process action you want to associate with the task, for example, disable or enable. A process can enable or disable a user's access to a resource. When the disable action is chosen, all tasks associated with the disable action are inserted. Note: If you do not want the process task to be associated with a particular process action, select No Effect from the box. |
|
Disable Manual Insert |
This check box determines if a user can manually add the current process task to the process. Select this check box to prevent the process task from being added to the process manually. Deselect this check box to enable a user to add the process task to the process. |
|
Allow Cancellation while Pending |
This check box determines if the process task can be canceled if its status is Pending. Select this check box to allow the process task to be canceled if it has a Pending status. Deselecting this check box to prevent the process task from being canceled if its status is Pending. |
|
Allow Multiple Instances |
This check box determines if the process task can be inserted into the current process more than once. Select this check box to enable multiple instances of the process task to be added to the process. Deselect this check box to enable the process task to be added to the current process only once. |
|
Retry Period in Minutes |
If a process task is rejected, this field determines the interval before Oracle Identity Manager inserts a new instance of that task with the status of Pending. When the value of the Retry Period in Minutes field is 30, it means that if the Create User process task is rejected, then in 30 minutes Oracle Identity Manager adds a new instance of this task and assigns it a status of Pending. Note: If you specify a value for this field, then you must ensure the following:
|
|
Retry Count |
Determines how many times Oracle Identity Manager retries a rejected task. When the value of the Retry Count field is 5, it means that if the Create User process task is rejected, then Oracle Identity Manager adds a new instance of this task, and assigns it a status of Pending. When this process task is rejected for the fifth time, Oracle Identity Manager no longer inserts a new instance of it. |
|
Child Table/ Trigger Type |
These boxes specify the action that Oracle Identity Manager performs in the child table of a custom form that is associated with the current process, as indicated by the Table Name field of the Process Definition form. From the Child Table box, select the child table of the custom form where Oracle Identity Manager will perform an action. From the Trigger Type box, specify the action that Oracle Identity Manager is to perform in the child table. These actions include:
Note: If the custom process form does not have any child tables associated with it, the Child Table box will be empty. In addition, the Trigger Type box will be grayed out. |
|
Off-line |
This flag is applicable only for user attribute propagation tasks. If the flag is set for a user attribute propagation task, the task insertion is asynchronous. |
2.5.1.3 Modifying a Process Task's General Information
To modify the general information for a process task:
2.5.1.4 Triggering Process Tasks for Events Defined in Lookup.USR_PROCESS_TRIGGERS Fields
When a user attribute is defined in Lookup.USR_PROCESS_TRIGGERS, for each modification of the attribute, the corresponding process task is triggered for each provisioned resource. This is same for the First Name, Last Name, Display Name (USR_DISPLAY_NAME) user attributes and custom user attributes. However, for the Lookup.USR_PROCESS_TRIGGERS fields USR_STATUS, USR_LOCKED, USR_LOCKED_ON, and USR_MANUALLY_LOCKED, the attached process task is not triggered.
The following sections describe how to trigger the process tasks for the Lookup.USR_PROCESS_TRIGGERS fields:
2.5.1.4.1 About the USR_STATUS Attribute
It is not possible to run a task via Lookup.USR_PROCESS_TRIGGERS for the USR_STATUS attribute because this attribute is processed separately by Oracle Identity Manager. This attribute is changed by enabling, disabling, or deleting a user. These operations have a special effect on the provisioned resources because the corresponding process tasks are started via the Task Effect setting, as described in Table 2-2. For these three operations, the Lookup.USR_PROCESS_TRIGGERS is not used. Therefore, when the status changes, perform the steps in the following sections to run the process task:
2.5.1.4.2 Triggering for the USR_STATUS Attribute For Transition from Disabled to Enabled Status
To run the process task for the USR_STATUS attribute for transition from Disabled to Enabled status:
- In the Process Definition form, create a process task named
Enable User. - Open the Editing Task window, and click the General tab.
- From the Task Effect list, select Enables Process or Access to Application.
- Select Conditional and specify the condition to be met for the task to be added to the process.
2.5.1.4.3 Triggering for the USR_STATUS Attribute For Transition from Enabled to Disabled Status
To run the process task for the USR_STATUS attribute for transition from Enabled to Disabled status:
- In the Process Definition form, create a process task named
Disable User. - Open the Editing Task window, and click the General tab.
- From the Task Effect list, select Enables Process or Access to Application.
- Select Conditional and specify the condition to be met for the task to be added to the process.
2.5.1.4.4 Triggering for the USR_STATUS Attribute for Transition From Enabled/Disabled/Provisioned to Revoked status
To run the process task for the USR_STATUS attribute for transition from Enabled/Disabled/Provisioned to Revoked status:
2.5.1.4.5 Triggering For the USR_LOCKED, USR_LOCKED_ON, USR_MANUALLY_LOCKED Attributes
The lock and unlock operations, are handled in Oracle Identity Manager as separate orchestrations. The orchestration is on:
entity-type="User" operation="LOCK"
Or:
entity-type="User" operation="UNLOCK"
The event handler that does the evaluation for Lookup.USR_PROCESS_TRIGGERS is:
oracle.iam.transUI.impl.handlers.TriggerUserProcesses
This is triggered only in the following user orchestrations:
-
MODIFY: For generic fields
-
CHANGE_PASSWORD, RESET_PASSWORD: For USR_PASSWORD propagation
-
ENABLE, DISABLE, DELETE: For handling the execution of process tasks
For lock/unlock operations, the TriggerUserProcesses event handler is not triggered. Therefore, for the attributes modified through lock/unlock operations, the Lookup.USR_PROCESS_TRIGGERS is not checked.
If you want to run custom code for these operations when these fields are changed, then you can create event handlers and register them on the orchestrations mentioned in this section.
2.5.2 Integration Tab
The Integration tab of the Editing Task window is used to automate process tasks and map task adapter variables.
The Integration tab is described in the following sections:
2.5.2.1 About the Integration Tab
By using the Integration tab, you can:
-
Automate a process task by attaching an event handler or task adapter to it.
-
Map the variables of the task adapter so that Oracle Identity Manager can pass the appropriate information when the adapter is triggered. This occurs when the process task's status is Pending.
-
Break the link between the adapter handler and the process task once the adapter or event handler is no longer applicable with the process task.
For example, suppose that the adpSOLARISCREATEUSER adapter is attached to the Create User process task. This adapter has nine adapter variables, all of which are mapped correctly as indicated by the Y that precedes each variable name.
Note:
-
Event handlers are preceded with tc (Thor class), such as
tcCheckAppInstalled. These are event handlers that Oracle provides. Customer-created event handlers cannot have a tc prefix in their name. Adapters are preceded with adp, for example,adpSOLARISCREATEUSER. -
From the Design Console, you cannot create or modify DOB event handlers. You can only view the existing event handlers.
-
See Using the Adapter Factory and Developing Event Handlers for more information about adapters and event handlers
2.5.2.2 Assigning an Adapter or Event Handler to a Process Task
This section describes how to assign an adapter or event handler to a process task.
Note:
If you assign an adapter to the process task, the adapter will not work until you map the adapter variables correctly. See Mapping Adapter Variables for details.
To assign an adapter or event handler to a process task:
2.5.2.3 Mapping Adapter Variables
To map an adapter variable:
Note:
-
To trigger a task associated with a change to a parent form field, the name of the task must be
fieldUpdated, wherefieldis the name of the parent form field. If the task is not named according to this convention, it is not triggered during a field update. -
See Adapter Mapping Information for more information about the items to select in this procedure.
2.5.3 Task Dependency Tab
The Task Dependency tab of the Editing Task window is used to determine the logical flow of process tasks in a process.
The Task Dependency tab is described in the following sections:
2.5.3.1 About the Dependency Tab
You use the Task Dependency tab to determine the logical flow of process tasks in a process. Through this tab, you can:
-
Assign preceding tasks to a process task.
These tasks must have a status of Completed before Oracle Identity Manager or a user can trigger the current process task.
-
Assign dependent tasks to a process task.
Oracle Identity Manager or a user can trigger these tasks only after the current process task has a status of Completed.
-
Break the link between a preceding task and the current task so that the preceding task's completion status no longer has any effect on the current task being triggered.
-
Break the link between the current task and a dependent task so that the current task's completion status no longer has any bearing on triggering the dependent tasks.
For example, the Create User process task does not have any preceding tasks. Oracle Identity Manager triggers this task whenever the task is inserted into a process (for example, when an associated resource is requested). The Create User process task has seven dependent tasks. Before completion of this process task, each dependent task will have a status of Waiting. Once this task achieves a status of Completed, each of these process tasks are assigned a status of Pending, and Oracle Identity Manager can trigger them.
2.5.3.3 Removing a Preceding Task from a Process Task
To remove a preceding task from a process task:
2.5.4 Responses Tab
The Responses tab of the Editing Task window is used to define response codes and conditional tasks and to remove the responses from a process task.
The Responses tab of the Editing Task window is described in the following sections:
2.5.4.1 About the Responses Tab
You use the Responses tab to do the following:
-
Define the response codes that can be received in conjunction with the execution of a particular process tasks. You can use response codes to represent specific conditions on the target system.
-
Define the conditional tasks that are started if a response code is received during execution of this process task. These tasks are called generated tasks.
-
Remove a response from a process task.
-
Remove a generated task from a process task.
For example, when a Create User process task is completed, the SUCCESS response is activated. This response displays a dialog box with the message "The user was created successfully." In addition, Oracle Identity Manager triggers the Enable User process task.
Note:
By default, the UNKNOWN response is defined for each process task that is rejected. This way, even when the system administrator does not add any responses to a process task, if this task is rejected, the user will be notified in the form of an error message in a dialog box.
2.5.5 Task to Object Status Mapping Tab
The Task to Object Status Mapping tab is used to create the link between the status of a process task and the provisioning status of the resource object to which it is assigned.
The Task to Object Status Mapping Tab is described in the following sections:
2.5.5.1 About the Task to Object Status Mapping Tab
A resource object contains data that is used to provision resources to users and applications.
In addition, a resource object is provided with predefined provisioning statuses, which represent the various statuses of the resource object throughout its life cycle as it is being provisioned to the target user or organization.
Note:
Provisioning statuses are defined in the Status Definition tab of the Resource Objects form.
The provisioning status of a resource object is determined by the status of its associated provisioning processes, and the tasks that comprise these processes. For this reason, you must provide a link between the status of a process task and the provisioning status of the resource object to which it is assigned.
The Task to Object Status Mapping tab is used to create this link. Also, when this connection is no longer required, or you want to associate a process task status with a different provisioning status for the resource object, you must break the link that currently exists.
For this example, there are five mappings among process task statuses and provisioning statuses of a resource object. When the Create User process task achieves a status of Completed, the associated resource object will be assigned a provisioning status of Provisioned. However, if this task is canceled, the provisioning status for the resource object will be Revoked. None indicates that this status has no effect on the provisioning status of the resource object.
The following sections describe how to map a process task status to a provisioning status and unmap a process task status from a provisioning status.
2.5.5.2 Mapping a Process Task Status to a Provisioning Status
To map an process task status to a provisioning status: