B Securing Communication
You need to perform the following tasks to secure communication:
Prerequisites to Setting up a Secure Communication between OAM Servers and Webgates
Before you proceed with setting up a secure Communication between OAM servers and webgates ensure the system level requirements are met.
-
If OAM Server mode is CERT mode, agents must use CERT mode.
-
During agent registration, at least one OAM Server instance must be running in the same mode as the agent. After agent registration, you can change the mode of the OAM Server.
See Also:
-
For details about the SSL automation tool, managing ports for WebLogic Server, Oracle HTTP Server, and Oracle Fusion Middleware.
Securing Communication Between OAM Servers and WebGates
Securing communication between OAM Servers and clients (WebGates) means defining the transport security mode for the NAP (also known as the OAP) channel within the component registration page.
The security level for the channel is specified as either:
-
Open: Un-encrypted communication
In Open mode, there is no authentication or encryption between the WebGate and OAM Server. The WebGate does not ask for proof of the OAM Server's identity and the OAM Server accepts connections from all WebGates. Use Open mode if communication security is not an issue in your deployment.
-
Simple: Encrypted communication through the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol with a public key certificate issued by Oracle.
Use Simple mode if you have some security concerns, such as not wanting to transmit passwords as plain text, but you do not manage your own Certificate Authority (CA). In this case, OAM Servers and WebGates use the same certificates, issued and signed by Oracle CA.
-
Cert: Encrypted communication through SSL with a public key certificate issued by a trusted third-party certificate authority (CA).
Use Cert mode if you want different certificates on OAM Servers and WebGates and you have access to a trusted third-party CA. In this mode, you must encrypt the private key using the DES algorithm. Access Manager components use X.509 digital certificates in PEM format only. PEM refers to Privacy Enhanced Mail, which requires a passphrase. The PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail) format is preferred for private keys, digital certificates, and trusted certificate authorities (CAs). The preferred keystore format is the JKS (Java KeyStore) format.
-
HTTP: User defined un-encrypted communication mode.
If the user defined parameter
OAMServerCommunicationModeis set to HTTP, then the webgate will communicate with the OAM managed servers using HTTP protocols. -
HTTPS: User defined encrypted communication mode through the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol.
If the user defined parameter
OAMServerCommunicationModeis set to HTTPS, then the webgate will communicate with the OAM managed servers using HTTPS protocols. - OAP: If the user defined parameter
OAMServerCommunicationModeis set toOAPthen WebGate communicates with the OAM managed servers using the legacy back channel Protocols, OAP over the TCP port, utilizing the communication mode of Open, Simple, or Cert.
Logically the request is to the Access Manager credential collector. However, when you have a Web server proxy in front of the WebLogic AdminServer, with a <LocationMatch "/*">, all requests are routed through the proxy. In this case, there is perimeter defense using the proxy.
Figure B-1 illustrates the communication channels used by OAM Servers and WebGates during user authentication and authorization.
Figure B-1 Communication Channels for OAM Servers and WebGates
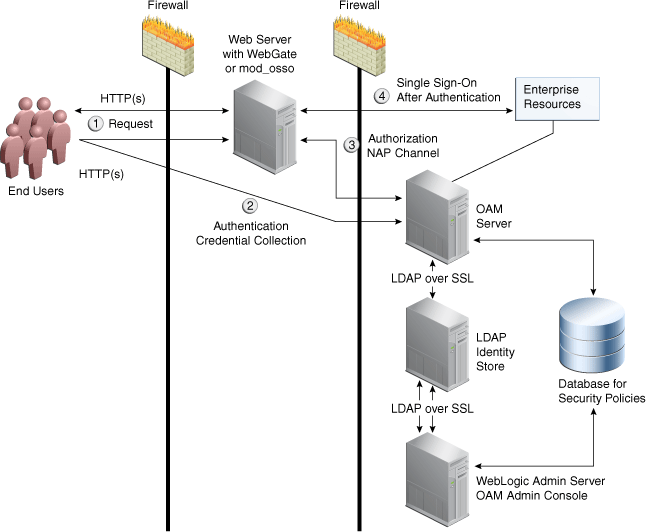
Description of "Figure B-1 Communication Channels for OAM Servers and WebGates"
Process overview: Authentication and authorization
-
Request is intercepted by WebGate.
-
Authentication (credential collection) occurs over HTTP(s) channel.
-
Authorization occurs over the NAP channel with OAM Agents only.
Using the secure-sockets layer (SSL) protocol helps prevent eavesdropping and successful man-in-the-middle attacks across the HTTP (HTTPS) channel. The SSL protocol is included as part of most Web server products and Web browsers. SSL uses the public-and-private key encryption system, which includes the use of a digital certificate. For details about enabling SSL communication for a Web server or directory server, see your vendor's documentation.
The PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail) format (BASE64-encoded ASCII) is preferred for private keys, digital certificates, and trusted certificate authorities (CAs). The preferred keystore format for OAM Servers is JCEKS and for OAM Clients is JKS (Java KeyStore) format. Access Manager components use X.509 digital certificates in DER (binary form of a certificate) format only.
See:
About Certificates, Authorities, and Encryption Keys
Digital certificates can be stored in a registry from which authenticating users can look up the public keys of other users.
Depending on the public key infrastructure, the digital certificate establishes credentials for Web-based transactions based on:
-
Certificate owner's name
-
Certificate serial number
-
Certificate expiration date
-
A copy of the certificate holder's public key, which is used to encrypt messages and digital signatures
-
The digital signature of the certificate-issuing authority is provided so that a recipient can verify that the certificate is real
In cryptography, a public key is a value provided by a designated authority to be used as an encryption key. The system for using public keys is called a public key infrastructure (PKI). As part of a public key infrastructure, a certificate authority checks with a registration authority (RA) to verify information provided by the requestor of a digital certificate. When the RA verifies the requestor's information, the CA can issue a certificate.
Private keys can be derived from a public key. Combining public and private keys is known as asymmetric cryptography, which can be used to effectively encrypt messages and digital signatures.
About Security Modes and X509Scheme Authentication
With the X509 authentication scheme (X509Scheme), the OAM Server SSL Port must differ from the Server Port, and must be configured to require Client Certificates. When X509Scheme is used, the X509 module is called after credential collection. X509Scheme requires the X509 challenge method and the X509 authentication module. The fully-qualified URL to the credential collector must be specified as the Challenge URL within X509Scheme. For example: https://managed_server_host:managed_server_ssl_port/oam/CredCollectServlet/X509
Note:
If a relative Challenge URL is specified with X509Scheme, the OAM Server uses the specified Server Host/Port to construct the fully-qualified URL of the X509 Credential Collector. However, this configuration will not work.
See Also:
The Importcert Tool
Administrators use the Oracle-provided importcert tool for several different procedures related to keystores, keys, and certificates.
Table B-1 provides the syntax for importcert commands.
Table B-1 importcert Command Syntax
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
keystore |
Follow this command with the path to an existing (or new) keystore. For example: /scratch/.oamkeystore or /scratch/clientKey.jks |
|
privatekeyfile |
Follow this option with the path to your private key. For example: /scratch/aaa_key.der |
|
signedcertfile |
Follow this option with the path to your signed certificate. For example: /scratch/aaa_cert.der |
|
alias |
Follow this option with your keystore entry alias. Required with genkeystore.: alias |
|
storetype |
Follow this option with your keystore type. By default, the store type is JCEKS (OAM Server keystore). For example: Server keystore .oamkeystore, of type: JCEKS Client keystore/scratch/clientTrustStore.jks and /scratch/clientKey.jks can be used. Both are type: JKS |
|
genkeystore |
This flag is required for generating OAM client certificates. The client does not expose the alias and alias password parameters. However, importcert tool sets the keystore password as the alias password. Specify: Yes or No Yes imports the certificates in a new keystore. No imports certificates into an existing keystore. |
|
Sample for OAM Server |
- java -cp importcert.jar oracle.security.am.common.tools.importcerts.CertificateImport -keystore <path to .oamkeystore> -privatekeyfile <path to aaa_key.der> -signedcertfile <path to aaa_cert.der> -alias oam.certmode -aliaspassword <password> -storetype <JCEKS> genkeystore <yes> Enter the keystore password and alias password when prompted. |
|
Sample for OAM Client See Also Generating Client Keystores for OAM Tester in Cert Mode |
- java -cp importcert.jar oracle.security.am.common.tools.importcerts.CertificateImport -keystore <path to clientkey.JKS> -privatekeyfile <path to aaa_key.der> -signedcertfile <path to aaa_cert.der> -storetype <JKS> genkeystore <yes> Enter the keystore password when prompted. |
TLS 1.3 and TLS 1.2 Support in Oracle Access Management
Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.3 and TLS 1.2 are supported with OAM 12c to provide communications security over the Internet. This protocol allows client/server applications to communicate in a way that is designed to prevent eavesdropping, tampering, or message forgery.
OAM supports TLS 1.3 across the Front channel only. It supports WebGate communication with the OAM managed servers using OAP over HTTP.
The following communication modes are not supported:
- OAP over TCP
- OHS
- OAM back-channel communication with the Oracle Database
- OAM back-channel communication with LDAP Identity Stores
OAM supports TLS 1.2 across the following channels:
| Channel | TLS 1.2 Status |
|---|---|
|
Front |
TLS 1.2 is fully supported since incoming traffic is terminated on the Load Balancer, Web Server or Weblogic Server. |
|
OAP Back |
The 12c Webgates fully support TLS 1.2. |
|
LDAP Back |
TLS 1.2 transport is supported with 11.1.2.3.0 BP8. However, TLS 1.2 is not supported when using an IDS Profile based User Identity Store. |
|
JDBC Back |
Databases are abstracted using WLS Datasources, which can be configured to use TLS 1.2 to connect to the database. OES uses JDBC as the Database abstraction and can be configured to use TLS 1.2. |
|
Outbound HTTPS |
All outbound calls are done using JSSE and rely on the JDK specific defaults. Starting with JDK 6 121 Update and JDK 7 Update 95, you can control the platform TLS protocols by setting the system property jdk.tls.client.protocols. |
TLS 1.2 supports cipher suites that gets installed with JDK.
In a freshly installed environment,
-
Consider 12c PS3 OAM server and 12c PS3 webgates, employing latest versions of OAM server and webgate. SSL communication between them will use TLSv1.2 protocol and SHA-2 certificates.
-
Consider 12c PS3 OAM server and 12CPS2/ R2PS3 webgates, employing older versions of webgate and OAM server. OAM can support TLSv1.2 and SHA-2 certificates but 12CPS2/ R2PS3 webgates cannot.
Since we have latest 12c OAM server combined with older versions of webgate/OAM servers where TLS1.2 and SHA2 is not supported, we need to relax the security posture in OAM by updating the
java.securityfile with the following changes:-
Open the
java.securityfile located atJAVA_HOME/jre/lib/security/in an editor. -
Remove TLSv1, TLSv1.1, MD5withRSA from the following key:
key - jdk.tls.disabledAlgorithms -
Remove MD5 from the following key:
key - jdk.certpath.disabledAlgorithms
-
Steps to enable TLSv1.2 in OAM 12c environment
Enable TLSv1.2 in OHS:
Update the below two files in 12c OHS:
/scratch/work/TLStest/OHS12c/Oracle_Home/user_projects/domains/base_domain/config/fmwconfig/components/OHS/ohs1/ssl.conf
/scratch/work/TLStest/OHS12c/Oracle_Home/user_projects/domains/base_domain/config/fmwconfig/components/OHS/instances/ohs1/ssl.confSSLProtocol -ALL +TLSv1.2Enable TLSv1.2 in DB:
Follow the below steps to enable in DB:
-
Create a wallet for server jnetadmin_s and one for client jnetadmin_c
mkdir root mkdir jnetadmin_s mkdir jnetadmin_c export ORACLE_HOME=/scratch/alice/work/db1427 export T_WORK=$ORACLE_HOME export ROOT_CERT_DIR=$T_WORK/root export TNS_ADMIN_SERVER=$T_WORK/jnetadmin_s export TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT=$T_WORK/jnetadmin_c ./orapki wallet create -wallet $ROOT_CERT_DIR -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet add -wallet $ROOT_CERT_DIR -dn "CN=Root,C=US" -keysize 2048 -self_signed -validity 3650 -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet export -wallet $ROOT_CERT_DIR -dn "CN=Root,C=US" -cert $ROOT_CERT_DIR/b64certificate.txt -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet create -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_SERVER -auto_login -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet add -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_SERVER -dn "CN=Server,OU=ST,O=Oracle,ST=California,C=US" -keysize 2048 -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet export -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_SERVER -dn "CN=Server,OU=ST,O=Oracle,ST=California,C=US" -request $TNS_ADMIN_SERVER/creq.txt -pwd welcome1 ./orapki cert create -wallet $ROOT_CERT_DIR -request $TNS_ADMIN_SERVER/creq.txt -cert $TNS_ADMIN_SERVER/cert.txt -validity 3650 -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet add -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_SERVER -trusted_cert -cert $ROOT_CERT_DIR/b64certificate.txt -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet add -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_SERVER -user_cert -cert $TNS_ADMIN_SERVER/cert.txt -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet create -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT -auto_login -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet add -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT -dn "CN=Client,OU=ST,O=Oracle,ST=CA,C=US" -keysize 2048 -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet export -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT -dn "CN=Client,OU=ST,O=Oracle,ST=CA,C=US" -request $TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT/creq.txt -pwd welcome1 ./orapki cert create -wallet $ROOT_CERT_DIR -request $TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT/creq.txt -cert $TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT/cert.txt -validity 3650 -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet add -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT -trusted_cert -cert $ROOT_CERT_DIR/b64certificate.txt -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet add -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT -user_cert -cert $TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT/cert.txt -pwd welcome1 ./orapki wallet add -wallet $TNS_ADMIN_CLIENT -trusted_cert -cert $TNS_ADMIN_SERVER/cert.txt -pwd welcome1 -
Create/Modify wallet.ora files
cd jnetadmin_svim wallet.oracontent as below:
WALLET_LOCATION= (SOURCE= (METHOD=FILE) (METHOD_DATA= (DIRECTORY=/scratch/alice/work/db1427/jnetadmin_s/) ) ) -
Modify sqlnet.ora
SSL_VERSION=1.2 ssl_client_authentication=false ifile=/scratch/alice/work/db1427/jnetadmin_s/wallet.ora -
Modify listener.ora
LISTENER = (DESCRIPTION_LIST = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC1521)) (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = slc03rvu.us.oracle.com)(PORT = 1521)) (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcps)(HOST=slc03rvu.us.oracle.com)(PORT=5551)) ) ) ADR_BASE_LISTENER = /scratch/work ssl_client_authentication=false ifile=/scratch/alice/work/db1427/jnetadmin_s/wallet.ora SSL_VERSION=1.2 SID_LIST_listener=(SID_LIST= (SID_DESC=(SID_NAME=db1427)(ORACLE_HOME=/scratch/alice/work/db1427)) (SID_DESC=(SID_NAME=db1427)(GLOBAL_DBNAME=db1427.us.oracle.com)) ) -
Restart database and listener
restart DBlsnrctl stoplsnrctl start -
Use openssl to verify TLSv1.2
openssl s_client -showcerts -tls1_2 -connect slc03rvu.us.oracle.com:5551
Add WLS JDBC TLS Datasources:
-
Import DB server cert generated in step 3 to WLS Demo Trust.jks
keytool -importcert -trustcacerts -alias dbroot -keystore $MW_HOME/wlserver/server/lib/DemoTrust.jks -storepass DemoTrustKeyStorePassPhrase -file $ROOT_CERT_DIR/b64certificate.txt -
Navigate to wls console->Service->Data Sources, update below JDBC Data Source with TLS connection details.
-
Open each data source, click Connection Pool, update URL and Properties as below:
URL example:
jdbc:oracle:thin:/@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS_LIST=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCPS)(HOST=slc03sfc.us.oracle.com)(PORT=2484)))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=db4758..us.oracle.com))(SECURITY=(SSL_SERVER_CERT_DN="CN=slc03sfc.us.oracle.com")))Properties example:
javax.net.ssl.trustStoreType=JKS javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=DemoTrustKeyStorePassPhrase javax.net.ssl.trustStore=/net/slc03sfc/scratch/work/mw4838/wlserver_10.3/server/lib/DemoTrust.jks -
Restart the servers.
Enable TLS for OAP channel on WLS using multiple modes:
See, Configuring Oracle HTTP Server WebGate for Oracle Access Manager to configure 12c Cert and Simple Mode.
jdk.certpath.disabledAlgorithms option in java.security file and add the following property in $OHS_ORACLE_HOME/user_projects/domains/base_domain/config/fmwconfig/components/OHS/ohs1/ohs.plugins.nodemanager.properties file, environment.ORACLE_SSL_ALLOW_MD5_CERT_SIGNATURES=1Enable TLS1.2 Communication between OAM and the User Identity Store
Follow the below steps:
-
Login to OAM console.
-
Create a new OAM ID Store.
-
Update the Default store to the ID store you just created.
-
Update LDAP Authentication Module to the ID Store you just created.
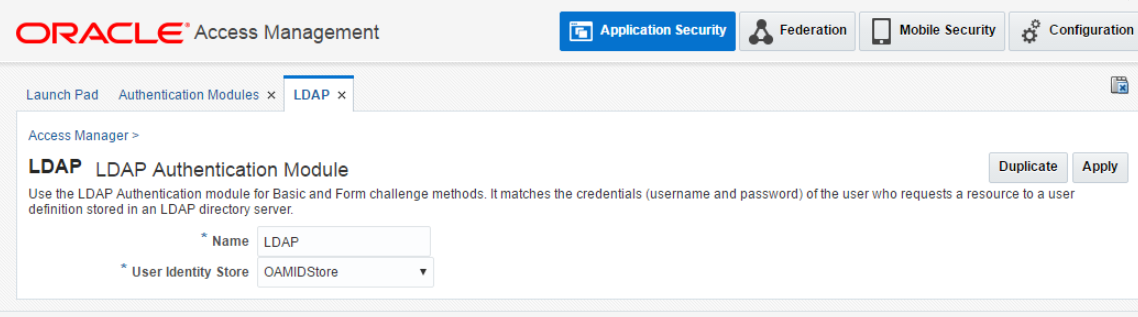
-
Shutdown all servers, and import OUD's certificate to JDK key store.
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect slc06bku.us.oracle.com:1636 </dev/null2>/dev/null|openssl x509 -outform PEM >cert.pem openssl x509 -outform der -in cert.pem -out cert.der keytool -importcert -alias oud -file cert.der -keystore cacerts -storepass changeit -
To support the TLSv1.2 connection to the LDAP server, add the
LDAP_SSL_PROTOCOLparameter with valueTLSv1.2after theLDAP_URLparameter in theoam-config.xmlfile.To set the parameters in theoam-config.xml:- Export the OAM configuration file to
/tmp/oam-config.xmlusing the export method. See Updating OAM Configuration for details. - Locate the IdentityStore section in the exported
/tmp/oam-config.xmlfile and search for the following line:<Setting Name="LDAP_URL" Type="xsd:string">ldaps://myldap.example.com:1636</Setting>Note:
If theLDAP_URLdoes not include theldapsprotocol and the LDAPS port of your Directory Services Identity Store, then update it to use LDAPS. For example, updateldap://myldap.example.com:1389toldaps://myldap.example.com:1636. - Add the
LDAP_SSL_PROTOCOLparameter after theLDAP_URLentry:<Setting Name="LDAP_SSL_PROTOCOL" Type="xsd:string">TLSv1.2</Setting>The entries in the
oam-config.xmlfile must look similar to the following example:<Setting Name="LDAP" Type="htf:map"> ... <Setting Name="LDAP_URL" Type="xsd:string">ldaps://myldap.example.com:1636</Setting> <Setting Name="LDAP_SSL_PROTOCOL" Type="xsd:string">TLSv1.2</Setting> - Import the updated configuration from
/tmp/oam-config.xmlusing the import method. See Updating OAM Configuration for details.
- Export the OAM configuration file to
-
Adding below lines to
config/fmwconfig/servers/oam_server1/logging.xmlandconfig/fmwconfig/servers/AdminServer/logging.xml<logger name='oracle.oam.user.identity.provider' level='TRACE:32'useParentHandlers='false'> <handler name='odl-handler'/> </logger> -
Start servers and access protected resources, you will see tls logs in oam_server1-diagnostic.log:
[2016-08-09T01:46:49.398-07:00] [oam_server1] [TRACE:32] [] [oracle.oam.user.identity.provider] [tid: [ACTIVE].ExecuteThread: '0' for queue: 'weblogic.kernel.Default (self-tuning)'] [userId: <anonymous>] [ecid: 036b5306-7533-4458-ad54-5f5be25adadf-00000106,0] [APP: oam_server] [partition-name: DOMAIN] [tenant-name: GLOBAL] [SRC_CLASS: oracle.security.am.engines.common.identity.provider.impl.ids.IDSLDAPConfigurator] [SRC_METHOD: getIDSInstance] Setting ssl protocol as TLSv1.2
Enable TLS for OAM using IDS Profile
Follow the below steps:
-
Log in to OAM console.
-
Create an IDS Profile.
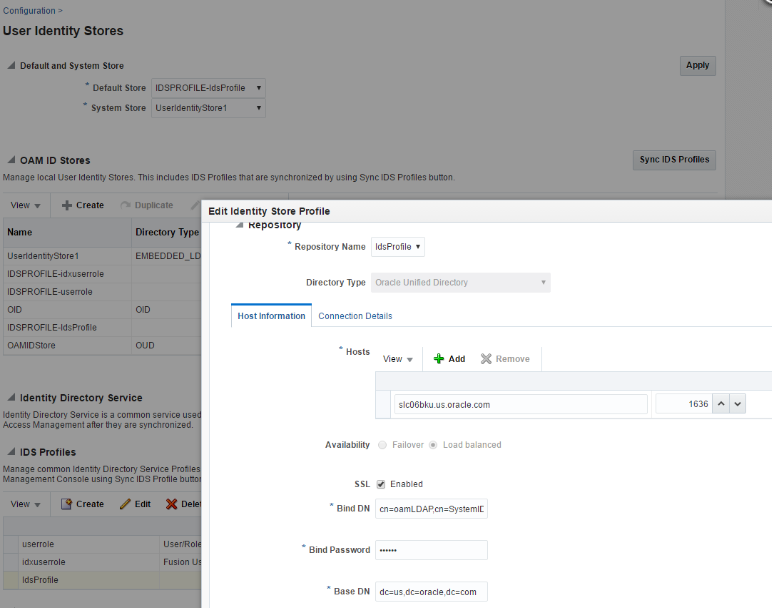
-
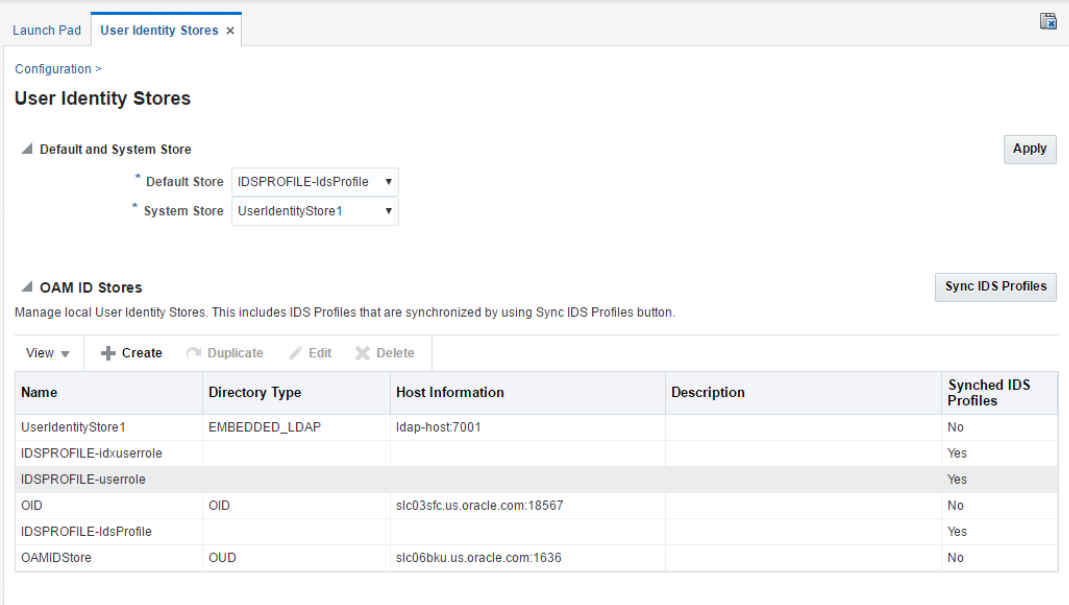
Click Sync IDS Profile and update Default store to the IDS profile you just created.
-
Update LDAP Authentication Module to the ID Store you just created.
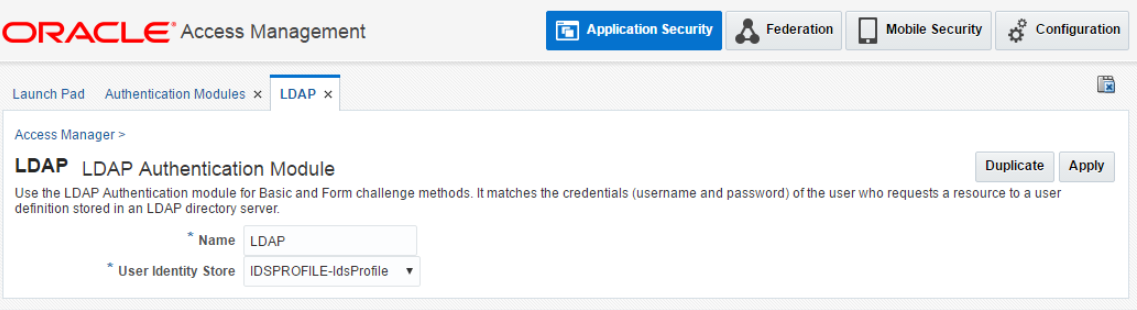
-
Add TLS parameter to ids libovd using wlst,
modifyLDAPAdapter(adapterName='IdsProfile', attribute='Protocols', value='TLSv1.2', contextName='ids') -
Create key store for ids libovd,
export ORACLE_HOME=/scratch/work/mw169export WL_HOME=/scratch/work/mw169/wlserverexport JAVA_HOME=/scratch/work/view/nowang_dte8461/bootstrap/java/1.8.0-51-16-150608.1.8.0.51.0016/jdk./libovdconfig.sh -host slc03sfc.us.oracle.com -port 22899 -userName weblogic -domainPath /scratch/work/mw169/user_projects/domains/WLS_IDM -createKeystore -contextName ids -
Add OUD certificate to libOVD key store,
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect slc06bku.us.oracle.com:1636 </dev/null 2>/dev/null|openssl x509 -outform PEM >cert.pemopenssl x509 -outform der -in cert.pem -out cert.derkeytool -import -keystore adapters.jks -storepass weblogic1 -alias oud -file cert.der -
Add
"-Dssl.debug=true -Dweblogic.StdoutDebugEnabled=true -Djavax.net.debug=all"tosetDomainEnv.shand check the logs to see the TLS connection messages from theoam_server1output console redirect file. -
Restart all servers, and access protected resources.
Generating Client Keystores for OAM Tester in Cert Mode
Generate JKS keystores to be used with OAM Tester that is in Cert mode only, else skip this topic.
This section describes how to use importcert commands to generate client keystores for OAM Tester in Cert mode to contain the imported trusted certificate chain.
See Also:
To generate client keystores for OAM Tester in Cert mode
Securing Communication between OAM Servers and WebGates using OAP over REST
OAP over REST uses HTTP(S) transport to ensure secure communication between OAM Servers and WebGates.
About OAP over REST Communication
OAP over REST enables the HTTP(S) transport mechanism between WebGate and OAM server. This transport mechanism reduces the operational cost for both cloud and hybrid deployments, where some components are on-premises and others are moved to cloud.
OAP provides an additional layer of security by encrypting, by default the messages sent to the server using RESTPayloadEncryption.
- REST endpoint as server filter deployed on managed server
/iam/access/binding/api/v10/oap. - Work Manager components. See Configuring Work Manager for OAP over REST
With this 12.2.1.4.0 release of Oracle Access Management, OAP over REST is the default way of communication. Whenever you create an SSO agent, the following additional parameters are set, by default.
OAMRestEndPointHostName=host1.com, OAMRestEndPointPort=443, and OAMServerCommunicationMode=HTTPS
Also see, Setting Up a Master and a Clone in Multi-Data Center
Configuring Load Balancer using Oracle mod_wl_proxy on OHS
Configure mod_wl_proxy plug-in as a load balancer between
WebGate and Managed Servers, to detect server loads and direct client requests
appropriately.
For information about the mod_wl_proxy plugin configuration, see
Configuring the WebLogic Proxy Plug-In.
Example
Consider a deployment where mod_wl_proxy is configured on OHS running on SSL port 443 and on host1.com, and two Managed server instances running on clst1.example.com:24100 & clst2.example.com:24100
The WebGate configuration looks like:
OAMRestEndPointHostName=host1.com
OAMRestEndPointPort=443
OAMServerCommunicationMode=HTTPSThe mod_wl_proxy configuration looks
like:
<IfModule weblogic_module>
WebLogicCluster clst1.example.com:24100,clst2.example.com::24100
DynamicServerList ON
MatchExpression /iam/access/binding/api/v10/oap
KeepAliveSecs 90
</IfModule>
mod_wl_proxy uses DyanamicServerList
property for load balancing, which detects the load dynamically and perfom addition
or removal of servers in clusters accordingly.
mod_wl_proxy
supports the following load balancing algorithms:
- Round-Robin - This is the default load balancing startegy that is used when no other algorithms is specified. The round-robin algorithm cycles through a list of server instances that host the clustered servlet in order.
- Weight-Based - This load balancing startegy determines carefully the relative weights to assign to each server instance.
- Random - Here requests are routed to servers at random, thre requests are evenly distributed across server instances in the cluster.
- Affinity Based - This algorithm is used in combination with one of the standard load balancing methods such as round-robin, weight-based, or, random.
Configuring Work Manager for OAP over REST
To support HTTP(S) operations, OAM server uses Work Manager wm/OAPOverRestWM specific for OAP over REST.
Configuring HTTP and HTTPS Communication between WebGate and Access Manager
This topic describes how to configure HTTP and HTTPS communication between WebGate and Access Manager.
Prerequisites:
Ensure you have performed the following steps:
- Configured SSL for the Proxy/Loadbalancer/WebLogic. For details, see Configuring SSL for the Web Tier.
- Created SSL Wallet and Enabled SSL for OHS. For details, see How to Enable SSL for Oracle HTTP Server by Using Fusion Middleware Control?
When the OAM server is installed and the WebGate is provisioned, by default, the parameters in the following table are configured and the values are automatically populated. The following mandatory configurations are set in the WebGate user defined parameters:
Table B-2 Mandatory Configurations in WegGate User Defined Parameters Field
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the communication mode that has to be set between the agent and the server. WebGate will communicate with OAM Managed server using the configured protocol (HTTP/HTTPS). Default value: Values Allowed: Ensure For HTTPS, there is a default trusted certificate file bundled in WebGate at
aaa_chain.pem is not configured then it
will default to cacert.pem.
You must copy the trusted certificate to
|
|
|
Specifies the host name of the server running the service or the Load Balancer URL pointing to the REST endpoint. Default value: Based on the value configured in Access Manager Settings for WebGate Traffic Load Balancer. |
|
|
Specifies the port of the server running the service. Default value: Based on the value configured in Access Manager Settings for WebGate Traffic Load Balancer. |
Note:
OAMServerCommunicationMode is set to HTTP or HTTPS:
- Security - The
Open,Simple, andCertmodes - Access Client Password
- Max Session Time
- Access Manager Primary and Secondary server list. The max and min connection pool size can be specified using the
MaxPoolSizeandMinPoolSizesettings. For details, see Connection Tuning for OAP over REST.
Following table provides the WebGate user defined configuration parameters specific to OAP over REST:
Table B-3 WebGate User Defined Configuration Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
OAMRestEndPointUrl |
Specifies the URL of the service. Default value: |
|
RESTPayloadEncryption |
Encrypts the OAP message using WebGate agent key. It is not used in OAP communication mode. Default value: True Allowed values: True/False |
|
IdleConnectionTimeout |
Idle time in seconds after which a connection is closed. Default value: 60 seconds |
|
MinPoolSize |
The minimum number of connections that will be kept open. Default value: 2 |
|
MaxPoolSize |
The maximum number of connections that WebGate can open. Default value: 100 |
|
SSLVerfifyHostname |
This option determines whether WebGate verifies that the server cert is for the server it is known as. Default value: True |
|
SSLVerifyPeerCert |
This option determines whether WebGate verifies the authenticity of the peer's certificate. Default value: True |
Enabling two-way SSL for OAP over REST
Perform the following steps to enable two-way SSL channel for OAP over REST between WebGates and the OAM Server
Note:
This feature is not supported for IHS WebGate on AIX platform.- Set the configurations as decribed in Configuring HTTP and HTTPS Communication between WebGate and Access Manager.
- Generate WebGate Certificate Signing Request (CSR) and get it signed by
Trusted CA or Root CA.
Note:
The generated certificate and private key must be in.pemformat.For example,- Generate private key either with passphrase or without passphrase:
- with
passphrase:
openssl genrsa -des3 -passout pass:1234 -out webgate_key.pem 2048 - without
passphrase:
openssl genrsa -out webgate_key.pem 2048
- with
passphrase:
- Generate CSR using the above private
key:
openssl req -out webgate.csr -new -nodes -key webgate_key.pem -sha256 - Send the CSR to trusted CA to get the signed certificate. The following
example shows signing CSR using self-signed CA
certificate:
openssl x509 -req -days 360 -in webgate.csr -CA ../ca.cert.pem -CAkey ../ca.key.pem -CAcreateserial -out webgate_cert.pem -sha256
- Generate private key either with passphrase or without passphrase:
- Place the generated
webgate_cert.pemandwebgate_key.pemfiles in the$WEBGATE_INSTANCE_DIR/webgate/config/directory. - If you have used passphrase to generate WebGate key then add the
passphrase to
$WEBGATE_INSTANCE_DIR/webgate/config/wallet/cwallet.ssowith map name asWG_Cert_PassPhrase, map key name asphrase_key, and key name asphrase.Set the WebGate Cert passphrase (if used to createwebgate_key.pem) in the wallet, using themkstoreutility.- Set
JAVA_HOME - Navigate to
<WebGate_Oracle_Home>/oracle_common/bin/mkstore - Run the following
mkstoreutility:./mkstore -wrl $WEBGATE_INSTANCE_DIR/config/wallet -createUserCredential <mapName> <mapkeyName> <name> <Passphrase>For example:./mkstore -wrl ./ -createUserCredential WG_Cert_PassPhrase phrase_key phrase 1234 - Verify if the map and key entry are stored in the
wallet:
./orapki wallet display -wallet wallet/This displays the secret store entry. For example,
WG_Cert_PassPhrase@#3#@phrase_keyNote:
If two way SSL is enabled, WebGate prints an INFO level log that shows"OAP over Rest (HTTPS): 2 way SSL config files are present in webgate instance directory"This log is printed only if both the
webgate_cert.pemandwebgate_key.pemfiles are added in the WebGate instance directory.
- Set
Connection Tuning for OAP over REST
WebGate uses a dynamic connection pool for connections between WebGate and the REST endpoint (for example, OAM Server). The number of connections opened by WebGate is not fixed and is controlled by the MinPoolSize and MaxPoolSize.
MinPoolSize. This is the minimum number of connections made by WebGate. WebGate always keeps the connections defined by MinPoolSize opened, irrespective of the load.
MaxPoolSize. This is the maximum number of connections that are opened in load scenarios. If the connections in excess of MinPoolSize are idle for the specified time duration defined by IdleConnectionTimeout, the WebGate closes the connections.
For example, WebGate checks after every 60 seconds if the connections that are in excess of the MinPoolSize have been idle for more than IdleConnectionTimeout defined seconds. If yes, it closes those connections.
The connections established by WebGate with OAM server or Load balancer is always persistent. But some servers or LoadBalancers do not allow connections to be persistent by default.
Therefore, you must change the settings for these Servers for the connection timeout to be greater than what is defined in WebGate IdleConnectionTimeout.
For example, for the mod_wl_proxy plugin running on OHS, add the following setting into the OHS httpd.conf file:
KeepAlive on
MaxKeepAliveRequests 0
KeepAliveTimeOut 90
And add KeepAliveSecs 90 settings into the mod_wl_proxy.conf file:
Assuming it is a two-node managed server cluster, the mod_wl_proxy file must look similar to the following sample:
<IfModule weblogic_module>
WebLogicCluster den01cbc.us.oracle.com:24100,den02kra.us.oracle.com:24100
WlSSLWallet /scratch/ranjakha/SSL_Certs
DynamicServerList ON
MatchExpression /oam
KeepAliveSecs 90
</IfModule>
Troubleshooting OAP over REST
This section provides troubleshooting steps for problems related to OAP over REST.
Error Performing Libcurl Operation
WebGate and OAM Server throws error after switching to a communication method other than the default, OAP over REST.
Problem
oracle.security.am.proxy.oam.requesthandler.ObMessageIntegrityFailException: Message Integrity Check FailedSolution 1
To solve the problem, perform the steps provided in either Solution 1 or Solution 2, as necessary.
- Validate access to
http(s)://<OAMHOST>:<OAMPort>/iam/access/binding/api/v10/oapthrough browser or the curl command.Note:
If a proxy is in front of OAM HTTP/HTTPS port, ensure the proxy setting includes mapping for/iam. - Update OAM Server setting to reference the REST endpoint:
- Login to the OAM console
- Click Configuration tab, and under Settings, select Access Manager.
- Update the following fields under WebGate Traffic Load Balancer, as necessary: OAM Server Host, OAM Server Port, and OAM Server Protocol.
- Click Apply.
- Update WebGate agent to reference the REST endpoint:
- In the OAM console, under the Application Security tab, click SSO Agents.
- In the Search SSO Agents window, search for the required 12c agent and click on the agent.
- In the User Defined Parameters, verify that the
following parameters reference the same data as specified under
WebGate Traffic Load
Balancer.
OAMRestEndPointHostName=<hostname> OAMRestEndPointPort=<port> OAMServerCommunicationMode=<HTTP/HTTPS> - Click Apply.
Solution 2
- Login to the OAM console
- In the OAM console, under the Application Security tab, click SSO Agents.
- In the Search SSO Agents window, search for the registered agent and click on the agent.
- From User Defined Parameters, remove the following
parameters:
OAMRestEndPointHostName OAMRestEndPointPort OAMServerCommunicationMode - Click Apply.
- Copy the newly created artifact files to the OHS/WebGate location.
- Delete the ObAccessClient.xml from the following cache
directory:
$DOMAIN_HOME/servers/<inst>/cache - Restart the OHS/WebGate server.
Enabling FIPS Mode on Oracle Access Management
Enabling FIPS Mode on OAM Server
To enable FIPS mode on OAM server:
Note:
-
As a prerequisite, OAM server must be installed and configured.
-
JDK used is Oracle JDK 1.8.0_271-b09.
-
See Enabling FIPS 140-2 Mode From Java Options in Administering Security for Oracle WebLogic Server for detailed steps.
Configuring SAML Federation for FIPS
- Enable FIPS on OAM Server. For det
- The signing key size must be 2048 bits or more. If not, generate keys with key
size 2048 by performing the following steps:
- Run the following
command:
<JAVA_HOME>/bin/keytool -genkeypair -alias samlsigning -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -sigalg sha256withrsa -dname cn="ACME SAML Signing" -validity 1000 -keystore $DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/.oamkeystore -storetype JCEKS - Run the following
command:
<JAVA_HOME>/bin/keytool -genkeypair -alias samlencryption -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -sigalg sha256withrsa -dname cn="ACME SAML Encryption" -validity 1000 -keystore $DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/.oamkeystore -storetype JCEKS - Login to the OAM Administration Console:
http(s)://<oam-admin-host>:<oam-admin-port>/oamconsole - Navigate to Configuration, Federation Settings
- In the Keystore section, create a new entry:
- In the Keystore section, click the + button
- Enter a KeyID for the new entry (for example,
saml-signing) - Select the alias for the new key entry from the drop-down, which
lists the key entries in the
.oamkeystore(for example,samlsigning) - Enter the password for the key entry that you set when creating that key.
- Repeat the process for other entries, if needed
- Click Apply
- In the General section,
- Select the Signing Key from the dropdown list of key entries
(these entries are defined in the Keystore section). For
example, select
saml-signing - Select the Encryption Key from the dropdown list of key entries
(these entries are defined in the Keystore section). For example
select
saml-encryption - Click Apply
- Select the Signing Key from the dropdown list of key entries
(these entries are defined in the Keystore section). For
example, select
- Redistribute certificates and/or SAML 2.0 metadata to partners
- Run the following
command:
- Download the metadata using the following URL:
http(s)://<oam-host>:<manage_server_port>/oamfed/idp/metadata?signid=saml_signing&encid=saml_encryption&sigalgm=SHA-256. Thesignidandencidvalue is as mentioned in the previous step. - Update the partners with new metadata.
- Connect to WLST and run the following
commands:
getStringProperty("/fedserverconfig/signaturedigestalgorithm")putStringProperty("/fedserverconfig/signaturedigestalgorithm", "SHA-256") - Restart servers and access the resource.
Enabling FIPS Mode on OAM Clients
WebGate
Note:
For WebGates, only OAP over TCP is FIPS compliant.ASDK Client
- Update security provider and Classpath settings. Add the following
security providers in the java security file:
<JAVA_HOME>/jre/lib/security/java.securityand modify the sequence of the existing providers accordinglysecurity.provider.1=com.rsa.jsafe.provider.JsafeJCE security.provider.2=com.rsa.jsse.JsseProvider - Invoke ASDK Client. Retrieve the
SimpleModeGlobalPassphraseusing WLST from your IDM Domain.<JAVA_HOME>/jre/bin/java -cp .:<ASDK_HOME>/lib/*:<MW_HOME>/oracle_common/modules/oracle.jps/jps-manifest.jar -Dopss.tenant.mode=JPS_API -Djava.util.logging.config.file= <ASDK_HOME>/log/log.properties -Djava.security.properties=<JAVA_HOME>/jre/lib/security/java.security -Dkeystore_passwd=<SimpleModeGlobalPassphrase> -Djava.security.debug=access TestASDK_OAM11g
Configuring ASDK clients in Simple and Cert Modes
For the ASDK clients to work in Simple and Cert mode, the password.xml file in
the ASDK configuration directory must include entries for both
passwd and keystore_passwd.
passwd value is created when the WebGate client is created in
Simple and Cert mode. For
example:<?xml version="1.0"?>
<ParamsCtlg xmlns="http://www.acme.com" CtlgName="password">
<ValNameList ListName="">
<NameValPair ParamName="passwd"
Value="9a5cec58ce96dadf07f68a3616a20a3ebfcff90e05e15db8d47f45f84a78f6cf775abf3
2c89beeb75ce3b3045a1e6fd0"/>
</ValNameList>
</ParamsCtlg>keystore_passwd value, perform the following:
- Navigate to
<OAM_DOMAIN_DIRECTORY>/output/webgate-ssl-SHA-256/and open the password.xml file. The following example shows a sample content of the file:<?xml version="1.0"?> <ParamsCtlg xmlns="http://www.acme.com" CtlgName="password"> <ValNameList ListName=""> <NameValPair ParamName="passwd" Value="02434507010457010c594505535b0d5f0e5b0d534b45025252500c0557"/> </ValNameList> </ParamsCtlg> - Copy the value from
passwdand add it under thekeystore_passwdentry of the password.xml in the ASDK configuration directory. For example,<?xml version="1.0"?> <ParamsCtlg xmlns="http://www.acme.com" CtlgName="password"> <ValNameList ListName=""> <NameValPair ParamName="passwd" Value="9a5cec58ce96dadf07f68a3616a20a3ebfcff90e05e15db8d47f45f84a78f6cf775abf3 2c89beeb75ce3b3045a1e6fd0"/> <NameValPair ParamName="keystore_passwd" Value="02434507010457010c594505535b0d5f0e5b0d534b45025252500c0557"/> </ValNameList> </ParamsCtlg> - Save the file.
Configuring Cert Mode Communication for Access Manager
Configure Cert mode communication for Access Manager with at least one OAM Server instance running in the same mode as the agent.
This topic describes how to configure Cert mode communication for Access Manager. The following tasks apply to Cert mode only.
Note:
In Simple mode, the bundled Access Manager-CA-signed certificates are used and most of the following tasks are not needed.
Prerequisites
During agent registration, at least one OAM Server instance must be running in the same mode as the agent. Otherwise, registration fails. After agent registration, however, you could change the communication mode of the OAM Server.
Task overview: Adding certificates for the OAM Server includes
About Cert Mode Encryption and Files
You must create a Cert request and send that to the CA. When the certificate is returned you must import it to the OAM Server (or copy it to the WebGate).
The certificate request for WebGate generates the request file aaa_req.pem, which you must send to a root CA that is trusted by the OAM Sever. The root CA returns the certificates, which must be copied to the Webgate instance area manually after OAM Webgate installation and configuration.
-
aaa_key.pem (reserved name for WebGate key file, which cannot be changed)
-
aaa_cert.pem (reserved name for WebGate certificate file, which cannot be changed)
-
aaa_chain.pem (reserved name for CA Cert for WebGate side)
During component installation in Cert mode, you are asked to present a certificate obtained from an external CA. If you do not yet have a certificate you can request one. Until you receive the certificate, you can configure the WebGate in Simple mode. However, you cannot complete OAM deployment until the certificates are issued and installed.
If you choose Cert mode when registering WebGate as an OAM Agent, a field appears where you can enter the Agent Key Password. When editing an OAM WebGate registration, password.xml is updated only when the mode is changed from Open to Cert or Simple to Cert. In cert mode, once generated, password.xml cannot be updated. Editing the agent Key Password does not result in creation of a new password.xml.
Generating a Certificate Request and Private Key for OAM Server
Retrieve the private key, certificate, and CA certificate for the OAM Server.
Note:
The certified tool is openSSL. Oracle recommends that you use openSSL rather than other tools to generate certificates and keys in PEM format.
To retrieve the private key and certificates for OAM Server
Retrieving the .OAMKeystore password stored in UDM
You can retrieve the keystore credential with Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control console.
Importing the Trusted, Signed Certificate Chain Into the Keystore
The Oracle-provided importcert tool is used to import existing private key, signed certificate (public key) files into the specified keystore format: JKS (client keystore format) or JCEKS (OAM Server keystore format; .oamkeystore for instance.).
The keystores associated with Access Manager accepts only PKCS8 DER format certificates:
-
If you have PEM format certificates signed by your certificate authority (CA), the following procedure describes how to convert and then import these using the
importcertshipped with Access Manager. -
If PEM format certificates are not available, create a certificate request and have it signed by your CA before beginning the following procedure.
Following are the steps for using the JDK version 8 keytool. If you have a different version of keytool, refer the documentation for your JDK version.
Note:
When you use the keytool utility, the default key pair generation algorithm is Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA). However, Oracle Access Management and WebLogic Server do not support DSA and you must specify another key pair generation and signature algorithm.
Prerequisites
To import the trusted certificate chain into the keystore:
-
For setting up OAM Server in CERT mode, before making any changes to .oamkeystore, download the artifacts using offline WLST command:
downloadAccessArtifacts(domainHome="/new/path/base_domain", propsFile="/path/dbschema.properties") ---- contents of dbschema.properties ---- oam.entityStore.schemaUser=MYPREFIX_OAM oam.entityStore.schemaPassword=Secret oam.entityStore.ConnectString=jdbc:oracle:thin:@dbhost.us.oracle.com:1521/servicename.us.oracle.comNote:
At every restart of Admin servers , changes are pulled in from DB . Hence we need to downloadAccessArtifacts and saveAccessArtifacts , to save the cert mode changes . -
Locate the keytool in the following path:
$MW_HOME/jdk8/bin/keytool -
Unzip importcert.zip and locate the Readme file in the following location:
$ORACLE_IDM_HOME/oam/server/tools/importcert/README
-
aaa_chain.pem: Using a text editor, modify the aaa_chain.pem file to remove all data except that which is contained within the CERTIFICATE blocks, then save the file.
----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... CERTIFICATE ... -----END CERTIFICATE----- -
Import the trusted certificate chain using the following command with details for your environment. For example:
keytool -importcert -file aaa_chain.pem -trustcacerts -storepass <password> -keystore $ORACLE_HOME\user_projects\domains\$DOMAIN\config\fmwconfig\ .oamkeystore -storetype JCEKS -
When prompted to trust this certificate, type
yes. -
aaa_cert.pem:
-
Edit aaa_certn.pem using TextPad to remove all data except that which is contained within the CERTIFICATE blocks, and save the file in a new location to retain the original. For example:
----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... CERTIFICATE ... -----END CERTIFICATE----- -
Enter the following command to convert the signed certificate (aaa_cert.pem) to DER format using openSSL or any other tool. For example:
openssl x509 -in aaa_cert.pem -inform PEM -out aaa_cert.der -outform DER
-
-
aaa_key.pem:
-
Edit aaa_key.pem to remove all data except that which is contained within the CERTIFICATE blocks, and save the file in a new location to retain the original. For example:
----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... CERTIFICATE ... -----END CERTIFICATE----- -
Enter the following command to convert the private key (aaa_key.pem) to DER format using openSSL or any other tool. For example:
openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -nocrypt -in aaa_key.pem -inform PEM -out aaa_key.der -outform DER
-
-
Import signed DER format certificates into the keystore. For example:
-
Import aaa_key.der using the following command line arguments and details for your environment. For example:
c:\Middleware\idm_home\oam\server\tools\importcert
- java -cp importcert.jar oracle.security.am.common.tools.importcerts.CertificateImport -keystore <> -privatekeyfile <path> -signedcertfile <path> -alias [ -storetype <> genkeystore <> -help]
Note:
Enter the key store password and alias password when prompted. On a Windows system, use a semicolon (;) instead of a colon (:) in the command line.
-
-
After making changes, please upload the changes to db using the following offline WLST command: saveAccessArtifacts(domainHome="/mwhome/user_projects/domains/base_domain", propsFile="/path/dbschema.properties").
- Proceed to Adding Certificate Details to Access Manager Settings.
Adding Certificate Details to Access Manager Settings
After importing the certificates into the keystore, add the alias and password that you specified earlier into Access Manager settings configuration in Oracle Access Management Console.
Note:
No explicit configuration is needed for Simple mode, which is provided out of the box.
See Also:
To add certificate details to Access Manager Settings
Generating a Private Key and Certificate Request for WebGates
Retrieve the private key, certificate, and CA certificate for the WebGate using openSSL.
To retrieve the private key and certificates for WebGates
Supporting Two-Way SSL for CERT Mode Communication
In two-way SSL support for CERT mode communication, the user certificate is shared with server while performing the SSL handshake. Therefore, the user certificate must be added to cwallet.sso.
You must manually add the user certificate to the cwallet.sso using the orapki utility. See, Keystore Management Tools in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware
DN of the user certificate before adding the user certificate to the wallet.
Updating WebGate to Use Certificates
For all communication modes (Open, Simple, or Cert), the Agent registration should be updated from the Oracle Access Management Console.
-
Registering an Agent: If you choose Cert mode when registering an OAM Agent, a field appears where you can enter the Agent Key Password.
-
Editing/Updating an Agent: When editing an OAM WebGate registration, password.xml is updated only when the mode is changed from Open to Cert or Simple to Cert.
Editing the agent Key Password does not result in creation of a new password.xml. In Cert mode, once generated, password.xml cannot be updated.
Prerequisites
Adding Certificate Details to Access Manager Settings
To update the communication mode in the WebGate Agent registration
About WebGate Usage of PFS and Approved Cipher Suites for OAP Simple/Cert Mode Communication
WebGate ensures that valid and approved cipher suites defined by the admin are used when the Simple/Cert mode OAP communication occurs.
Administrators use WebGate user-defined parameter TLSCipherSuite to define ciphers. The default cipher used for Simple/Cert mode OAP communication is PFS cipher suites. Following are the supported cipher suites in PFS cipher suites:
Table B-4 PFS Cipher Suites
| Cipher Name |
|---|
|
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
|
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
Following are the supported and approved cipher suites that administrators use for defining ciphers:
Table B-5 Supported Cipher Suites
| Cipher Name |
|---|
|
TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
|
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
|
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
|
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 |
|
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
|
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
|
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
|
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
|
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
|
TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
|
TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
|
TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
|
TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
|
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
|
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA |
|
TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
Configuring Simple Mode Communication with Access Manager
Note:
Communication between the agent and server works when the WebGate mode matches (or is higher) than the OAM Server mode.
When you register an OAM Agent or a new OAM Server, you can specify the Security mode. However, changing the global passphrase requires that you reconfigure all agents to use the mode and the new global passphrase.
Note:
During agent registration, at least one OAM Server instance must be running in the same mode as the agent. Otherwise, registration fails. After agent registration, however, you could change the communication mode of the OAM Server.
The highest level of security is Cert mode, the lowest is Open mode. The agent mode can be higher but not lower. For example, Open mode can be updated to SIMPLE or CERT.
This section provides the information you need to configure Simple mode communication.
Task overview: Configuring Simple mode communication includes
About Simple Mode, Encryption, and Keys
For Simple mode encryption, Access Manager includes a certificate authority with its own private key, which is installed across all WebGates and OAM Servers.
During installation, the OAM Server generates and saves the private-public keypair for the server. Similarly, for the OAM agent, an Oracle certificate authority is installed with the agent installation.
The installer generates a random global passphrase initially, which can be edited or viewed as needed. When an agent is registered in SIMPLE mode, the following client certificates are generated to be consumed by clients:
-
aaa_key.pem: Contains private key
-
aaa_cert.pem: Signed certificate
-
password.xml: Contains the random global passphrase in obfuscated format
Note:
Changing the global passphrase requires reconfiguring all agents that are already configured in Simple mode.
Retrieving the Global Passphrase for Simple Mode
Retrieve the random global passphrase generated by Access Manager for Simple mode communication during installation.
To retrieve the random global passphrase for Simple mode communication
Updating WebGate Registration for Simple Mode
Artifacts generated for Simple Security mode use the Global Pass phrase and any change must be propagated to WebGates.
To update an existing WebGate registration for Simple mode, you can delete the WebGate registration using the Oracle Access Management Console, then re-register it (specifying Simple mode and disabling the automatic generation of policies). Alternatively, you can edit the WebGate registration and then copy the artifacts as described here.
To update the WebGate registration for Simple mode