Create pipelines
Learn to create a data replication process using pipelines and recipes.
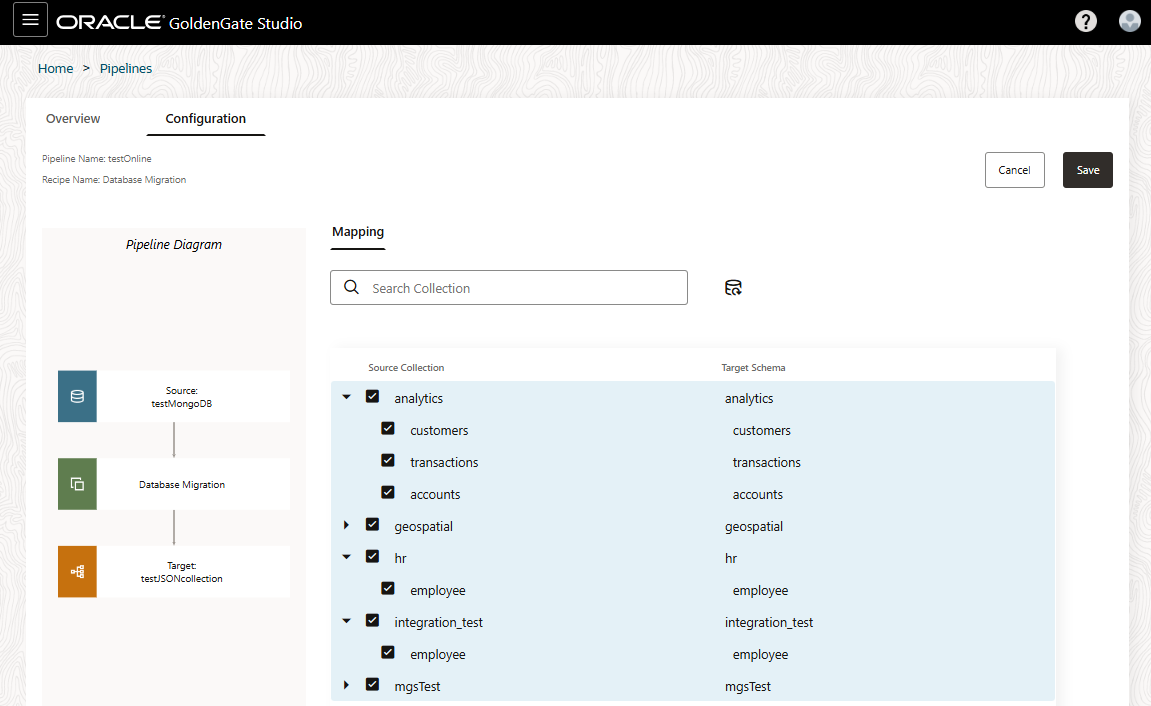
About pipelines
A pipeline is an instance of a recipe. It enables you to select your source connection, the type of replication action(s) to apply, and the target connection. After a pipeline starts, you can observe the replication process in real time.
- Check source and target database
- Extract Source Database
- Load Target Database
- Create GoldenGate credentials (Online migration only)
- Create and run Extract (Capture) (Online migration only)
- Create and run Replicat (Apply) (Online migration only)
These steps can be observed during the pipeline's Initialization phase on the Pipeline Details page.
You can view pipelines on the Home page, as well as the Pipelines page. Before you create a pipeline, ensure that you have source and target connections created, and existing target databases/schemas are ORDS and REST API enabled.
Create a pipeline
Learn to create a pipeline by following a recipe.
Watch this short video to learn how to create a pipeline.
Tip:
Ensure that you have a source and target connection before creating a pipeline.Configure a pipeline
After you create a pipeline, you're brought to its Configuration screen. If you're revisiting a pipeline after you created it, you can select the pipeline from the Pipelines page to view its details, and then click Configuration to return to the Configuration screen.