Components of Oracle GoldenGate Microservices Architecture
Directories and Variables in Microservices Architecture
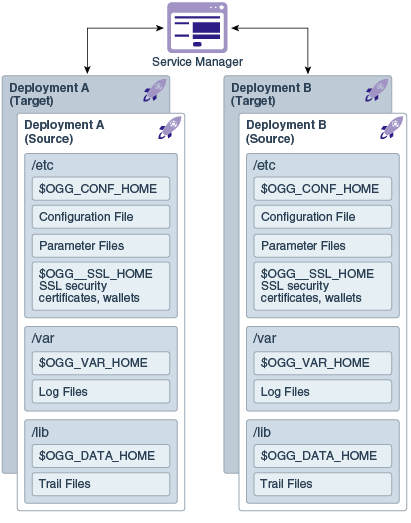
The Microservices Architecture is designed with a simplified installation and deployment directory structure.
This directory structure is based on the Linux Foundation Filesystem Hierarchy Standard. Additional flexibility has been added to allow parts of the deployment subdirectories to be placed at other locations in the file system or on other devices, including shared network devices. The design comprises a read-only Oracle GoldenGate home directory where Oracle GoldenGate Microservices Architecture is installed and custom deployment specific directories are created as follows:
bincfgtoollogsdeinstalldiagnosticsincludeinstallinventoryjdkjliblibinstantclientsqlutl
OPatchoraInst.locouisrvm
The following figure shows the files and directories under the Services Manager (srvm) directory:
The following table describes the key MA directories and the variables that are used when referring to those directories during an Oracle GoldenGate installation. When you see these variables in an example or procedure, replace the variable with the full path to the corresponding directory path in your enterprise topology.
| Directory Name | Variable | Description | Default Directory Path |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Oracle GoldenGate home |
|
The Oracle GoldenGate home that is created on a host computer is the directory that you choose to install the product. This read-only directory contains binary, executable, and library files for the product. |
|
|
Deployment |
|
The location where your deployment configuration files are stored including parameter files. |
|
|
Deployment configuration home |
|
The location where each deployment information and configuration artifacts are stored. |
|
|
Deployment security home |
|
The location where each deployment security artifacts (certificates, wallets) are stored. |
|
|
Deployment variable home |
|
The location where each deployment logging and reporting processing artifacts are stored. |
|
|
Deployment data home |
|
The location where each deployment data artifacts (trail files) are stored. |
|
You can change the default location of all of these to customize where you want to store these files.
In a configuration where the OGG_VAR_HOME is a local directory and the OGG_HOME is a shared read-only remote directory, many deployments with local OGG_VAR_HOME can share one read-only shared OGG_HOME.
This directory design facilitates a simple manual upgrade. To upgrade, you stop the services and then set the OGG_HOME in the web interface (or via a REST command) and then restart the processes. On restart, Oracle GoldenGate picks up the updated environment variables. You simply switch a deployment to use a new Oracle GoldenGate release by changing the Oracle GoldenGate home directory path in the Service Manager to a new Oracle GoldenGate home directory, which completes the upgrade. Restart the microservices, Extract and Replicat processes.
About Service Manager
A Service Manager acts as a watchdog for other services available with Microservices Architecture.
A Service Manager allows you to manage one or multiple Oracle GoldenGate deployments on a local host. A Service Manager has a one to many relationship with the Administration Service. Each Oracle GoldenGate installation has a single Service Manager that is responsible for multiple deployments.
Optionally, Service Manager may run as a system service and maintains inventory and configuration information about your deployments and allows you to maintain multiple local deployments. Using Service Manager, you can start and stop instances, and query deployments and the other services.
About Administration Server
The Administration Server supervises, administers, manages, and monitors processes within an Oracle GoldenGate deployment.
The Administration Server operates as the central control entity for managing the replication components in your Oracle GoldenGate deployments. You use it to create and manage your local Extract and Replicat processes without the need to access the server where Oracle GoldenGate is installed. The key feature of the Administration Server is the REST API service Interface that can be accessed from any HTTP or HTTPS client, such as the Microservices Architecture service interfaces or other clients like Perl and Python.
In addition, the Admin Client can be used to make REST API calls to communicate directly with the Administration Server. See Admin Client for details.
The Administration Server is responsible for coordinating and orchestrating Extracts, Replicats, and paths to support greater automation and operational managements. Its operation and behavior is controlled through published query and service interfaces. These interfaces allow clients to issue commands and control instructions to the Administration Server using REST JSON-RPC invocations that support REST API interfaces.
The Administration Server includes an embedded web application that you can use directly with any web browser and does not require any client software installation.
Use the Administration Server to create and manage:
- Extract and Replicat processes
- Add, alter, and delete
- Register and unregister
- Start and stop
- Review process information, statistics, reports, and status including LAG and checkpoints
- Retrieve the report and discard files
- Configuration (parameter) files
- Checkpoint, trace, and heartbeat tables
- Supplemental logging for procedural replication, schema, and tables
- Tasks both custom and standard, such as auto-restart and purge trails
- Credential stores
- Encryption keys (
MASTERKEY) - Add users and assign their roles
About Distribution Server
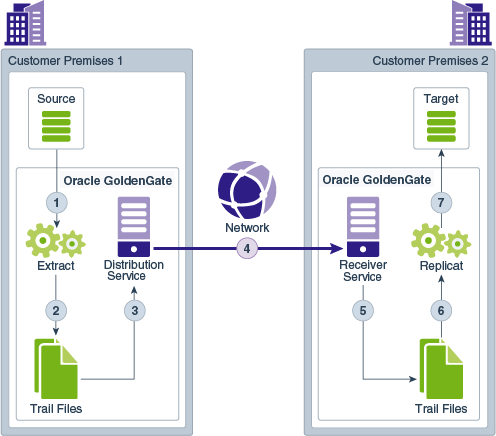
Distribution Server functions as a networked data distribution agent in support of conveying and processing data and commands in a distributed deployment. It is a high performance application that is able to handle multiple commands and data streams from multiple source trail files, concurrently.
Distribution Server replaces the classic multiple source-side data pumps with a single instance service. This service distributes one or more trails to one or more destinations and provides lightweight filtering only (no transformations).
Multiple communication protocols can be used, which provide you the ability to tune network parameters on a per path basis. These protocols include:
-
Oracle GoldenGate protocol for communication between the Distribution Server and the Collector in a non services-based (classic) target. It is used for inter-operability.
Note:
TCP encryption does not work in a mixed environment of Classic and Microservices architecture. The Distribution Server in Microservices Architecture cannot be configured to use the TCP encryption to communicate with the Server Collector in Classic Architecture running in a deployment. Also, the Receiver Service in Microservices Architecture cannot accept a connection request from a data pump in Classic Architecture configured with
RMTHOST ... ENCRYPTparameter running in a deployment. -
WebSockets for HTTPS-based streaming, which relies on SSL security.
-
UDP protocols.
-
Proxy support for cloud environments:
-
SOCKS5 for any network protocol.
-
HTTP for HTTP-type protocols only, including WebSocket.
-
-
Passive Distribution Server to initiate path creation from a remote site. Paths are source-to-destination replication configurations though are not included in this release.
Note:
Distribution Server cannot filter data in the trail. A distribution path will send all trail data from source to target based on the specified target authentication protocol.
About Receiver Server
A Receiver Server is the central control service that handles all incoming trail files. It interoperates with the Distribution Service and it replaces multiple discrete target-side Collectors with a single instance service.
Use Receiver Server to:
- Monitor path events
- Add target-initiated paths
- Query the status of incoming paths
- View the statistics of incoming paths
- Diagnose path issues
WebSockets (ws) is the default HTTPS initiated full-duplex streaming protocol used by the Receiver Server. It enables you to fully secure your data using SSL security. The Receiver Server seamlessly traverses through HTTP forward and reverse proxy servers.
Additionally, the Receiver Server supports the following protocols:
-
UDP-based protocol for wide area networks: For more information, see http://udt.sourceforge.net/.
-
Classic Oracle GoldenGate protocol for classic deployments so that the Distribution Service communicates with the Collector and the Data Pump communicates with the Receiver Server.
Note:
TCP encryption does not work in a mixed environment of Classic and Microservices
architecture. The Distribution Service in Microservices Architecture
cannot be configured to use the TCP encryption to communicate with
the Server Collector in Classic Architecture running in a
deployment. Also, the Receiver Server in Microservices Architecture
cannot accept a connection request from a data pump in Classic
Architecture configured with RMTHOST ... ENCRYPT
parameter running in a deployment.
:
About Target-Initiated Distribution Path
Target-initiated paths for microservices enable the Receiver Service to initiate a path to the Distribution Service on the target deployment and pull trail files. This feature allows the Receiver Service to create a target initiated path for environments such as Demilitarized Zone Paths (DMZ) or Cloud to on-premise, where the Distribution Service in the source Oracle GoldenGate deployment cannot open network connections in the target environment to the Receiver Service due to network security policies.
If the Distribution Service cannot initiate connections to the Receiver Service, but Receiver Service can initiate a connection to the machine running the Distribution Service, then the Receiver Service establishes a secure or non-secure target initiated path to the Distribution Service through a firewall or Demilitarized (DMZ) zone using Oracle GoldenGate and pull the requested trail files.
The Receiver Service endpoints display that the retrieval of the trail files was initiated by the Receiver Service.
About Performance Metrics Server
All Oracle GoldenGate processes send metrics to the Performance Metrics Server, which enables you to monitor the performance of all processes from a single interface.
The Performance Metrics Server uses metrics to collect and store instance deployment performance results. This metrics collection and repository is separate from the administration layer information collection. You can monitor performance metrics using other embedded web applications and use the data to tune your deployments for maximum performance.
Use the Performance Metrics Server to:
- Query for various metrics and receive responses in the services JSON format or the classic XML format
- Integrate third party metrics tools
- View error logs
- View active process status
- Monitor system resource utilization