Add a Deployment
Follow the instructions on this page to add a deployment using the OGGCA wizard.
Using OGGCA Wizard for Deployment
This section discusses using the OGGCA wizard for deployment.
Start the OGGCA Wizard
Adding deployments is the first task in the process of setting up a data replication platform. Deployments are managed from the Service Manager. After completing the Oracle GoldenGate MA installation, you can add initial and subsequent deployments using the Oracle GoldenGate Configuration Assistant (OGGCA) wizard.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you maintain a single Service Manager per host, to avoid redundant upgrade and maintenance tasks with Oracle GoldenGate releases.
To start the OGGCA wizard:
-
Navigate to the $OGG_HOME/bin directory to access the Oracle GoldenGate Configuration Assistant (oggca) utility.
-
Run the
oggca.shprogram on UNIX oroggca.baton Windows.
The Oracle GoldenGate Configuration Assistant (oggca) wizard is displayed.
The following topics provide details on the configuration that you can set on each of the OGGCA screens.
Select Service Manager Options
-
Select the Create a New Service Manager option if you are running OGGCA for the first time. When you run OGGCA for the first time, the Existing Service Manager option is disabled. If it's not the first time, then you can choose the Existing Service Manager option, which would load the Service Manager port and other settings as configured for the existing Service Manager. The deployment would be added to this Service Manager. In most configurations, there is only one Service Manager to manage multiple deployments.
-
For a new Service Manager, browse and enter the directory that you want to use for your deployment in the Service Manager Deployment Home text box. Oracle recommends that you create a
ServiceManagerdirectory within the deployment sub-directory structure to store the Service Manager files. -
Enter the connection details for the Service Manager:
-
Listening hostname/address: Enter a hostname such as localhost or the IP address of the server where Service Manager will run.
- Listening Port: Enter a unique port number that the Service Manager will listen on, or choose the port already in use if selecting an existing Service Manager.
-
-
(Optional) Select the option Register the Service Manager as a system service (daemon) to avoid manually starting and stopping it if the machine is rebooted. If there is an existing Service Manager registered as a service and you select a new Service Manager to register as a service, an alert is displayed indicating that you cannot register the new one as a system service. All other Service Managers are started and stopped using scripts installed in the
bindirectory of the deployment.You cannot register an existing Service Manager as a system service. Enter a unique port number that the Service Manager will listen on, or choose the port already in use, if selecting an existing Service Manager.
-
(Optional) Select the Integrate with XAG option to integrate your deployment with an Oracle Grid Infrastructure for Oracle Database. This is only available for Oracle database in a cluster environment. This option cannot be used when running your Service Manager as a system service.
-
Click Next.
Configuration Options
In the Configuration Options step, you can add or remove deployments.
You can only add or remove one deployment for one Service Manager at a time.
Note:
Ensure that your Service Manager is up and running prior to launching OGGCA.Deployment Details
Deployment Details
-
Enter the deployment name using these conventions:
-
Must begin with a letter.
-
Can be a standard ASCII alphanumeric string not exceeding 32 characters.
-
Cannot include extended ASCII characters.
-
Special characters that are allowed include underscore (‘_’), forward slash (‘/’), dash (‘-’), period (‘.’).
-
Cannot be “ServiceManager”.
-
-
Select the Enable FIPS check box to enable Oracle GoldenGate services to use FIPS-compliant libraries.
-
(Oracle Database only) Select Enable Sharding to use the database sharding feature in your deployment. The schema must be
ggadmin. -
Enter or select the Oracle GoldenGate installation directory. If you have set the
$OGG_HOMEenvironment variable, the directory is automatically populated. Otherwise, the parent directory of theoggca.sh(Linux) oroggca.bat(Windows) script is used. -
Click Next.
Select Deployment Directories
Select Deployment Directories
-
Enter or select a deployment directory where you want to store the deployment registry and configuration files. When you enter the deployment directory name, it is created if it doesn’t exist. Oracle recommends that you do not locate your deployment directory inside your
$OGG_HOMEand that you create a separate directory for easier upgrades. The additional fields are automatically populated based on the specified deployment directory.Note:
The deployment directory name (user deployment directory) needs to be different than the directory name chosen in the first screen (Service Manager deployment directory). -
You can customize the deployment directories so that they are named and located differently from the default.
-
Enter or select different directories for the various deployment elements.
-
Click Next.
Specify Environment Variables
Environment Variables
Enter the requested values for the environment variables. Double-click in the field to edit it. You can copy and paste values in the environment variable fields. Make sure that you tab or click outside of the field after entering each value, otherwise it’s not saved. If you have set any of these environment variables, the directory is automatically populated.
- OGG_HOME
-
The directory where you installed Oracle GoldenGate. This variable is fixed and cannot be changed.
Note:
On a Windows platform, ensure that there's no space in theOGG_HOMEdirectory path otherwise OGGCA will not run.
- LD_LIBRARY_PATH
-
This variable is used to specify the path to search for libraries on UNIX and Linux. It may have a different name on some operating systems, such as
LIBPATHon IBM AIX on POWER Systems (64-Bit), andSHLIB_PATHon HP-UX. This path points to the Oracle GoldenGate installation directory and the underlying instant client directory by default.If you are using User Exits, then append the
LD_LIBRARY_PATHvariable with the path to the additional shared libraries of the User Exit. - TNS_ADMIN
-
Valid for Oracle database.
This variable is recommended and points to the directory location containingtnsnames.ora, which has the database connection details. If this variable is not set, Oracle GoldenGate looks for$HOME/.tnsnames.oraor/etc/tnsnames.oraYou need to create thetnsnames.orafile with the connection data and place it in the$OGG_HOME/etc. Here's a sample structure of the file:# tnsnames.ora Network Configuration File: # Generated by Oracle configuration tools. LISTENER_ORCL19 = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = eastdb.us.oracle.com)(PORT = 1521)) ORCL = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = eastdb.oracle.com)(PORT = 1521)) ) (CONNECT_DATA = (SERVER = DEDICATED) (SERVICE_NAME = orcl.us.oracle.com) ) )For example:
TNS_ADMIN=/u01/app/oracle/network/admin - STREAMS_POOL_SIZE
-
For Oracle Database Sharding only. This variable is mandatory for sharded databases. Use the default or set your pool size value that is at least 1200MB.
- TZ
-
Valid for MySQL.
Use the following query to determine the timezeone of the MySQL database:
SELECT @@global.time_zone;mysql> select @@global.time_zone;+--------------------+| @@global.time_zone |+--------------------+| SYSTEM |+--------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)2If it returns the timezone as
SYSTEM, then it indicates that the database timezone is the same as the system timezone.To know the system timezone, you can run the following query on your MySQL database:
mysql> select @@system_time_zone;+--------------------+| @@system_time_zone |+--------------------+| UTC |+--------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)3Make sure that the database timezone and the timezone of the system where the Oracle GoldenGate instance is running are the same.
Alternatively, you can set the
TZvariable for the deployment to the same value as the database timezeone. Use the following command to check theTZvariable on the shell where you are going to invokeTZ:linux# echo $TZaUse the following command to set
TZon the shell where you start your Oracle GoldenGate command line (Admin Client) from:linux# export TZ UTC - ODBCINI
-
Valid for Oracle GoldenGate installed on Linux for PostgreSQL databases.
Specifies the full path of the ODBC file used to store Data Source Names (DSN) for connectivity to a PostgreSQL database. For example,
ODBCINI=/etc/odbc.ini - JAVA_HOME
-
If this variable is present during deployment creation, it will automatically be populated, otherwise you can set it to be:
export JAVA_HOME=$OGG_HOME/jdk
You can add additional environment variables to customize your deployment or remove variables.
Click Next.
Service Manager Administrator Account
Administrator Account
To choose between Identity Cloud Service (IDCS) or local credential setup, define your Service Manager administrator user.
Note:
The option to set up IDCS-enabled administrator account is not applicable when you run OGGCA for the first time. Only after creating and enabling the Authorization Profile, you can set up the Administrator Account for accessing IDCS.-
Enter a user name and password that you want to use to sign in to the Oracle GoldenGate MA Service Manager and the other services. This user is the security user for this deployment.
If you are adding a deployment to an exisiting Service Manager and intend to use IDCS (as your external Identity Provider) for user authentication, then specify the user credentials for the IDCS server. As a prerequisite to providing the credentials for accessing the IDCS server, you need to enable the Authorization Profile from the Service Manager deployment.Note:
For Administrator Account, you must enter a user and password for a provisioned external IDP identity that is mapped to the SECURITY group previously configured for the Service Manager deployment.Select the Enable strong password policy in the new deployment checkbox to ensure setting a highly secure password for your user account. This password policy applies for your localCredentialStore only but not for IDCS default settings.
The strong password policy for localCredentialStore has the following requirements:
-
At least one lowercase character [a...z]
-
At least one upposercase character [A...Z]
-
At least one digit [0...9]
-
At least one special character [- ! @ % & * . #]
-
The length should be between 8 and 30 characters.
For details on the different types of users, see How to Add Users. If you are using an existing Service Manager, you must enter the same log in credentials that were used when adding the first deployment.
-
-
Select the check box that allows you to enable a strong password policy for your new deployment. If you select this option, then the password must adhere to restrictions, otherwise an error occurs, which requires you to specify a stronger password.
-
Click Next.
Local Administrator Account Credentials
Note:
If Service Manager is enabled for IDCS, it can continue to manage the new deployment, which uses local administrator credentials, even if the new deployment is not enabled for IDCS.Specify Security Options
Security Options
-
You can choose whether or not you want to secure your deployment. Oracle recommends that you enable SSL/TLS security.
If you do not want to use security option on the source endpoint, deselect the check box.
-
When you deselect the SSL/TLS check box, the option This non-secure deployment will be used to send trail data to a secure deployment stays enabled. Select this check box to set up a secure target deployment to communicate with a non-secure source deployment. In this case, certificates are required for the client only.
However, you must enable security if configuring for Oracle GoldenGate sharding support for Oracle Database.
-
For the Server (wallet or certificate), select the option to use a Wallet or Certificate. Provide the location of the wallet directory and if you are using an existing wallet, it must have the appropriate certificates already imported into it. If you choose to use a certificate, enter the corresponding pass phrase.
When using a self-signed certificate, a new Oracle Wallet is created in the new deployment and these certificates are imported into it. For certificates, enter the location of the private key file and the pass phrase. The private key files must be in the
PKCS#8format. -
For the Client side, select either the wallet directory or certificate. Provide the wallet directory on the client side or the certificate details for the client. If you select the This non-secure deployment will be used to send trail data to a secure deployment, then you only need to specify the client side details (wallet or certificate of the target deployment). This option is useful when the Distribution Service from the source deployment is unsecured whereas the Receiver Service on the target deployment is secured. So, the sender may be configured for public access while the Receiver Service requires authentication and authorization, which is established using PKI before the incoming data is applied.
For more information, see Creating a Self-Signed Root Certificate .
Also see: Add a Target-Initiated Distribution Path.
-
Click Next.
Advanced Security Settings
If security is enabled, then this screen is displayed with the encryption options TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2. TLS 1.2 is selected by default. When you open the Advanced Security Settings for the first time with TLS 1.2, the available cipher suites are listed.
- Use the arrows to add or remove cipher suites.
- Use Up and Down to reorder how the cipher suites are applied and click Next.
Advanced Security Settings
(If Security is enabled) On the page, the encryption options TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2 are available. TLS 1.2 is selected by default.
When you open the Advanced Security Settings for the first time with TLS 1.2, the following cipher suites are listed:
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384-
Use the arrows to add or remove cipher suites or the Up and Down to reorder how the cipher suites will be applied.
-
Click Next.
Sharding Options
Sharding Options
If Sharding was enabled in the previous step, then you can configure the sharding options on this screen.
-
Locate and import your Oracle GoldenGate Sharding Certificate. Enter the distinguished name from the certificate that will be used by the database sharding code to identify itself when making REST API calls to the Oracle GoldenGate MA services.
-
Enter a unique name for the certificate.
-
Click Next.
Port Settings
Port Settings
-
Enter the Administration Server port number, and then when you leave the field the other port numbers are populated in ascending numbers. Optionally, you can enter unique ports for each of the services.
-
Select Enable Monitoring to use the Performance Metrics Server.
-
Click inside the Performance Metrics Server port fields to populate or enter the ports you want to use. Ensure that you choose available ports for TCP. See Protocols for Performance Monitoring on Different Operating Systems.
You can change the TCP port from the Service Manager console after the deployment is done. For more information on
PMSRVR, seeENABLEMONITORING. -
Select the type of datastore that you want the Performance Metrics Server to use, the default Berkeley Database (BDB) data store or Open LDAP Lightning Memory-Mapped Database (LMDB). You can also designate the Performance Monitor as a Critical Service if integrating the Service Manager with XAG.
For LMDB information, see http://www.lmdb.tech/doc/.
-
Select the location of your datastore. BDB and LMDB are in-memory and disk-resident databases. The Performance Metrics Server uses the datastore to store all performance metrics information.
-
Click Next.
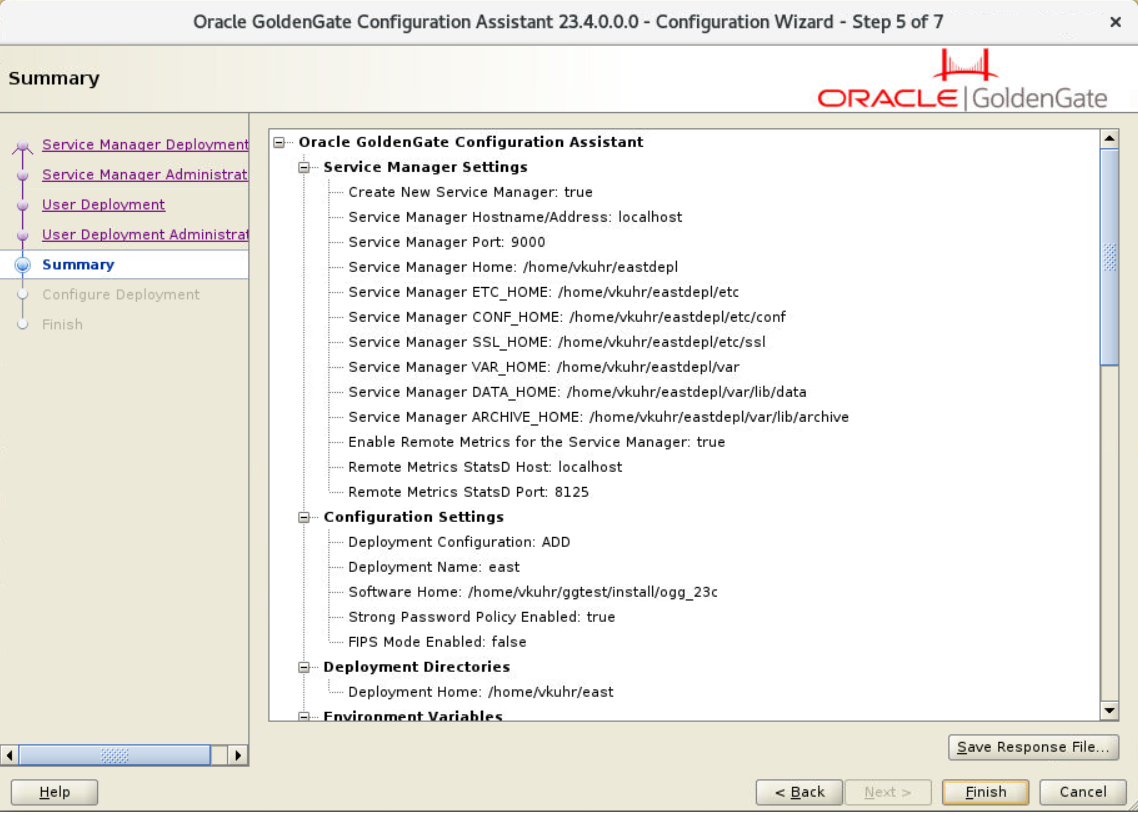
Summary
-
Review the detailed configuration settings of the deployment before you continue, as shown in the following image.
-
(Optional) You can save the configuration information to a response file. Oracle recommends that you save the response file. You can run the installer from the command line using this file as an input to duplicate the results of a successful configuration on other systems. You can edit this file or a new one from the provided template.
Note:
When saving to a response file, the administrator password is not saved for security reasons. You must edit the response file and enter the password if you want to reuse the response file for use on other systems.
-
Click Finish and then click Next.
Configure Deployment
This screen displays the progress of the deployment creation and configuration. There could be some notifications during the progress if the Service Manager is registered as a service.
A pop-up appears that directs you how to run the script to register the service. The Configuration Assistant verifies that these scripts have been run. If you did not run them, you are queried if you want to continue. When you click Yes, the configuration completes successfully. When you click No, a temporary failed status is set and you click Retry to run the scripts.
Click Ok after you run the script to continue.
After the creation and configuration process completes, you'll see a message that the deployment is added successfully. Click Next.