8.5 Realtime Parquet Ingestion into AWS S3 Buckets with Oracle GoldenGate for Distributed Applications and Analytics 23.8 and later
This Quickstart covers a step-by-step process showing how to ingest parquet files into AWS S3 buckets in real-time with Oracle GoldenGate for Distributed Applications and Analytics (GG for DAA).
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service provided by Amazon Web Services.
GG for DAA S3 handler works in conjunction with File Writer Handler and Parquet Handler (if parquet is required). File Writer Handler produces files locally, optionally Parquet Handler converts to parquet format and S3 Handler loads into S3 buckets.
- Prerequisites
- Install Required Dependency Files
- Create a Replicat in Oracle GoldenGate for Distributed Applications and Analytics
Parent topic: Quickstarts
8.5.1 Prerequisites
To successfully complete this Quicktart, you must have the following:
- Amazon S3 Bucket
- Amazon S3 Access Key & Secret
In this Quickstart, a sample trail file (named tr) which is shipped with
GG for DAA is used. If you want to continue with sample trail file, then it is located
at GG_HOME/opt/AdapterExamples/trail/ in your GG for DAA
instance.
8.5.2 Install Required Dependency Files
GG for DAA uses client libraries in the replication process and these libraries need to be downloaded before setting up the replication process. You can use dependency downloader to download the client libraries. Dependency downloader is a set of shell scripts that downloads dependency jar files from Maven and other repositories.
GG for DAA uses a 3-step process to ingest parquet into s3 buckets:
- Generating local files from trail files
- Converting local files to Parquet format
- Loading files into AWS S3 buckets
For generating local parquet files with GG for DAA, replicat uses File Writer Handler and Parquet Handler. To load the parquet files into AWS S3, GG for DAA uses S3 Event Handler in conjunction with File Writer and Parquet Event Handler.
GG for DAA uses 3 different set of client libraries to create parquet files and loading into AWS S3.
- In your GG for DAA VM, go to dependency downloader utility. It is
located at
GG_HOME/opt/DependencyDownloader/ - Run
parquet.sh,hadoop.sh, ands3.shwith the required versions.Note:
Runnings3.shdownloads every dependency needed for AWS sdk version 2.x, if it is required to download the dependencies for version 1.x, use theaws.shinstead.Figure 8-27 Install Required Dependency Files
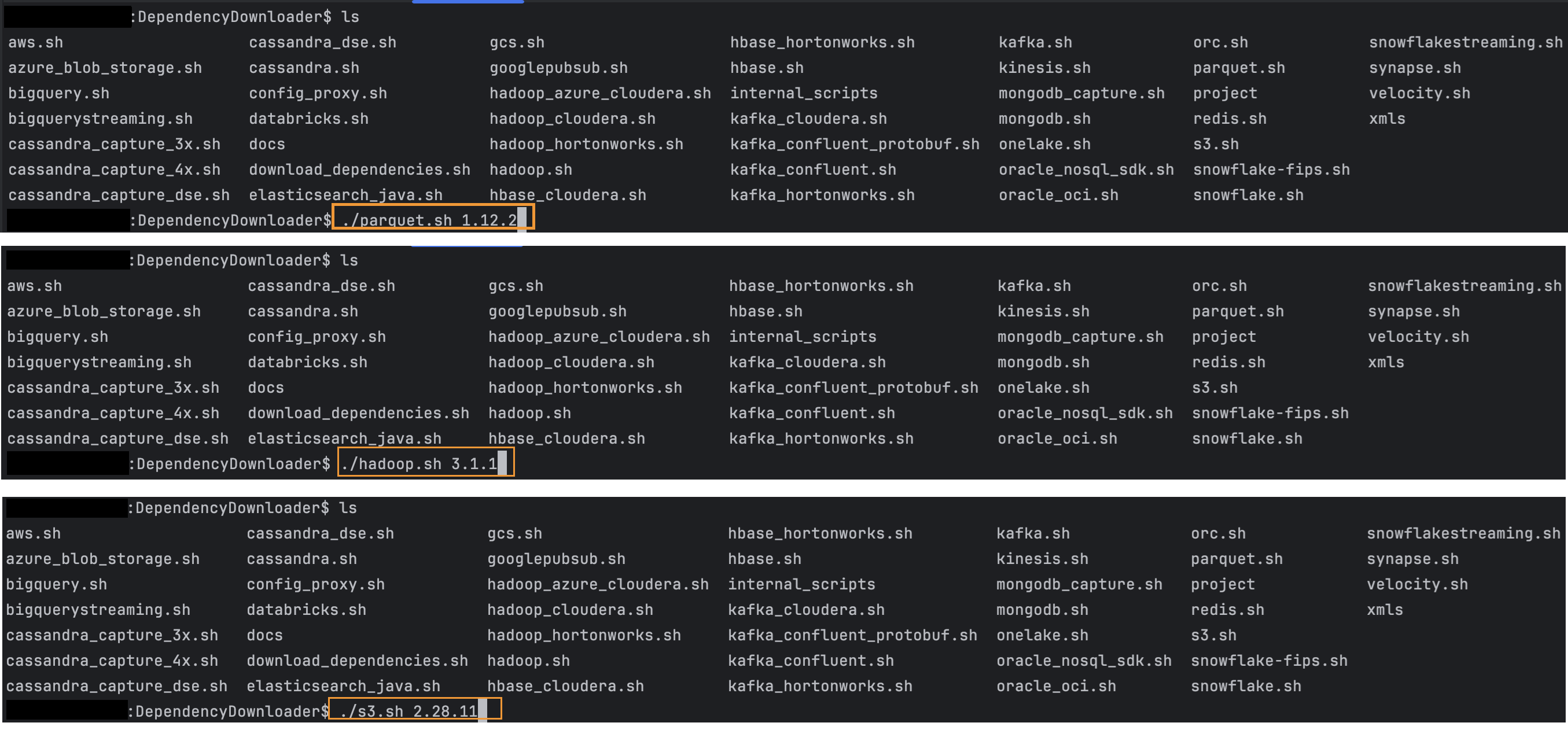
- 3 directories will be created in
GG_HOME/opt/DependencyDownloader/dependencies. Make a note of these directories:/u01/app/ogg/opt/DependencyDownloader/dependencies/s3_2.28.11/*/u01/app/ogg/opt/DependencyDownloader/dependencies/hadoop_3.4.0/*/u01/app/ogg/opt/DependencyDownloader/dependencies/parquet_1.12.3/*
8.5.3 Create a Replicat in Oracle GoldenGate for Distributed Applications and Analytics
- Go to Administration Service and click + sign to add a replicat.
Figure 8-28 Administration Service
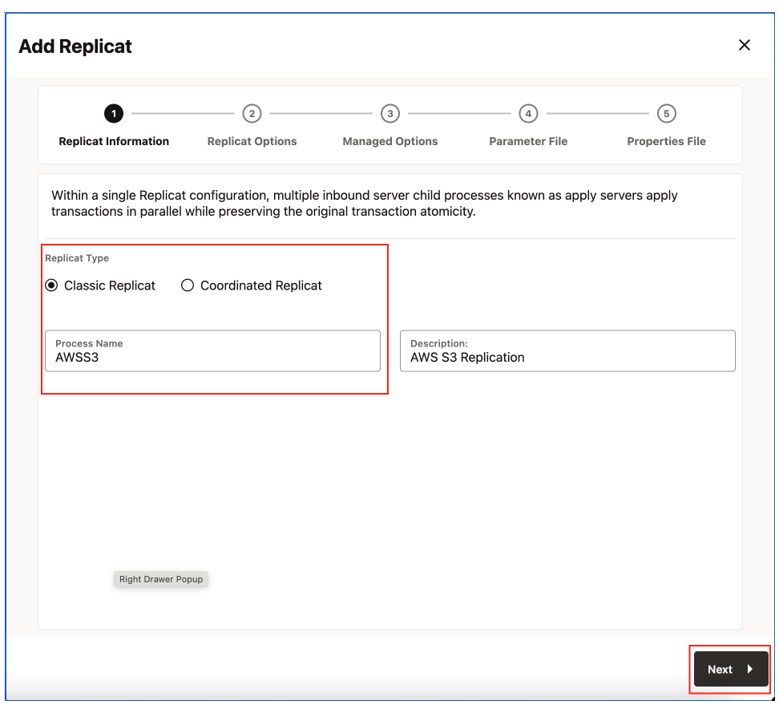
- Select the Replicat Type and click Next.
There are two different Replicat types available: Classic and Coordinated. Classic Replicat is a single threaded process whereas Coordinated Replicat is a multithreaded one that applies transactions in parallel.
Figure 8-29 Replicat Options
- Provide Replicat Options and click Next.
- Replicat Trail: Name of the required trail file. For
sample trail, provide
tr. - Subdirectory: Provide as
GG_HOME/opt/AdapterExamples/trail/if using the sample trail. - Target: Amazon S3
- Format: Select the file format.
Figure 8-30 Add Replicate
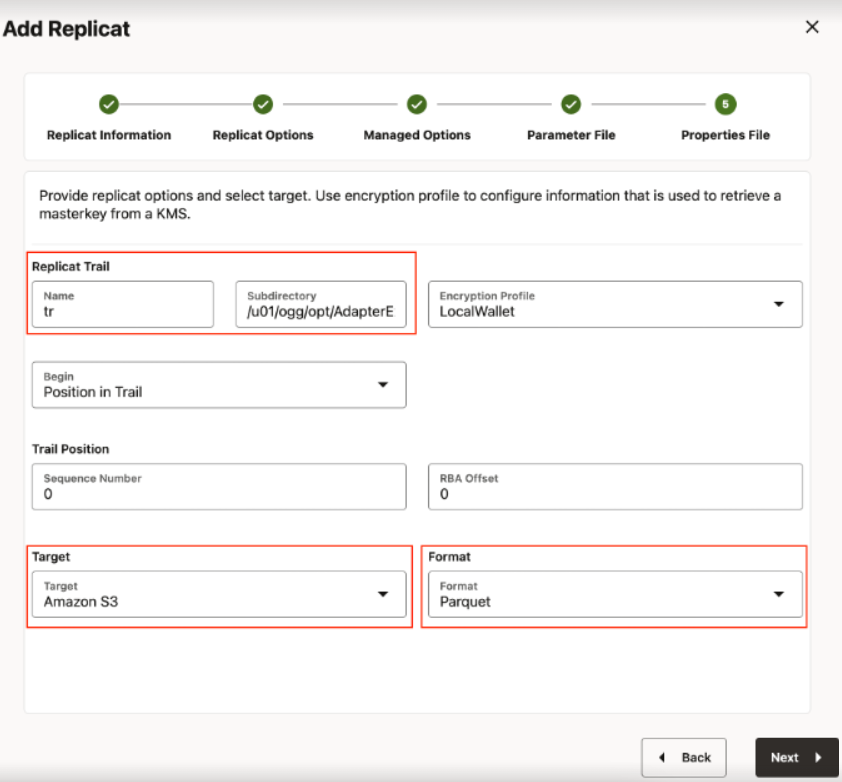
- Replicat Trail: Name of the required trail file. For
sample trail, provide
- Leave Managed Options as is and click Next.
Figure 8-31 Managed Options
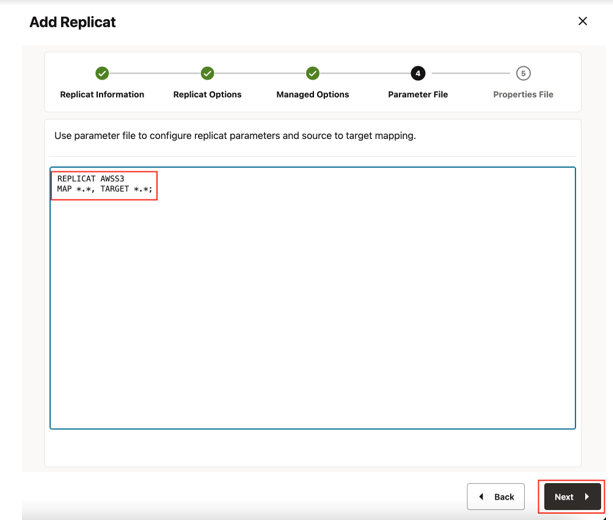
- In Parameter File, provide parameter file details and click
Next.
In the Parameter File, you can either specify source to target mapping or leave it as-is with a wildcard selection. If Coordinated Replicat is selected as the Replicat Type, an additional parameter needs to be provided:
TARGETDB LIBFILE libggjava.so SET property=<ggbd-deployment_home>/etc/conf/ogg/your_replicat_name.properties
.Figure 8-32 Parameter File
- In Properties File, update the properties marked as #TODO and click Create
and Run. For example:
# Properties file for ReplicatS3 gg.target=s3#TODO: format can be 'parquet' or 'orc' or one of the pluggable formatter types. Default is 'parquet'. gg.format=parquet #TODO: Update S3 region gg.eventhandler.s3.region= #TODO: Uncomment and configure the proxy host and port. #gg.eventhandler.s3.proxyServer= #gg.eventhandler.s3.proxyPort= #TODO: Update S3 bucket details gg.eventhandler.s3.bucketMappingTemplate= gg.eventhandler.s3.pathMappingTemplate= gg.eventhandler.s3.finalizeAction=none #TODO: Set the AWS credentials. gg.eventhandler.s3.accessKeyId= gg.eventhandler.s3.secretKey= gg.eventhandler.s3.enableBucketAdmin=false #TODO: Set to the location of the AWS SDK. gg.classpath=/path/to/aws-deps/*:/path/to/hadoop-deps/:/path/to/parquet_deps/*
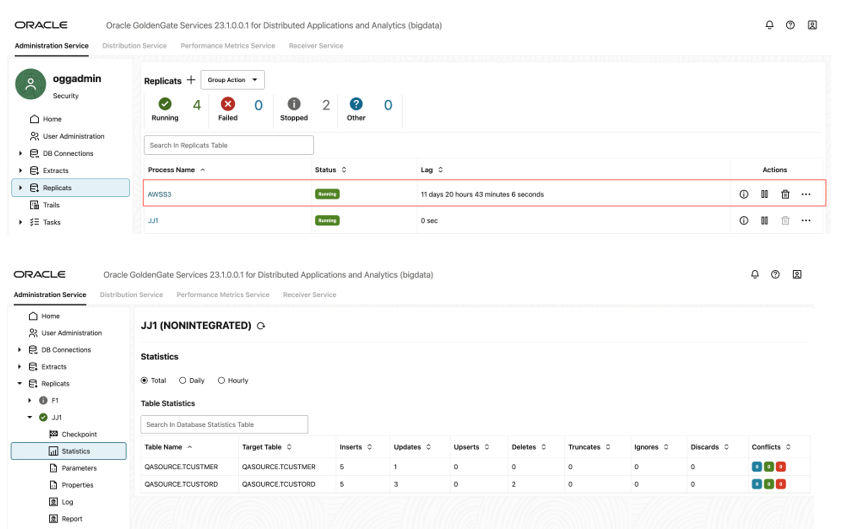
- When replicat starts successfully, it is in running state. You can click
on the replicat name, select Statistics to see the replication statistics.
Figure 8-33 Replication Statistics
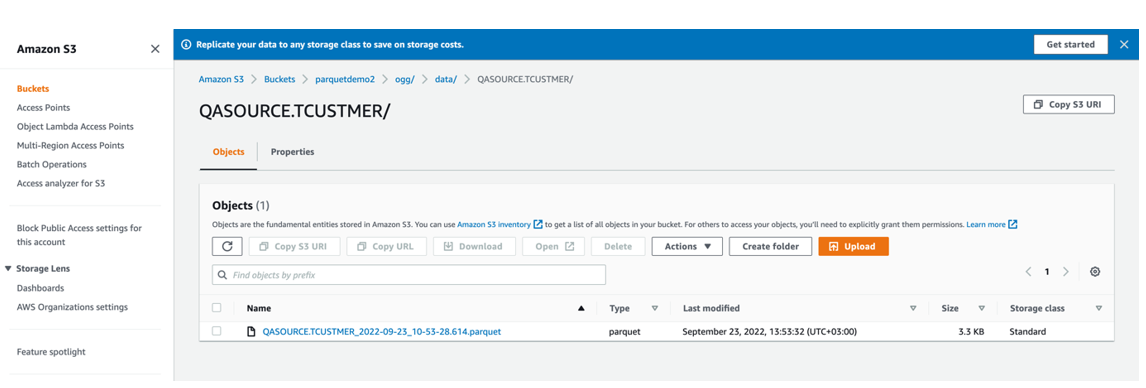
- You can go to AWS s3 console and check the bucket.
Figure 8-34 AWS s3 console.
Note:
- If target S3 bucket does not exist, it can be auto crated by GGBD. You can use Template Keywords to dynamically assign S3 bucket names.
- S3 Handler can be configured for proxy server. For more information, see S3 Event Handler.
- You can use different properties to control the behaviour of file writing. You can set file sizes, inactivity periods and more. You can get more details in the File Writer blog post.