3 Filtering WebLogic Server Log Messages
For related information, see:
-
For information about setting up a log filter for a WebLogic Server instance, see Filter Log Messages in Oracle WebLogic Remote Console Online Help.
-
Subscribing to Messages for information about creating and subscribing a message handler.
- The Role of Logger and Handler Objects
When WebLogic Server message catalogs and theNonCatalogLoggergenerate messages, they distribute their messages to ajava.util.logging.Loggerobject. TheLoggerobject publishes the messages to any message handler that has subscribed to theLogger. - Filtering Messages by Severity Level or Other Criteria
When WebLogic Server message catalogs and theNonCatalogLoggergenerate messages, they convert the message severity to aweblogic.logging.WLLevelobject. - Setting the Severity Level for Loggers and Handlers
To filter the messages by severity level, you can set the severity level for aHandlerandLoggerobject using the WLST commands. - Setting a Filter for Loggers and Handlers
When you set a filter on theLoggerobject, the filter specifies which messages the object publishes; therefore, the filter affects all handlers that are registered with theLoggerobject as well. When you set a filter onHandler, the filter affects only the behavior of the specific handler.
The Role of Logger and Handler Objects
When WebLogic Server message catalogs and the NonCatalogLogger generate messages, they distribute their messages to a java.util.logging.Logger object. The Logger object publishes the messages to any message handler that has subscribed to the Logger.
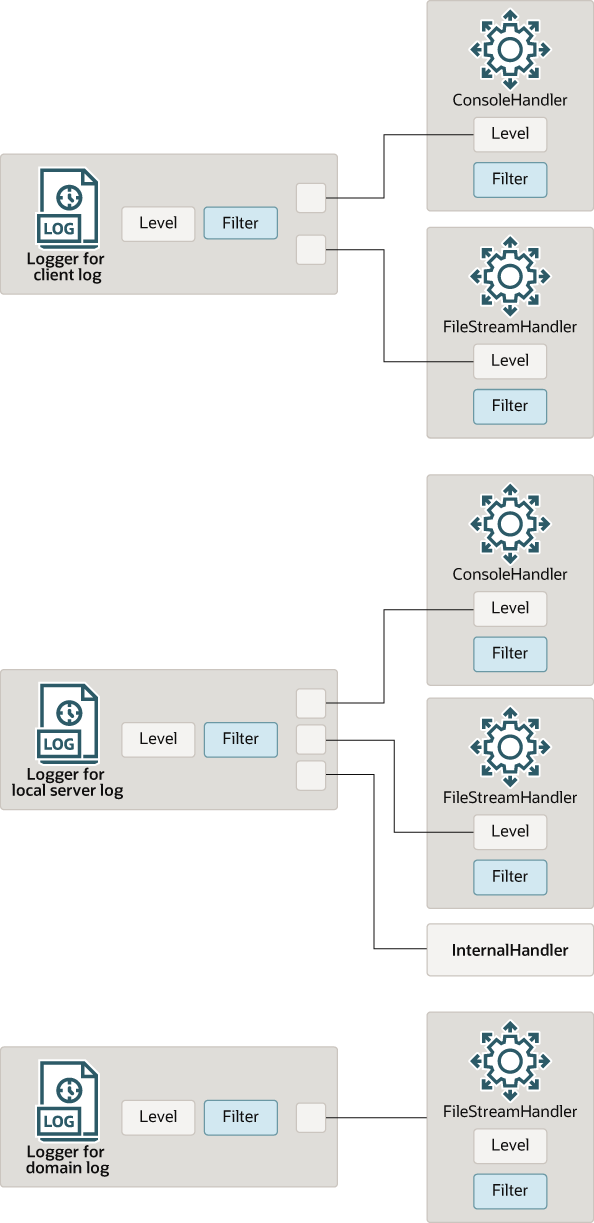
WebLogic Server instantiates Logger and Handler objects in three distinct contexts. See Figure 3-1 for more details:
-
In client JVMs that use WebLogic logging services. This client
Loggerobject publishes messages that are sent from client applications running in the client JVM.The following handlers subscribe to the
Loggerobject in a client JVM:-
ConsoleHandler, which prints messages from the client JVM to the client's standard out.If you use the
-Dweblogic.log.StdoutSeverityLevelJava startup option for the client JVM, WebLogic logging services create a filter for this handler that limits the messages that the handler writes to standard out. See Writing Messages from a Client Application in Adding WebLogic Logging Services to Applications Deployed on Oracle WebLogic Server. -
FileStreamHandler, which writes messages from the client JVM to the client's log file.
-
-
In each instance of WebLogic Server. This server
Loggerobject publishes messages that are sent from subsystems and applications that run on a server instance.The following handlers subscribe to the server
Loggerobject:-
ConsoleHandler, which makes messages available to the server's standard out. -
FileStreamHandler, which writes messages to the server log file. -
An internal handler, which broadcasts messages to the domain log and JMX clients, and publishes messages to the Administration Server.
-
-
The Administration Server maintains a domain
Loggerobject in addition to a serverLoggerobject. The domainLoggerobject receives messages from each Managed Server'sLoggerobject.The following handler subscribes to the domain
Loggerobject:-
FileStreamHandler, which writes messages to the domain log file.
-
Figure 3-1 WebLogic Logging Services Contexts
Description of "Figure 3-1 WebLogic Logging Services Contexts"
Parent topic: Filtering WebLogic Server Log Messages
Filtering Messages by Severity Level or Other Criteria
NonCatalogLogger generate messages, they convert the message severity to a weblogic.logging.WLLevel object. A WLLevel object can specify any of the following values, from lowest to highest impact:
Trace,Debug,Info,Notice,Warning,Error,Critical,Alert,Emergency
By default, a Logger object publishes messages of all levels. To set the lowest-level message that a Logger object publishes, you use a simple Logger.setLevel API. When a Logger object receives an incoming message, it checks the message level with the level set by the setLevel API. If the message level is below the Logger level, it returns immediately. If the message level is above the Logger level, the Logger allocates a WLLogRecord object to describe the message.
For example, if you set a Logger object level to Warning, the Logger object publishes only Warning, Error, Critical, Alert, or Emergency messages.
To provide more control over the messages that a Logger object publishes, you can also create and set a filter. A filter is a class that compares data in the WLLogRecord object with a set of criteria. The Logger object publishes only the WLLogRecord objects that satisfy the filter criteria. For example, a filter can configure a Logger to publish only messages from the JDBC subsystem. To create a filter, you instantiate a java.util.logging.Filter object and use the Logger.setFilter API to set it for a Logger object.
Instead of (or in addition to) setting the level and a filter for the messages that a Logger object publishes, you can set the level and filters on individual message handlers.
For example, you can specify that a Logger publishes messages that are of the Warning level or higher. Then you can do the following for each handler:
-
For the
ConsoleHandler, set a level and filter that selects onlyAlertmessages from the JDBC, JMS, and EJB subsystems. This causes standard out to display onlyAlertmessages from the JDBC, JMS, and EJB subsystems. -
For the
FileStreamHandler, set no additional level or filter criteria. Because theLoggerobject has been configured to publish only messages of theWarninglevel or higher, the log file will contain all messages from all subsystems that are ofWarningseverity level or higher. -
Publish all messages of
Warningseverity level or higher to the domain-wide message log on the Administration Server.
Parent topic: Filtering WebLogic Server Log Messages
Setting the Severity Level for Loggers and Handlers
To filter the messages by severity level, you can set the severity level for a Handler and Logger object using the WLST commands.
The WLST commands provide a way to set the severity level for a Handler object through standard MBean commands. To set the Severity level for a Logger object, you can use the Logger API. You can also set the Severity level for a Logger via the WLST or the command line; see Specifying Severity Level for Loggers. To configure Logger and Handler severity level for WLS clients (such as EJB and Web Service clients), you must use the Java Logging API.
Parent topic: Filtering WebLogic Server Log Messages
Setting the Level for Loggers
To set the severity level for a Logger object, create a class that does the following:
Parent topic: Setting the Severity Level for Loggers and Handlers
Setting the Level for Handlers
To set the severity level for a Handler object using the API, create a class that does the following (See Example 3-1):
Parent topic: Setting the Severity Level for Loggers and Handlers
Example: Setting the Level for Handlers
The following example demonstrate how to set level for handlers using API.
Example 3-1 Example: Setting Level for a Handler Object Using the API
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import java.util.logging.Handler;
import weblogic.logging.LoggingHelper;
import weblogic.logging.WLLevel;
public class LogLevel {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
Logger serverlogger = LoggingHelper.getServerLogger();
Handler[] handlerArray = serverlogger.getHandlers();
for (int i=0; i < handlerArray.length; i++) {
Handler h = handlerArray[i];
if(h.getClass().getName().equals
("weblogic.logging.ConsoleHandler")){
h.setLevel(WLLevel.Alert);
}
}
}
}
Parent topic: Setting the Level for Handlers
Example: Setting the Severity Level for the Stdout Handler
You can configure the severity level for a Handler object through the LogMBean interface using the command line:
-
The WLST commands in Example 3-2 set the severity level for the Stdout Handler to
Info.
See Using the WebLogic Scripting Tool in Understanding the WebLogic Scripting Tool. For more information about setStdoutSeverity, see LogMBean in MBean Reference for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Example 3-2 Setting the Severity Level for the Stdout Handler
C:\>java weblogic.WLST
wls:/offline> connect('username','password')
wls:/mydomain/serverConfig> edit()
wls:/mydomain/edit> startEdit()
wls:/mydomain/edit !> cd("Servers/myserver/Log/myserver")
wls:/mydomain/edit/Servers/myserver/Log/myserver !> cmo.setStdoutSeverity("Info")
wls:/mydomain/edit/Servers/myserver/Log/myserver !> save()
wls:/mydomain/edit/Servers/myserver/Log/myserver !> activate()
Parent topic: Setting the Level for Handlers
Setting a Filter for Loggers and Handlers
When you set a filter on the Logger object, the filter specifies which messages the object publishes; therefore, the filter affects all handlers that are registered with the Logger object as well. When you set a filter on Handler, the filter affects only the behavior of the specific handler.
The WLST provides a way to set a filter on the Handler object through standard MBean commands. To set a filter on the Logger object, you must use the Logger API. For client-side logging, the only way to set a filter is through using the Java Logging API.
To set a filter:
-
Create a class that implements
java.util.logging.Filter.The class must include the
Filter.isLoggablemethod and logic that evaluates incoming messages. If the logic evaluates as true, theisLoggablemethod enables theLoggerobject to publish the message. -
Place the filter object in the classpath of the JVM on which the
Loggerobject is running. -
To set a filter for a
Loggerobject, create a class that does the following:Invokes one of the following
LoggingHelpermethods:-
getClientLoggerif the current context is a client JVM. -
getServerLoggerif the current context is a server JVM and you want to filter theLoggerobject that a server uses to manage its local server log. -
getDomainLoggerif the current context is the Administration Server and you want to filter theLoggerobject that manages the domain server log.
Invokes the
Logger.setFilter(Filter newFilter)method. -
-
To set a filter for a
Handlerobject using the API, create a class that does the following:Invokes one of the following
LoggingHelpermethods:-
getClientLoggerif the current context is a client JVM. -
getServerLoggerif the current context is a server JVM and you want to filter theLoggerobject that a server uses to manage its local server log. -
getDomainLoggerif the current context is the Administration Server and you want to filter theLoggerobject that manages the domain server log.
-
Iterates through the list of handlers until it finds the
Handlerobject for which you want to set a level.Use
Handler.getClass().getName()to determine the type of handler to which the current array index refers. -
Invokes the
Handler.setFilter(Filter newFilter)method.
-
The following is an example class that rejects all messages from the Deployer subsystem.
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import java.util.logging.Filter;
import java.util.logging.LogRecord;
import weblogic.logging.WLLogRecord;
import weblogic.logging.WLLevel;
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
public boolean isLoggable(LogRecord record) {
if (record instanceof WLLogRecord) {
WLLogRecord rec = (WLLogRecord)record;
if (rec.getLoggerName().equals("Deployer")) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
You can configure a filter for a Handler object through the LogMBean interface using the command line:
-
The WLST commands in the following example creates and sets a filter on the Domain Log Broadcaster.
C:\>java weblogic.WLST wls:/offline> connect('username','password') wls:/mydomain/serverConfig> edit() wls:/mydomain/edit> startEdit() wls:/mydomain/edit !> cmo.createLogFilter('myFilter') wls:/mydomain/edit !> cd("Servers/myserver/Log/myserver") wls:/mydomain/edit/Servers/myserver/Log/myserver !> cmo.setDomainLogBroadcastFilter(getMBean('/LogFilters/myFilter')) wls:/mydomain/edit/Servers/myserver/Log/myserver !> save() wls:/mydomain/edit/Servers/myserver/Log/myserver !> activate()
For more information about using WLST, see Using the WebLogic Scripting Tool in Understanding the WebLogic Scripting tool. For more information about setDomainLogBroadcastFilter, see LogMBean in the MBean Reference for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Filtering Domain Log Messages
To filter the messages that each Managed Server publishes to the domain log, you can create a log filter for the domain log using WLST or WebLogic Remote Console. For information about creating log filters using Remote Console, see Create a Log Filter in Oracle WebLogic Remote Console Online Help.
Any Java Logging severity level or filter that you set on the Logger object that manages a server instance's log file supersedes a domain log filter. For example, if the level of the server Logger object is set to Warning, a domain log filter will receive only messages of the Warning level or higher.
You can define a domain log filter which modifies the set of messages that one or more servers send to the domain log. By default, all messages of severity Notice or higher are sent.
Note:
Messages of severity Debug are never sent to the domain log, even if you use a filter.
For information about configuring a domain log filter for a WebLogic Server instance using the WebLogic Remote Console, see Filter Log Messages in Oracle WebLogic Remote Console Online Help.
Parent topic: Setting a Filter for Loggers and Handlers