3 Understanding SNMP Proxies
This chapter includes the following sections:
SNMP Agent as Proxy for Other Agents
WebLogic SNMP agents can function as primary agents that forward (proxy) requests to other SNMP agents. To use the primary agent functionality of a WebLogic Server agent, you assign branches of the registration tree (OID tree) as the responsibility of other SNMP agents. When an SNMP manager sends a request to a WebLogic SNMP agent, if the OID of the requested object is under the branch of the OID tree assigned to a proxied agent, then the WebLogic SNMP agent forwards the request to the proxied agent.
Note:
You cannot use a WebLogic Server SNMP agent as a proxy for SNMP agents in other WebLogic Server domains. For example, a WebLogic Server agent in domainA cannot proxy requests to a WebLogic Server agent in domainB. This limitation is in effect because all WebLogic Server agents use the same MIB root.
Instead of proxying requests to multiple WebLogic Server domains, you can place all of your server instances in a single domain and send requests directly to each Managed Server. See Narrowing the Scope of a Request.
- Configuring the SNMP Protocols for Proxied Communication
- Specifying Credentials for Proxied Communication
- Choosing Listen Ports for Proxied Agents
Parent topic: Understanding SNMP Proxies
Configuring the SNMP Protocols for Proxied Communication
When a WebLogic SNMP agent proxies requests to another agent, the communication process consists of separate events (conversations), each of which can use different SNMP protocols (see Figure 3-1):
-
Communication between the SNMP manager and the WebLogic SNMP agent.
WebLogic SNMP agents can receive requests that use the SNMP v1, v2, or v3 protocols.
-
Communication between the WebLogic SNMP agent and the proxied agent.
Regardless of the protocol used between a manager and a WebLogic SNMP agent, you can specify whether a WebLogic SNMP agent forwards SNMP v1 or v3 requests to proxied agents.
If you specify a security name when you configure a proxy, then the WebLogic SNMP agent will always use SNMP v3 to communicate with the proxied agent. If you do not specify a security name, the WebLogic SNMP agent will always use SNMP v1.
Figure 3-1 Separate Conversations for Proxied SNMP Communication
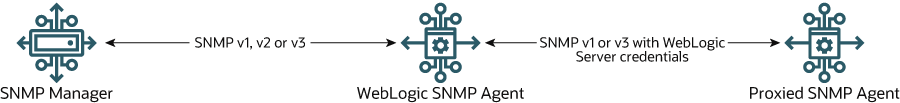
Description of "Figure 3-1 Separate Conversations for Proxied SNMP Communication"
Parent topic: SNMP Agent as Proxy for Other Agents
Specifying Credentials for Proxied Communication
When the WebLogic SNMP agent receives a request from a manager, it always authenticates and performs other security operations on the request before determining if it should process the request itself or forward it to a proxied agent. Therefore, regardless of the protocol or the credentials that are used for communication between the SNMP manager and the WebLogic SNMP agent, the WebLogic SNMP agent supplies its own credentials for its conversation with the proxied agent.
Parent topic: SNMP Agent as Proxy for Other Agents
Choosing Listen Ports for Proxied Agents
By default a WebLogic SNMP agent listens for management requests on port 161. If a WebLogic SNMP agent is to proxy for other SNMP agents, then those other agents must be configured to listen for SNMP management requests on some other port.
Parent topic: SNMP Agent as Proxy for Other Agents
The Microsoft Windows SNMP Service
While a WebLogic Server SNMP agent can be a proxy for other SNMP agents, it cannot be configured as a subagent of the Microsoft Windows SNMP agent service.
Using Microsoft Extension Agent API, the Microsoft Windows SNMP agent service can be a proxy for other SNMP agents. However, WebLogic Server does not support this feature and cannot use the Windows SNMP agent as a proxy.
Parent topic: Understanding SNMP Proxies