6 Using WLST to Manage JMS Servers and JMS System Module Resources
This chapter includes the following sections:
- Understanding JMS System Modules and Subdeployments
A JMS system module is described by thejms-system-resourceMBean in theconfig.xmlfile. - How to Create JMS Servers and JMS System Module Resources
Creating JMS servers and JMS system module resources using WLST include the basic tasks of starting an edit session, creating a JMS system module, and creating a JMS server resource. - How to Modify and Monitor JMS Servers and JMS System Module Resources
You can modify or monitor JMS objects and attributes by using the appropriate method available from the MBean. - Best Practices When Using WLST to Configure JMS Resources
Learn about best practices when using WLST to configure JMS servers and JMS system module resources.
Understanding JMS System Modules and Subdeployments
A JMS system module is described by the jms-system-resource MBean in the config.xml file.
Basic components of a jms-system-resource MBean are:
-
name: Name of the module. -
target: Server, cluster, or migratable target the module is targeted to. -
sub-deployment: A mechanism by which JMS system module resources (such as queues, topics, and connection factories) are grouped and targeted to a server resource (such as a JMS server instance, WebLogic Server instance, or cluster). -
descriptor-file-name: Path and file-name of the system module file.
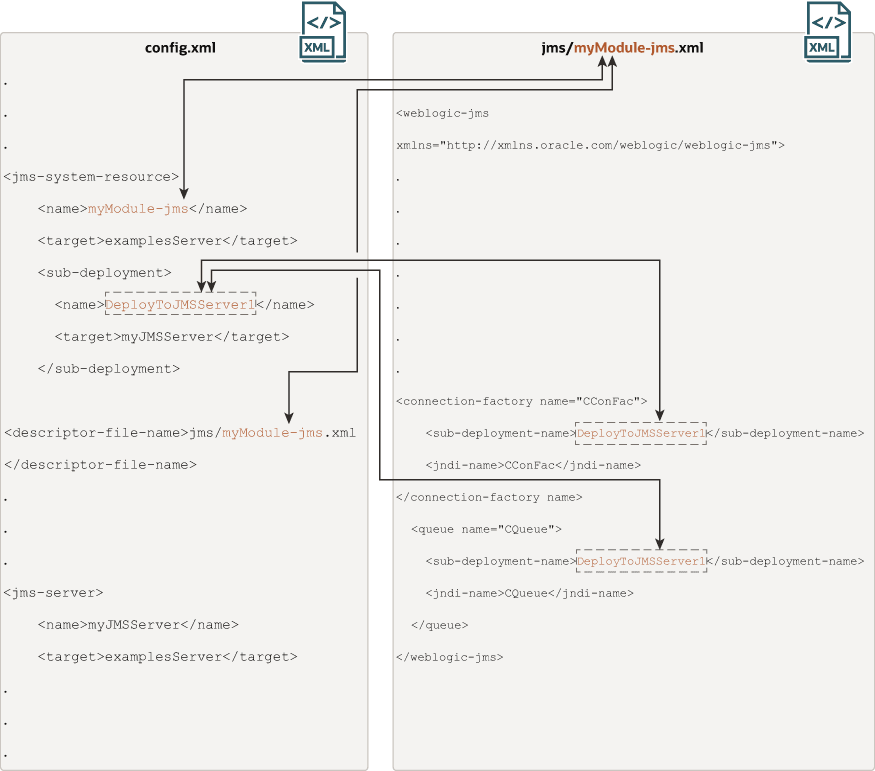
The JMS resources of a system module are located in a module descriptor file that conforms to the weblogic-jmsmd.xml schema. In Figure 6-1, the module is named myModule-jms.xml and it contains JMS system resource definitions for a connection factory and a queue. The sub-deployment-name element is used to group and target JMS resources in the myModule-jms.xml file to targets in the config.xml. You have to provide a value for the sub-deployment-name element when using WLST. For more information on subdeployments, see JMS System Module and Resource Subdeployment Targeting. In Figure 6-1, the sub-deployment-name DeployToJMSServer1 is used to group and target the connection factory CConfac and the queue CQueue in the myModule-jms module.
For more information about how to use JMS resources, see What Are JMS Configuration Resources?.
How to Create JMS Servers and JMS System Module Resources
Creating JMS servers and JMS system module resources using WLST include the basic tasks of starting an edit session, creating a JMS system module, and creating a JMS server resource.
After you have established an edit session, use the following steps to configure JMS servers and system module resources:
Example 6-1 WLST Script to Create JMS System Resources
"""
This script starts an edit session, creates a JMS Server,
targets the jms server to the server WLST is connected to and creates
a JMS System module with a jms queue and connection factory. The
jms queues and topics are targeted using sub-deployments.
"""
import sys
from java.lang import System
print "@@@ Starting the script ..."
myJmsSystemResource = "CapiQueue-jms"
factoryName = "CConFac"
jmsServerName = "myJMSServer"
queueName = "CQueue"
url = sys.argv[1]
usr = sys.argv[2]
password = sys.argv[3]
connect(usr,password, url)
edit()
startEdit()
//Step 1
servermb=getMBean("Servers/examplesServer")
if servermb is None:
print '@@@ No server MBean found'
else:
//Step 2
jmsMySystemResource = create(myJmsSystemResource,"JMSSystemResource")
//Step 3
jmsMySystemResource.addTarget(servermb)
//Step 4
theJMSResource = jmsMySystemResource.getJMSResource()
//Step 5
connfact1 = theJMSResource.createConnectionFactory(factoryName)
jmsqueue1 = theJMSResource.createQueue(queueName)
//Step 6
connfact1.setJNDIName(factoryName)
jmsqueue1.setJNDIName(queueName)
//Step 7
jmsqueue1.setSubDeploymentName('DeployToJMSServer1')
connfact1.setSubDeploymentName('DeployToJMSServer1')
//Step 8
jmsserver1mb = create(jmsServerName,'JMSServer')
//Step 9
jmsserver1mb.addTarget(servermb)
//Step 10
subDep1mb = jmsMySystemResource.createSubDeployment('DeployToJMSServer1')
//Step 11
subDep1mb.addTarget(jmsserver1mb)
.
.
.How to Modify and Monitor JMS Servers and JMS System Module Resources
You can modify or monitor JMS objects and attributes by using the appropriate method available from the MBean.
-
Modify JMS objects and attributes using the set, target, untarget, and delete methods.
-
Monitor JMS runtime objects using get methods.
Example 6-2 shows a sample WLST script to modify JMS objects.
See Navigating MBeans (WLST Online) in Understanding the WebLogic Scripting Tool.
Example 6-2 WLST Script to Modify JMS Objects
.
.
print '@@@ delete system resource'
jmsMySystemResource = delete("CapiQueue-jms","JMSSystemResource")
print '@@@ delete server'
jmsserver1mb = delete(jmsServerName,'JMSServer')
.
.
.Best Practices When Using WLST to Configure JMS Resources
Learn about best practices when using WLST to configure JMS servers and JMS system module resources.
-
Trap for Null MBean objects (such as servers, JMS servers, modules) before trying to manipulate the MBean object.
-
Use a meaningful name when providing a subdeployment name. For example, the subdeployment name DeployToJMSServer1 tells you that all subdeployments with this name are deployed to JMSServer1.