D WLDF Instrumentation Library
The WebLogic Diagnostics Framework (WLDF) instrumentation library contains diagnostic monitors and diagnostic actions.
For information about using items from the instrumentation library, see Configuring Instrumentation.
- Diagnostic Monitor Library
Diagnostic monitors are broadly classified as server-scoped and application-scoped monitors. - Diagnostic Action Library
WLDF includes a library of diagnostic actions that you can use with delegating monitors.
Diagnostic Monitor Library
All monitors are preconfigured with their respective pointcuts. However, the actual locations affected by them may vary depending on the classes they instrument. For example, the Servlet_Before_Service monitor adds diagnostic code at the entry of servlet or java server page (JSP) service methods at different locations in different servlet implementations.
For any delegating monitor, only compatible actions may be attached. The compatibility is determined by the nature of the monitor.
The following table lists and describes the diagnostic monitors that can be used within server scope; that is, in WebLogic Server classes. For the diagnostic actions that are compatible with each monitor, see the Compatible Action Type column in Table D-1.
Table D-1 Diagnostic Monitors for Use Within Server Scope
| Monitor Name | Monitor Type | Compatible Action Type | Pointcuts |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Connector_Before_Inbound |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods handling inbound connections. |
|
Connector_After_Inbound |
Server |
Stateless |
At exit of methods handling inbound connections. |
|
Connector_Around_Inbound |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exit of methods handling inbound connections. |
|
Connector_Before_Outbound |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods handling outbound connections. |
|
Connector_After_Outbound |
After |
Stateless |
At exit of methods handling outbound connections. |
|
Connector_Around_Outbound |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exit of methods handling outbound connections. |
|
Connector_Before_Tx |
Before |
Stateless |
Entry of transaction register, unregister, start, rollback and commit methods. |
|
Connector_After_Tx |
After |
Stateless |
At exit of transaction register, unregister, start, rollback and commit methods. |
|
Connector_Around_Tx |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exit of transaction register, unregister, start, rollback and commit methods. |
|
Connector_Before_Work |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods related to scheduling, starting and executing connector work items. |
|
Connector_After_Work |
After |
Stateless |
At exit of methods related to scheduling, starting and executing connector work items. |
|
Connector_Around_Work |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exit of methods related to scheduling, starting and executing connector work items. |
|
DyeInjection |
Before |
Built-in |
At points where requests enter the server. |
|
JDBC_Before_Commit_Internal |
Before |
Stateless |
JDBC subsystem internal code |
|
JDBC_After_Commit_Internal |
After |
Stateless |
JDBC subsystem internal code |
|
JDBC_Before_Connection_ Internal |
Before |
Stateless |
Before calls to methods: Driver.connect DataSource.getConnection |
|
JDBC_After_Connection_ Internal |
Before |
Stateless |
JDBC subsystem internal code |
|
JDBC_Before_Rollback_ Internal |
Before |
Stateless |
JDBC subsystem internal code |
|
JDBC_After_Rollback_Internal |
After |
Stateless |
JDBC subsystem internal code |
|
JDBC_Before_Start_Internal |
Before |
Stateless |
JDBC subsystem internal code |
|
JDBC_After_Start_Internal |
After |
Stateless |
JDBC subsystem internal code |
|
JDBC_Before_Statement_ Internal |
Before |
Stateless |
JDBC subsystem internal code |
|
JDBC_After_Statement_ Internal |
After |
Stateless |
JDBC subsystem internal code |
|
JDBC_After_Reserve_Connection_Internal |
After |
Stateless |
After a JDBC connection is reserved from the connection pool. |
|
JDBC_After_Release_Connection_Internal |
After |
Stateless |
After a JDBC connection is released back to the connection pool. |
Table D-2 lists the diagnostic monitors that can be used within application scopes; that is, in deployed applications. The Compatible Action Type column identifies the diagnostic action type that is compatible with each monitor.
Table D-2 Diagnostic Monitors for Use Within Application Scopes
| Monitor Name | Monitor Type | Compatible Action Type | Pointcuts |
|---|---|---|---|
|
EJB_After_EntityEjbBusiness Methods |
After |
Stateless |
At exits of all EntityBean methods, which are not standard ejb methods. |
|
EJB_Around_EntityEjbBusinessMethods |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of all EntityBean methods that are not standard ejb methods. |
|
EJB_After_EntityEjbMethods |
After |
Stateless |
At exits of methods: EnitityBean.setEntityContext EnitityBean.unsetEntityContext EnitityBean.ejbRemove EnitityBean.ejbActivate EnitityBean.ejbPassivate EnitityBean.ejbLoad EnitityBean.ejbStore |
|
EJB_Around_EntityEjbMethods |
Around |
Around |
At exits of methods: EnitityBean.setEntityContext EnitityBean.unsetEntityContext EnitityBean.ejbRemove EnitityBean.ejbActivate EnitityBean.ejbPassivate EnitityBean.ejbLoad EnitityBean.ejbStore |
|
EJB_After_EntityEjbSemantic Methods |
After |
Stateless |
At exits of methods: EnitityBean.set* EnitityBean.get* EnitityBean.ejbFind* EnitityBean.ejbHome* EnitityBean.ejbSelect* EnitityBean.ejbCreate* EnitityBean.ejbPostCreate* |
|
EJB_Around_EntityEjbSemanticMethods |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of methods: EnitityBean.set* EnitityBean.get* EnitityBean.ejbFind* EnitityBean.ejbHome* EnitityBean.ejbSelect* EnitityBean.ejbCreate* EnitityBean.ejbPostCreate* |
|
EJB_After_SessionEjbMethods |
After |
Stateless |
At exits of methods: SessionBean.setSessionContext SessionBean.ejbRemove SessionBean.ejbActivate SessionBean.ejbPassivate |
|
EJB_Around_SessionEjbMethods |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of methods: SessionBean.setSessionContext SessionBean.ejbRemove SessionBean.ejbActivate SessionBean.ejbPassivate |
|
EJB_After_SessionEjbBusinessMethods |
After |
Stateless |
At exits of all SessionBean methods, which are not standard ejb methods. |
|
EJB_Around_SessionEjb BusinessMethods |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of all SessionBean methods, which are not standard ejb methods. |
|
EJB_After_SessionEjbSemanticMethods |
After |
Stateless |
At exits of methods: SessionBean.ejbCreateSessionBean.ejbPostCreate |
|
EJB_Around_SessionEjb SemanticMethods |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of methods: SessionBean.ejbCreate SessionBean.ejbPostCreate |
|
EJB_Before_EntityEjbBusinessMethods |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of all EntityBean methods, which are not standard ejb methods. |
|
EJB_Before_EntityEjbMethods |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: EnitityBean.setEntityContext EnitityBean.unsetEntityContext EnitityBean.ejbRemove EnitityBean.ejbActivate EnitityBean.ejbPassivate EnitityBean.ejbLoad EnitityBean.ejbStore |
|
EJB_Before_EntityEjbSemanticMethods |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: EnitityBean.set* EnitityBean.get* EnitityBean.ejbFind* EnitityBean.ejbHome* EnitityBean.ejbSelect* EnitityBean.ejbCreate* EnitityBean.ejbPostCreate* |
|
EJB_Before_SessionEjb BusinessMethods |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of all SessionBean methods, which are not standard ejb methods. |
|
EJB_Before_SessionEjbMethods |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: SessionBean.setSessionContext SessionBean.ejbRemove SessionBean.ejbActivate SessionBean.ejbPassivate |
|
EJB_Before_SessionEjb SemanticMethods |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: SessionBean.ejbCreate SessionBean.ejbPostCreate |
|
HttpSessionDebug |
Around |
Built-in |
getSession - Inspects returned HTTP session Before and after calls to methods: getAttribute setAttribute removeAttribute At inspection points, the approximate session size is computed and stored as the payload of a generated event. The size is computed by flattening the session to a byte-array. If an error is encountered while flattening the session, a negative size is reported. |
|
JDBC_Before_CloseConnection |
Before |
Stateless |
Before calls to methods: Connection.close |
|
JDBC_After_CloseConnection |
After |
Stateless |
After calls to methods: Connection.close |
|
JDBC_Around_CloseConnection |
Around |
Around |
Before and after calls to methods: Connection.close |
|
JDBC_Before_CommitRollback |
Before |
Stateless |
Before calls to methods: Connection.commit Connection.rollback |
|
JDBC_After_CommitRollback |
After |
Stateless |
After calls to methods: Connection.commit Connection.rollback |
|
JDBC_Around_CommitRollback |
Around |
Around |
Before and after calls to methods: Connection.commit Connection.rollback |
|
JDBC_Before_Execute |
Before |
Stateless |
Before calls to methods: Statement.execute* PreparedStatement.execute* |
|
JDBC_After_Execute |
After |
Stateless |
After calls to methods: Statement.execute* PreparedStatement.execute* |
|
JDBC_Around_Execute |
Around |
Around |
Before and after calls to methods: Statement.execute* PreparedStatement.execute* |
|
JDBC_Before_GetConnection |
Before |
Stateless |
Before calls to methods: Driver.connect DataSource.getConnection |
|
JDBC_After_GetConnection |
After |
Stateless |
After calls to methods: Driver.connect DataSource.getConnection |
|
JDBC_Around_GetConnection |
Around |
Around |
Before and after calls to methods: Driver.connect DataSource.getConnection |
|
JDBC_Before_Statement |
Before |
Stateless |
Before calls to methods: Connection.prepareStatement Connection.prepareCall Statement.addBatch RowSet.setCommand |
|
JDBC_After_Statement |
After |
Stateless |
After calls to methods: Connection.prepareStatement Connection.prepareCall Statement.addBatch RowSet.setCommand |
|
JDBC_Around_Statement |
Around |
Around |
Before and after calls to methods: Connection.prepareStatement Connection.prepareCall Statement.addBatch RowSet.setCommand |
|
JMS_Before_AsyncMessage Received |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: MessageListener.onMessage |
|
JMS_After_AsyncMessage Received |
After |
Stateless |
At exits of methods: MessageListener.onMessage |
|
JMS_Around_AsyncMessage Received |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of methods: MessageListener.onMessage |
|
JMS_Before_MessageSent |
Before |
Stateless |
Before call to methods: QueSender send |
|
JMS_After_MessageSent |
After |
Stateless |
After call to methods: QueSender send |
|
JMS_Around_MessageSent |
Around |
Around |
Before and after call to methods: QueSender send |
|
JMS_Before_SyncMessage Received |
Before |
Stateless |
Before calls to methods: MessageConsumer.receive* |
|
JMS_After_SyncMessage Received |
After |
Stateless |
After calls to methods: MessageConsumer.receive* |
|
JMS_Around_SyncMessage Received |
Around |
Around |
Before and after calls to methods: MessageConsumer.receive* |
|
JMS_Before_TopicPublished |
Before |
Stateless |
Before call to methods: TopicPublisher.publish |
|
JMS_After_TopicPublished |
After |
Stateless |
After call to methods: TopicPublisher.publish |
|
JMS_Around_TopicPublished |
Around |
Around |
Before and after call to methods: TopicPublisher.publish |
|
JNDI_Before_Lookup |
Before |
Stateless |
Before calls to javax.naming.Context lookup methods Context.lookup* |
|
JNDI_After_Lookup |
After |
Stateless |
After calls to javax.naming.Context lookup methods: Context.lookup* |
|
JNDI_Around_Lookup |
Around |
Around |
Before and after calls to javax.naming.Context lookup methods Context.lookup* |
|
JTA_Before_Commit |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: UserTransaction.commit |
|
JTA_After_Commit |
After |
Stateless advice |
At exits of methods: UserTransaction.commit |
|
JTA_Around_Commit |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of methods: UserTransaction.commit |
|
JTA_Before_Rollback |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: UserTransaction.rollback |
|
JTA_After_Rollback |
After |
Stateless advice |
At exits of methods: UserTransaction.rollback |
|
JTA_Around_Rollback |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of methods: UserTransaction.rollback |
|
JTA_Before_Start |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: UserTransaction.begin |
|
JTA_After_Start |
After |
Stateless advice |
At exits of methods: UserTransaction.begin |
|
JTA_Around_Start |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of methods: UserTransaction.begin |
|
MDB_Before_MessageReceived |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: MessageDrivenBean.onMessage |
|
MDB_After_MessageReceived |
After |
Stateless |
At exits of methods: MessageDrivenBean.onMessage |
|
MDB_Around_MessageReceived |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of methods: MessageDrivenBean.onMessage |
|
MDB_Before_Remove |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: MessageDrivenBean.ejbRemove |
|
MDB_After_Remove |
After |
Stateless |
At exits of methods: MessageDrivenBean.ejbRemove |
|
MDB_Around_Remove |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of methods: MessageDrivenBean.ejbRemove |
|
MDB_Before_SetMessageDriven Context |
Before |
Stateless |
At entry of methods: MessageDrivenBean.setMessage DrivenContext |
|
MDB_After_SetMessageDriven Context |
After |
Stateless |
At exits of methods: MessageDrivenBean.setMessageDrivenContext |
|
MDB_Around_SetMessageDriven Context |
Around |
Around |
At entry and exits of methods: MessageDrivenBean.setMessageDrivenContext |
|
Servlet_Before_Service |
Before |
Stateless |
At method entries of servlet/jsp methods: HttpJspPage._jspService Servlet.service HttpServlet.doGet HttpServlet.doPost Filter.doFilter |
|
Servlet_After_Service |
After |
Stateless |
At method exits of servlet/jsp methods: HttpJspPage._jspService Servlet.service HttpServlet.doGet HttpServlet.doPost Filter.doFilter |
|
Servlet_Around_Service |
Around |
Around |
At method entry and exits of servlet/jsp methods: HttpJspPage._jspService Servlet.service HttpServlet.doGet HttpServlet.doPost Filter.doFilter |
|
Servlet_Before_Session |
Before |
Stateless |
Before calls to servlet methods: HttpServletRequest.getSession HttpSession.setAttribute/ putValue HttpSession.getAttribute/ getValue HttpSession.removeAttribute/ removeValue HttpSession.invalidate |
|
Servlet_Around_Session |
Around |
Around |
Before and after calls to servlet methods: HttpServletRequest.getSession HttpSession.setAttribute/ putValue HttpSession.getAttribute/ getValue HttpSession.removeAttribute/ removeValue HttpSession.invalidate |
|
Servlet_After_Session |
After |
Stateless |
After calls to servlet methods: HttpServletRequest.getSession HttpSession.setAttribute/ putValue HttpSession.getAttribute/ getValue HttpSession.removeAttribute/ removeValue HttpSession.invalidate |
|
Servlet_Before_Tags |
Before |
Stateless |
Before calls to jsp methods: Tag.doStartTag Tag.doEndTag |
|
Servlet_After_Tags |
After |
Stateless |
After calls to jsp methods: Tag.doStartTag Tag.doEndTag |
|
Servlet_Around_Tags |
Around |
Around |
Before and after calls to jsp methods: Tag.doStartTag Tag.doEndTag |
Parent topic: WLDF Instrumentation Library
Diagnostic Action Library
The diagnostic action library includes the following actions:
- TraceAction
- DisplayArgumentsAction
- TraceElapsedTimeAction
- TraceMemoryAllocationAction
- StackDumpAction
- ThreadDumpAction
- MethodInvocationStatisticsAction
- MemoryAllocationStatisticsAction
Parent topic: WLDF Instrumentation Library
TraceAction
TraceAction is a stateless action that is compatible with Before and After monitor types.
TraceAction generates a trace event at the affected location in the program execution. The following information is generated:
-
Timestamp
-
Context identifier from the diagnostic context which uniquely identifies the request
-
Transaction identifier, if available
-
User identity
-
Action type (that is, TraceAction)
-
Domain
-
Server name
-
Instrumentation scope name (for example, application name)
-
Diagnostic monitor name
-
Module name
-
Location in code from where the action was called. The location information includes:
-
Class name
-
Method name
-
Method signature
-
Line number
-
Thread name
-
-
Payload carried by the diagnostic context, if any
Parent topic: Diagnostic Action Library
DisplayArgumentsAction
DisplayArgumentsAction is a stateless action that is compatible with Before and After monitor types.
DisplayArgumentsAction generates an instrumentation event at the affected location in the program execution to capture method arguments or a return value.
When executed, this action causes an instrumentation event that is dispatched to the events archive. When attached to Before monitors, the instrumentation event captures input arguments to the joinpoint (for example, method arguments). When attached to After monitors, the instrumentation event captures the return value from the joinpoint. The event carries the following information:
-
Timestamp
-
Context identifier from the diagnostic context that uniquely identifies the request
-
Transaction identifier, if available
-
User identity
-
Action type (that is, DisplayArgumentsAction)
-
Domain
-
Server name
-
Instrumentation scope name (for example, application name)
-
Diagnostic monitor name
-
Module name
-
Location in code from where the action was called. The location information includes:
-
Class name
-
Method name
-
Method signature
-
Line number
-
Thread name
-
-
Payload carried by the diagnostic context, if any
-
Input arguments, if any, when attached to Before monitors
-
Return value, if any, when attached to After monitors
Parent topic: Diagnostic Action Library
TraceElapsedTimeAction
TraceElapsedTimeAction is an Around action that is compatible with Around monitor types.
TraceElapsedTimeAction generates two events: one before and one after the location in the program execution.
When executed, this action captures the timestamps before and after the execution of an associated joinpoint. It then computes the elapsed time by computing the difference. It generates an instrumentation event which is dispatched to the events archive. The elapsed time is stored as event payload. The event carries the following information:
-
Timestamp
-
Context identifier from the diagnostic context that uniquely identifies the request
-
Transaction identifier, if available
-
User identity
-
Action type (that is TraceElapsedTimeAction)
-
Domain
-
Server name
-
Instrumentation scope name (for example, application name)
-
Diagnostic monitor name
-
Module name
-
Location in code from where the action was called. This location information consists of:
-
Class name
-
Method name
-
Method signature
-
Line number
-
Thread name
-
-
Payload carried by the diagnostic context, if any
-
Elapsed time processing the joinpoint, as event payload, in nanoseconds
Parent topic: Diagnostic Action Library
TraceMemoryAllocationAction
TraceMemoryAllocationAction uses the HotSpot ThreadMXBean API to trace the number of bytes allocated by a thread during a method call. This action is very similar to TraceElapsedTimeAction, with the exception that the memory allocated within a method call is traced.
The TraceMemoryAllocationAction action:
-
Creates an instrumentation event that is persisted.
-
Can be used from delegating and custom monitors.
Parent topic: Diagnostic Action Library
StackDumpAction
StackDumpAction is a stateless action that is compatible with Before and After monitor types.
StackDumpAction generates an instrumentation event at the affected location in the program execution to capture a stack dump.
When executed, this action generates an instrumentation event that is dispatched to the events archive. It captures the stack trace as an event payload. The event carries following information:
-
Timestamp
-
Context identifier from the diagnostic context that uniquely identifies the request
-
Transaction identifier, if available
-
User identity
-
Action type (that is, StackDumpAction)
-
Domain
-
Server name
-
Instrumentation scope name (for example, application name)
-
Diagnostic monitor name
-
Module name
-
Location in code from where the action was called. This location information consists of:
-
Class name
-
Method name
-
Method signature
-
Line number
-
Thread name
-
-
Payload carried by the diagnostic context, if any
-
Stack trace as an event payload
Parent topic: Diagnostic Action Library
ThreadDumpAction
ThreadDumpAction is a stateless action that is compatible with Before and After monitor types.
ThreadDumpAction generates an instrumentation event at the affected location in the program execution to capture a thread dump, if the underlying VM supports it. JDK 8 and later (Oracle HotSpot) supports this action.
This action generates an instrumentation event that is dispatched to the events archive. This action may be used only with HotSpot. It is ignored when used with other JVMs. It captures the thread dump as event payload. The event carries the following information:
-
Timestamp
-
Context identifier from the diagnostic context that uniquely identifies the request
-
Transaction identifier, if available
-
User identity
-
Action type (that is, ThreadDumpAction)
-
Domain
-
Server name
-
Instrumentation scope name (for example, application name)
-
Diagnostic monitor name
-
Module name
-
Location in code from where the action was called. This location information consists of:
-
Class name
-
Method name
-
Method signature
-
Line number
-
Thread name
-
-
Payload carried by the diagnostic context, if any
-
Thread dump as an event payload
Parent topic: Diagnostic Action Library
MethodInvocationStatisticsAction
MethodInvocationStatisticsAction is an Around action that is compatible with Around monitor types.
MethodInvocationStatisticsAction captures performance metrics around a joinpoint in memory without persisting an event in the Archive for each invocation. The statistics are collected and made available through the WLDFInstrumentationRuntimeMBean. The collected statistics are also consumable by the Harvester and the Policies and Actions components. This makes it possible to create watch rules that can combine request information from the instrumentation system and metric information from other run-time MBeans.
Some of the statistics that can be captured include the following:
-
Number of invocations
-
Average execution time (in nanoseconds)
-
Standard deviation in observed execution time
-
Minimum execution time
-
Maximum execution time
The WLDFInstrumentationRuntimeMBean instance for a given scope exposes the data collected from MethodInvocationStatisticsAction instances, which are attached to configured Diagnostic Around monitors, using the MethodInvocationStatistics attribute. The MethodInvocationStatistics attribute contains a hierarchy of Map objects, keyed as shown in Figure D-1.
Figure D-1 Structure of MethodInvocationStatistics Attribute
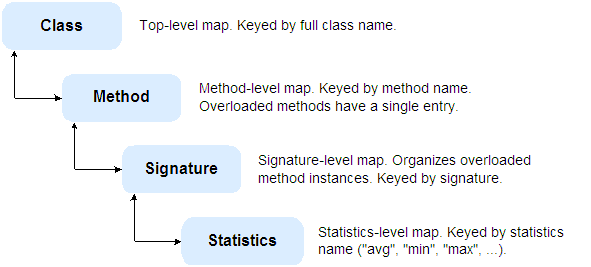
Description of "Figure D-1 Structure of MethodInvocationStatistics Attribute"
The following semantics are used in the MethodInvocationStatistics attribute:
MethodInvocationStatistics::= Map<className, MethodMap> MethodMap::= Map<methodName, MethodParamsSignatureMap> MethodParamsSignatureMap::= Map<MethodParamsSignature, MethodDataMap> MethodDataMap::= <MetricName, Statistic> MetricName:= min | max | avg | count | sum | sum_of_squares | std_deviation
Because the MethodInvocationStatisticsAction only captures information in memory, and does not persist that information in the Archive, this action does not incur the I/O overhead of other instrumentation actions. This makes this action a lightweight mechanism for capturing performance statistics and helping identify bottlenecks in your application. You can navigate through the map structures and identify the low performing parts of your application.
- Instrumenting an Application with MethodInvocationStatisticsAction and Querying the Results
- Configuring the Harvester to Collect MethodInvocationStatisticsAction Data
- Configuring Policies Based on MethodInvocationStatistics Metrics
- Using JMX to Collect Data
Parent topic: Diagnostic Action Library
Instrumenting an Application with MethodInvocationStatisticsAction and Querying the Results
This section shows an example of instrumenting the Avitek Medical Records (MedRec) sample application with a custom monitor that uses MethodInvocationStatisticsAction. This example then shows using WLST online to query the performance statistics that have been collected, which can be done by navigating the WLDFInstrumentationRuntimeMBean instance associated with the instrumented application.
WLST online provides simplified access to MBeans. While JMX APIs require you to use JMX object names to interrogate MBeans, WLST enables you to navigate a hierarchy of MBeans in a similar fashion to navigating a hierarchy of files in a file system. See Navigating and Interrogating MBeans in Understanding the WebLogic Scripting Tool.
The following subsections are included in this example:
Note:
Code examples demonstrating Java EE APIs and other WebLogic Server features are provided with your WebLogic Server installation. To work with these examples, select the custom installation option when installing WebLogic Server, and select to install the Server Examples. See Code Examples and Sample Applications in Understanding Oracle WebLogic Server.
- Configuring the Custom Monitor to Use MethodInvocationStatisticsAction
- Using WLST to Query Method Performance Statistics
Parent topic: MethodInvocationStatisticsAction
Configuring the Custom Monitor to Use MethodInvocationStatisticsAction
As of WebLogic Server 10.3, it is no longer necessary to create a weblogic-diagnostics.xml file in the application's META-INF directory to configure a custom monitor. Instead, you can complete all the required steps from the WebLogic Server Administration Console, as described in the following steps for instrumenting the MedRec sample application:
-
In the Domain Structure pane of the WebLogic Server Administration Console, select Deployments.
-
On the Summary of Deployments page, select Control, and click medrec in the Deployments table.
The Settings for medrec page is displayed.
-
Select Configuration > Instrumentation.
-
In the Diagnostic Monitors in this Module table, click Add Custom Monitor.
-
In the Add Custom Monitors page, enter
MethodStatsMonitoras the monitor name. Optionally, you can enter a brief description. -
In the Location Type selection box, select Around.
-
In the Pointcut text box, enter the following pointcut expression:
execution(public * com.bea.medrec.* *(...)) AND NOT execution(public * com.bea.medrec.* get*(...)) OR execution(public * com.bea.medrec.* set*(...)) OR execution(public * com.bea.medrec.* __WL_*(...)));
This pointcut expression specifies joinpoints for all public methods in classes within packages whose name starts with com.bea.medrec, but excludes the following methods:
-
All accessor methods
-
Methods that begin with the string
__WL_
This pointcut expression encompasses a wide variety of public methods and classes in MedRec, but ignores all getter and setter methods, as well as code generated by WebLogic Server.
-
-
Below the pointcut expression text box, click OK.
-
On the Save Deployment Plan page, enter a new path for the deployment plan, or accept the default location, and click OK.
-
Select Configuration > Instrumentation, and click the name of the new custom monitor,
MethodStatsMonitor, which is listed in the Diagnostic Monitors in this Module table.The Settings for MethodStatsMonitor page is displayed.
-
In the Actions table, assign MethodInvocationStatisticsAction to the custom monitor, as shown in Figure D-2:
Figure D-2 Choosing MethodInvocationStatisticsAction for Custom Monitor
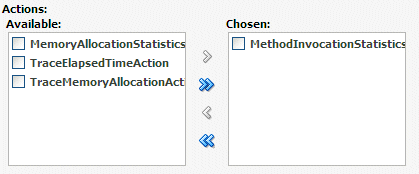
Description of "Figure D-2 Choosing MethodInvocationStatisticsAction for Custom Monitor" -
Click Save, at the bottom of the Settings for MethodStatsMonitor page.
-
Apply the updated deployment plan to the MedRec application:
-
In the Domain Structure pane, select Deployments.
-
On the Summary of Deployments page, select Control, and click the selection box adjacent to medrec in the Deployments table, as shown in Figure D-3:
Figure D-3 Selecting the MedRec Deployment
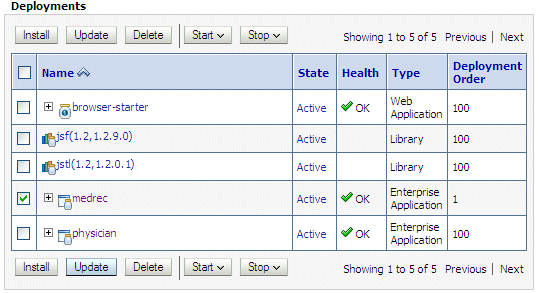
Description of "Figure D-3 Selecting the MedRec Deployment" -
Click Update.
-
In the Update Application Assistant page, select Redeploy this application using the following deployment files.
-
Click Next, then click Finish.
-
The MedRec application is now redeployed, and the custom monitor MethodStatsMonitor is active.
Note:
If Java HotSwap is not enabled, to add a new pointcut to the application's configuration, you need to redeploy the application to enable a custom monitor to be woven into the application code. (However, you can modify most of an application's monitor configuration without requiring a redeploy. This includes changes to the custom monitor's Actions, Properties, EnableDyeFiltering, and Description attributes — that is, anything that does not require bytecode weaving.
However, with HotSwap enabled, you can change any monitor attribute and update the application without the need to redeploy it. See Using Deployment Plans to Dynamically Control Instrumentation Configuration.
Using WLST to Query Method Performance Statistics
Once MedRec is redeployed, the MethodInvocationStatisticsAction begins capturing method performance statistics as the instrumented code is executed. This section shows how to generate statistics quickly and simply by navigating the MedRec patient application with the custom monitor enabled. This section then shows how to examine those statistics using WLST online.
To capture method performance statistics using the custom monitor configured for MedRec and query the results using WLST, complete the following steps:
-
Start the MedRec application, as described in Sample Applications and Code Examples in Understanding Oracle WebLogic Server.
Log in as a patient, administrator, or physician, and perform a small number of operations.
-
Invoke WLST online and navigate to the WLDFInstrumentationRuntimeMBean instance, as shown in the following example steps:
-
Connect to the MedRec server:
wls:/offline> connect('weblogic','password','localhost:7011') Connecting to t3://localhost:7011 with userid weblogic ... Successfully connected to Admin Server 'MedRecServer' that belongs to domain 'medrec'. -
Use the
cdcommand to navigate to the WLDFInstrumentationRuntimeMBean instance associated with the MedRec application:cd('serverRuntime:/WLDFRuntime/WLDFRuntime/WLDFInstrumentationRuntimes/medrec') Location changed to serverRuntime tree. This is a read-only tree with ServerRuntimeMBean as the root. For more help, use help(serverRuntime)
-
-
Access specific values collected by MethodInvocationStatisticsAction by invoking the following method on the WLDFInstrumentationRuntimeMBean:
public Object getMethodInvocationStatisticsData(String expr) throws ManagementException;
Using WLST interactively, you can pass a lookup expression to this method. The lookup expression specifies the particular subset of values that you are interested in viewing. These values are obtained from the map structure created by MethodInvocationStatisticsAction. For example, the following WLST command returns the average execution time (in nanoseconds) of all methods instrumented by MethodInvocationStatisticsAction:
cmo.getMethodInvocationStatisticsData("(com.bea%)(*)(?)(avg)") array(java.lang.Object,[3352.0, 3632.0, 145270.0, 4050.5, 8450.916666666666, 1798645.75, 583538.0, 3610515.0, 1.9541031E7, 1.2796319E7, 3.07897E8, 4470.0, 3073.0, 3073.0, 2.4644752E7, 3492.5, 1051530.0, 2794.0, 390552.3333333333, 3632.0, 2095.5, 189409.33333333334, 2607.6666666666665, 2793.6666666666665, 4749.333333333333, 5308.0, 65930.0, 3.3950405E7, 3353.0, 3911.5])
Note that if you display the entire set of data values that have been collected, a large amount of information could be displayed in the WLST console, as shown in Figure D-4:
Figure D-4 Displaying All Data Values Collected by MethodInvocationStatisticsAction
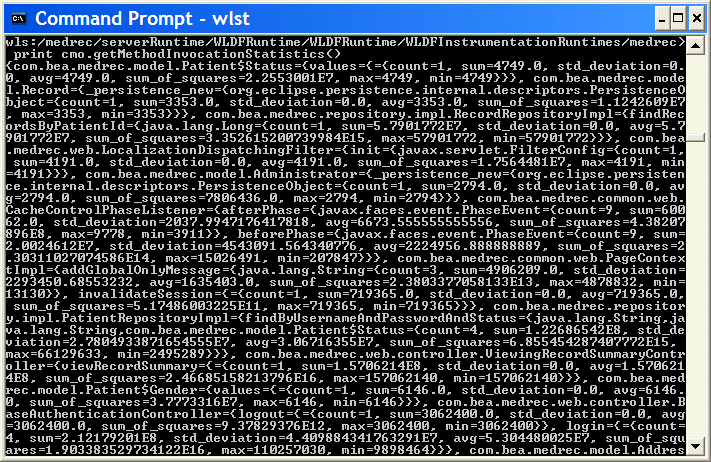
Description of "Figure D-4 Displaying All Data Values Collected by MethodInvocationStatisticsAction"
As an alternative, you can create a WLST script to invoke MethodInvocationStatistics and to format the collected data so that it is more easily read, as in Example D-1:
Example D-1 Using WLST to Invoke MethodInvocationStatistics and Display Results
import sys
def getPositionalArgument(pos, default):
value=None
try:
value=sys.argv[pos]
except:
value=default
return value
url = getPositionalArgument(1, "t3://localhost:7001")
user = getPositionalArgument(2, "weblogic")
password = getPositionalArgument(3, "password")
appName = getPositionalArgument(4, "myapp")
connect(user,password,url)
serverRuntime()
cd('/WLDFRuntime/WLDFRuntime/WLDFInstrumentationRuntimes/' + appName)
print "# Class Method | Count | Min | Max | Average | Std-dev |"
stats=cmo.getMethodInvocationStatistics()
for className in stats.keySet():
classMap=stats.get(className)
for methodName in classMap.keySet():
methodMap=classMap.get(methodName)
for sig in methodMap.keySet():
str= className + " " + methodName + "(" + sig + ")"
sigMap=methodMap.get(sig)
count=sigMap.get('count')
min=sigMap.get('min')
max=sigMap.get('max')
avg=sigMap.get('avg')
std_deviation=sigMap.get('std_deviation')
print str, "|", count, "|", min, "|", max, "|", avg, "|", std_deviation, "|"
The following shows the output produced by the WLST script shown in Example D-1:
# Class Method | Count | Min | Max | Average | Std-dev | jsp_servlet.__index _isStale() | 1 | 1378000 | 1378000 | 1378000.0 | 0.0 | jsp_servlet.__index _getBytes(java.lang.String) | 3 | 1000 | 754000 | 252666.66666666666 | 354497.1399351795 | jsp_servlet.__index _staticIsStale(weblogic.servlet.jsp.StaleChecker) | 1 | 861000 | 861000 | 861000.0 | 0.0 | jsp_servlet.__index _jspService(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest,javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse) | 2 | 70000 | 2113000 | 1091500.0 | 1021500.0 | jsp_servlet.__index$MyMap containsKey(java.lang.Object) | 2 | 2000 | 101000 | 51500.0 | 49500.0 | jsp_servlet.__index$MyMap containsValue(java.lang.Object) | 2 | 1000 | 2000 | 1500.0 | 500.0 |
Configuring the Harvester to Collect MethodInvocationStatisticsAction Data
To configure the Harvester to collect data gathered by MethodInvocationStatisticsAction instances, you must configure an instance of WLDFHarvesterBean using the following attribute:
Name=weblogic.management.runtime.WLDFInstrumentationRuntimeMBean
The scope is selected by the instance configuration.
The attribute specification defines the data that is collected by the Harvester. You can access the successive elements of the map by using the following notation:
MethodInvocationStatistics(className)(methodName)(methodParamSignature) (metricName)
In the preceding notation:
-
classNamerepresents the fully qualified Java class name. You can use the asterisk (*) wildcard character in a class name. -
methodNameselects a specific method from the given class. You can use the asterisk (*) wildcard character in a method name. -
methodParamSignaturerepresents a string that is a comma-separated list of a method's input argument types. Only the Java type names, without the argument names, are included in the signature specification. As in the Java language, the order of the parameters in the signature is significant.This element also supports the asterisk (
*) wildcard character, which can be used to specify the entire list of input argument types for a given method. The asterisk (*) wildcard character matches zero or more argument types at the position following its occurrence in themethodParamSignatureexpression.You can also use the question mark (
?) wildcard character to match a single argument type at any given position in the ordered list of parameter types.Both of these wildcard characters can appear anywhere in the expression. See MethodInvocationStatisticsAction Examples.
-
metricNamerepresents the statistics to be harvested. You can use the asterisk (*) wildcard character in this key to harvest all of the supported metrics.
MethodInvocationStatistics Examples
Consider a class with the following overloaded methods:
package.com.foo;
public interface Bar {
public void doIt();
public void doIt(int a);
public void doit(int a, String s)
public void doIt(Stringa, int b);
public void doIt(String a, String b);
public void doIt(String[] a);
public void doNothing();
public void doNothing(com.foo.Baz);
}
Table D-3 provides examples that show to use MethodInvocationStatisticsAction to harvest various statistics.
Table D-3 MethodInvocationStatisticsAction Examples
| The following MethodInvocationStatisticsAction instance configuration . . . | . . . causes the following to be harvested |
|---|---|
MethodInvocationStatistics(com.foo.Bar)(*)(*)(*) |
All statistics for all methods on |
MethodInvocationStatistics(com.foo.Bar)(doIt)()(*) |
All statistics for the |
MethodInvocationStatistics(com.foo.Bar)(doIt)(*)(*) |
All statistics for all |
MethodInvocationStatistics(com.foo.Bar)(doIt)(int,
*)(*) |
All statistics for the |
MethodInvocationStatistics(com.foo.Bar)(doIt)(String[])(*) |
All statistics for the Note that array parameters are specified by the use of a pair of square brackets ( |
MethodInvocationStatistics(com.foo.Bar)(doIt)(String,
?)(*) |
All statistics for
|
MethodInvocationStatistics(com.foo.Bar)(doNothing)(com.foo.Baz)(min,max) |
The |
Note:
Using a wildcard character in the className specification can have a negative impact on performance.
Parent topic: MethodInvocationStatisticsAction
Configuring Policies Based on MethodInvocationStatistics Metrics
You can use the same syntax described in the previous sections to use MethodInvocationStatistics metrics in a policy expression. You can create meaningful watch rules that do not use a wildcard character in the MetricName element by specifying whether you want the min, max, avg, count, sum, sum_of_squares, or std_deviation variable for a given method.
Parent topic: MethodInvocationStatisticsAction
Using JMX to Collect Data
When using straight JMX to collect data, you can potentially impact server performance negatively if you invoke the getAttribute("MethodInvocationStatistics") method on the WLDFInstrumentationRuntimeMBean. This occurs because, depending on the instrumented classes, the nested map structure can contain a lot of data that involves expensive serialization.
When you use JMX to collect data, Oracle recommends using the getMethodInvocationStatisticsData(String) method.
Parent topic: MethodInvocationStatisticsAction
MemoryAllocationStatisticsAction
The MemoryAllocationStatisticsAction uses the HotSpot ThreadMXBean API API to track the number of bytes allocated by a thread during a method call. Statistics are kept in-memory on the memory allocations, and no instrumentation events are created by this action.
The MemoryAllocationStatisticsAction is very similar to the existing MethodInvocationStatisticsAction. However, statistics tracked by MemoryAllocationStatisticsAction are related to the memory allocated within a method call.
The MemoryAllocationStatisticsAction does not create an instrumentation event. When HotSpot is available, the statistics are available through the WLDFInstrumentationRuntimeMBean.
The following statistics for each method are kept:
-
count -
min -
max -
avg -
sum -
sum_of_squares -
std_deviation
Parent topic: Diagnostic Action Library