7 Common Oracle CQL DDL Clauses
A reference to clauses in the data definition language (DDL) in Oracle Continuous Query Language (Oracle CQL) is provided.
7.1 Introduction to Common Oracle CQL DDL Clauses
Oracle CQL supports the following common DDL clauses:
For more information on Oracle CQL statements, see Oracle CQL Statements.
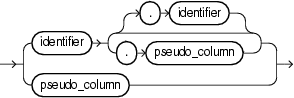
7.2 attr
Purpose
Use the attr clause to specify a stream element or pseudocolumn.
You can use the attr clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
Prerequisites
None.
Semantics
identifier
Specify the identifier of the stream element.
You can specify
-
StreamOrViewName.ElementName -
ElementName -
CorrelationName.PseudoColumn -
PseudoColumn.
Example 7-1 pseudo_column
Specify the timestamp associated with a specific stream element, all stream elements, or the stream element associated with a correlation name in a MATCH_RECOGNIZE clause.
For examples, see:
For more information, see Pseudocolumns.
7.3 attrspec
Purpose
Use the attrspec clause to define the identifier and data type of a stream element.
Prerequisites
None.
Semantics
identifier
Specify the identifier of the stream element.
fixed_length_datatype
Specify the stream element data type as a fixed-length data type.
For syntax, see fixed_length_datatype::= .
variable_length_datatype
Specify the stream element data type as a variable-length data type.
For syntax, see variable_length_datatype::=.
integer
Specify the length of the variable-length data type.
7.4 const_bigint
Purpose
Use the const_bigint clause to specify a big integer numeric literal.
You can use the const_bigint clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
For more information, see Numeric Literals.
Prerequisites
None.
Syntax
const_bigint::=
7.5 const_int
Purpose
Use the const_int clause to specify an integer numeric literal.
You can use the const_int clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
For more information, see Numeric Literals.
Prerequisites
None.
Syntax
const_int::=
7.6 const_string
Purpose
Use the const_string clause to specify a constant String text literal.
You can use the const_string clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
For more information, see Text Literals.
Prerequisites
None.
Syntax
Figure 7-3 const_string::=
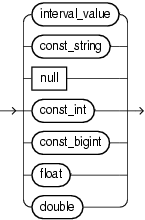
7.7 const_value
Purpose
Use the const_value clause to specify a literal value.
You can use the const_value clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
For more information, see Literals.
Prerequisites
None.
Example 7-2 interval_value
Specify an interval constant value as a quoted string. For example:
INTERVAL '4 5:12:10.222' DAY TO SECOND(3)
For more information, see Interval Literals.
const_string
Specify a quoted String constant value.
For more information, see Text Literals.
null
Specify a null constant value.
For more information, see Nulls.
const_int
Specify an int constant value.
For more information, see Numeric Literals.
bigint
Specify a bigint constant value.
For more information, see Numeric Literals.
float
Specify a float constant value.
For more information, see Numeric Literals.
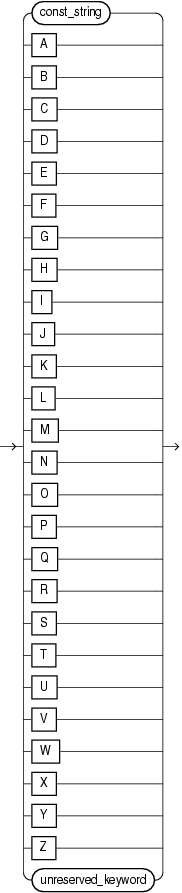
7.8 identifier
Purpose
Use the identifier clause to reference an existing Oracle CQL schema object.
You can use the identifier clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
Prerequisites
The schema object must already exist.
Example 7-3 unreserved_keyword::=
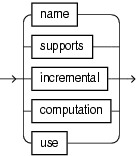
Semantics
const_string
Specify the identifier as a String.
[A-Z]
Specify the identifier as a single uppercase letter.
unreserved_keyword
These are names that you may use as identifiers.
reserved_keyword
These are names that you may not use as identifiers, because they are reserved keywords: add, aggregate, all, alter, and, application, as, asc, avg, between, bigint, binding, binjoin, binstreamjoin, boolean, by, byte, callout, case, char, clear, columns, constraint, content, count, create, day, days, decode, define, derived, desc, destination, disable, distinct, document, double, drop, dstream, dump, duration, duration, element_time, else, enable, end, evalname, event, events, except, external, false, first, float, from, function, group, groupaggr, having, heartbeat, hour, hours, identified, implement, in, include, index, instance, int, integer, intersect, interval, is, istream, java, key, language, last, level, like, lineage, logging, match_recognize, matches, max, measures, metadata_query, metadata_system, metadata_table, metadata_userfunc, metadata_view, metadata_window, microsecond, microseconds, millisecond, milliseconds, min, minus, minute, minutes, monitoring, multiples, nanosecond, nanoseconds, not, now, null, nulls, object, of, on, operator, or, order, orderbytop, output, partition, partitionwin, partnwin, passing, path, pattern, patternstrm, patternstrmb, prev, primary, project, push, query, queue, range, rangewin, real, register, relation, relsrc, remove, return, returning, rows, rowwin, rstream, run, run_time, sched_name, sched_threaded, schema, second, seconds, select, semantics, set, silent, sink, slide, source, spill, start, stop, storage, store, stream, strmsrc, subset, sum, synopsis, system, systemstate, then, time, time_slice, timeout, timer, timestamp, timestamped, to, true, trusted, type, unbounded, union, update, using, value, view, viewrelnsrc, viewstrmsrc, wellformed, when, where, window, xmlagg, xmlattributes, xmlcolattval, xmlconcat, xmldata, xmlelement, xmlexists, xmlforest, xmlparse, xmlquery, xmltable, xmltype, or xor.
7.9 l-value
Purpose
Use the l-value clause to specify an integer literal.
Prerequisites
None.
Syntax
l-value::=
7.10 non_mt_arg_list
Purpose
Use the non_mt_arg_list clause to specify one or more arguments as arithmetic expressions involving stream elements.
You can use the non_mt_arg_list clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
Prerequisites
If any stream elements are referenced, the stream must already exist.
Semantics
arith_expr
Specify the arithmetic expression that resolves to the argument value.
7.11 non_mt_attr_list
Purpose
Use the non_mt_attr_list clause to specify one or more arguments as stream elements directly.
You can use the non_mt_attr_list clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
Prerequisites
If any stream elements are referenced, the stream must already exist.
Syntax
Figure 7-7 non_mt_attr_list::=
Semantics
attr
Specify the argument as a stream element directly.
7.12 non_mt_attrname_list
Purpose
Use the non_mt_attrname_list clause to one or more stream elements by name.
You can use the non_mt_attrname_list clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
Prerequisites
If any stream elements are referenced, the stream must already exist.
Syntax
Figure 7-8 non_mt_attrname_list::=
Semantics
identifier
Specify the stream element by name.
7.13 non_mt_attrspec_list
Purpose
Use the non_mt_attrspec_list clause to specify one or more attribute specifications that define the identifier and data type of stream elements.
Prerequisites
If any stream elements are referenced, the stream must already exist.
Syntax
non_mt_attrspec_list::=
Semantics
attrspec
Specify the attribute identifier and data type.
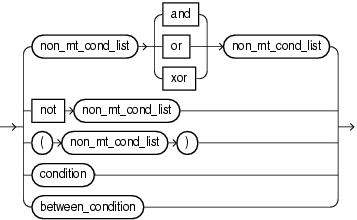
7.14 non_mt_cond_list
Purpose
Use the non_mt_cond_list clause to specify one or more conditions using any combination of logical operators AND, OR, XOR and NOT.
You can use the non_mt_cond_list clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
For more information, see Conditions.
Prerequisites
None.
Semantics
condition
Specify a comparison condition.
For more information, see Comparison Conditions.
For syntax, see condition::=.
between_condition
Specify a condition that tests for inclusion in a range.
For more information, see Range Conditions.
For syntax, see between_condition::=.
7.15 out_of_line_constraint
Purpose
Use this out_of_line_constraint clause to restrict a tuple of any data type by a primary key integrity constraint.
If you plan to configure a query on a relation with USE UPDATE SEMANTICS, you must declare one or more stream elements as a primary key. Use this constraint to specify a compound primary key made up of one or more stream element values.
You can use the out_of_line_constraint clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
For more information, see:
Prerequisites
A tuple that you specify with an out_of_line_constraint may not contain a null value.
Syntax
out_of_line_constraint::=
Semantics
non_mt_attrname_list
Specify one or more tuples to restrict by a primary key integrity constraint.
7.16 param_list
Purpose
Use the param_list clause to specify a comma-separated list of zero or more parameters, similar to a function parameter list, for an Oracle CQL data cartridge complex type method or constructor.
You can use the param_list clause in the following Oracle CQL data cartridge statements:
Prerequisites
None.
7.17 query_ref
Purpose
Use the query_ref clause to reference an existing Oracle CQL query by name.
Prerequisites
The query must already exist (see Query).
Syntax
Figure 7-9 query_ref::=
Semantics
identifier
Specify the name of the query. This is the name you use to reference the query in subsequent Oracle CQL statements.
7.18 time_spec
Purpose
Use the time_spec clause to define a time duration in days, hours, minutes, seconds, milliseconds, or nanoseconds.
Default: if units are not specified, GGSA assumes [second|seconds].
You can use the time_spec clause in the following Oracle CQL statements:
-
windows_type in Query Semantics
Prerequisites
None.
Syntax
Figure 7-10 time_spec::=
Figure 7-11 time_unit::=
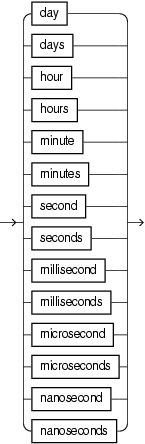
Semantics
integer
Specify the number of time units.
time_unit
Specify the unit of time.