1 Getting Started with Oracle Cloud Marketplace
Oracle Data Integrator on Oracle Cloud Marketplace is a product offering that enables customers to quickly set up and run Oracle Data Integrator (ODI) on Oracle Cloud. It provides a fully unified solution for building, deploying, and managing complex data warehouses or as part of data- centric architectures in a SOA or business intelligence environment. In addition, it combines all the elements of data integration - data movement, data synchronization, data quality, data management, and data services - to ensure that information is timely, accurate, and consistent across complex systems.
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Prerequisites
- Selecting Your Product
- Launching Your Oracle Data Integrator Instance
- Connecting to ODI Compute Instance
- Accessing the ODI Compute Instance
- Using Autonomous Databases in ODI
- Installation Locations
- Log Files Location
- Patching
Note:
Refer to Launching Your First Linux Instance documentation before creating the ODI instance.1.1 Prerequisites
Make sure you have the following prerequisites before using Oracle Data Integrator on Oracle Cloud Marketplace:
- Oracle Cloud Account
- Have access to assigned Oracle Cloud Tenant
- Compute node resources within Oracle Cloud Tenant
Go through the following prerequisites carefully before creating the ODI instance:
- Refer to Creating Dynamic Group Polices for compartment, before provisioning ODI and ADB Instances.
- Read thoroughly the password policies provided in the Stack UI and create passwords accordingly during provisioning.
- Wait till the completion of ODI instance creation, check for its status
and then proceed working on it.
For more information, refer to the usage instructions in Launching Your Oracle Data Integrator Instance.
Supported Browsers
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure supports the latest desktop versions of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Internet Explorer 11, Safari, Firefox, and Firefox ESR. Note that mobile browsers as well as private browsing mode is not supported for Firefox, Internet Explorer, or Edge.
Creating an SSH/RSA Key
To work with the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure once the Oracle Data Integrator Compute Node is built, you have to provide a SSH Public Key to allow you to login to the node.
In order to build your SSH keys, perform the following steps:
- In a terminal window, generate the SSH key using the following
command:
$ ssh-keygen Generating public/private rsa key pair. - Enter the path to store this file. By default, this gets saved in
your home directory under a hidden folder called .ssh. Change this default
location, if
required.
Enter file in which to save the key (/Users/johndoe/.ssh/id_rsa): <Return> - Enter a passphrase using your
key.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): <passphrase> - Re-enter the passphrase to confirm
it.
Enter same passphrase again: <passphrase> - Check the results.
The key fingerprint (a colon separated series of two digit hexadecimal values) is displayed. Check if the path to the key is correct. In the above example, the path is
/Users/johndoe/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. You have now created a public and private key pair.
Creating Dynamic Group and Policies
- Create a dynamic group to include matching rules for instances in a specified compartment. For example,
ALL {instance.compartment.id = 'ocid1.compartment.oc1..aaaaaaaabgr34tpuanpvq6xfb667nsmy2jz45zj6dexojhxdsv4mjayem3cq'}For more information, refer to Create Dynamic Groups and Policy.
- Navigate to Identity -> Policies -> Create Policy to create policy statements as specified below :
If you set policy at:
- ODI compartment level, then all ADW/ATP instances from the compartment where ODI instance is created are listed.
For example - To List ADW/ATP instances only from the ODI instance compartment, you have to setup the following policy:
Allow dynamic-group odi_group to inspect autonomous-database-family in compartment odi Allow dynamic-group odi_group to read autonomous-database-family in compartment odi Allow dynamic-group odi_group to inspect compartments in compartment odi - ODI tenant level, then all ADW/ATP instances from all the compartments of the tenancy are listed.
For example - To list ADW/ATP instances from all the compartments of tenancy, you have to setup the following policy:
Allow dynamic-group odi_group to inspect autonomous-database-family in tenancy Allow dynamic-group odi_group to read autonomous-database-family in tenancy Allow dynamic-group odi_group to inspect compartments in tenancy
- ODI compartment level, then all ADW/ATP instances from the compartment where ODI instance is created are listed.
- To configure email delivery service for specified groups on Oracle Cloud Marketplace:
An email approved sender must be in a group that has IAM policy permissions to send emails. An approved sender must be in a compartment with permissions to manage approved senders. You have to create a policy to manage approved senders in the entire tenant, if the approved senders exist in root compartment.
Add the following policy statement to enable
odi_groupto manage approved senders:Allow dynamic-group odi_group to use approved-senders in compartment odi
Creating an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Policy in an Identity Domain
Create a policy to grant permissions to users in a domain group to work with Oracle Integration instances within a specified tenancy or compartment.
Note:
This topic applies only to cloud accounts that use identity domains. See About Setting Up Users and Groups.
-
Open the navigation menu and click Identity & Security. Under Identity, click Policies.
-
Click Create Policy.
-
In the Create Policy window, enter a name (for example,
IntegrationGroupPolicy) and a description. -
In the Policy Builder, select Show manual editor and enter the required policy statements.
Syntax:
-
allow groupdomain-name/group_nametoverb resource-typein compartmentcompartment-name -
allow groupdomain-name/group_nametoverb resource-typein tenancy
Example:
allow group admin/oci-integration-admins to manage integration-instance in compartment OICCompartmentNote:
If you omit the domain name, the default domain is assumed.
This policy statement allows the
oci-integration-adminsgroup in theadmindomain tomanageinstanceintegration-instancein compartmentOICCompartment.You can create separate groups for different permissions, such as a group with
readpermission only.Want to learn more about policies? See How Policies Work and Policy Reference, or click Help in the window.
-
When defining policy statements, you can specify either verbs (as used in these steps) or permissions (typically used by power users).
-
The
readandmanageverbs are most applicable to Oracle Integration. Themanageverb has the most permissions (create,delete,edit,move, andview).Verb Access readIncludes permission to view Oracle Integration instances and their details.
manageIncludes all permissions for Oracle Integration instances.
-
-
If desired, you can add a policy to allow members of the group to view message metrics, as described in Viewing Message Metrics.
For example:
allow group oci-integration-admins to read metrics in compartment OICPMCompartment -
If you intend to use custom endpoints, add one or more additional policy statements. Otherwise, skip this step.
Add policies that specify the compartment in which vaults and secrets reside and allow the admin group to manage secrets in it. See Configure a Custom Endpoint for an Instance.
Note that you should specify the resource to return in
resource-type, as described in Details for the Vault Service. Also note that Oracle Integration requires thereadverb only butmanageis recommended if the same group will also be administering the secrets (uploading/lifecycle operations).Examples::
-
allow group admin/oci-integration-admins to manage secrets in compartment SecretsCompartment -
allow group admin/oci-integration-admins to manage vaults in compartment SecretsCompartment
-
-
Click Create.
The policy statements are validated and syntax errors are displayed.
1.2 Selecting Your Product
To search for the product Oracle Data Integrator on Oracle Cloud Marketplace, enter the product name in the search text box and click Go.
From the listings related to Oracle Data Integrator, choose either one of the following.
- Data Integrator: Classic: Full ODI functionality for loading data to Oracle Database Cloud Services.
- Data Integrator: Classic BYOL: Full ODI functionality for loading data to other targets.
You are navigated to the respective product listing page which has all the basic usage information along with the product documentation.
Note:
The information described in this guide is applicable to Data Integrator: Classic and Data Integrator: Classic BYOL. Oracle Cloud Marketplace also displays listings related to Data Integrator: Web Edition. For instructions about getting started with Data Integrator: Web Edition, see Getting Started with Oracle Data Transforms.- From your respective product listing page, select Get App.
- Select OCI Region or Login using your Single Sign-On credentials.
- OCI Region – Select the desired region and click Create Stack.
- Provide the OCI tenant details.
- Sign-in to the Identity provider.
- On the Oracle Data Integrator page, provide the following information:
- Type - It is Stack by default.
- Compartment - Specifies the compartment where the compute node will be built. It is generally the location that you have access to build the compute node.
- Terms of Use - This check-box is selected by default. Oracle recommends to review the licenses before proceeding.
- Launch Stack - It launches the stack in the OCI environment. After selecting all the required information, click Launch Stack.
Note:
Provisioning your instance on Oracle Cloud Marketplace greatly depends on your product selection. You cannot use the same VM instance for multiple product offerings. The procedure listed below are product specific and may differ based on the product version.
1.2.1 Terminology Information
The Terminology Information used in Oracle Data Integrator Studio are:
| Oracle Data Integrator Studio | Functions |
|---|---|
|
Data Server |
Represents the physical object where data is stored. Examples include Database Instances, File Servers, Cloud Application Instances.The properties contain all information required to connect and access data. |
|
Technology |
Examples include Oracle, IBM DB2, Oracle Netsuite, Oracle Object Storage. For the list of supported technologies, see Setting Up the Connections. |
|
Physical Schema |
Examples include Database Schema, File server Folder, Object Storage Bucket. |
|
Data Store |
A Tabular representation of a data structure. Examples include Database Tables, Files. |
|
Reverse Engineering |
The process of obtaining the metadata for a filtered set of objects in a Schema. Examples include Table Definitions from an Oracle Schema, VOs from a Cloud Applications Offering. |
|
Model |
The container for the imported objects. The properties define the rules for importing (how to filter and so on). |
|
Project |
Container for the Transformation Design components (Mappings, Packages, Jobs). This doesn't include Data Servers, Schemas, Data Stores and Folders (which are shared between Projects) |
|
Mapping |
The Transformation Design. Defines how data flows from one Data Store to another, and how it is transformed. |
|
Package |
Defines the sequence in which Mappings will be executed, together with what happens of failure conditions. |
|
Job / Session |
The execution of a Package, Mapping or Reverse Engineer. |
|
Schedule |
The rules for when a session executes. |
|
Resource |
Something you can schedule (a mapping or package). |
1.3 Launching Your Oracle Data Integrator Instance
Once you click Launch Stack, you are navigated to the Create Stack page.
1.4 Connecting to ODI Compute Instance
Note:
This section is applicable only for Advanced administrative users.You can connect to an ODI compute instance by using a Secure Shell (SSH) connection. Most Linux distributions include an SSH client by default. For Windows, you can download a free SSH client called PuTTY from http://www.putty.org.
-
To connect to your ODI compute instance from linux,
- Log in to your instance using SSH.
- Use the following command to set the file permissions so that only you can read the file:
where$ chmod 400 <private_key><private_key>is the full path and name of the file that contains the private key associated with the instance you want to access. - Use the following SSH command to access the instance.
where$ ssh –i <private_key> <username>@<public-ip-address><private_key>is the full path and name of the file that contains the private key associated with the instance you want to access.<username>is the default name for the instance. The default user name isoracle.<public-ip-address>is your instance IP address that you retrieved from the Console.
-
To connect to your ODI compute instance from windows,
- Open putty.exe.
- In the Category pane, select Window, and then select Translation.
- In the Remote character set drop-down list, select UTF-8. The default locale setting on Linux-based instances is UTF-8, and this configures PuTTY to use the same locale.
- In the Category pane, select Session and enter the following:
- Host Name (or IP address):
<username>@<public-ip-address>, where<username>is the default name for the instance. For Oracle Linux and CentOS images, the default user name is oracle. For the Ubuntu image, the default name is ubuntu and<public-ip-address>is your instance public IP address that you retrieved from the console. - Port: 22
- Connection type: SSH
- Host Name (or IP address):
- In the Category pane, expand Connection, expand SSH, and then click Auth.
- Click Browse, and then select your private key.
- Click Open to start the session.
If this is your first time connecting to the compute instance, you might see a message that the server's host key is not cached in the registry. Click Yes to continue the connection.
1.5 Accessing the ODI Compute Instance
- Log in to the provisioned Oracle Data Integrator instance on Oracle Cloud Marketplace using SSH as opc user:
ssh –i <private_key> opc@<IP Address> - Execute the following firewall commands to open the VNC ports:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --new-service=odissh sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --service=odissh --set-description="ODI SSHserver" sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --service=odissh --add-port=5901-5905/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=odissh sudo firewall-cmd –reload - Install a VNC viewer on your local computer.
- Use SSH to connect to the compute instance running the Oracle Data Integrator Image, as described in Connecting to ODI Compute Instance.
- On your local computer, connect to your instance and create a ssh tunnel for port 5901 (for display number 1):
$ ssh -L 5901:localhost:5901 –i id_rsa oracle@<IP Address> - On your local computer, for the VNC to work, add an Ingress rule as follows:
No 0.0.0.0/15 TCP All 5901 TCP traffic for ports: 5901 - On your local computer, start a VNC viewer and establish a VNC connection to
localhost:1. - Enter the VNC password that you had provided during the stack creation.
- For connecting multiple users, after the vncpasswd utility exits, start the VNC server by typing
vncserver. This will start a VNC server with display number 1 for the oracle user, and the VNC server starts automatically if your instance is rebooted. For examplevncserver@:2orvncserver@:3.
To start developing your data flows or data mappings/transformations, launch studio from the available options.
- From the Applications menu, navigate to Programming -> ODI Studio,
or
Double click the short icon for ODI Studio present in your Desktop,or
Navigate to the location$MW_HOME/oracle/odi/studio/bin/odiin the VNC. -
Connect to the repository with already populated login credentials. The Login Name value varies based on the selected repository. For ADB repository, the Login Name is
ODI_ADW_REPOand for MySQL Embedded repository it isODISA_MYSQL. -
Post successful configuration, click Topology navigator -> Technologies -> Oracle to check if the newly created data server is available for use.
-
In ODI studio, navigate to
Topology -> Physical Architecture -> Agent -> OracleDIAgent1and click Test, to check if the Standalone Agent is working.Note:
For more details on services, refer to Managing ODI App Server. -
Click Test connection, to check if the created ADB Data Server is working.
1.6 Using Autonomous Databases in ODI
The newly created repository for Oracle Data Integrator will be pre-populated with Oracle Data Servers representing all accessible Autonomous Databases based on defined policies. If you aim to use any of these as a part of your Oracle Data Integrator transformations, then you have to add the username and password to the Data Server properties in the Topology tab in Oracle Data Integrator Studio.
If, at a later date, more Autonomous Databases become available to you, you can use the "Discover ADB's" feature available in Create New Data Server on Oracle Technology of Oracle Data Integrator Studio, to quickly setup the additional instances that were not available at the time when the instance was created. When you select the required ADB instance from displayed instance list, the wallet gets auto downloaded and once you provide the Data Server name, credentials and then select connection details/service profiles and save, the new Oracle Dataserver for the selected ADB instance is created.
Follow the below procedure to create an Autonomous (ADB) Data Server in Oracle Data Integrator repository:
1.6.1 Connecting to the Pre-created ADB Dataservers in ODI Repository
Connect to the readily available or pre-created ADB dataservers in ODI studio. You have to add actual username and password by connecting to the dataserver, do a test connection and continue with your data integration project in ODI studio.
Note:
You need to provide the username and password for the created instance as prepopulated login credentials may not work.1.6.2 Using Dataserver Setup in ODI Studio
You can create additional ADB Dataservers using the Oracle technologies Dataserver setup in ODI Studio.
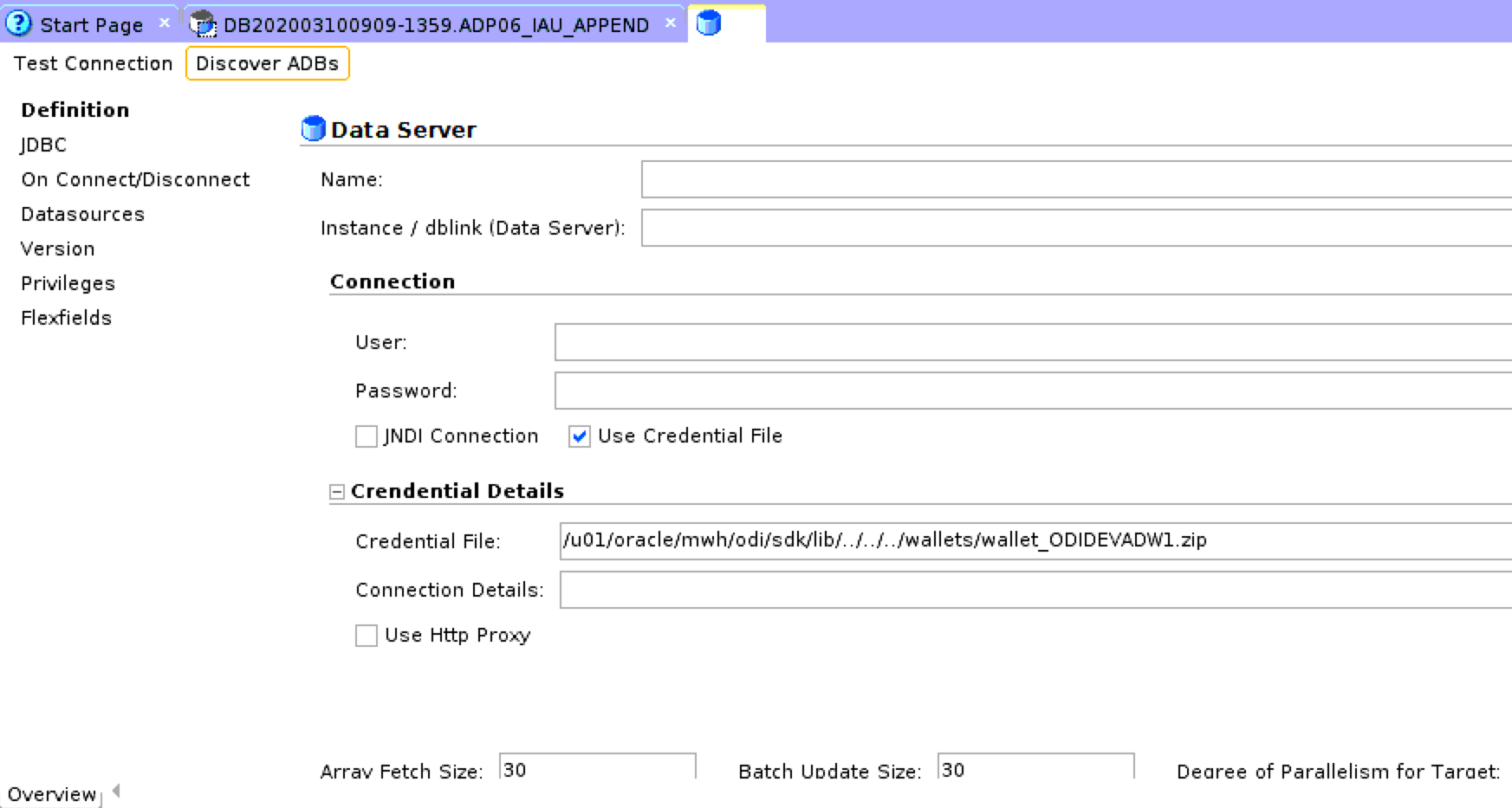
- In the Definition tab, click Discover ADBs. The list of available ADB instances are displayed.
- Select the required ADB instance from the Discover Autonomous Databases drop-down list.
Upon selection, Use Credential File checkbox is auto-selected in the connection node.
In the Credential Details node, Credential File text box is auto-populated with the respective mapped credential file. - In the Data Server node,
- Name: Enter the name of the newly created data server.
- Instance/dblink(Data Server): TNS Alias used for this Oracle instance. It will be used to identify the Oracle instance when using database links and SQL*Loader.
- In the Connection node,
- User/Password: Oracle user (with its password), having select privileges on the source schemas, select/insert privileges on the target schemas and select/insert/object creation privileges on the work schemas that will be indicated in the Oracle physical schemas created under this data server.
- JNDI Connection: Select this check-box to configure the JNDI connection settings. Navigate to the JNDI tab, and fill in the required fields.
- In the Credentials Details node,
- Connection Details - Click the Connection Details drop down arrow to choose the required connection URL from the list of available connection URLs retrieved from tnsnames.ora.
- Click Test Connection.
Upon successful test connection, the new Dataserver gets created in the ODI repository.
1.6.3 Manually Registering the Created ODI Instance to Autonomous Database
If you wish to manually register the ODI instance to Autonomous Database after creating your instance,
- Connect to the compute instance running the Oracle Data Integrator Image, as described in Connecting to ODI Compute Instance.
- Navigate to your ODI studio desktop and double click the Register with ADP shortcut icon.
A terminal window appears allowing you to enter the following details of the Autonomous Database instance which you had already created in Launching Your Oracle Data Integrator Instance step:
- Admin username - User name of the Autonomous Database instance.
- Admin password - Password of the Autonomous Database instance.
- URL Scheme - Press Enter to select the default value - http.
- IP Address - IP address of the computer which you wish to register to Autonomous Database.
Note:
You are prompted to provide all the above details repeatedly until you provide a valid IP address.
After configuring the above details, the created instance is successfully registered to the Autonomous Database. After successful registration, you can launch Oracle Data Transforms directly from the Autonomous Database, Database Actions page.
Note:
In some cases, you may encounter an error ("
401 Not Authorised") when launching Oracle Data Transforms from the Database Actions page. To resolve this issue, you will need to restart the Jetty server.
1.7 Installation Locations
Please note, the following installation locations are used by this image. You may need this information if you want to change any aspects of the installation:
Table 1-1 Installation Locations
| Area | Location on Server |
|---|---|
|
|
|
OPatch Home |
$MW_HOME/OPatch |
|
MySQL Home |
$MW_HOME/../mysql_home |
1.8 Log Files Location
| Log Files | Location |
|---|---|
| ODI Image Creation Logs | /u01/oracle/logs/odi_install_config.log |
| ODI Configuration Logs | /u01/oracle/logs/odiConfigure.log |
| ODI Agent Logs | $MW_HOME/app_logs/odiagent.log |
| ODI Rest Logs | $MW_HOME/app_logs/odi_adp_rest_txt.log |
| ODI Studio Logs | $MW_HOME/odi/log/studio.log |
1.9 Patching
The ODI image on the Oracle Cloud Marketplace contains an Enterprise installation of ODI.
Patching is manual using OPatch.
You can upgrade your existing ODI image to the latest version available on the Oracle Marketplace directly, by either reusing your existing repository database or by creating a new repository database.
Note:
Before upgradation backup your work (db export), create a new instance and then restore (db import) it, to proceed with your upgradation process.Patching an Existing ODI Marketplace Instance
To manually patch an existing ODI marketplace instance,
- Log in to your instance using SSH.
$ ssh –i <private_key> opc @<public-ip-address> - Use the following command to change the user access to
root$ sudo su - Navigate to the location
/etc/securityand locate the filelimits.conf, to modify the ulimit parameter using the following commands:vi /etc/security/limits.confAdd the following lines before the end of the file:
oracle soft nofile 8192 oracle hard nofile 8192 oracle soft nproc 4096 oracle hard nproc 8192 oracle soft core unlimited oracle hard core unlimited opc soft nofile 8192 opc hard nofile 13072 - Save changes and exit the file.
- Use the following command to change the user access to
oraclesudo su - oracle - Run OPatch to apply the patch.
$ opatch apply
To upgrade an existing repository,
Prerequisites
cd /u01/oracle/mwh/odi/common/scripts and get the schema password and superivsor password using the following commands:python manageCredentials.py read odiSchemaPassword
python manageCredentials.py read odiSupervisorPasswordFor more details on running the Upgrade Assisstant, refer to Upgrading Product Schemas Using the Upgrade Assistant.
To upgrade your ADW Instance
Without SSL:
Follow the below procedure for running Upgrade Assisstant on your ADW instance without SSL:
- Export
TNS_ADMIN=<wallet_extracted_path>, for example -/u01/oracle/mwh/wallets/wallet_DB20200310xxxx - Run Upgrade Assistant for the repository using the following commands:
$cd mwh/oracle_common/upgrade/bin $./uaNote:
ForDatabase connect string, enter a short URL during upgrade process. For example -db20200310xxxx_low. You can get this short URL from the filetnsnames.oraavailable in the wallet.
With SSL:
Follow the below procedure for running Upgrade Assisstant on your ADW instance with SSL:
- Export
TNS_ADMIN=<wallet_extracted_path>, for example -/u01/oracle/mwh/wallets/wallet_DB20200310xxxx - Export
UA_PROPERTIES, for example -export UA_PROPERTIES="-Dua.SSL_DB_CONNECTIONS.enabled=true" - Run Upgrade Assistant for the repository using the following commands:
$cd mwh/oracle_common/upgrade/bin $./uaNote:
ForDatabase connect string, enter a short URL during upgrade process. For example -
You can get this short URL from the file(description= (retry_count=20)(retry_delay=3)(address=(protocol=tcps)(port=<port_number>)(host=<host_name>))(connect_data=(service_name=<service_name>))(security=<ssl_certificate>))tnsnames.oraavailable in the wallet. - Use
TNS_ConnectasDatabase connect stringafter running Upgrade Assistant. - Click SSL Settings and modify the following parameters:
- From the TrustStore Type drop-down menu, select SSO.
- Beside to the TrustStore Location text box, click Browse to search and select the location of the
cwallet.ssowallet file. - From the KeyStore Type drop-down menu, select SSO.
- Beside to the KeyStore Location text box, click Browse to search and select the location of the
cwallet.ssowallet file. - Leave TrustStore Password and KeyStore Password fields blank.
- Click Close.
Note:
Your existing repository is upgraded automatically when you create a new ODI Marketplace instance.To upgrade your MySQL Instance
Follow the below procedure for running Upgrade Assistant on your MySQL instance:
- Run Upgrade Assistant for the repository using the following commands:
$cd mwh/oracle_common/upgrade/bin $./ua - Configure
Database connectstring parameter as follows:Database URL - //localhost:3307/sys DBA user - publicNote:
Public password configured above is same as schema password.