8 Simulating Process Behavior
Use Oracle Business Process Composer to run simulations to improve the performance of your business processes. Learn how to create simulation models and simulation definitions, and how to run a simulation and analyze the results.
8.1 Introduction to Simulations
Oracle Business Process Management (Oracle BPM) provides functionality for simulating the behavior and performance of Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) processes. Using Oracle Business Process Composer, process designers can run simulations during the design phase.
After creating and configuring a simulation, you run it in Oracle Business Process Composer to determine the efficiency of the process using the resources allocations you have defined. Using simulations, you can:
-
Define multiple simulation models for a given process so that different conditions can be analyzed.
-
Run multi-process simulations to learn how working in different business processes can affect shared resources such as human participants.
Note:
In Oracle Business Process Composer you can only run simulations based on test data you define using Oracle Business Process Composer. You can run simulations on real-world data using Oracle BPM Studio.
8.1.1 Simulation Models and Simulation Definitions
Before running a simulation, you must define the simulated behavior of the project and the processes you want to include in the simulation. To define a simulation you must create and configure the following in your BPM Project:
-
Simulation definition
Simulation definitions define the processes and resources for a specific scenario. In a simulation definition you specify the processes included in the simulation by selecting the simulation models associated to those processes. A process can have multiple simulation models defined for it. If a process has multiple simulation models defined, then you must select one of those models to use in the simulation definition.
Within a BPM project you can define multiple simulation definitions, each with its own parameter definitions and simulation models. This allows you to compare multiple scenarios.
-
Simulation model
Simulation models define the simulated behavior of an individual process model. You can have multiple simulation models for each business process, allowing you to simulate different scenarios.
Simulations do not call each individual task within a process. For example, they do not run the service associated to a service task, variables are not assigned values, and external resources are not updated.
8.1.2 Simulation Parameters
In addition to the general parameters defined for a simulation definition and a simulation model, you can also define simulation parameters for the start events and activities within a BPMN process.
8.1.2.1 General Simulation Definition Parameters
The following parameters define the general behavior of a simulation definition.
-
Simulation definition: Defines the name of the simulation definition.
-
Duration: Defines the period the simulation runs.
This interval is specified in months, days, hours, minutes, and seconds.
-
Start time: Defines the start time for the simulation.
This time is used only for logging. It is not used for scheduling purposes.
-
Let in-flight instances finish before simulation ends: If selected, simulation ends only when the specified number of instances completes.
If deselected, simulation stops after the simulation duration is completed. At that point, all incomplete instances are shown in either in-process or queue status.
You must define these parameters when creating a simulation definition. However, you can redefine them later if necessary.
8.1.2.2 Simulation Model Parameters
The following parameters define the general behavior of a simulation model:
-
Model name: Defines the name of the simulation model.
-
Specify number of process instances to be created: Specifies the number of simulated instances that are created during simulation.
-
Interactive tasks: Defines the distribution type used for interactive tasks.
The available distribution types are:
-
Constant
-
Uniform
-
Exponential
-
Normal
These are identical to the distribution methods defined for specific activities within a process. When you change distribution type or other parameters for a specific activity within a process, these values override the general values defined in the simulation model. See Activity Parameters for more information.
-
-
Automatic tasks: Defines the number of simulated threads available when performing an automatic task.
This parameter is identical to the Threads parameter you can define for individual activities within your process. See Activity Parameters for more information.
8.1.2.3 Resource Parameters
Resources define the simulated resources within your organization. Resources are defined in a simulation definition and can be shared between each of the process models that are included. These resources can be associated with a specific role within your project. You can use these parameters together to create a resource profile that determines the expense, time, and efficiency of a person or group.
The following resource parameters are supported:
-
Name: Defines the name of the resource.
-
Cost per hour: Specifies the cost of the resource per hour when performing an activity.
-
Efficiency: Specifies how efficient the resource is when performing an activity.
This parameter is used when selecting the Maximum efficiency policy when defining how organizational resources are allocated.
See Activity Parameters for more information.
-
Capacity: Specifies how many activities can be performed at one time.
-
Availability: Specifies the percentage of time this resource is available.
-
Roles: Specifies the roles associated to this resource.
8.1.2.4 Start Event Parameters
To simulate the behavior and performance of start events, Oracle BPM uses a statistical model that simulates the probability of a certain behavior. You must select the statistical distribution that Oracle BPM uses.
The following distribution types are available:
-
Constant: Triggers the start event at a specific interval.
For example, if you specify a period of 1 minute and 15 seconds, the event is triggered every 1 minute and 15 seconds. Each time the event is triggered, a new instance of the process is created.
-
Uniform: Triggers the start event at intervals within a specific margin specified by the mean and delta parameters.
For example, if you define the mean as 30 seconds and the delta as 3 seconds, the start event creates a new instance in intervals between 27 and 33 seconds, with an equal probability.
-
Exponential: Triggers the start event a specified number of times within a certain interval.
For example, if you define the frequency as 10 and the interval as 1 hour, the event is triggered 10 times per hour. The distribution of events is based on exponential distribution.
-
Normal: Triggers the start event based on normal, or Gaussian, distribution.
This is a continuous probability distribution that is based on a bell curve. For example, if you define a mean of 10 minutes and a standard deviation of 2 minutes, the event triggers according to the probabilities shown in Figure 8-1.
Figure 8-1 Simulation - Normal Distribution in a Start Event
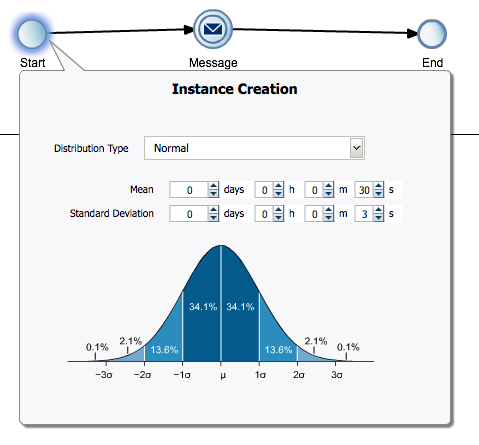
Description of "Figure 8-1 Simulation - Normal Distribution in a Start Event"In this example, the event has a 62.8 percent probability of triggering in an interval between 8 and 12 minutes.
-
Real: Triggers the start event based on user-specified intervals: hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly.
You can define the mean and standard deviation for each interval. Using these parameters, the start event creates new process instances using normal distribution.
For example, you can specify a daily distribution with a mean of 5 minutes and a standard deviation of 1 minute for weekdays and a mean of 1 hour and a standard deviation of 10 minutes for weekends.
8.1.2.5 Activity Parameters
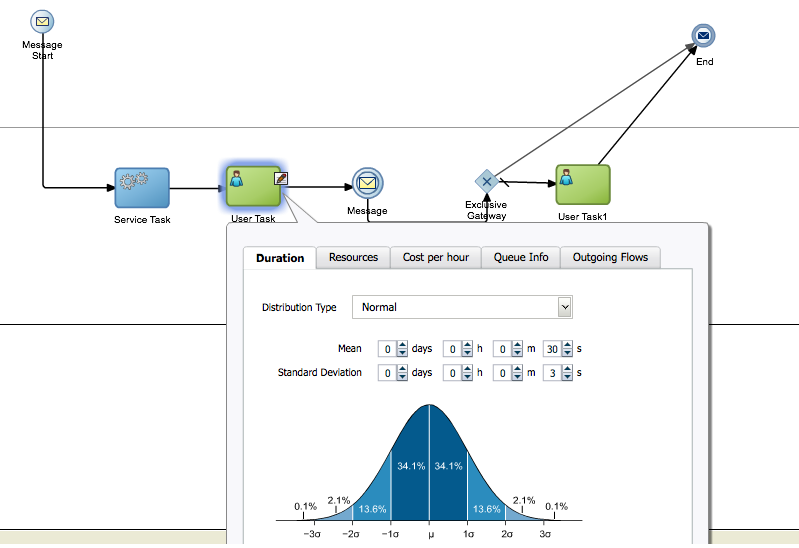
In addition to start events, you can define parameters that determine the simulated behavior or interactive and automatic activities within a process. You define these parameters using the tabbed panes of the simulation editor. Figure 8-2 shows an example of the tabbed panes of an interactive activity.
Figure 8-2 Simulation Parameters for an Interactive Activity
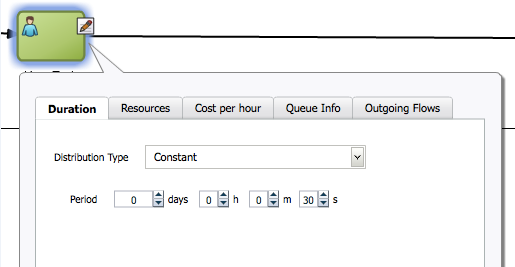
Description of "Figure 8-2 Simulation Parameters for an Interactive Activity"
The simulation parameters for activities are:
-
Duration: Defines the statistical model used to determine the amount of time required to perform an activity.
The statistical models used are similar to those defined for start events except, instead of defining how often an event is triggered, they define how long it takes to perform the work of a specific activity.
See Start Event Parameters for a description of each distribution type.
-
Resources (interactive activities only): Defines how many interactive activities can be performed simultaneously.
You can define how simulated resources are allocated to this activity.
-
Organizational resources: Resources shared between all the processes within a simulation definition.
You must specify the policy that determines how the simulated participants are selected to perform the activity.
-
Minimum cost: Selects less costly resources first.
-
Maximum efficiency: Selects the most efficient resources first.
-
Random: Randomly selects between Minimum cost and Maximum efficiency.
See Resource Parameters for information on defining organization resources within a simulation definition.
-
-
Fixed resources: explicitly defines the number of resources available to perform the interactive activity.
-
-
Threads (available only for automatic activities): Defines the number of simulated threads that are used to perform an automatic activity.
-
Cost per hour: Defines the cost required to perform the activity.
Use this parameter to create cost-base reports.
-
Activity Cost Type: Can be defined as a base cost or as a base cost plus the cost of resources assigned to perform the activity.
-
Activity Fixed Base Cost: Defines the value (specified as a decimal number) of the fixed base cost.
See Resource Parameters for information on defining organization resources within a simulation definition.
-
-
Queue info: Specifies the maximum size of the queue for this activity.
This is the number of instances that are currently waiting at this activity. When this number reaches the maximum size, the simulation issues a warning.
-
Outgoing flows: Specifies the probability (defined as a decimal number) of a process instance continuing along each of the outgoing sequence flow.
If only one outgoing sequence flow is defined, the probability is specified as 1 and cannot be changed.
8.2 Creating and Running a Simulation
To run a simulation, you must first define a simulation model for your project and at least one simulation definition for each of the processes you want to include in your simulation. You can create multiple simulation definitions to test and compare the performance of your processes.
To create and run a simulation:
8.3 Working with Simulation Definitions
Simulation definitions define the simulated behavior of your BPM project as a whole.
Within a simulation definition, you can define general parameters, including the organizational resources, and select which simulation models to include in a simulation. You can define multiple simulation definitions to test different combinations of parameters and processes.
After creating a simulation definition, you can edit its resources, add simulation models, and so on, as described in the following sections.
8.3.1 How to Create a Simulation Definition
In a simulation definition, you can change the values of different parameters to see how they influence the performance of a project. The parameters you can define include:
-
The start time and duration of the simulation
-
Which process simulation models you want to include in the project simulation
-
Participant resources you want to include in the simulation
Oracle Business Process Composer provides a wizard that walks you through the process of creating and configuring a new simulation definition, creating and configuring new simulation models, and configuring organizational resources.
To create and configure a simulation definition:
-
Click Simulations from the Project Welcome Page.
-
Click the New (+) icon to start the simulation wizard.
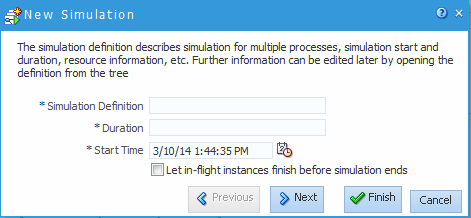
The New Simulation dialog appears, as shown in Figure 8-3.
-
Enter a name for the simulation definition and values for the duration and start time of the simulation definition.
Select the check box to let in-flight instances finish before simulation ends.
You must define these parameters when creating a simulation definition. However, you can redefine them later if necessary.
See General Simulation Definition Parameters for more information about each of these parameters.
-
Click Next.
-
Create a new simulation model for each process you want to include in the simulation definition.
Simulation models can be shared across simulation definitions. However, the first time you create a simulation definition, you must create at least one simulation model for each process if you have not created one previously.
You can also create a new model in the simulation definition editor when you add an association between a model and a process. For more information, see How to Associate a Simulation Model to a Simulation Definition.
-
Click the Add (+) icon to create a new simulation model.
A simulation model defines the simulated behavior of a process. You can define multiple simulation models for a process, however only one simulation model is used for each process within a simulation definition.
-
Provide information for each of the fields as shown in Figure 8-4.
Figure 8-4 The New Simulation Model Editor
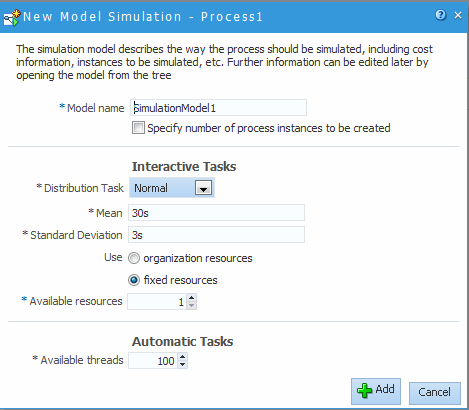
Description of "Figure 8-4 The New Simulation Model Editor"See Simulation Model Parameters for more information about these parameters.
-
Click Add.
Create additional simulation models as necessary. You should create at least one simulation model for each process in your project even if you do not include it in the simulation definition. This allows you to create additional simulation models later and add them to other simulation definitions.
-
-
Select the check box next to each process whose simulation model you want to include in the simulation definition.
If you have not created a simulation model for a process, you cannot select the process.
-
Click Next.
-
Optionally, click the Add resource icon to add resources to the simulation definition.
See Resource Parameters for information on the resource parameters you can define.
-
Click Finish.
8.3.2 What Happens When You Create a Simulation Definition
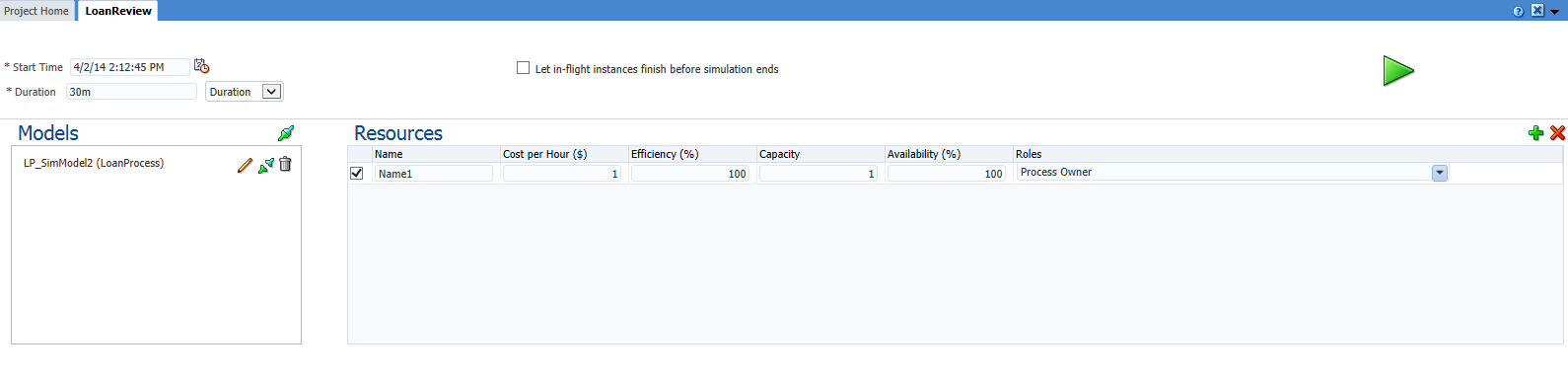
After creating a new simulation definition and simulation models, the simulation panel appears as shown in Figure 8-5.
Figure 8-5 Project Welcome Page - Simulations: After Creating Simulation Definitions
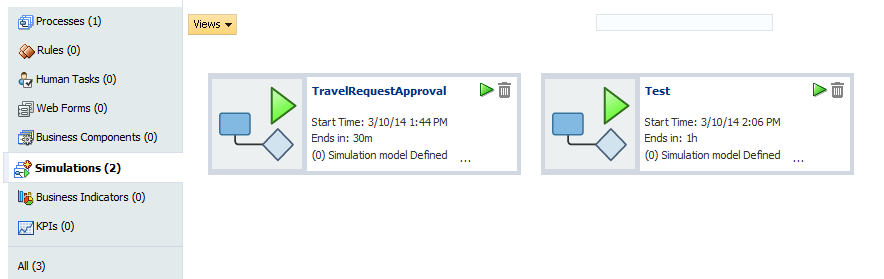
Description of "Figure 8-5 Project Welcome Page - Simulations: After Creating Simulation Definitions"
This panel displays all the simulation definitions defined in your project.
From this panel you can open a simulation definition and perform the following tasks:
-
Edit a simulation definition.
See How to Edit a Simulation Definition for more information.
-
Run a simulation.
See How to Run a Simulation for more information.
-
Edit a simulation model.
See How to Edit a Simulation Model for more information.
8.3.3 How to Edit a Simulation Definition
After creating a simulation definition, you can edit it from the simulation panel.
To edit a simulation definition:
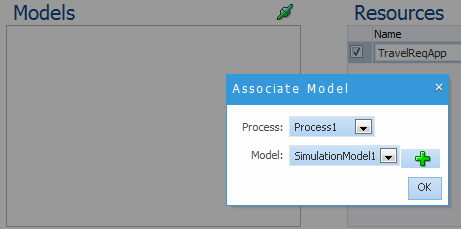
8.3.4 How to Associate a Simulation Model to a Simulation Definition
Before creating a new simulation model, you must create at least one simulation definition. See How to Create a Simulation Definition for more information.
To associate a simulation model to a simulation definition:
8.4 Working with Simulation Models
Simulation models allow you to simulate the behavior of an individual process. They allow you to define how a process behaves as part of a simulation definition.
You can define multiple simulation models for each process, creating different simulations based on different combinations of resource allocation and activity behavior.
8.4.1 How to Create a New Simulation Model
You can create multiple simulation models for a process. Different models can be included in different simulation definitions to determine performance based on different parameter settings.
Note:
You cannot directly create the first simulation model for a process. The first simulation model for a process must be created using the simulation definition wizard. After creating the initial simulation model, you can create additional models using the following procedures.
See How to Create a Simulation Definition for information about creating a simulation model when creating a simulation definition.
To create a new simulation model for a process
The new simulation model is created. You can use this model when creating a new situation definition or editing an existing one. See How to Associate a Simulation Model to a Simulation Definition for more information.
8.5 Running Simulations
After defining a simulation model and simulation definitions, you can run the simulation to view the performance of your BPM project.
To run a simulation, you must have created at least one simulation definition and simulation model for each of the processes you want to test.